Stamping Automotive Latches: Precision Process & Design Guide
TL;DR
Stamping automotive latches is a specialized, high-precision manufacturing process essential for producing safety-critical locking mechanisms like door catches, pawls, and strikers. This process predominantly utilizes progressive die stamping and fine blanking technologies to transform high-strength steel into complex geometries with rigorous dimensional tolerances. To ensure vehicle safety and durability, manufacturers must strictly adhere to IATF 16949 quality standards, ensuring every component from the housing to the internal spring retention meets global OEM specifications.
The Anatomy of Stamped Latch Mechanisms
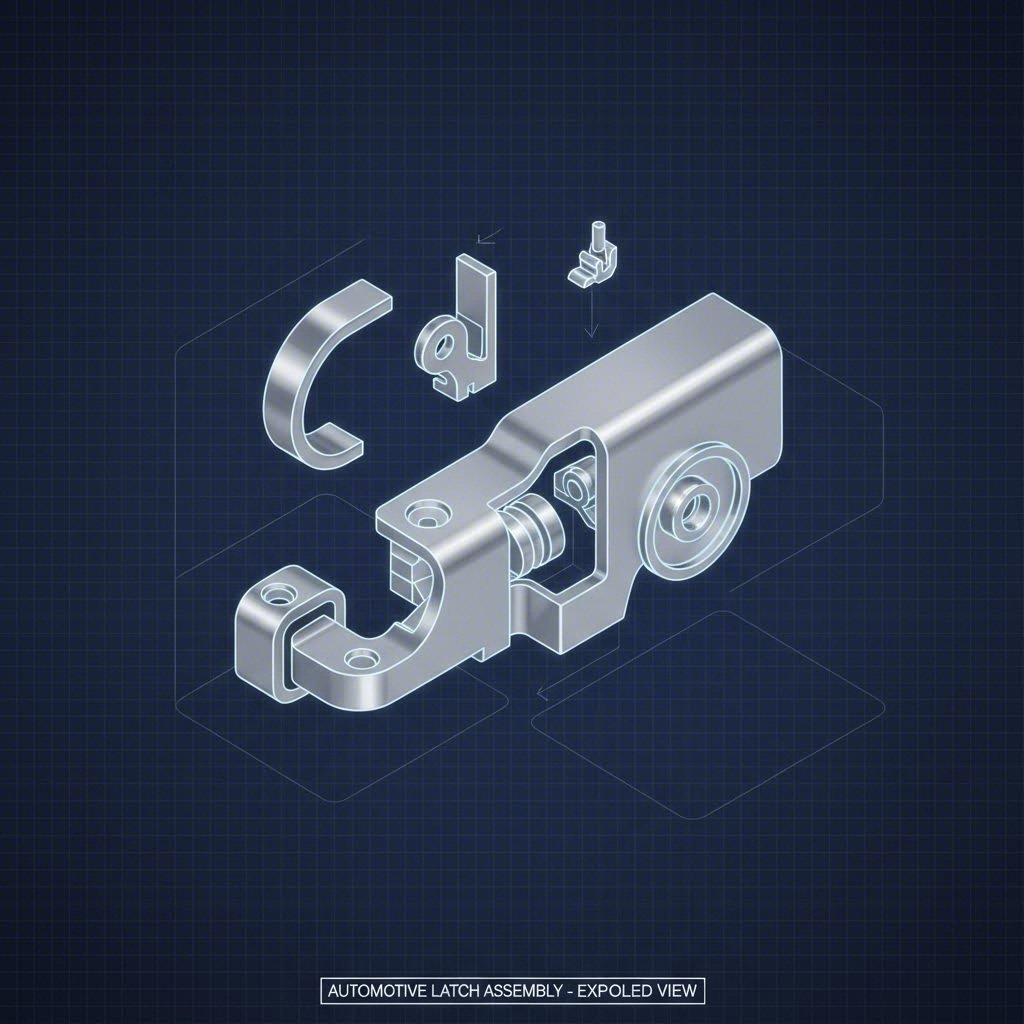
Automotive latches are deceptively complex assemblies. While they appear to be simple locking devices, they are actually intricate kinematic systems composed of multiple stamped metal parts working in unison. Understanding the specific stamping requirements for each component is critical for engineers and procurement managers alike.
The core of any automotive door latch consists of the fork bolt (or catch) and the pawl (or ratchet). These two components are the primary load-bearing elements responsible for keeping a door closed during a crash. Consequently, they require the highest level of precision. Stamping these parts often involves fine blanking or precision stamping with shaving operations to achieve 100% sheared edges. This ensures smooth interaction surfaces without the need for secondary grinding, which is vital for the tactile "feel" of the door closing and the mechanical reliability of the lock.
Surrounding these mechanisms is the latch housing or backplate. Typically stamped from galvanized or cold-rolled steel, the housing acts as the chassis for the assembly. The stamping process here focuses on creating complex bending geometries and stiffening ribs to maintain structural integrity under load. Unlike the internal mechanisms, the housing often prioritizes corrosion resistance and mounting point accuracy over edge surface finish.

Key Manufacturing Processes: Progressive Die & Fine Blanking
Producing latch components at automotive volumes—often running into millions of units per year—requires manufacturing processes that balance speed, cost, and extreme precision.
Progressive Die Stamping
For the majority of latch components, including brackets, levers, and housings, progressive die stamping is the standard. In this process, a metal strip is fed through a press with multiple stations. Each station performs a specific operation—cutting, bending, coining, or piercing—as the part moves progressively through the die. This method is ideal for high-volume production, allowing for rates of hundreds of parts per minute while maintaining consistent tolerances.
