Automotive Roof Rail Stamping: Structural vs. Accessory Processes
TL;DR
Automotive roof rail stamping refers to two distinct manufacturing pathways depending on the component's function: structural safety or exterior utility. Structural roof rails (integrated into the Body-in-White) typically utilize Hot Stamping of ultra-high strength steel (UHSS) to ensure crashworthiness and rollover protection. In contrast, accessory roof rails (luggage racks) primarily rely on Aluminum Extrusion and Stretch Bending, with stamping used secondarily for mounting brackets and feet. Understanding this distinction is critical for engineers selecting the correct production methodology for vehicle programs.
The Two Critical Categories of Automotive Roof Rails
In automotive engineering, the term "roof rail" describes two fundamentally different components, each requiring a specialized manufacturing approach. A failure to distinguish between these types often leads to confusion in procurement and supply chain specifications.
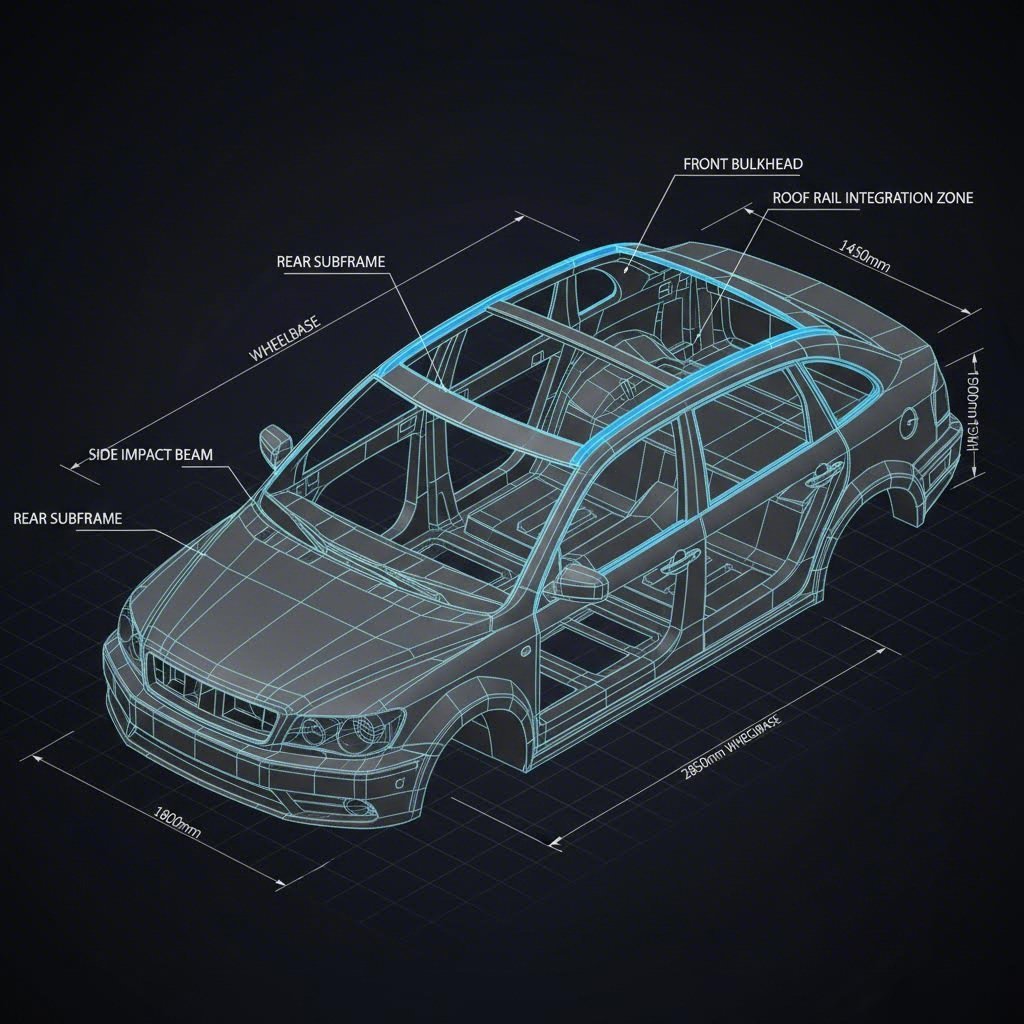
Type A: Structural Roof Rails (Body-in-White)
These are integral parts of the vehicle's chassis, welded directly to the A-pillars, B-pillars, and roof bows. Their primary function is energy management during a crash, particularly improving roof crush resistance ratings. As noted by industry leaders like Magna International, these components require ultra-high strength materials to protect occupants.
