Automotive Shock Tower Stamping: From AHSS to Giga Casting
TL;DR
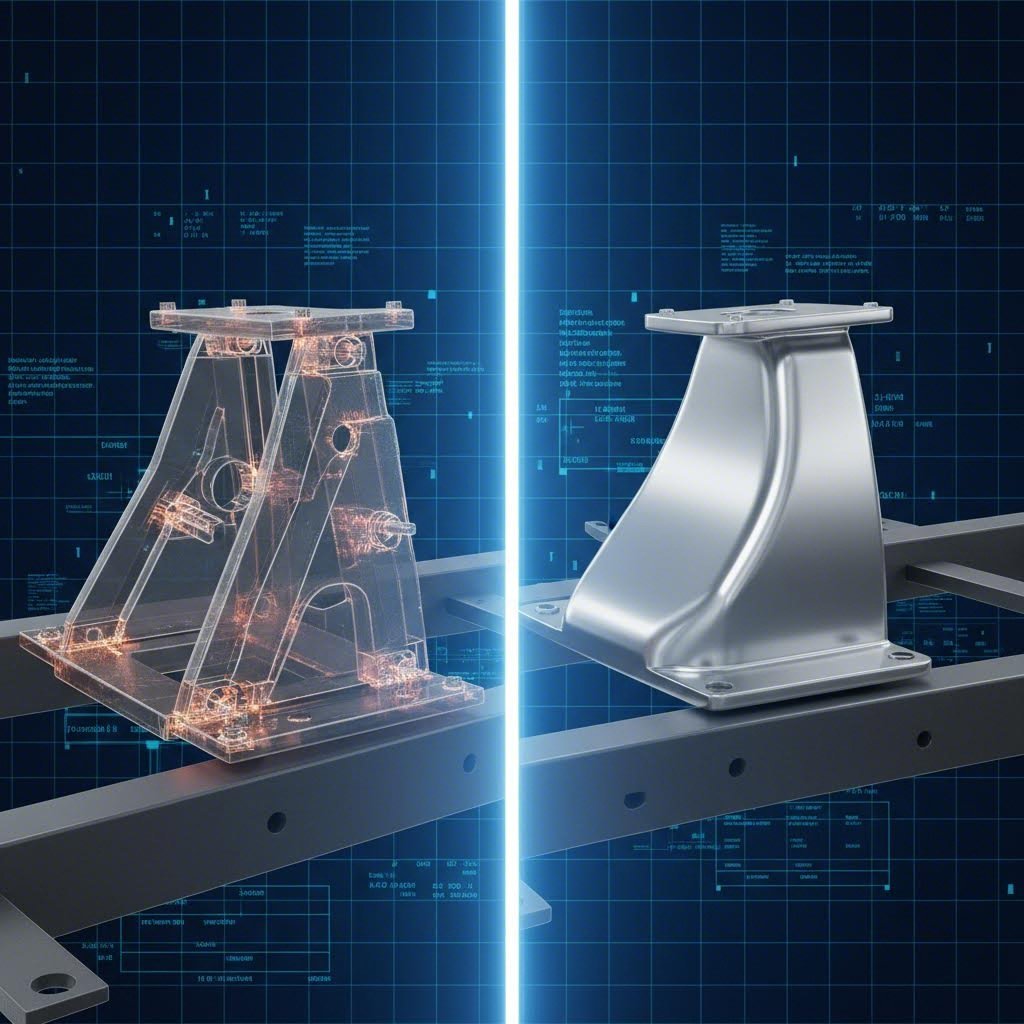
Automotive shock tower stamping is a critical manufacturing process undergoing a seismic shift. Traditionally, shock towers are fabricated as multi-piece assemblies using stamped high-strength steel (AHSS) to connect a vehicle's suspension to the Body-in-White (BIW). However, the industry is increasingly adopting single-piece aluminum die-casting (Giga Casting) to reduce weight and assembly complexity.
For engineers and procurement professionals, the choice between shock tower stamping automotive solutions and casting involves analyzing trade-offs in tooling costs, repairability, and material performance. This guide explores the technical evolution from traditional AHSS stamping to the emerging "Giga Stamping" technologies designed to compete with the casting revolution.
The Anatomy of an Automotive Shock Tower
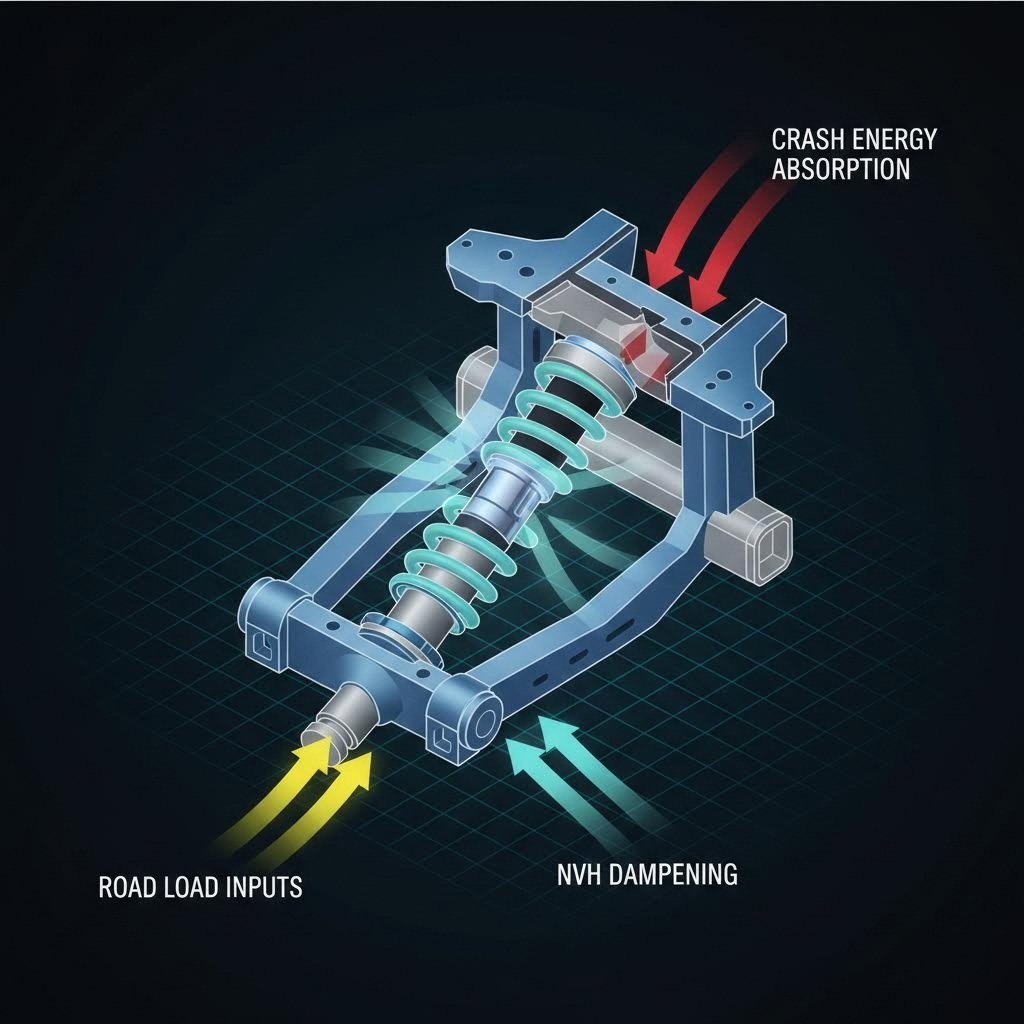
The shock tower (also known as a strut tower) is a safety-critical component that serves as the primary interface between the vehicle's suspension system and its frame. It must withstand immense road load inputs, dampen Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH), and absorb significant energy during crash events.
In a traditional stamped configuration, a shock tower is not a single part but a complex assembly. It typically consists of 10 to 15 separate stamped steel components—including the tower cap, reinforcements, and side aprons—that are spot-welded together. This multi-piece architecture allows for the use of varying material thicknesses and grades, optimizing strength where it is needed most while managing cost.
However, modern manufacturing is challenging this complexity. Leading suppliers like GF Casting Solutions highlight that integrating these functions into a single cast aluminum solution can significantly reduce weight and eliminate assembly steps. As Steffen Dekoj, Head of R&D Asia at GF, notes, the lightweight potential of shock towers is becoming a template for other structural parts of the BIW.
The Stamping Process: High-Strength Steel (AHSS) Fabrication
Despite the rise of casting, stamping remains the dominant method for high-volume production, particularly due to advancements in Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS). Fabricating a shock tower from materials like Dual Phase (DP) or TRIP steel allows for thinner gauges without compromising structural integrity.
Critical Stamping Challenges
- Springback: As tensile strength increases (often exceeding 590 MPa or 700 MPa), the metal tends to return to its original shape after forming. Engineers must use advanced simulation software to design dies with "die compensation" to counteract this effect.
- Work Hardening & Tool Wear: The deep-draw nature of shock tower geometries puts immense stress on tooling. Scoring and galling are common issues that can lead to increased scrap rates.
- Lubrication Requirements: Specialized lubricants are essential. A case study by IRMCO demonstrated that switching to a specific synthetic lubricant on 700MPa HSLA steel (3.4mm thickness) could reduce fluid consumption by 35% while eliminating scoring, proving that chemistry is just as important as press tonnage.
