Precision Metal Stamping for EV Battery: Manufacturing Critical Components at Scale

TL;DR
Precision metal stamping for EV batteries is a high-speed manufacturing process critical for mass-producing components like busbars, battery cans, and current collectors with micron-level tolerances. Unlike machining, it offers unmatched scalability and material efficiency, making it the standard for millions of battery cells required in modern electric vehicles. Key technologies include progressive die stamping for complex connectors and deep draw stamping for leak-proof enclosures, all requiring strict adherence to technical cleanliness standards.
The Critical Role of Metal Stamping in EV Battery Ecosystems
As the electric vehicle (EV) market accelerates toward mass adoption, the manufacturing pressure shifts from producing thousands of prototypes to delivering millions of reliable, identical units. Precision metal stamping has emerged as the dominant manufacturing method for this scale, primarily because it bridges the gap between high-speed production and extreme dimensional accuracy.
While CNC machining and die casting have their place in low-volume or structural applications, they cannot match the cycle times of metal stamping for high-volume battery components. A high-speed stamping press can produce hundreds of complex parts per minute, a rate essential for satisfying the demand for the thousands of individual cells found in a single battery pack. This process ensures that critical features, such as the flatness of a busbar or the lip profile of a battery can, remain consistent across millions of cycles.
Material efficiency is another decisive factor. EV battery production relies heavily on expensive conductive metals like copper and aluminum. Metal stamping processes maximize material usage through optimized strip layouts, significantly reducing scrap compared to subtractive manufacturing methods. This efficiency is not just an economic advantage but a sustainability mandate in a supply chain focused on reducing carbon footprints.
Essential Stamped Components: Busbars, Enclosures, & Connectors
The battery pack is the heart of an EV, and stamped components are its nervous system and skeleton. The complexity of these parts goes far beyond simple metal bending; they require intricate geometries to manage high currents and thermal loads.
Busbars and Interconnects
Busbars are the primary conductors transferring energy between battery modules and the inverter. Precision stamping creates these from thick copper or aluminum strips, often incorporating complex bends to navigate the tight spaces of a battery pack. Advanced "Current Collector Assemblies" (CCA) and "Cell Contacting Systems" (CCS) rely on stamped busbars that must maintain perfect flatness to ensure low contact resistance. Any deviation can lead to hotspots, reducing battery efficiency or causing safety failures.
Battery Cans and Enclosures
For cylindrical and prismatic cells, the "can" is the first line of defense. These are typically manufactured using deep draw stamping, where a metal blank is drawn into a die to form a seamless, cup-like shape. Precision deep draw capabilities allow for thin walls that maximize energy density while maintaining enough structural integrity to contain internal pressure and electrolyte.
Connectors and Terminals
The thousands of connections within a pack utilize stamped terminals, tabs, and clips. These components often feature "compliant pin" designs or specific plating requirements (like silver or tin) to prevent corrosion and ensure consistent conductivity over the vehicle's 10-15 year lifespan. High-speed progressive dies are used to stamp these delicate parts on a massive scale.
Material Science: Copper, Aluminum, & Clad Metals
Selecting the right material is a balancing act between conductivity, weight, and cost. Precision stampers must be adept at handling a variety of specialized alloys tailored for EV applications.
Copper (C11000/C10100): The gold standard for conductivity. Copper is essential for high-current pathways but is heavy and expensive. Stamping copper requires specific tooling coatings to prevent galling and ensure clean edges.
Aluminum (3003/6061): Favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio. Aluminum busbars are increasingly common in weight-critical applications. However, stamping aluminum presents challenges like springback, which requires sophisticated die engineering to control.
Clad and Bimetals: Innovation in materials has led to clad metals, such as copper-clad aluminum. These hybrid materials offer the surface conductivity of copper with the core weight savings of aluminum. Stamping these materials requires precise clearance control to avoid delaminating the layers during the forming process.