Type B: Accessory Roof Rails (Exterior Trim)
These are the visible rails mounted on top of the vehicle, used for securing luggage, bicycles, or cargo boxes. While they must bear static and dynamic loads, their manufacturing prioritizes aesthetics, aerodynamics, and corrosion resistance. Manufacturers like FSM Group and Wellste specialize in this domain, utilizing aluminum extrusion and bending technologies rather than traditional sheet metal stamping.
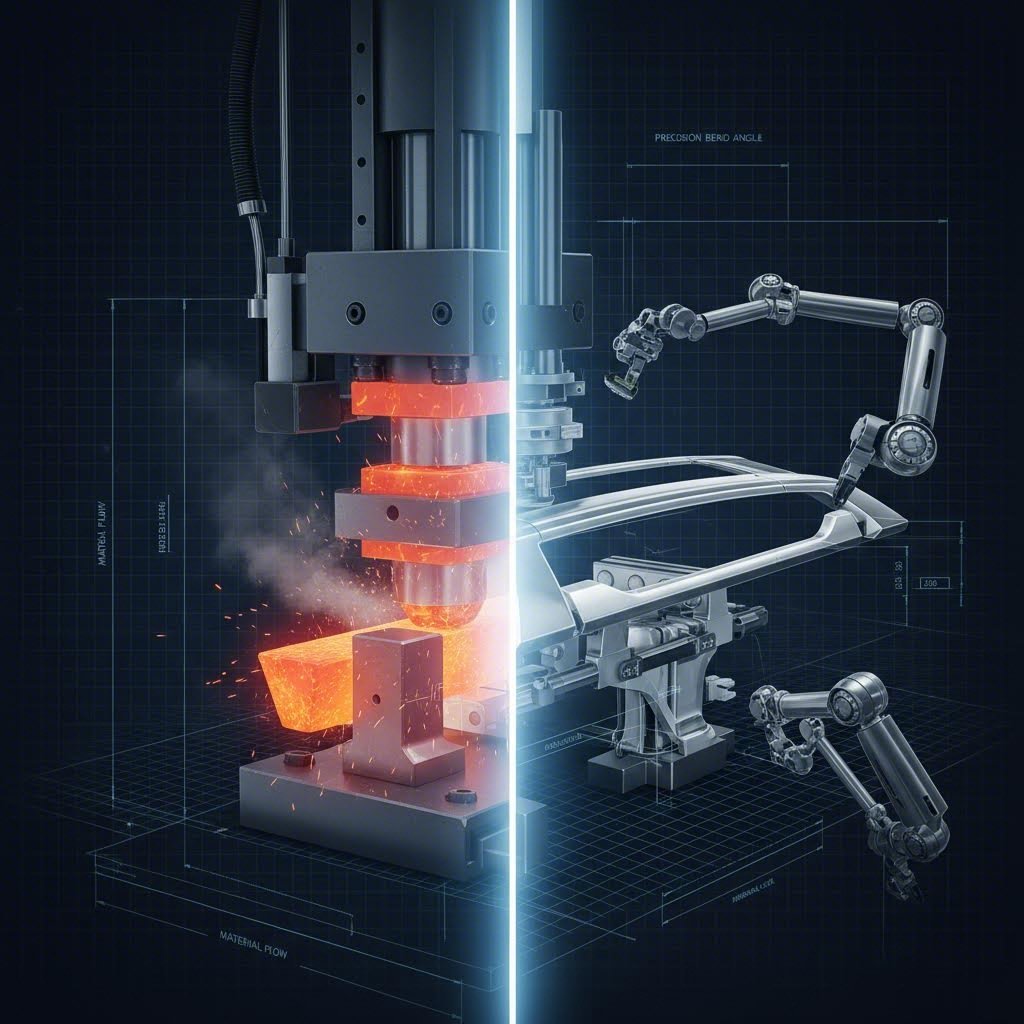
Process 1: Hot Stamping for Structural Roof Rails
For structural applications where passenger safety is paramount, Hot Stamping (also known as Press Hardening) is the dominant manufacturing process. This method allows engineers to produce complex geometries with exceptionally high tensile strength, often exceeding 1,500 MPa.