Fine Blanking for Functional Criticality
However, for the functional "heart" of the latch (the catch and pawl), standard progressive stamping may introduce too much die break (fracture) on the part edge. This is where fine blanking becomes essential. Fine blanking uses a special press that applies counter-pressure to the material during shearing. The result is a part with fully sheared, smooth edges and superior flatness. This process eliminates the need for secondary machining steps like broaching or milling, significantly reducing the total cost per part while improving the fatigue strength of the locking mechanism.
| Feature | Progressive Die Stamping | Fine Blanking |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Application | Housings, Brackets, Levers | Catch, Pawl, load-bearing gears |
| Edge Quality | Rougher fracture zone (approx. 1/3 shear) | Smooth, 100% sheared edge |
| Tolerances | ±0.05mm - ±0.10mm | ±0.01mm - ±0.05mm |
| Production Speed | Very High | Moderate |
Material Selection for Safety-Critical Latches
The choice of material in stamping automotive latches is dictated by the component's function within the assembly. Because these are safety-critical parts (designated as strict validation items by OEMs), the material must withstand high impact loads and repetitive cycling without failure.
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel is frequently used for structural components like the mounting plate. HSLA offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for thinner gauge materials that reduce overall vehicle weight without compromising crash safety. For the internal locking mechanisms, hardened carbon steels (such as SAE 1050 or 4140) are common. These materials are often stamped in an annealed state and then heat-treated (case hardened or through-hardened) to resist wear from the repeated sliding action of the door opening and closing.
Stainless Steel (304 or 316 series) is typically reserved for exterior-facing components or latches used in corrosive environments, such as trunk latches or hood catches. While more expensive and difficult to stamp due to work hardening, stainless steel eliminates the need for post-process plating, offering long-term reliability.
Design Guidelines & Engineering Challenges
Designing stamped parts for automotive latches introduces specific engineering challenges that must be addressed early in the Design for Manufacturability (DFM) phase. One of the primary issues is springback—the tendency of metal to return to its original shape after bending. In high-strength steels used for latches, springback is significant and difficult to predict. Experienced stampers use simulation software to over-bend the material precisely so that it relaxes into the correct tolerance.
Another critical design constraint is the hole-to-edge ratio. Latch mechanisms are often compact, forcing designers to place pivot holes near the edge of the part. Standard stamping rules suggest a minimum distance of 1.2 times the material thickness to prevent bulging or cracking. However, through specialized tooling designs and active stripping forces, competent manufacturers can push these limits to accommodate the tight packaging space inside a vehicle door.
- Burr Direction: In moving mechanisms, the direction of the stamping burr is critical. Engineers must specify the "burr side" on drawings to ensure that sharp edges face away from mating surfaces or are removed via tumbling.
- Flatness Control: The pawl and catch must remain perfectly flat to engage correctly. Stamping releases internal stresses that can cause warping; secondary coining operations are often required to restore flatness.
Quality Standards & Supplier Selection (IATF 16949)
In the automotive industry, quality is not optional—it is a regulatory mandate. Manufacturers stamping automotive latches must almost universally hold IATF 16949 certification. This standard goes beyond general ISO 9001 requirements, emphasizing defect prevention, supply chain variation reduction, and continuous improvement.
When vetting a supplier, procurement teams should look for robust PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) capabilities. This involves rigorous validation, including dimensional layout reports, material certifications, and functional cycle testing. A supplier must demonstrate that their stamping process is stable (CpK > 1.33) and capable of delivering zero-defect parts consistently.
For companies needing to navigate the complex transition from initial design to mass production, partnering with an experienced manufacturer is vital. Shaoyi Metal Technology specializes in this exact niche, offering comprehensive automotive stamping solutions that bridge the gap from rapid prototyping to high-volume manufacturing. With press capabilities up to 600 tons and strict adherence to global OEM standards, they provide the technical expertise necessary to validate complex latch geometries before committing to expensive hard tooling.

Conclusion: Securing Success in Automotive Stamping
Stamping automotive latches is more than just bending metal; it is a discipline that merges material science, kinematic design, and precision engineering. For B2B buyers and engineers, success lies in understanding the nuances of the process—from the necessity of fine blanking for locking parts to the critical management of springback in high-strength steels.
Choosing the right manufacturing partner requires looking beyond basic press capacity. The ideal partner must demonstrate deep expertise in DFM for safety-critical mechanisms, a robust quality management system rooted in IATF 16949, and the ability to scale from prototype to millions of units. By prioritizing these technical and operational competencies, automotive OEMs can ensure their latch systems deliver both the safety passengers rely on and the seamless performance the market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 7 steps in the stamping method?
The seven common steps in the metal stamping process, often used in progressive dies for latches, include: Blanking (cutting the initial shape), Piercing (punching holes), Drawing (stretching material into a shape), Bending (forming angles), Air Bending (punching into a die without bottoming out), Coining (squeezing material for precision and strength), and Trimming (removing excess material). For complex latch parts, these steps are combined into a single automated press run.
2. Is metal stamping expensive?
Metal stamping requires a significant upfront investment in hard tooling (dies), which can be expensive. However, for high-volume automotive production, it is extremely cost-effective. Once the tooling is built, the per-part cost drops dramatically compared to machining or casting, making it the most improved economic choice for mass-producing millions of latch components.
3. What are automotive stampings?
Automotive stampings are metal parts formed by pressing sheet metal into specific shapes using dies. These range from massive body panels like hoods and fenders to small, precision mechanisms like door latches, brackets, and electrical terminals. They are fundamental to vehicle structure, safety, and functionality.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
