Stamping Seat Rails and Tracks: Manufacturing & Standards Guide
TL;DR
Stamping seat rails and tracks is a critical manufacturing process that demands precision engineering to meet rigorous automotive safety standards. This guide explores the technical trade-offs between progressive die stamping and press hardening, specifically for high-volume production of safety-critical components. We analyze material selection strategies—focusing on High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel versus Aluminum 7075-T6—and detail the compliance requirements of FMVSS 207 and FIA regulations. For automotive engineers and procurement specialists, understanding these variables is essential for optimizing cost, weight, and structural integrity in seating systems.
Manufacturing Process: Progressive Die Stamping vs. Press Hardening
The manufacturing of seat rails involves transforming coil stock into complex, high-precision profiles capable of withstanding dynamic loads. Two primary methodologies dominate the industry: progressive die stamping and press hardening (hot stamping). The choice between them is dictated by the required tensile strength and production volume.
Progressive Die Stamping is the standard for high-volume production of components using High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel. In this cold-forming process, a metal coil is fed through a multi-station die. Each station performs a specific operation—blanking, piercing, forming, or bending—simultaneously. This method is highly efficient, capable of producing rails with tight tolerances (often ±0.05mm) at rapid cycle times. It is ideal for standard automotive slider profiles where material strength requirements are within the 590–980 MPa range.
Press Hardening, or hot stamping, is utilized when design specifications call for ultra-high-strength steel (UHSS), typically exceeding 1200 MPa. The steel blank is heated to an austenitic state (above 900°C) and then stamped and quenched simultaneously in a cooled die. This creates a martensitic structure, resulting in a seat rail that offers exceptional crash performance with thinner gauge material. While the tooling and energy costs are significantly higher than cold stamping, press hardening is increasingly favored for modern vehicle seating architectures that require weight reduction without compromising safety.
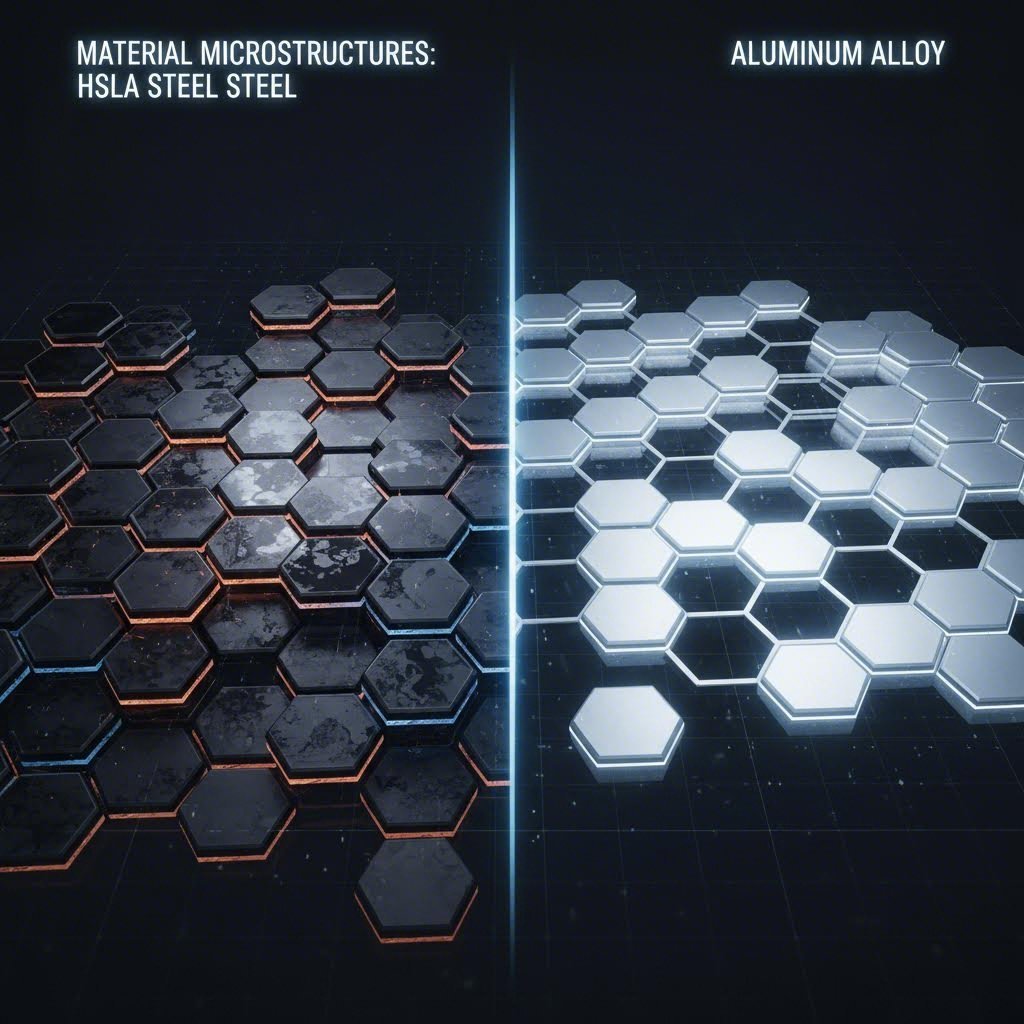
Material Selection: HSLA Steel vs. Aluminum Alloys
Selecting the right material for stamping seat rails and tracks is a balance between weight optimization, cost, and mechanical properties. The material must withstand the high stress of crash loads while allowing for smooth sliding mechanisms.
