Metal Cutting Companies Decoded: From Quote Request To Finished Parts
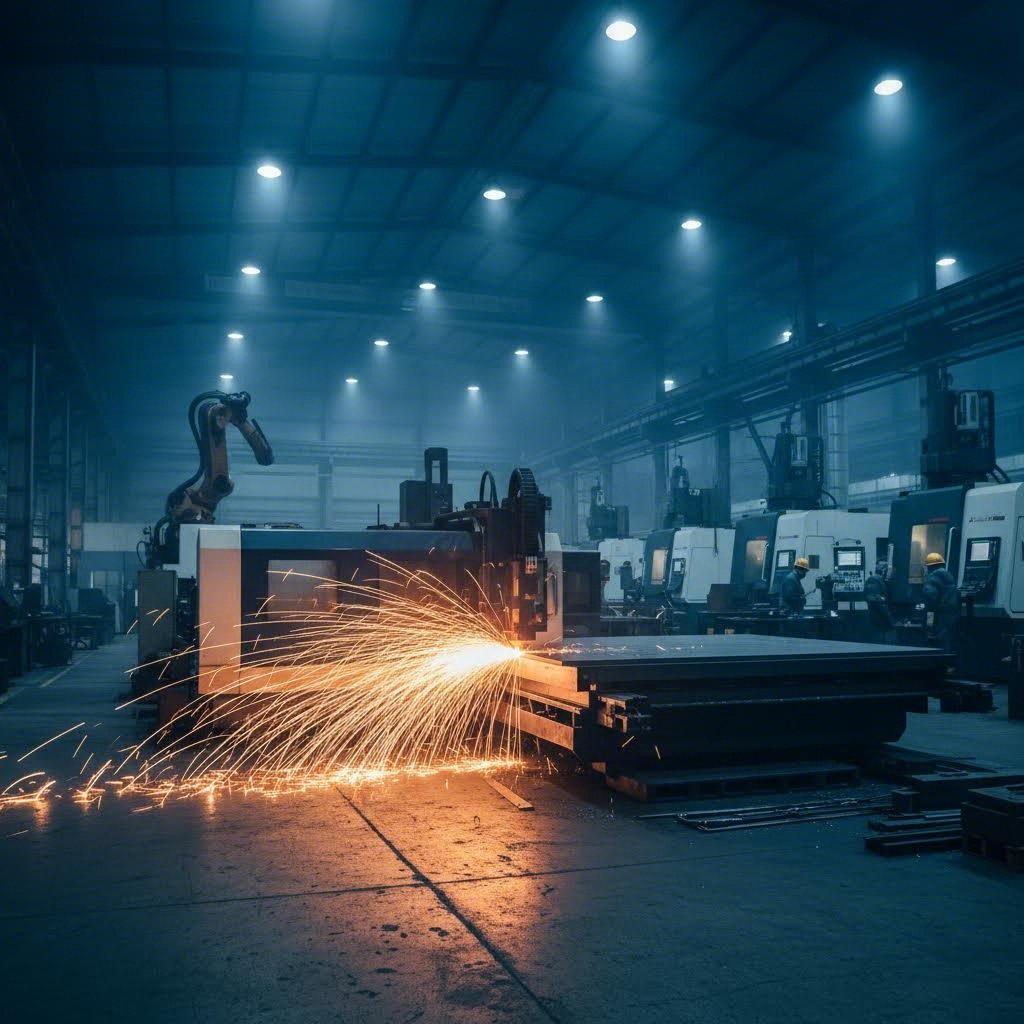

Understanding Metal Cutting Companies and Their Manufacturing Role
When you need custom metal parts—whether for a prototype, a production run, or a specialized project—where do you turn? The answer lies with metal cutting companies, the specialized manufacturers that transform raw metal sheets and stock into precisely shaped components. These service providers form a critical link between your design concepts and tangible, functional parts.
What Metal Cutting Companies Actually Do
Metal cutting companies are specialized manufacturers that remove material from metal workpieces to create desired shapes and sizes. According to Mark Metals, metal cutting encompasses a broad range of techniques including sawing, shearing, drilling, grinding, waterjet cutting, and laser cutting. But these companies typically offer far more than cutting alone.
