How Digitalization in Die Casting Unlocks Peak Efficiency
TL;DR
Digitalization in the die casting industry, often called 'Die-Casting 4.0,' is a strategic shift that integrates advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and digital twins into the manufacturing process. This transformation enables real-time data monitoring and predictive analysis, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, a drastic reduction in material waste, and enhanced process control. Ultimately, this data-driven approach allows foundries to produce higher quality components more consistently and build more resilient production systems.
The Driving Force: Why Digitalization is Redefining the Die-Casting Industry
The die casting industry, a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, is undergoing a profound transformation. Driven by global challenges and an intense need for greater efficiency and cost transparency, foundries are moving away from traditional, experience-based operations toward data-driven, intelligent systems. This evolution, known as digitalization, is not merely about adopting new software; it's a fundamental rethinking of how metal parts are designed, produced, and perfected. The core motivation is to overcome long-standing challenges such as process variability, material waste, and the high costs associated with defects and downtime.
In traditional die casting, processes often rely on generational expertise, where adjustments are made reactively based on past experience. While valuable, this approach can lead to inconsistencies and makes it difficult to pinpoint the root causes of defects. Digitalization changes this paradigm by introducing real-time process security and control. According to industry experts, the goal is to make processes more efficient in terms of costs and resource use, which has become essential for survival in a competitive market. By capturing and analyzing vast amounts of data from every stage of production, foundries can move from a reactive to a proactive model, anticipating issues before they impact the final product.
Collaboration has also emerged as a critical catalyst for this digital wave. As noted in discussions among industry leaders, many foundries are small to medium-sized enterprises that may lack extensive IT resources to harness their data effectively. By fostering partnerships and sharing knowledge, the industry can develop a 'joint digital backbone,' creating shared tools and platforms for production optimization and supply chain transparency. This collaborative mindset accelerates the adoption of new technologies and ensures that the entire sector becomes more robust and innovative.
Traditional vs. Digital Die-Casting
| Aspect | Traditional Die-Casting | Digital Die-Casting (Die-Casting 4.0) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Control | Manual monitoring; relies on operator experience | Automated, real-time monitoring with IoT sensors |
| Maintenance | Reactive (fix when broken) | Predictive (AI algorithms forecast failures) |
| Quality Assurance | Manual inspection; sample-based checks | Automated quality control with machine vision; 100% inspection |
| Decision Making | Based on historical data and intuition | Data-driven insights from real-time analytics |