The Hot Stamping Mechanism
The process begins by heating boron steel blanks in a furnace to approximately 900°C–950°C until the material reaches an austenitic state. The malleable red-hot steel is then transferred quickly to a water-cooled stamping die. As the press closes, the part is formed and simultaneously quenched (cooled rapidly). This quenching transforms the microstructure from austenite to martensite, locking in the ultra-high strength properties.
Engineering Advantages
- Crash Safety: Hot-stamped rails provide the rigid "backbone" required for modern safety standards without adding excessive weight.
- Springback Elimination: Unlike cold stamping, where the metal tries to return to its original shape, hot stamping virtually eliminates springback, ensuring precise dimensional accuracy for robotic welding assembly.
- Complex Integration: This process allows for the integration of multiple features—such as pillar connections and hinge reinforcements—into a single component, reducing part count.
Process 2: Extrusion and Stretch Bending for Accessory Rails
Accessory roof rails, often seen on SUVs and crossovers, demand a different manufacturing philosophy. Here, the goal is lightweight durability and visual perfection. The primary process is Aluminum Extrusion, often followed by specialized forming techniques.
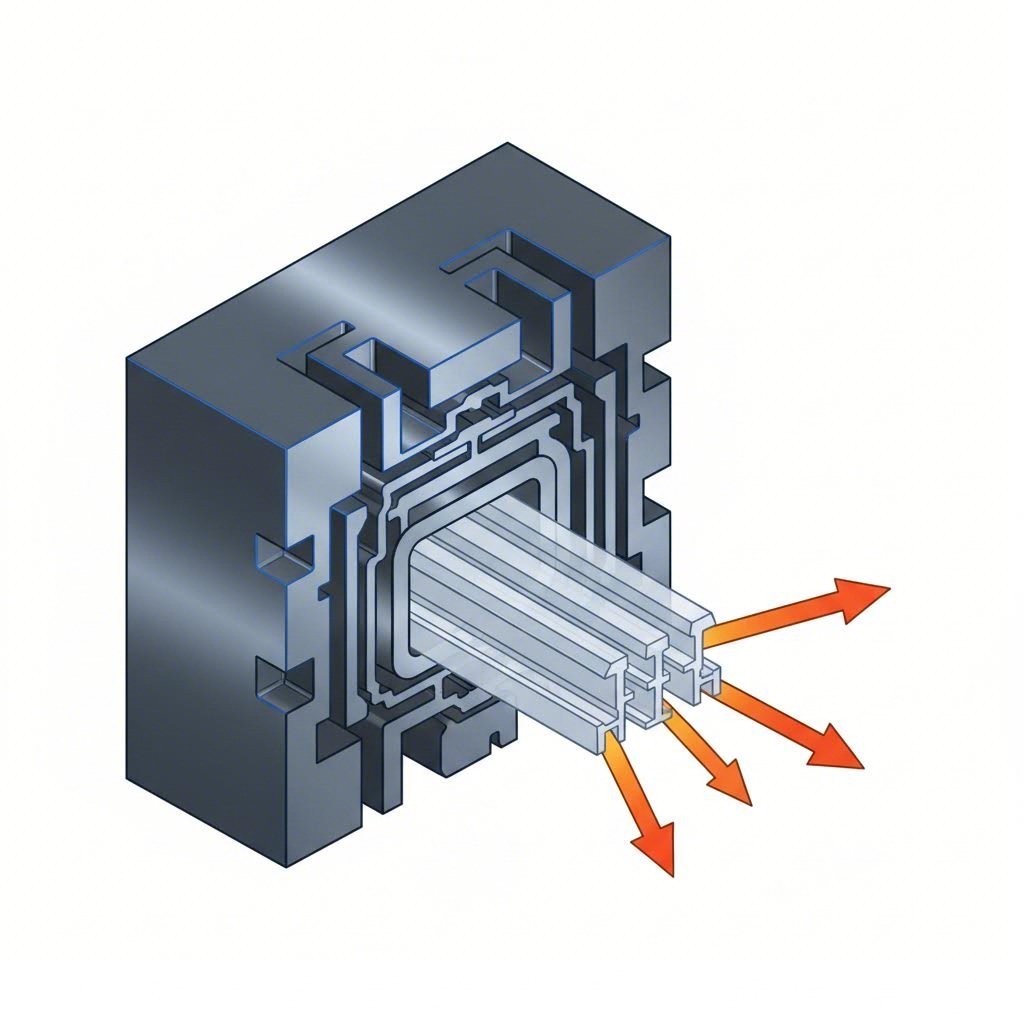
From Billet to Bent Profile
The process starts with aluminum billets (typically 6000-series alloys like 6061 or 6063) being forced through a die to create a continuous profile with a specific cross-section. According to AEC (Aluminum Extruders Council), using alloys like 6082 can deliver the necessary toughness while converting multiple steel stampings into a single efficient extrusion, as seen in the Ford F-150's roof header which saved 2.9 kg.
The Role of Stretch Bending and Stamping
Once extruded, the straight rails must be contoured to match the vehicle's roofline. This is achieved through Stretch Bending, a process where the profile is stretched to its yield point and then wrapped around a die. This ensures the rail retains its cross-sectional shape without collapsing or wrinkling.
Where Stamping Fits In:
While the main rail is extruded, stamping remains critical for the peripheral components. The mounting brackets, feet, and internal reinforcement plates that secure the rail to the car roof are typically stamped from high-strength steel or aluminum sheet. Companies like Hatch Stamping Company excel in these precision stamped assemblies, ensuring that even large panoramic structures meet rigorous quality standards.