Think of a metal cutting company as your one-stop manufacturing partner. They handle everything from precision laser cutting of intricate designs to large-scale industrial fabrication for structural components. Many metal cutting service companies also provide secondary operations—forming, joining, and finishing processes that take your parts from raw cut pieces to ready-to-use components.
The scope of services varies widely. Some companies that cut metal specialize in specific technologies like fiber laser or waterjet systems, while others operate as full-service fabricators offering:
- Laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and plasma cutting
- CNC bending and forming operations
- Welding and assembly services
- Surface finishing like powder coating, anodizing, and plating
- Quality inspection and certification documentation
The Manufacturing Backbone You Rely On
Why should you care about understanding this industry? Because whether you're an engineer designing automotive brackets, a product developer prototyping consumer electronics enclosures, or a contractor sourcing structural components, you'll likely work with these manufacturers at some point.
Modern metal cutting service companies serve virtually every industry imaginable. As Xometry notes, they regularly support aerospace, defense, automotive, energy, industrial, medical, dental, and consumer product sectors. Their capabilities range from low-volume, high-mix prototypes to high-volume production runs numbering in the thousands or millions.
The efficiency these companies offer comes from specialized equipment and expertise. Metal cutting tool companies invest heavily in advanced machinery—fiber lasers that cut with micron-level precision, waterjets that slice through virtually any material, and automated systems that maintain consistent quality across large production batches. This specialization means reduced lead times and improved quality control compared to handling fabrication in-house.
In the sections ahead, you'll discover how different cutting technologies work, which methods suit specific materials and applications, and how to navigate the process from initial quote request to finished parts delivery. You'll also learn practical criteria for evaluating metal cutting tools companies and preparing your projects for success. Consider this your comprehensive guide to becoming an informed customer in the metal fabrication marketplace.

Metal Cutting Technologies and How Each Method Works
So you know what metal cutting companies do—but how exactly do they cut through steel, aluminum, or titanium with such precision? The answer depends entirely on which technology they use. Each cutting method operates on fundamentally different principles, and understanding these differences helps you choose the right approach for your project.
Let's break down the five major cutting technologies you'll encounter when working with metal laser cutting companies and other fabrication service providers.
Laser Cutting Explained
Imagine focusing sunlight through a magnifying glass—now multiply that intensity by thousands. That's the basic principle behind laser cutting. A highly concentrated beam of light delivers enough energy to melt, burn, or vaporize metal along a precisely controlled path.
Two types of lasers dominate the industry today: fiber lasers and CO2 lasers. According to HPC Laser, fiber laser cutting machines use optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements like ytterbium to generate their beam. This technology excels at cutting reflective metals including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and titanium.
The advantages of fiber lasers are compelling:
- Exceptional precision with minimal kerf width
- High cutting speeds, especially on thin materials
- Lower maintenance requirements than CO2 systems
- Superior energy efficiency
- Excellent performance on reflective metals
CO2 lasers, operating at a different wavelength (10.6 micrometers), remain the preferred choice for cutting non-metals like acrylic and certain plastics. However, fiber laser metal cutting machine companies have largely captured the market for metal processing applications due to their speed and efficiency advantages.
When should you specify laser cutting? According to Wurth Machinery, laser technology takes the lead when you need fine details, precise holes, or clean edges on thin sheets. It's ideal for electronics, medical devices, and precision parts manufacturing where even slight deviations can compromise functionality. Sheet metal laser cutting machine companies often achieve tolerances within ±0.005 inches on thin gauge materials.
Waterjet vs Plasma Technology
What if heat is your enemy? Certain materials warp, harden, or lose their properties when exposed to high temperatures. This is where waterjet cutting shines.
A metal waterjet cutting company uses an entirely different approach: high-pressure water (typically 60,000 PSI or higher) mixed with abrasive particles like garnet. This stream cuts through metal without generating heat, eliminating heat-affected zones entirely. Zintilon notes that waterjet cutting is particularly suitable for heat-sensitive materials like aluminum and titanium where thermal distortion would be problematic.