| Optimization | Trial-and-error on physical machines | Simulation and optimization using digital twins |
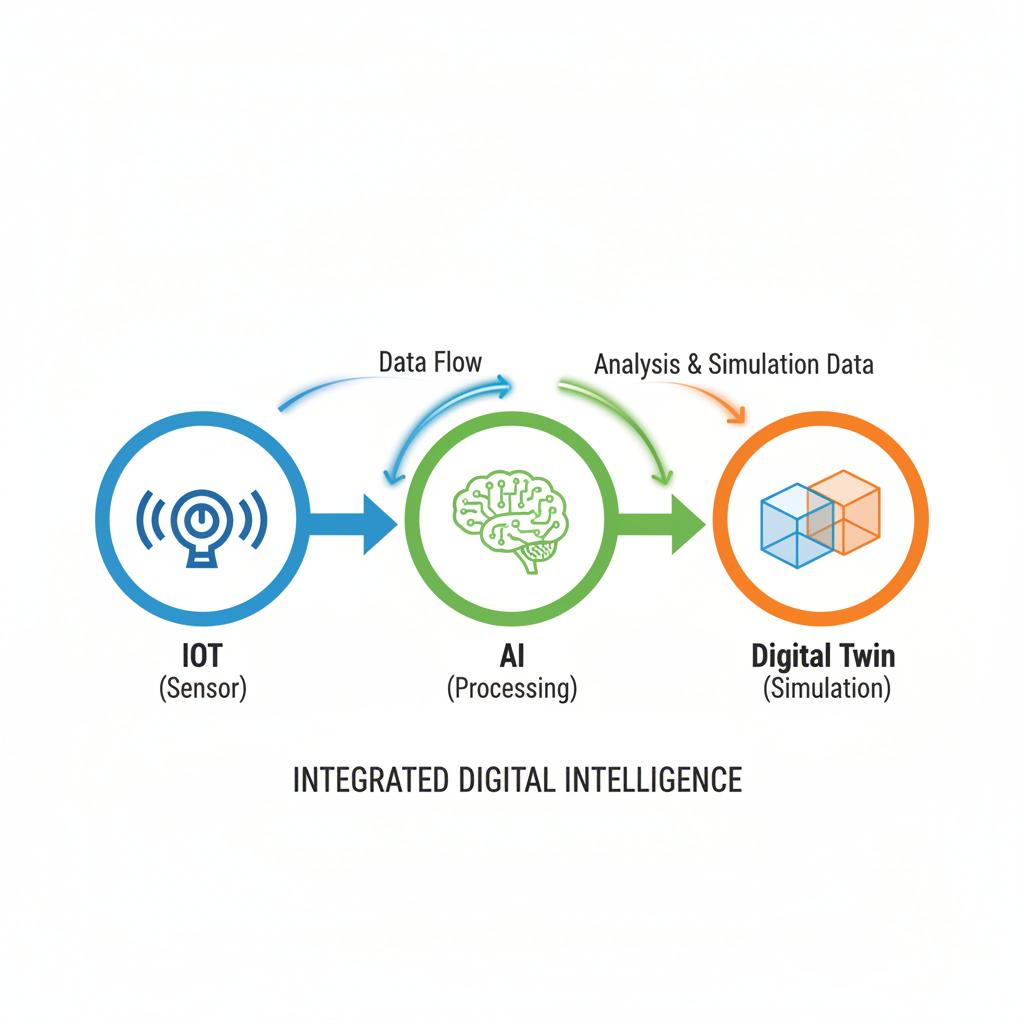
Core Technologies of the Smart Foundry: AI, IoT, and Digital Twins
The vision of a 'smart foundry' is built upon a foundation of interconnected technologies that enable machines to communicate, analyze, and self-optimize. At the heart of this transformation are three pillars: the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Digital Twin technology. Together, they create a cohesive ecosystem that provides unprecedented visibility and control over the entire die casting process, turning raw data into actionable intelligence.
The Internet of Things (IoT) serves as the nervous system of the smart foundry. It involves embedding sensors into die casting machines and related equipment to collect real-time data on critical parameters like temperature, pressure, cycle time, and material quality. This constant stream of information allows manufacturers to monitor the health and performance of their operations with extreme precision. Instead of relying on periodic checks, operators can instantly detect deviations from optimal conditions, enabling immediate adjustments that lead to better quality and less waste.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) acts as the brain, processing the massive datasets collected by IoT sensors. AI algorithms can identify complex patterns and correlations that are invisible to the human eye, enabling powerful capabilities like predictive maintenance. As detailed in industry analyses, AI can analyze machine data to predict potential failures before they occur, dramatically reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Furthermore, AI optimizes process parameters by learning which combinations yield the best results, continuously improving product quality and reducing defect rates.
Digital Twin technology provides a virtual sandbox for innovation. A digital twin is a dynamic, virtual replica of a physical die casting process or machine. By modeling potential issues before they occur in the real world, digital twins allow engineers to simulate and validate changes without risking physical assets or interrupting production. For example, a new die design or a change in alloy composition can be tested virtually to perfect the process, improve process control, and reduce material waste before a single part is cast. This capability dramatically accelerates innovation and enhances overall productivity.
These technologies are not standalone solutions but are deeply interconnected:
- IoT collects the high-volume, real-time data.
- AI analyzes this data to provide insights, predictions, and optimization recommendations.
- Digital Twins use this data and AI-driven insights to simulate and test improvements in a risk-free virtual environment.
A practical example of their synergy is an IoT sensor detecting a subtle pressure fluctuation in a die casting machine. An AI algorithm immediately analyzes this anomaly against historical data and predicts a potential die failure within the next 50 cycles. This alert is then used in a digital twin to simulate the effect of adjusting machine parameters to mitigate the issue, confirming the optimal solution before applying it to the physical machine, thereby preventing a costly shutdown.
Implementing 'Die-Casting 4.0': Frameworks and Practical Applications
The strategic implementation of these digital technologies is known as 'Die-Casting 4.0,' which applies the principles of Industry 4.0 to the foundry environment. It represents a move toward a fully integrated, automated, and intelligent production system where data flows seamlessly from the shop floor to top-floor decision-making. Achieving this vision is not just a technological challenge but also an organizational one, requiring a clear roadmap, strategic investment, and a cultural shift toward data-driven operations.
A successful transition to Die-Casting 4.0 begins with establishing a robust digital framework. This involves more than just purchasing software; it requires a holistic approach to integrating systems for production planning, resource management, and process control. As described in a case study on the topic, a key goal is to achieve cost transparency and process security in real time. Systems like Foundry Resource Planning (FRP) create a 'digital twin' of the entire operation, from inquiry to dispatch, allowing for precise tracking of costs, materials, and efficiency on a single platform. This level of detail replaces guesswork with accurate data, enabling foundries to understand their true costs and profitability for every part they produce.
Automation is a cornerstone of Die-Casting 4.0. The integration of robotics for tasks such as pouring molten metal, extracting parts, and performing quality inspections significantly enhances efficiency, consistency, and worker safety. Automation streamlines the production flow, reduces human error, and allows for continuous, high-speed operation, which is critical in today's demanding manufacturing landscape.
This digital transformation also strengthens the supply chain, as OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers increasingly rely on partners with proven expertise in advanced manufacturing. For instance, specialists in advanced metal forming leverage data-driven processes and CAE simulations, reflecting the precision and efficiency that Industry 4.0 principles bring to the entire metal components ecosystem. Such capabilities are becoming a prerequisite for competing in sectors like automotive, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable.
For a foundry beginning its journey, the path to Die-Casting 4.0 can be broken down into actionable steps:
- Assess Digital Maturity: Evaluate current processes, systems, and workforce skills to identify gaps and opportunities for digitalization.
- Develop a Strategic Roadmap: Define clear goals, prioritize areas for improvement (e.g., quality control, energy efficiency), and create a phased implementation plan.
- Invest in Foundational Technology: Start with core infrastructure like IoT sensors and data collection systems to begin capturing valuable production data.
- Train the Workforce: Equip employees with the skills to work alongside new technologies and foster a culture that embraces data-driven decision-making.
- Launch a Pilot Project: Implement a solution on a single machine or production line to demonstrate value, refine the approach, and build momentum for broader adoption.

The Future is Forged in Data
The digitalization of the die casting industry is not a distant trend; it is a transformation happening now. By embracing Die-Casting 4.0, foundries are evolving from traditional manufacturers into agile, intelligent factories capable of meeting the complex demands of modern supply chains. The integration of AI, IoT, and digital twins provides the tools to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
This shift is fundamentally about harnessing the power of data to make smarter decisions at every level of the operation. From optimizing a single machine's cycle time to managing the entire production workflow, digitalization provides the clarity and control needed to thrive. Companies that invest in these technologies and cultivate a digital-first mindset will not only enhance their competitiveness but also lead the way in forging the future of manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the new technologies in die casting?
The most impactful new technologies in die casting are centered around Industry 4.0 principles. These include the Internet of Things (IoT), which uses sensors for real-time process monitoring of temperature and pressure; Artificial Intelligence (AI) for data analysis, predictive maintenance, and process optimization; and Digital Twins, which are virtual replicas of physical processes used for simulation and testing. Automation through robotics for tasks like part extraction and quality inspection is also becoming standard.
2. Can die casting be automated?
Yes, die casting is highly suitable for automation. Robots are commonly used to perform repetitive and hazardous tasks such as pouring molten metal, extracting finished castings from the die, and spraying the die with lubricant. Further automation includes robotic systems for quality inspection, trimming, and other post-processing steps. This integration increases production speed, ensures consistent quality, and improves worker safety, forming a key component of Die-Casting 4.0.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 