| Material Category | Grade Examples | Tensile Strength | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSLA Steel | HSLA 340, 420, 590 | 340–700 MPa | Standard automotive seat tracks; balances formability and strength. |
| Ultra-High Strength Steel | Boron Steel (Hot Stamped) | 1200–1700 MPa | Critical safety reinforcements; lightweighting for EVs. |
| Aluminum Alloy | 7075-T6, 6061 | 280–570 MPa | Aerospace and performance automotive; maximizes weight savings. |
HSLA Steel remains the dominant material for mass-market vehicles. Its ability to work-harden during the stamping process provides sufficient strength for meeting standard crash test requirements. However, as the industry shifts toward electric vehicles (EVs), the weight penalty of steel becomes a concern.
Aluminum Alloys, particularly 7075-T6, offer significant weight reduction—often saving 40-50% compared to steel. However, stamping aluminum presents challenges such as lower formability and a higher tendency for springback (elastic recovery) after stamping. Specialized lubricants and die coatings are often required to prevent galling during the forming of aluminum tracks. For specialized applications, adjustable seat rail sliders in the aftermarket sector often utilize reinforced steel to ensure universal compatibility and durability.
Design Standards & Safety Regulations (FMVSS & FIA)
Seat rails are not merely structural supports; they are integral safety components that must prevent seat detachment during a collision. Engineering designs are strictly governed by federal and international standards.
FMVSS 207 (Seating Systems) is the primary regulation in the United States. It mandates that the seat assembly, including the rails, must withstand forces equal to 20 times the weight of the seat in both forward and rearward directions. This "20g load" requirement dictates the thickness of the stamped rail and the strength of the locking mechanism. Manufacturers must also consider FMVSS 210, which governs seat belt anchorages often integrated into the rail system.
For motorsport and high-performance applications, FIA Homologation standards are even more stringent. FIA regulations often require transverse mounting systems to prevent twisting and mandate the use of specific high-grade materials to prevent tear-out failure during high-speed impacts. Unlike standard road car rails, racing seat tracks prioritize rigidity and positive locking over adjustability range.
Common Defects & Quality Control
Achieving zero-defect production in stamping seat rails and tracks requires rigorous quality control, particularly given the complex geometries of slider profiles. Two prevalent issues in this domain are springback and burr formation.
Springback is the tendency of metal to return to its original shape after bending. This is particularly problematic in HSLA and stainless steels used for seat rails. If not calculated correctly, springback can cause the rail profile to deviate from tolerance, leading to "sticky" slides or rattling mechanisms. Advanced simulation software and "over-bending" techniques in the progressive die design are employed to counteract this physical property.
Burrs and Surface Defects can compromise the smooth operation of the seat track rollers. In precision stamping, die maintenance is critical. As punch edges wear, they produce larger burrs that can interfere with the sliding motion or cause premature wear on plastic bushings. Automated optical inspection systems are frequently used to verify profile consistency and surface finish inline.
Applications and Strategic Sourcing
The application of stamped rails spans across automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors, each requiring distinct profile designs. Automotive OEM applications typically use C-channel or U-channel profiles with integrated locking teeth. Aerospace applications favor T-slot designs often machined or stamped from high-strength aluminum for modularity.
For OEMs requiring consistent precision across high-volume orders, partnering with a manufacturer capable of handling complex stamping operations is essential. Companies like Shaoyi Metal Technology leverage IATF 16949-certified processes and presses up to 600 tons to deliver automotive components that meet rigorous global standards, supporting projects from prototype to mass production. Whether sourcing for a commercial truck fleet or a passenger EV, validating a supplier's ability to maintain tight tolerances (±0.05mm) over millions of cycles is a key procurement criterion.
Understanding the distinction between universal aftermarket rails and OEM-specific designs is also vital. While generic rails offer flexibility, they often lack the vehicle-specific crash validation of an OEM stamped component. Engineers typically advise against modifying seat tracks or drilling new holes, as this introduces stress concentrators that can lead to catastrophic failure under load.

Conclusion
Successful stamping of seat rails and tracks relies on a synergistic approach combining advanced material science, precision die engineering, and strict adherence to safety regulations. As vehicle designs evolve toward lighter architectures, the industry is seeing a shift toward higher-strength steels and complex aluminum forming. For manufacturers and buyers alike, prioritizing process capability—from press tonnage to quality certification—ensures that these critical safety components perform reliably throughout the vehicle's lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the technical terms for car seat rails?
In automotive engineering, these components are formally referred to as seat tracks, seat sliders, or seat guide rails. They are part of the broader "seat adjuster assembly," which includes the locking mechanism and the manual or power actuation system.
2. Can damaged seat rails be repaired or welded?
Generally, it is not recommended to repair or weld stamped seat rails. Because they are safety-critical components treated for specific strength properties (often heat-treated), welding can alter the material's microstructure, creating heat-affected zones (HAZ) that are brittle and prone to failure in a crash. Replacement with an OEM-validated part is the standard safety protocol.
3. Why do seat rails use High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel?
HSLA steel is used because it offers a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to conventional carbon steel. This allows manufacturers to stamp thinner rails that are lighter (aiding fuel efficiency) while still meeting the high-load retention requirements of safety standards like FMVSS 207.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
