Maximize Die Lifespan: Automotive Production Strategies
TL;DR
Optimizing die life in automotive production is a multi-faceted process essential for maximizing efficiency and return on investment. Success hinges on a strategic combination of advanced die design, proactive maintenance, precise thermal management, and careful material selection. By integrating these core principles, manufacturers can significantly extend a tool's operational lifespan, reduce production costs, and ensure consistent, high-quality part output.
The Critical Role of Die Design and Simulation
The foundation of a long-lasting and effective die is laid long before the first piece of metal is cast. Optimal die design, guided by the principles of Design for Manufacturability (DFM), is the single most important factor in preventing premature wear and ensuring efficient production. DFM is an engineering practice focused on designing parts and molds in a way that simplifies manufacturing, reduces costs, and enhances durability. By addressing potential issues at the design stage, companies can avoid costly downstream corrections and production delays.
Several key DFM parameters are critical for die casting molds. Draft angles, for instance, are slight tapers incorporated into the mold cavity walls that facilitate easy removal of the cast part, reducing stress on both the component and the die itself. Smooth radii and fillets on internal and external edges are also crucial, as they prevent stress concentrations and improve the flow of molten metal, mitigating defects. Other important considerations include uniform wall thickness to ensure consistent cooling and prevent warping, and the strategic placement of parting lines to minimize flash and simplify part extraction. When these elements are thoughtfully integrated, the result is a more robust and reliable die. For instance, companies that specialize in high-quality tooling, like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology Co., Ltd., leverage their expertise in custom automotive stamping dies to deliver solutions that are optimized from the very beginning for longevity and precision, serving top-tier automotive suppliers.
Modern die design is heavily reliant on advanced simulation software. Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) tools, such as THERCAST®, allow engineers to simulate the entire die casting process before manufacturing begins. These simulations can predict metal flow patterns, identify potential thermal stress points, and forecast defects like gas porosity or shrinkage. As noted in a guide for automotive engineers, this virtual testing allows for the optimization of process parameters—like melt temperature and shot curve—and mold design adjustments before committing to expensive physical tooling. This proactive approach not only saves time and resources but is critical to achieving high-quality cast parts with fewer iterations.
A die designed with DFM principles and validated through simulation stands in stark contrast to one created without them. The optimized die will have a longer operational life, produce parts with greater consistency and fewer defects, and contribute to shorter cycle times. This translates directly to lower scrap rates, reduced maintenance downtime, and a higher overall return on investment. To put this into practice, engineers should follow a clear set of best practices during the design phase.
- Prioritize Draft: Ensure all surfaces parallel to the mold opening have adequate draft angles to prevent dragging and wear upon ejection.
- Incorporate Fillets and Radii: Avoid sharp corners wherever possible to distribute stress and improve metal flow.
- Maintain Uniform Wall Thickness: Design parts with consistent thickness to promote even cooling and reduce the risk of warping or sink marks.
- Strategically Place Parting Lines: Position parting lines to be as simple as possible and on edges that allow for easy and inconspicuous flash removal.
- Use Ribs for Strength: Add ribs to strengthen thin walls and aid metal flow rather than increasing overall wall thickness.

Advanced Thermal Management and Cooling Strategies
One of the most significant contributors to die failure is thermal fatigue. The relentless cycle of injecting molten metal at high temperatures followed by rapid cooling places immense stress on the die steel. Over thousands of cycles, this thermal shock leads to micro-cracks, which can eventually grow into catastrophic failures, causing warping, cracking, and a loss of dimensional accuracy. Therefore, advanced thermal management is not just a performance enhancer but a critical necessity for prolonging die life in automotive production.
The core of effective thermal management lies in the die's cooling system. Well-designed cooling channels are essential for extracting heat uniformly and efficiently from the mold. The goal is to maintain a consistent temperature across the die surface, which helps control the solidification of the casting and mitigates the damaging effects of thermal stress. According to best practices in the industry, proper thermal management can improve cycle times by as much as 25% while also enhancing part quality, making it a key area of focus for optimization.
To achieve this, engineers employ various strategies. The strategic placement and sizing of cooling channels are fundamental, ensuring that areas with greater thermal mass receive adequate cooling. Modern techniques have advanced beyond simple drilled lines. Conformal cooling channels, for example, are designed to follow the complex contours of the die cavity, providing much more effective and uniform heat transfer. This leads to faster and more consistent cooling, which directly translates to improved die longevity and higher-quality parts. Using die materials with high thermal conductivity can further enhance the efficiency of the cooling system.
Optimizing a cooling system requires a systematic, data-driven approach. It involves more than just the initial design; it extends to ongoing maintenance and analysis. Blockages or inefficiencies in the cooling system can quickly lead to hotspots and premature die failure. By implementing a robust thermal strategy, manufacturers can significantly reduce downtime, lower replacement costs, and produce parts with superior surface finishes and mechanical properties.
