Surface Treatment Methods and Test Plans for Automotive Metal Parts
Thank you for reading Shaoyi's blog. We specialize in providing industry insights and the latest manufacturing trends for the metal parts manufacturing sector. Shaoyi focuses on producing automotive metal components through diverse manufacturing processes. Today, we'll explore a common practice in the automotive industry: surface treatment.
Article Summary
Surface treatment technology preserves the base material's original properties while enhancing surface performance—improving physical and mechanical characteristics. This article outlines suitable surface treatments for metal parts produced via machining, stamping, casting, forging, etc. It analyzes treatment test plans (e. g. , electroplating, shot blasting, sandblasting, shot peening, spraying), offering references for developing and verifying surface-treated automotive metal parts to ensure quality and effectiveness.
Surface Treatment of Automotive Metal Parts
In automotive manufacturing, metal parts constitute 60%-70% of total components, while most of them requiring surface treatment. auto parts manufacturers through his process maintains base material integrity while adding new surface properties, altering surface conditions to enhance performance. Widely used surface treatments fall into two categories:
- Chemical treatments (electroplating, electrophoresis, passivation).
- Mechanical treatments (shot blasting, sandblasting, spraying) [1].
Different techniques have distinct purposes and processes, necessitating varied test plans in part verification. Inadequate plans directly impact new part development quality and timelines.

Plating Hanging Plating
1. Functions of Surface Treatment
Surface treatment creates a surface layer with properties distinct from the base material via physical/chemical methods. Key objectives include:
-
Decorative Enhancement
Polishes surfaces for aesthetic appeal (e. g. , car logos, bumpers, wheel hubs). Chrome/zinc plating improves visual appeal, boosting consumer preference.
- Performance Upgrades
- Corrosion/wear resistance: Carburizing/nitriding hardens surfaces of high-load engine parts (pistons, connecting rods) while maintaining core ductility.
- Anti-corrosion: Zinc/nickel plating or oxidation treatments protect fasteners (bolts, nuts).
-
Surface Refinement
Shot blasting/polishing removes burrs and scale from cast/forged blanks, enhancing flatness.
-
Thermal Property Modification
High-conductivity coatings for heat transfer parts; insulating materials for thermal insulation.
-
Electrical Property Adjustment
Electroplating with copper/silver for conductivity; insulating paints/films for non-conductive surfaces.
-
Adhesion Improvement
Sandblasting/phosphating prepares surfaces for painting, enhancing coating-bond strength.