Supply Chain Strategy: From Prototype to Mass Production
Selecting the right manufacturing partner involves analyzing production volume and tooling investment. For high-volume structural rails, the high capital cost of hot stamping dies is amortized over millions of units. For accessory rails or lower-volume variants, extrusion dies offer a lower entry cost.
However, the transition from design to production often requires specialized support. Suppliers like Shaoyi Metal Technology bridge this gap by offering comprehensive stamping solutions that scale from rapid prototyping to high-volume manufacturing. Their ability to handle press capabilities up to 600 tons allows for the precision fabrication of both structural brackets and complex reinforcement parts, ensuring compliance with global OEM standards like IATF 16949.
Comparative Analysis: Stamping vs. Extrusion vs. Hydroforming
When defining the specifications for a new vehicle program, engineers must weigh the trade-offs between different forming technologies. The following table outlines the decision matrix for roof rail applications.
| Feature | Hot Stamping (Steel) | Aluminum Extrusion | Hydroforming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Application | Structural Body-in-White (Safety) | Accessory Roof Racks (Trim/Load) | Tubular Structural Rails |
| Material | Boron Steel / UHSS | Aluminum Alloys (6061, 6063, 6082) | Steel or Aluminum Tube |
| Strength Potential | Very High (1500+ MPa) | Moderate (200-350 MPa) | High (varies by material) |
| Shape Complexity | High (variable cross-section) | Low (constant cross-section) | High (complex 3D shapes) |
| Tooling Cost | High (requiring cooling channels) | Low to Moderate | High |
Quality Control and Defect Prevention
Regardless of the process, maintaining zero-defect production is non-negotiable in the automotive sector. For hot stamping, the primary defect risks are surface cracking and inconsistent hardness, which are mitigated through precise temperature control and thermographic monitoring. In extrusion and bending, the challenges shift to surface cosmetics and profile distortion. Automated inspection systems, including 3D laser scanning, are standard protocols to detect minute deviations in curvature or surface finish before the parts reach the assembly line.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —