Progressive Die Stamping Car Parts: The High-Volume Guide
TL;DR
Progressive die stamping is a high-speed metal forming process where a continuous strip of metal is fed through a series of sequential stations, creating a finished part with every press stroke. For the automotive industry, this method is the gold standard for mass-producing small-to-medium precision components—such as brackets, electrical connectors, and sensor clips—with tight tolerances (often ±0.001 inches) and minimal waste. Unlike transfer stamping, which handles individual parts for larger structural components, progressive stamping maximizes efficiency for high-volume runs, making it essential for Just-in-Time (JIT) supply chains.
Progressive Die Stamping: The Engine of Automotive Production
In the high-stakes world of automotive manufacturing, where production volumes often reach millions of units annually, speed and consistency are non-negotiable. Progressive die stamping serves as the backbone of this ecosystem, transforming raw metal coils into finished components at rates that can exceed 1,000 parts per minute. The process relies on a unique feeding mechanism: a continuous strip of metal is unrolled from a coil and fed automatically into a stamping press.
Inside the press, the progressive die acts as a multi-station tool. As the strip advances incrementally, it stops at precise intervals where different operations—such as blanking, bending, punching, piercing, and coining—are performed simultaneously at each station. Crucially, the part remains attached to the metal strip (the "web") until the very final station, where it is cut loose and ejected. This continuous attachment ensures superior alignment and control compared to manual methods, drastically reducing cycle times and labor costs.
For automotive engineers, the primary value lies in repeatability. Once a progressive die is built and validated, it can produce millions of identical parts with virtually zero dimensional drift. This capability is vital for automated assembly lines where even a micron-level deviation in a connector or bracket can cause jamming or failure. Furthermore, the ability to integrate secondary operations—like tapping threads or inserting contacts—directly into the die (in-die assembly) further streamlines the manufacturing footprint.
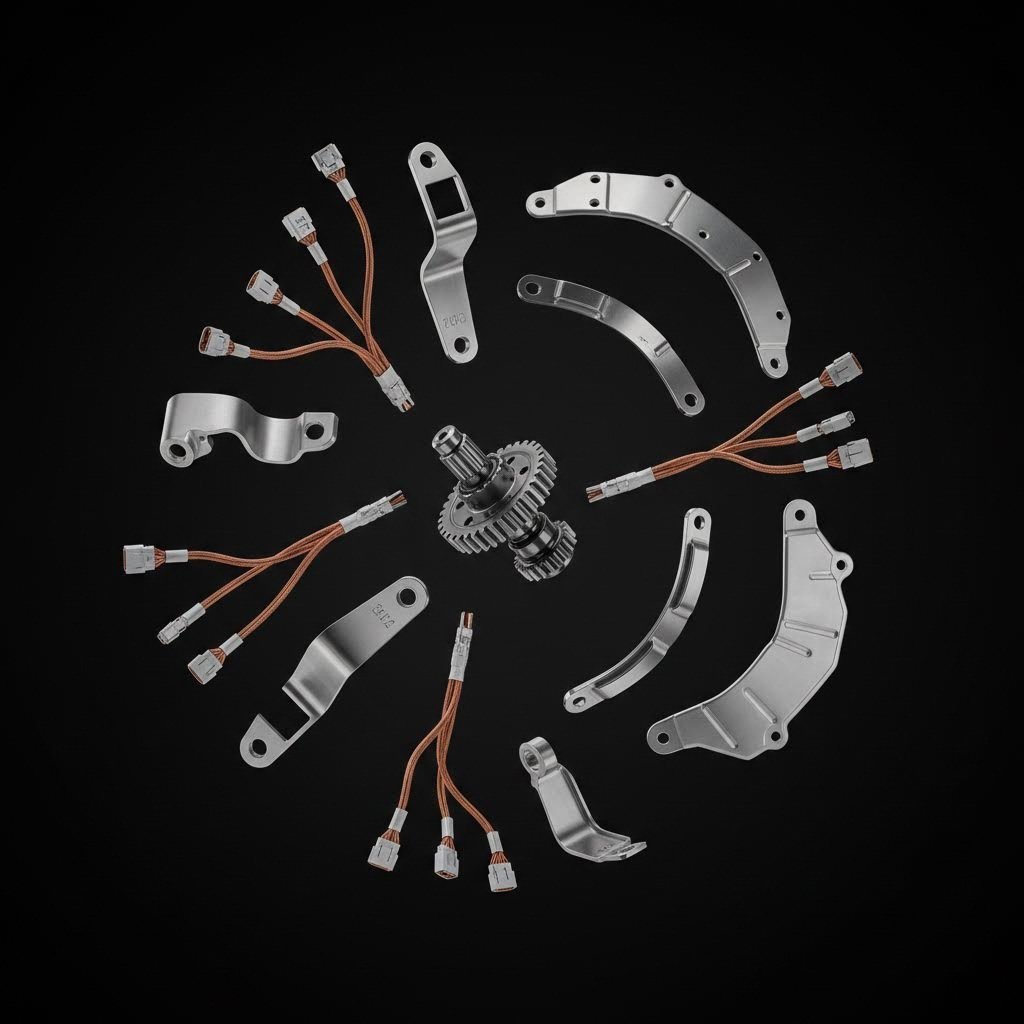
Essential Car Parts Manufactured via Progressive Stamping
While large body panels are typically made using transfer dies or tandem lines, progressive die stamping dominates the production of the thousands of smaller, intricate parts that make a vehicle function. These components can be categorized by the vehicle systems they support.
Body and Structural Components
The structural integrity of a vehicle depends on countless reinforcement parts hidden behind the upholstery. Progressive stamping is ideal for manufacturing high-strength steel seat tracks, recliner mechanisms, and safety belt brackets. These parts require robust mechanical properties but must be produced in high volumes to match vehicle assembly rates. Other common applications include:
- Door lock latches and strikers
- Window regulator components
- Guide rails and reinforcement beams
- Airbag housing components
Electrical and EV Systems
As the industry shifts toward electric vehicles (EVs), the demand for stamped electrical components has surged. Copper and brass are stamped into complex geometries to facilitate conductivity and connectivity. Busbars, which distribute power in EV battery packs, are a prime example of parts that benefit from the precision of progressive stamping. The process allows for the creation of intricate terminal shapes and spring contacts without damaging the delicate material surface. Key electrical parts include:
- Lead frames and pin connectors
- Sensor housings and covers
- Fuse clips and relay terminals
- Battery contact plates
Engine and Chassis Hardware
Under the hood, components must withstand extreme heat, vibration, and corrosive environments. Stainless steel and specialized alloys are stamped into fuel injection clips, valve covers, and heat shields. The chassis also utilizes stamped brake clips, ABS sensor mounts, and shim washers. For these safety-critical applications, the consistent grain flow provided by the stamping process ensures that parts maintain their structural integrity under cyclic loading.
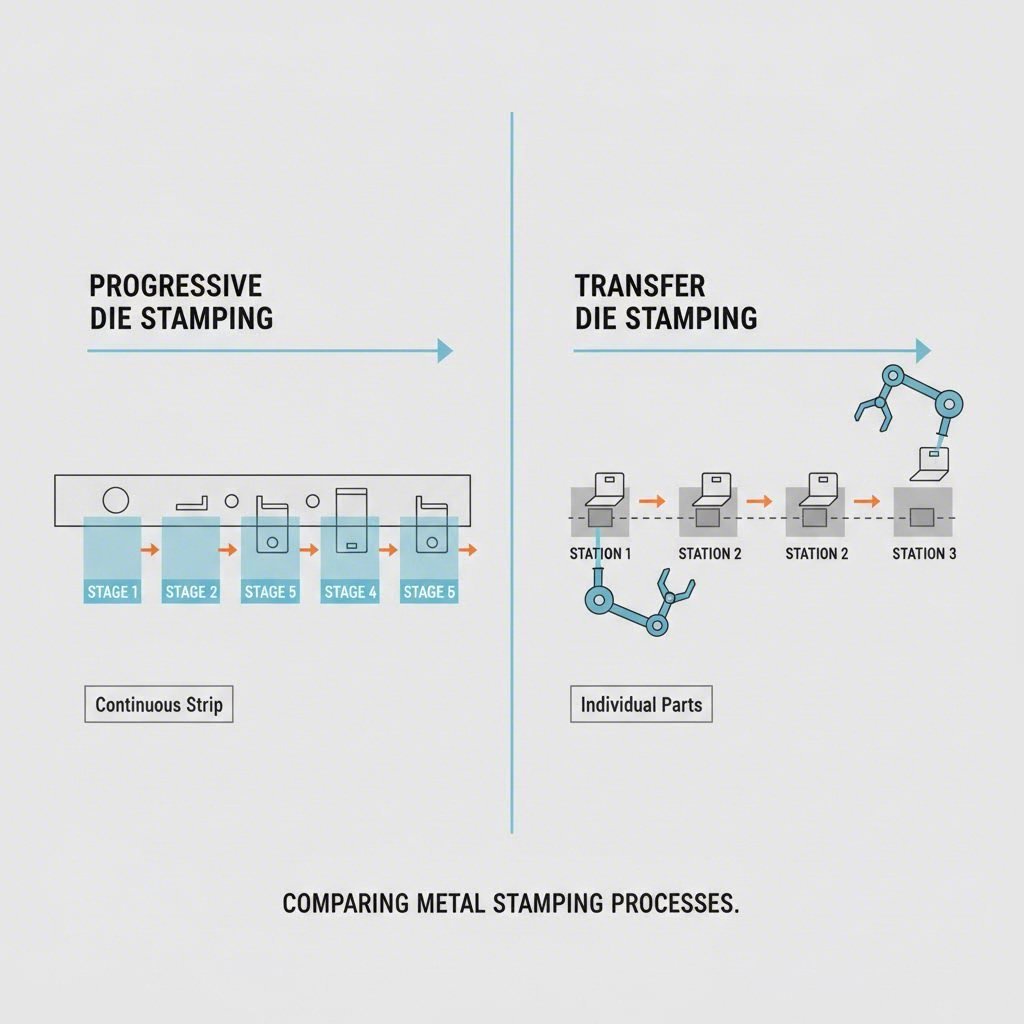
Progressive Die vs. Transfer Die: Choosing the Right Method
One of the most critical decisions for an automotive sourcing manager is selecting the correct stamping method. While progressive stamping is powerful, it is not a universal solution. The choice often comes down to part size, geometry, and volume.
| Feature | Progressive Die Stamping | Transfer Die Stamping |
|---|---|---|
| Part Handling | Part stays attached to the metal strip until the end. | Part is cut free (blanked) first, then moved by mechanical fingers. |
| Ideal Part Size | Small to medium (e.g., connectors, brackets). | Large (e.g., cross-members, frame rails, deep shells). |
| Production Speed | Extremely high (continuous cycle). | Moderate (limited by transfer mechanism speed). |
| Tooling Cost | Higher initial investment (complex single tool). | Variable, but often higher per-part cost due to slower speed. |
| Best For | High-volume, intricate parts with tight tolerances. | Deep-drawn parts or large structural components. |
Progressive die stamping is the clear winner for smaller parts that require high production speeds and strict tolerances. The "strip" approach eliminates the need for complex transfer mechanisms, reducing the chance of part misalignment. However, it cannot handle deep-draw operations well (where the depth of the part exceeds its diameter) because the strip limits the material flow.
Transfer die stamping, by contrast, is necessary for larger parts like suspension control arms or oil pans. Since the part is separated from the strip immediately, it can be manipulated freely—rotated or tilted—between stations. This allows for deeper draws and more complex forming operations that would tear the strip in a progressive die setup.
Material Selection for Automotive Performance
The versatility of progressive stamping allows manufacturers to work with a diverse range of materials, each selected for specific performance criteria in the automotive environment.
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel is the workhorse for structural and safety components. It offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it critical for crash-safety parts like bumper reinforcements and pillar brackets. Stamping these hardened materials requires robust tooling made from carbide or premium tool steels to prevent premature wear.
Aluminum is increasingly favored for lightweighting initiatives to improve fuel economy and EV range. While aluminum is more prone to springback (returning to its original shape after bending) than steel, advanced progressive die designs compensate for this by over-bending. Common applications include heat shields, brackets, and trim components.
Copper and Brass are indispensable for the electrified future of driving. Their superior electrical conductivity makes them the standard for terminals, connectors, and busbars. In progressive stamping, these soft metals can be formed at high speeds, but care must be taken to manage scrap and prevent surface marring.
Quality Standards and Strategic Sourcing
In the automotive supply chain, quality is governed by strict global standards, most notably IATF 16949. This certification ensures that a stamping supplier has robust quality management systems in place, focusing on defect prevention and reduction of variation. When vetting a partner, engineers should look for capabilities that go beyond basic stamping, such as in-line vision systems that inspect 100% of parts for critical dimensions.
A common challenge for automotive OEMs is finding a supplier that can bridge the gap between initial design and full-scale production. While some shops only handle massive orders, agile partners like Shaoyi Metal Technology offer comprehensive stamping solutions that scale from rapid prototyping to high-volume manufacturing. Leveraging IATF 16949-certified precision and press capabilities up to 600 tons, they can deliver critical components like control arms and subframes while adhering to global OEM standards. This flexibility allows engineers to validate designs with a prototype run before committing to the heavy tooling investment required for millions of parts.
Ultimately, the right sourcing decision involves balancing piece-price with risk. A domestic supplier might offer faster communication, but an established international partner with IATF credentials can often provide significant cost advantages without compromising on material quality or delivery timelines.

Conclusion: Driving Efficiency in Auto Manufacturing
Progressive die stamping remains a critical technology for the automotive industry, enabling the mass production of the complex, durable, and precise components that modern vehicles demand. From the electrical connectors in an EV battery to the high-strength brackets securing a seat, this process delivers the scalability and cost-efficiency required to keep assembly lines moving. For procurement teams and engineers, understanding the mechanics, material constraints, and sourcing standards of this method is essential for optimizing the automotive supply chain and ensuring vehicle quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between progressive die and transfer die stamping?
The primary difference lies in how the part is handled. In progressive die stamping, the part remains attached to a continuous metal strip as it moves through various stations. In transfer die stamping, the part is cut from the strip first and then mechanically moved (transferred) from station to station. Progressive is generally faster and better for small parts, while transfer is suited for larger, deep-drawn parts.
2. What materials are most commonly used in progressive die stamping for cars?
Automotive stamping frequently uses High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel for structural parts due to its durability. Aluminum is widely used for lightweighting components like heat shields and brackets. Copper and brass are standard for electrical components, such as connectors and busbars, because of their high conductivity.
3. Why is IATF 16949 certification important for stamping suppliers?
IATF 16949 is the international quality management standard specifically for the automotive industry. It ensures that a stamping supplier adheres to rigorous defect prevention, waste reduction, and continuous improvement practices. Sourcing from an IATF-certified supplier is often a mandatory requirement for OEMs to ensure part safety and reliability.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