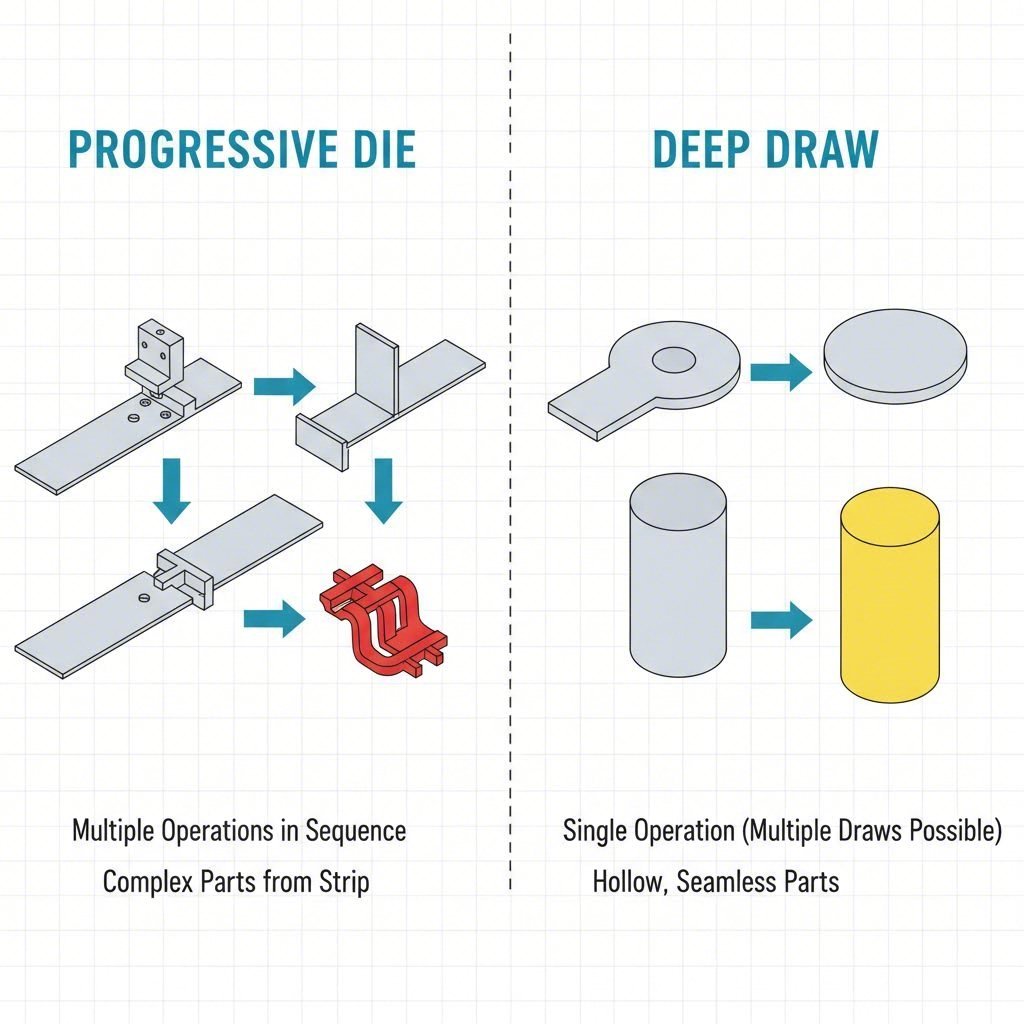
Advanced Manufacturing Processes: Deep Draw vs. Progressive Die
Achieving the necessary geometries for battery parts requires selecting the correct stamping discipline. The choice often dictates the cost, speed, and feasibility of the project.
Progressive Die Stamping
This process is the workhorse for busbars, connectors, and lead frames. A metal strip feeds through a series of stations in a single die, with each station performing a specific cut, bend, or form. By the time the strip exits the die, the part is complete. Progressive die heavy stamping is particularly effective for complex, multi-feature parts that need to be produced at speeds exceeding 1,000 strokes per minute.
Deep Draw Stamping
Used primarily for battery cans and deep housings, this process involves pulling metal material into a die cavity. It is distinct from progressive stamping because it deals with radial tension and material flow rather than simple bending. Deep draw is essential for creating seamless, leak-proof containers that progressive dies cannot achieve.
From Prototype to Mass Production
Moving from a design concept to millions of parts is a critical phase. Manufacturers often start with soft tooling or laser cutting for prototypes before investing in hard tooling. Partners like Shaoyi Metal Technology bridge this gap by offering comprehensive solutions that range from rapid prototyping to high-volume manufacturing. With press capabilities up to 600 tons, they can handle large structural components and complex multi-cavity dies, ensuring a smooth transition to mass production while maintaining IATF 16949 standards.
Engineering Challenges: Tolerances, Heat, & Cleanliness
EV battery manufacturing introduces constraints that are far stricter than traditional automotive stamping. The margin for error is virtually non-existent when dealing with high-voltage systems.