Electroplated parts
2. Surface Treatment Methods and Test Plans
Automotive metal fabrication mainly encompasses machining, stamping, die-casting, forging, and powder metallurgy. Metal components produced by different processes exhibit distinct physical and mechanical properties, which lead to varied objectives for surface treatment. Consequently, the applicable surface treatment methods and corresponding component verification test plans differ accordingly. The most commonly used surface treatment methods for metal auto parts include electroplating, shot blasting, sandblasting, shot peening, and spray coating, as analyzed in detail below.
2. 1 Electroplating
Electroplating deposits metal ions onto conductive substrates from an electrolytic solution [3], widely used for body panels and fasteners to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Coatings (zinc, chrome, copper, etc. ) vary by purpose (Table 1).
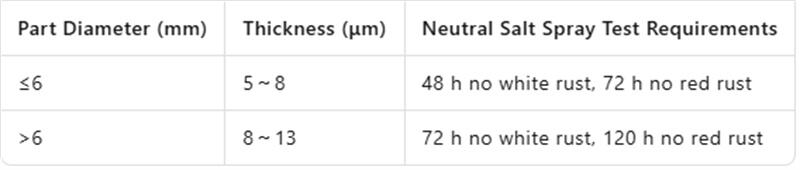
2. 2 Zinc plating (40-50% of applications): Corrosion resistance correlates with thickness (Table 2). Hydrogen embrittlement risks in high-strength fasteners (>10. 9 grade) require post-plating de-hydrogenation and GB/T 3098. 17 compliance.
Table 1 Electroplating Coating Comparisons
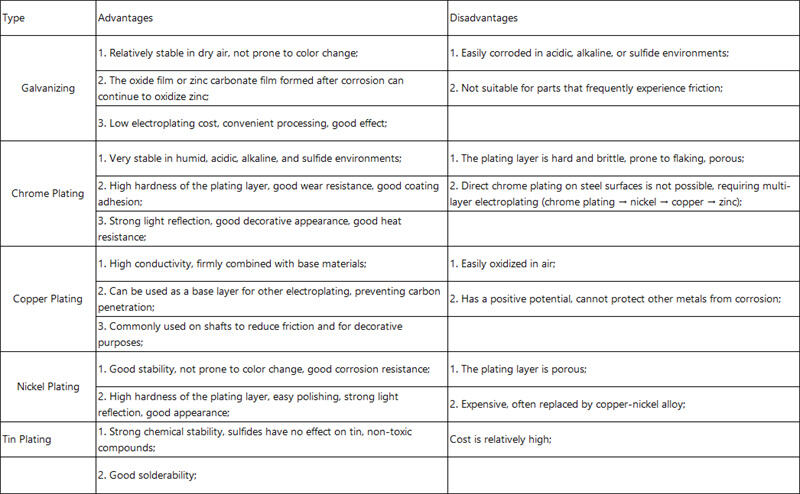
Table 2 Zinc-Plated Fasteners Salt Spray Test Standards
2.3 Shot Blasting
Using centrifugal force, 0. 2-3. 0mm pellets (stainless steel/cast steel) remove contaminants, burrs, and stress while roughening surfaces for better coating adhesion [5]. Post-treatment tests include:
Appearance inspection: No rust/scale.
Cleaning level: Graded by shadow/color difference area ratio.
Surface roughness/coverage: Measured via specified standards (Table 3).

Table3 Shot Blasting Test Criteria
2. 3 Sandblasting
Compressed air propels abrasive (iron sand/emery) to clean surfaces, improve cleanliness, and adjust roughness. Ideal for high-demand applications. Tests include:
lVisual inspection: Ensure no missed corners.
lCleanliness/roughness: Measured under adequate lighting.
2. 4 Shot Peening
Similar to shot blasting but using 0. 2-2. 5mm metal pellets, primarily for complex cast/forged blanks to remove scale/rust. Tests mirror shot blasting due to comparable surface effects.
2. 5 Spraying
Air/electrostatic spraying applies atomized coatings. Electrostatic spraying offers higher efficiency but requires conductive substrates [6].
For spray-coated parts, inspections typically involve appearance checks, coating thickness/surface hardness measurements, and tests for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and environmental durability. Common surface defects—such as particle formation, sagging, orange peel, whitening, and wrinkling—are detected via visual inspection or comparison with standard samples.
Surface hardness testing uses the HB pencil method: a non-sharpened HB pencil is drawn at 45° across the surface with normal handwriting pressure. After wiping with a damp dust-free cloth, only slight scratches (no substrate exposure) are acceptable.
Adhesion testing follows ISO 2409 cross-cut standards: a 10×10 grid (1mm spacing) is cut through the coating using a blade. 3M adhesive tape is applied, left for 1 minute, then rapidly peeled at 45°. Adhesion grades are determined by coating detachment area (see Table 4). Additional tests—including thermal cycling, solvent resistance, and abrasion resistance—are performed based on application requirements to validate weather, solvent, and friction resistance.
Different automotive metal component processes and specifications dictate surface treatment choices, requiring tailored verification protocols for each method. Robust testing ensures surface treatment quality meets customer needs. As components account for 60%-70% of total vehicle costs, manufacturers continuously develop energy-efficient, eco-friendly, and high-performance surface treatments to reduce costs and improve technology.
References
[1] Industry standards for surface treatment classification.
[3] Electroplating process fundamentals.
[4] Correlation between zinc coating thickness and corrosion resistance.
[5] Shot blasting mechanism and applications.
[6] Spraying technology guidelines for automotive components.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