- Utilize Thermal Analysis Tools: Employ simulation software during the design phase to analyze the die's thermal performance and identify potential hotspots before manufacturing.
- Implement Conformal Cooling: Where feasible, use conformal cooling channels that follow the shape of the part for more efficient and uniform heat removal.
- Ensure Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean cooling channels to prevent blockages from sediment or scale, which can severely impede cooling efficiency.
- Select Appropriate Die Materials: Choose tool steels with high thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock to complement the cooling system design.
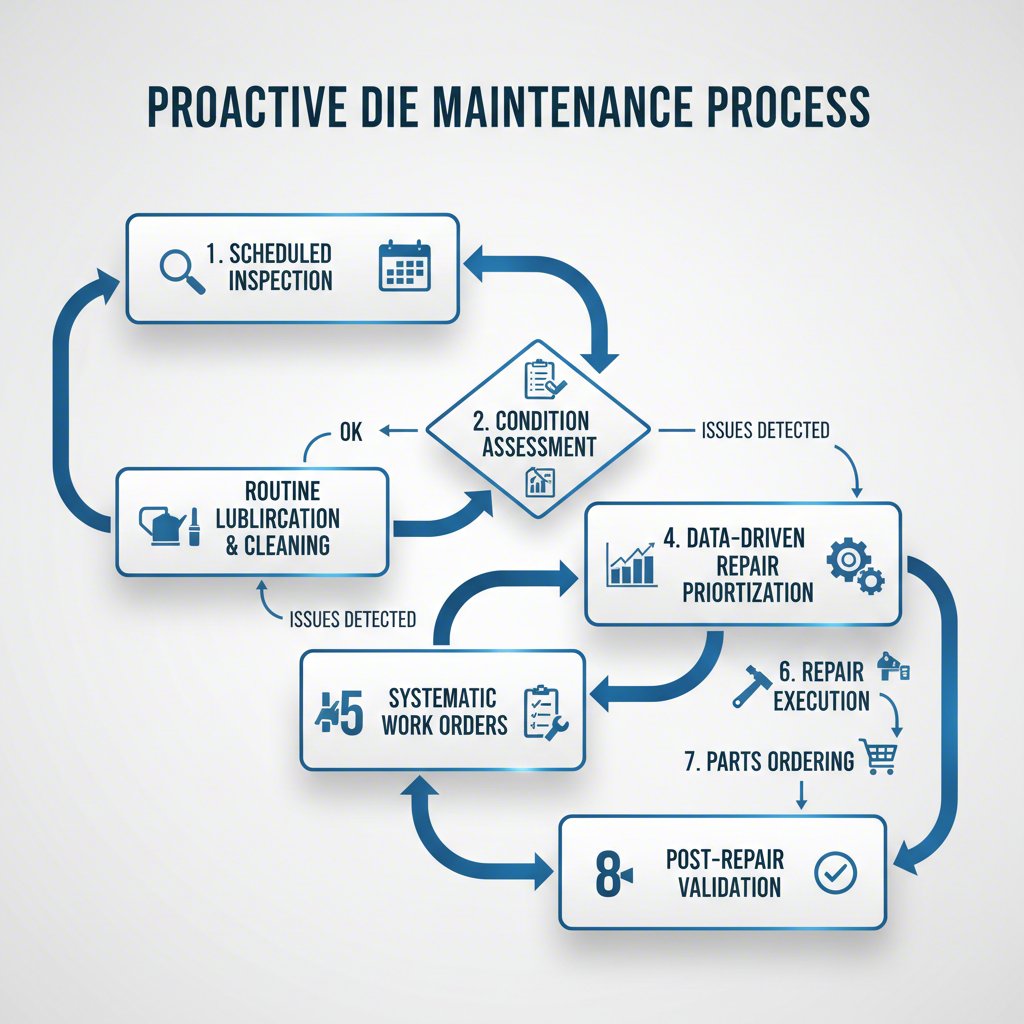
Proactive Maintenance and Systematic Repair Strategies
In a high-pressure production environment, it is easy to fall into a reactive maintenance cycle—fixing dies only when they break. However, this approach leads to unexpected downtime, increased costs, and inconsistent part quality. A far more effective strategy is a proactive and systematic approach to die maintenance and repair. This involves routine inspections, preventative actions, and a data-driven system for prioritizing work, ensuring that resources are allocated to the most critical tasks to maintain productivity and quality.
The costs associated with poor die maintenance are substantial. Beyond the obvious expense of emergency repairs, it leads to quality defects that require costly sorting, increases scrap rates, and risks shipping faulty parts to customers. As detailed in a comprehensive guide on the topic, lost press time for temporary fixes and subsequent permanent corrections can double maintenance costs. A robust die shop management system transforms maintenance from a cost center into a value-driver by preventing these issues before they occur.
A cornerstone of a modern maintenance program is a data-based prioritization system, sometimes referred to as a decision tree. This framework allows die shop managers to prioritize open work orders based on production needs, customer satisfaction, and ROI. For example, a work order related to a formal customer quality complaint or a "No Build" condition would take precedence over a minor formability issue. This ensures that the most meaningful and impactful work is addressed first, improving the effectiveness of the entire department.
This systematic approach is supported by a comprehensive work order system. This system documents, tracks, and schedules all maintenance activities, serving as a vital communication tool. It identifies the root problem, details the corrective steps, and documents the work performed. This historical data is invaluable for tracking recurring issues and refining preventative maintenance plans. For instance, knowing that a zinc mold can typically last for one million shots while an aluminum mold lasts for around 100,000 to 150,000 shots helps in scheduling refurbishments before failures occur. By moving from a reactive to a proactive culture, manufacturers can dramatically extend die life, reduce unplanned downtime, and maintain control over part quality.
| Task | Frequency | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect for core wear and gate erosion | Every 10,000 cycles | Clean, measure critical dimensions, and perform weld repairs or refurbish as needed. |
| Check for micro-cracks on die surfaces | Daily | Perform non-destructive testing (NDT) and address any cracks before they propagate. |
| Clean and lubricate moving components | After each production run | Disassemble, clean vents and slides, lubricate pins and moving parts, and reassemble. |
| Verify cooling channel flow | Daily or after each production run | Flush cooling system to remove scale and ensure unrestricted coolant flow. |
Material Selection and Surface Treatments
The choice of material for the die itself is a critical decision that directly impacts its durability, resistance to wear, and overall lifespan. A die must withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses, so selecting high-performance, heat-resistant tool steels is essential for prolonging its life. The material must possess a combination of properties, including high thermal shock resistance to endure rapid temperature changes, toughness to resist cracking, and hardness to combat erosion and corrosion from molten metal.
One of the most commonly used materials for die casting is H13 tool steel, valued for its excellent balance of toughness, wear resistance, and high-temperature strength. However, the selection should be tailored to the specific application. For instance, dies used for casting zinc alloys, which have a lower melting point, may have different material requirements than those used for aluminum or magnesium. According to industry experts, using premium materials can extend die life by as much as 30%, making the initial investment in higher-quality steel a cost-effective decision in the long run.
Beyond the base material, advanced surface treatments and coatings play a pivotal role in enhancing die performance. These treatments modify the surface of the die to improve its properties without changing the core material. Techniques like nitriding, for example, introduce nitrogen into the surface of the steel, creating a very hard outer case that significantly improves resistance to wear and erosion. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coatings apply a thin, ultra-hard ceramic layer to the die surface, which can reduce friction, prevent material sticking (soldering), and further protect against wear.
Making the right choice requires a careful analysis of production requirements and common failure modes. A comparison of different materials and treatments against key performance metrics can guide engineers toward the optimal solution for their specific needs. By combining a high-quality base material with an appropriate surface treatment, manufacturers can create a robust die capable of withstanding the rigors of high-volume automotive production.
| Material / Treatment | Relative Cost | Expected Lifespan | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard H13 Tool Steel | Medium | Good | General-purpose aluminum and zinc casting. |
| Premium H13 (ESR) | High | Excellent | High-stress applications, complex geometries, and extended production runs. |
| Nitriding Treatment | Low (add-on) | +20-40% Lifespan | Reduces erosion and wear on core pins and cavity surfaces. |
| PVD Coating | Medium (add-on) | +30-50% Lifespan | Prevents soldering (aluminum sticking) and reduces friction in high-wear areas. |
When selecting a die material and treatment, engineers should consider the following:
- Casting Metal: What is the melting temperature and corrosiveness of the alloy being cast?
- Production Volume: What is the total number of parts expected from the die?
- Part Complexity: Does the part have intricate features or thin walls that increase stress on the die?
- Observed Failure Modes: What are the primary causes of failure in similar existing dies (e.g., heat checking, erosion, cracking)?
A Holistic Approach to Maximizing Die Longevity
Achieving maximum die life in the demanding environment of automotive production is not the result of a single action but the outcome of a holistic, integrated strategy. As we've explored, success begins with a foundation of intelligent design, fortified by advanced simulation, and is sustained through diligent thermal management and proactive maintenance. Each element—from the choice of draft angles to the scheduling of preventative repairs—plays a crucial role in the overall system.
The key takeaway for engineers and production managers is that these areas are interconnected. A well-designed die is easier to maintain. An effective cooling system reduces the thermal stress that maintenance aims to correct. And the selection of superior materials and surface treatments provides a greater buffer against the inevitable wear and tear of production. Neglecting one area will invariably undermine the effectiveness of the others.
By adopting this comprehensive viewpoint, manufacturing operations can shift from a reactive, problem-solving mode to a proactive, optimization-focused culture. This not only extends the operational lifespan of valuable tooling but also drives significant improvements in productivity, part quality, and profitability, ensuring a competitive edge in the automotive industry.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —