Semi-Solid Metal Casting for Automotive Component Mastery

TL;DR
Semi-solid metal (SSM) casting is an advanced manufacturing process, blending elements of casting and forging, where metal alloys are shaped in a semi-solid, slurry-like state. For the automotive industry, this technique is critical for producing lightweight, high-integrity components with complex geometries, such as suspension parts and transmission casings. The process yields parts with superior mechanical strength and minimal porosity compared to conventional die casting methods.
Understanding Semi-Solid Metal (SSM) Casting: Fundamentals and Principles
Semi-solid metal (SSM) casting is a near-net-shape manufacturing technology that operates at a unique intersection between traditional casting and forging. The process involves shaping a metal alloy at a temperature between its liquidus (fully liquid) and solidus (fully solid) points. In this state, often referred to as a 'mushy state' or slurry, the metal consists of solid, globular particles suspended in a liquid matrix. This composition gives the material a unique property known as thixotropy: it behaves like a solid when at rest but flows like a liquid when shear force is applied, such as during injection into a mold.
The scientific principle underpinning SSM's advantages is its non-dendritic microstructure. In conventional casting, molten metal cools to form long, tree-like crystals called dendrites, which can trap gases and create porosity, weakening the final part. SSM processing, however, encourages the formation of fine, spherical or globular primary solid particles. This is achieved by stirring or agitating the alloy as it cools through the solidification range. The resulting slurry can be injected into a die with a smooth, laminar flow, minimizing the turbulence that causes gas entrapment and defects in high-pressure die casting (HPDC).
This fundamental difference in microstructure translates directly to superior mechanical properties. As detailed by industry experts at CEX Casting, components made via SSM exhibit higher tensile strength, improved ductility, and greater fatigue resistance. The dense, uniform structure makes SSM parts ideal for applications requiring pressure tightness and high structural integrity. By combining the ability to form complex shapes like casting with the material quality of forging, SSM provides a powerful tool for engineers aiming to optimize component performance and reliability.
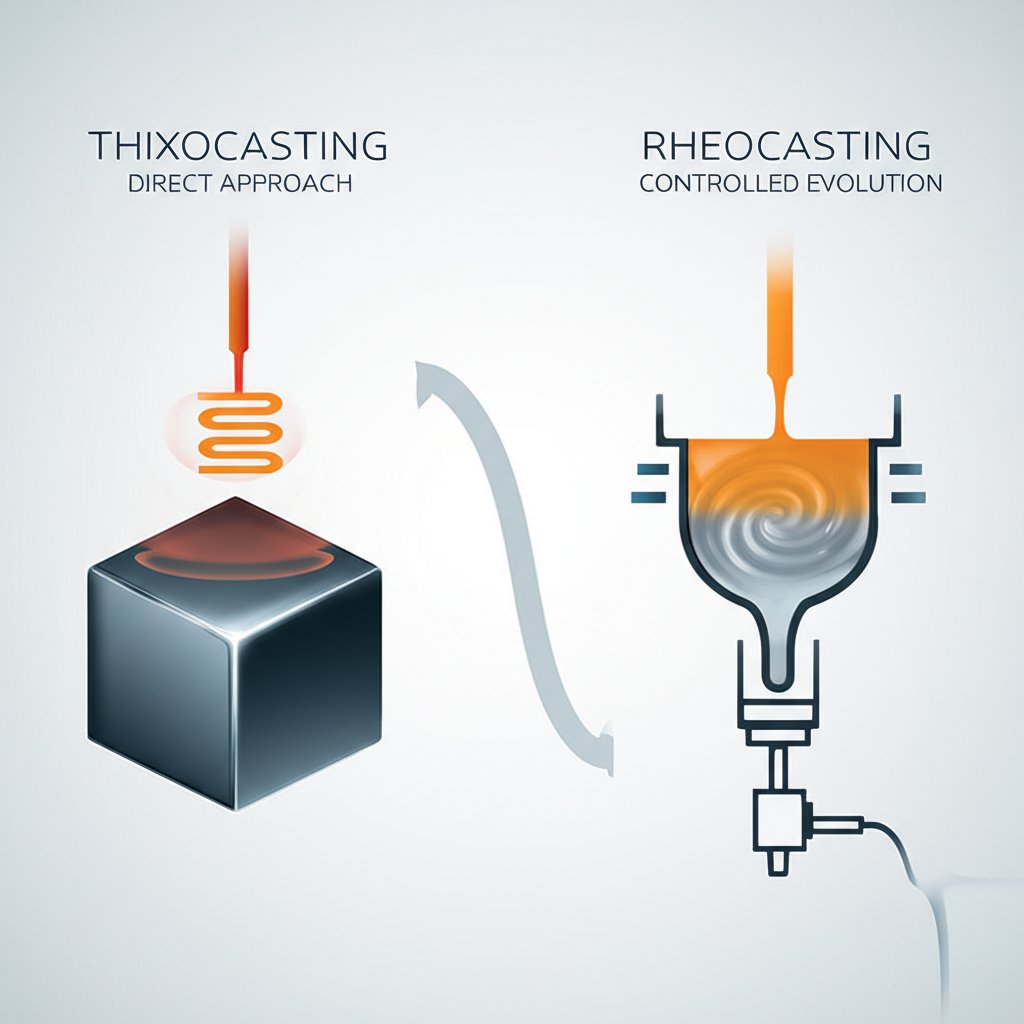
Core SSM Processes: Thixocasting vs. Rheocasting
The two primary methodologies within semi-solid metal casting are Thixocasting and Rheocasting, distinguished mainly by their starting material and slurry preparation. Understanding their differences is key to selecting the appropriate process for a given application. Each offers a distinct balance of cost, control, and material handling requirements.
Thixocasting begins with a specially prepared billet of feedstock material that already possesses the required globular, non-dendritic microstructure. This billet is produced through processes like magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) stirring or grain refinement. In the Thixocasting process, this pre-conditioned billet is cut to a specific slug size and then reheated into the semi-solid temperature range using an induction furnace. Once it reaches the desired solid-liquid fraction, a robot transfers the slug to a shot sleeve, and it is injected into the die. This method offers excellent process control and consistency because the initial microstructure is precisely engineered.
Rheocasting, in contrast, creates the semi-solid slurry directly from standard molten metal, making it potentially more cost-effective. In this process, a charge of molten alloy is cooled to the semi-solid range while being vigorously agitated or stirred. This mechanical or electromagnetic stirring breaks up the forming dendrites and promotes the formation of the desired globular structure. Once the slurry is prepared, it is transferred and injected into the die. While Rheocasting avoids the need for expensive, pre-conditioned billets, it requires sophisticated real-time monitoring and control to ensure the slurry's consistency and quality.
A related process, Thixomolding®, is often mentioned in the context of SSM and is particularly prominent for magnesium alloys. It functions similarly to plastic injection molding, where chips of magnesium alloy are fed into a heated barrel and sheared by a screw to create a thixotropic slurry before being injected. Choosing between these processes depends on production volume, component complexity, and cost targets. Thixocasting is often favored for critical components requiring the highest integrity, while Rheocasting is gaining traction for high-volume automotive production due to its potential for lower material costs.
Key Advantages & Automotive Applications of SSM Casting
The adoption of semi-solid metal casting in the automotive sector is driven by a compelling set of advantages that directly address the industry's core challenges: lightweighting, performance, and cost-efficiency. As noted in a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, SSM is ideally suited for producing lightweight, high-strength components with complex geometries, making it a pivotal technology for improving fuel economy and vehicle dynamics.
The primary benefits of SSM casting for automotive applications include:
- Reduced Porosity: The laminar, less turbulent flow of the semi-solid slurry into the mold drastically reduces gas entrapment, leading to components that are virtually free of porosity. This makes them suitable for pressure-tight applications like fluid and vacuum systems.
- Superior Mechanical Properties: The fine, globular microstructure results in parts with enhanced strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance compared to those made with conventional casting. This allows for the design of thinner-walled, lighter parts without sacrificing performance.
- Near-Net-Shape Production: SSM casting produces parts with high dimensional accuracy and an excellent surface finish, significantly reducing the need for costly and time-consuming secondary machining operations.
- Heat Treatable: The low porosity of SSM components allows them to be heat-treated (e.g., T5 or T6 conditions for aluminum alloys) to further enhance their mechanical properties, an option often not viable for HPDC parts due to the risk of blistering from trapped gases.
These advantages make SSM the preferred method for a growing number of critical automotive components. Specific applications include suspension joints, transmission casings, engine mounts, steering knuckles, brake components, and integral chassis parts. For instance, creating a suspension joint with SSM ensures the high fatigue resistance needed to withstand millions of cycles of road stress. While SSM offers unique benefits by blending casting and forging principles, other specialized processes remain vital. For example, some high-stress components still rely on dedicated forming techniques; specialists in automotive forging parts provide solutions where maximum strength from a wrought microstructure is paramount, illustrating the diverse engineering toolset available to automakers.

Challenges and Future Outlook for SSM Technology
Despite its significant advantages, the widespread adoption of semi-solid metal casting faces several challenges that have historically limited its application. The primary hurdles are related to the complexity and cost of the process. Implementing an SSM production line requires a high initial capital investment in specialized equipment, including induction heating systems, slurry-making machinery, and sophisticated process monitoring tools. The process itself demands extremely precise control over temperature—often within a few degrees Celsius—to maintain the desired solid-to-liquid ratio, which is critical for part quality.
Furthermore, the design of molds and dies for SSM casting is more complex than for traditional die casting. The flow characteristics of the semi-solid slurry are different from fully liquid metal, requiring specialized simulation software and engineering expertise to design gates and runners that ensure complete die filling without defects. The cost of raw materials, particularly the pre-conditioned billets used in Thixocasting, can also be higher than that of standard ingots used in other processes, impacting the overall cost per part.
However, the future outlook for SSM technology in the automotive industry is bright. As highlighted in research published by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the process has firmly established itself as a competitive and viable manufacturing technique. Ongoing advancements in sensor technology, process automation, and computer modeling are making SSM more reliable, repeatable, and cost-effective. The development of more efficient Rheocasting methods that use standard alloys is particularly promising for reducing costs and opening the door to mass production for a wider range of components. As automakers continue to push the boundaries of lightweighting and vehicle electrification, the demand for high-performance, defect-free components will only grow, positioning semi-solid metal casting as a key enabling technology for the future of mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the process of semi-solid casting?
Semi-solid casting is a manufacturing technology where a metal alloy is heated to a state between fully solid and fully liquid, creating a slurry. This slurry, which has a globular microstructure, is then injected into a mold to form a near-net-shape part. The process minimizes turbulence during injection, resulting in dense components with high mechanical strength and very low porosity.
2. What are the disadvantages of HPDC?
A primary disadvantage of High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is the high potential for porosity. The rapid, turbulent injection of fully molten metal can trap air and gases within the die, creating voids in the final part. This porosity can compromise the component's mechanical properties, particularly its strength and pressure tightness, and typically prevents the part from being effectively heat-treated.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