For manufacturers seeking a partner to navigate these complexities, Shaoyi Metal Technology offers comprehensive stamping solutions ranging from rapid prototyping to high-volume production. Their IATF 16949-certified facilities and presses up to 600 tons are equipped to handle critical components like shock towers and control arms with the precision required by global OEMs.
Stamping vs. Die Casting: The Industry Disruption
The automotive industry is currently witnessing a battle between traditional stamping and "Giga Casting." This trend, popularized by Tesla, involves replacing large stamped assemblies with massive, single-piece aluminum die-castings.
Comparative Analysis: Steel Assembly vs. Aluminum Casting
| Feature | Stamped Steel Assembly | Aluminum Die-Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Part Count | High (10–15 parts welded) | Low (1 single monolithic part) |
| Weight | Heavier (Steel density) | Lighter (Aluminum density) |
| Tooling Cost | Lower (Progressive/Transfer dies) | High (Massive Giga Press molds) |
| Repairability | High (Individual parts can be replaced) | Low (Often requires full replacement) |
| Cycle Time | Fast (Stamping strokes per minute) | Slower (Cooling time required) |
This shift is quantifiable. As reported by MetalForming Magazine, Audi replaced 10 stamped components with a single casting for the A6 front shock tower. Similarly, the Tesla Model Y rear end replaced roughly 70 stamped parts with a single casting, eliminating hundreds of spot welds. While casting offers weight and assembly advantages, stamped steel retains the upper hand in material cost and repairability, making it the preferred choice for many economy and mid-range vehicles.
Future Technologies: Hybrid Casting & Giga Stamping
The steel industry is not standing still. To counter the threat of Giga Casting, a new concept known as "Giga Stamping" is emerging. This involves hot-stamping extremely large Laser-Welded Blanks (LWBs) or overlap-patched blanks to create massive, single-piece steel structures that rival castings in integration.
ArcelorMittal refers to this as "Multi-Part-Integration" (MPI). By laser-welding different grades of steel (e.g., PHS1000 for deformation zones and PHS2000 for the safety cage) into a single blank before stamping, manufacturers can achieve the benefits of part consolidation without abandoning steel. This technology is already seen in the door rings of vehicles like the Acura MDX and Tesla Cybertruck, and is rapidly expanding to shock tower and floor panel applications.
This hybrid approach allows OEMs to maintain existing stamping infrastructure while achieving the weight reduction and simplified assembly lines previously thought possible only with aluminum casting.

Market Context: Restoration & Aftermarket
While the OEM sector focuses on Giga presses, a robust secondary market exists for traditional shock tower stamping. Restoration enthusiasts restoring vintage platforms—such as the Ford Mustang or Mopar B-Bodies—rely heavily on accurate stamped reproductions.
In this niche, authenticity is paramount. The "shock tower stamping" often refers not just to the manufacturing process but to the VIN numbers and date codes stamped into the metal. High-quality aftermarket parts are stamped from heavy-gauge steel using exclusive tooling to match the original factory specifications, ensuring that structural integrity and historical accuracy are preserved for classic vehicles.
Strategic Outlook: The Road Ahead
The future of automotive body structures will likely be a hybrid landscape. While premium electric vehicles push toward aluminum Giga Castings to offset battery weight, the high cost of aluminum and the non-repairability of cast structures ensure that stamped steel remains vital. The evolution of Giga Stamping proves that steel technology is adaptable, offering a middle ground that combines the efficiency of integration with the cost-effectiveness of traditional materials. For manufacturers, the key to survival lies in flexibility—mastering both advanced AHSS forming and the integration of these parts into increasingly modular vehicle architectures.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary function of an automotive shock tower?
A shock tower, or strut tower, connects the vehicle's suspension strut to the chassis. It is a structural component designed to absorb road impacts, support the vehicle's weight, and maintain suspension geometry. In a unibody construction, it is critical for ensuring rigidity and crash safety.
2. Why are manufacturers switching from stamped steel to cast aluminum shock towers?
The primary drivers are weight reduction and assembly simplification. A cast aluminum shock tower can replace over a dozen stamped steel parts, eliminating the need for complex welding and assembly stations. This reduces the overall vehicle weight, which is crucial for extending the range of electric vehicles.
3. Can stamped shock towers be repaired after a collision?
Yes, stamped steel shock towers are generally easier to repair than cast aluminum ones. Because they are assembled from multiple welded parts, a body shop can often drill out spot welds and replace individual damaged sections. Cast aluminum towers, however, are brittle and prone to cracking; they typically cannot be straightened or welded and must be replaced entirely if damaged.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