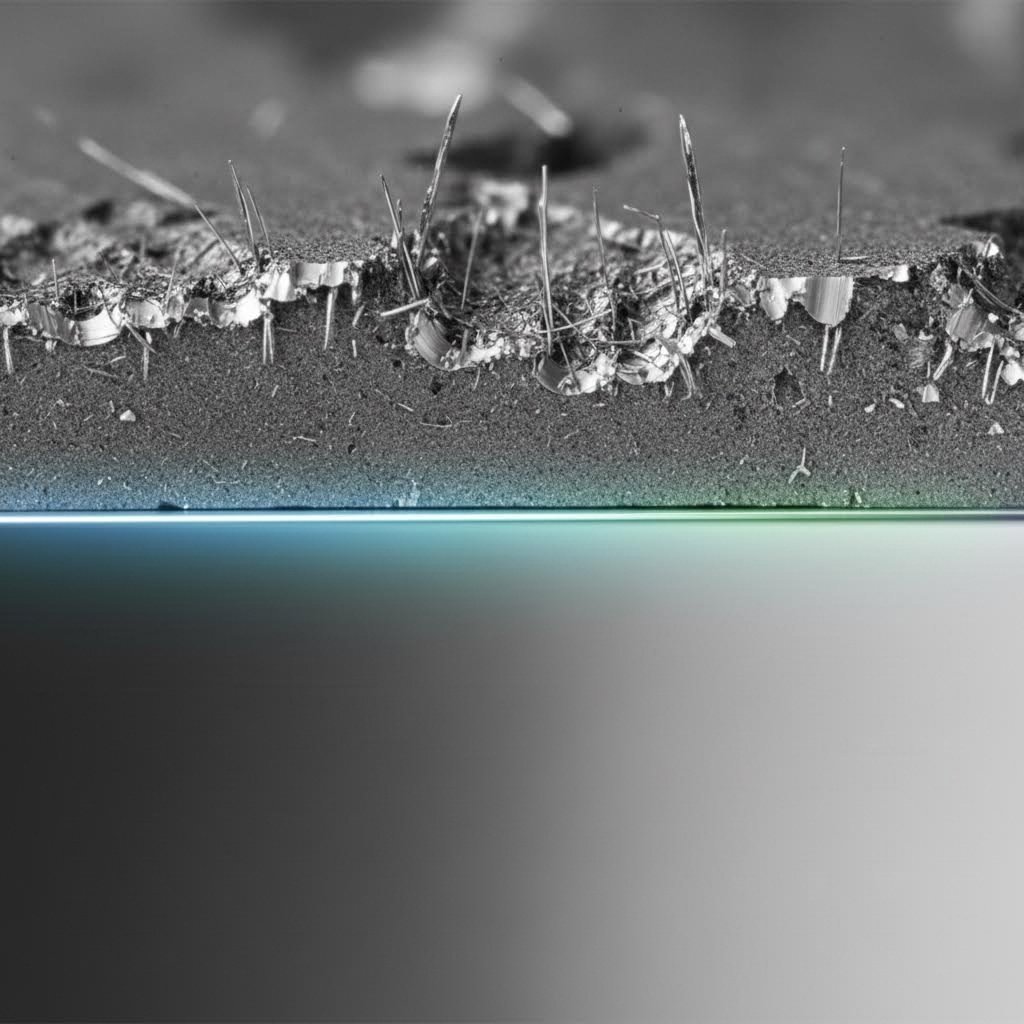
Technical Cleanliness (VDA 19.1): Perhaps the most critical hidden requirement is cleanliness. Metallic burrs or loose particles from the stamping process can detach inside a battery module, causing a short circuit and potentially a thermal runaway event. Stampers must employ strict deburring processes and wash systems to meet cleanliness standards like VDA 19.1, ensuring parts are free of conductive debris.
Thermal Management: Stamped cooling plates and heat sinks must be perfectly flat to maximize contact with battery cells. Even a micron of air gap acts as an insulator, reducing cooling efficiency. Achieving this flatness requires precision levelers and often in-die sensing to monitor part geometry in real-time.
Quality Control & Validation (Vision Systems)
In the EV sector, a defect rate of "parts per million" is often considered too high; the goal is zero defects. To achieve this, modern stamping lines are equipped with integrated vision systems.
These high-speed cameras inspect 100% of the parts inline, checking for critical dimensions, missing features, or surface defects without slowing down the press. Automated quality assurance systems ensure that every connector pin is straight and every busbar is within tolerance before it is packed. This level of scrutiny, backed by certifications like IATF 16949, provides the traceability and confidence required by major automotive OEMs.
Conclusion
Precision metal stamping is more than just a manufacturing process; it is a foundational technology enabling the electric vehicle revolution. By delivering scalability, material efficiency, and micron-level precision, stamping allows engineers to design battery packs that are safer, lighter, and more powerful. As the industry evolves, the collaboration between battery designers and stamping specialists will continue to drive innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in energy storage and mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between progressive die and deep draw stamping for EV parts?
Progressive die stamping feeds a metal strip through multiple stations to cut, bend, and form complex parts like busbars and connectors at high speeds. Deep draw stamping, conversely, stretches a flat metal blank into a die to create hollow, seamless shapes like battery cans. Progressive dies are best for intricate, flat-to-formed components, while deep draw is essential for cylindrical or box-like enclosures.
2. Why is technical cleanliness important in EV battery stamping?
Technical cleanliness is vital because conductive metallic particles or burrs left on stamped parts can cause internal short circuits within a battery pack. These shorts can lead to battery failure or dangerous thermal runaway events. Standards like VDA 19.1 dictate strict limits on particle size and count to ensure the safety of high-voltage systems.
3. What materials are most commonly stamped for EV battery components?
Copper and aluminum are the most common materials due to their electrical conductivity and weight characteristics. Copper is used for high-current applications like main busbars, while aluminum is used for lightweighting and structural casings. Clad metals, which bond layers of copper and aluminum, are also growing in popularity to balance performance and cost.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