Key waterjet advantages include:
- No heat-affected zones or material distortion
- Ability to cut virtually any material—metals, stone, glass, composites
- Excellent for thick materials and stacked cutting
- No hardening of cut edges
- Environmentally friendly with minimal waste
Plasma cutting operates on the opposite end of the spectrum. It uses an electrical arc combined with compressed gas to create superheated plasma that melts through conductive metals. Plasma cutting thin sheet metal companies and heavy fabricators alike rely on this technology for its exceptional speed on thick materials.
According to Wurth Machinery's testing, plasma cutting 1-inch steel runs approximately 3-4 times faster than waterjet, with operating costs roughly half as much per foot. If you're working with structural steel, heavy equipment components, or shipbuilding applications, plasma offers unmatched cost-effectiveness.
However, plasma cutting painted metal companies face limitations—the process works only on electrically conductive materials and produces a wider kerf than laser cutting. For thick conductive metals where precision isn't paramount, plasma remains the workhorse of the industry.
When Mechanical Cutting Makes Sense
Not every cutting job requires high-tech solutions. CNC metal cutting companies often employ mechanical methods like routing, sawing, shearing, and punching for specific applications.
CNC routing uses rotating cutting tools to remove material, similar to milling operations. This method works well for softer metals and applications requiring specific edge profiles or complex 3D contours. Laser metal cutting machine companies sometimes complement their laser capabilities with routing for applications where lasers aren't ideal.
Mechanical shearing and punching remain cost-effective for high-volume production of simple shapes. These processes are fast, require minimal setup, and produce consistent results on thin sheet metal. Turret punch presses can produce dozens of holes per minute—speeds that even lasers struggle to match for certain operations.
Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) fills a unique niche. This process uses electrical discharges from a thin wire to erode material with extreme precision. Zintilon explains that wire EDM excels with hard metals and complex geometries requiring tight tolerances, making it invaluable for tool-and-die work, aerospace components, and intricate mechanical parts.
| Technology | Best Materials | Thickness Range | Precision Level | Speed Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser | Steel, stainless, aluminum, brass, copper, titanium | Up to 1" (varies by power) | ±0.005" typical | Very fast on thin materials; slows on thick |
| CO2 Laser | Metals, acrylics, plastics, wood | Up to 1" on metals | ±0.005" typical | Fast; slightly slower than fiber on metals |
| Waterjet | Any material (metals, stone, glass, composites) | Up to 12"+ depending on material | ±0.003" to ±0.010" | Slower than plasma/laser; no heat limitations |
| Plasma | Conductive metals only (steel, aluminum, copper) | 26 gauge to 6"+ thick | ±0.020" typical | Fastest on thick conductive metals |
| CNC Routing | Softer metals, plastics, composites | Varies by material | ±0.005" to ±0.010" | Moderate; good for 3D contours |
| Wire EDM | Any conductive metal, especially hardened steels | Up to 16" typical | ±0.0001" possible | Slow; prioritizes precision over speed |
Understanding these technologies helps you communicate effectively with fabrication partners and select the right cutting method for your specific requirements. But technology is only part of the equation—the materials you're cutting play an equally important role in determining the optimal approach.
Materials and Thickness Capabilities Across Cutting Methods
Now that you understand how each cutting technology works, here's the critical question: which method works best for the specific metal you need cut? The answer isn't always straightforward because material properties dramatically influence cutting performance. Reflectivity, thermal conductivity, hardness, and thickness all play decisive roles in determining the optimal approach.
Sheet metal cutting companies encounter dozens of different alloys daily. Understanding how these materials interact with various cutting technologies helps you specify the right process—and avoid costly mistakes that lead to project delays.
Material-to-Method Matching Guide
Every metal brings unique characteristics to the cutting table. Let's examine the most common materials and their ideal cutting approaches.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel's combination of corrosion resistance and strength makes it a favorite across industries. Sheet metal laser cutting companies typically recommend fiber laser cutting for stainless up to 1" thick due to excellent edge quality and speed. For thicker sections, plasma cutting offers cost-effective processing, while waterjet cutting preserves material properties when heat sensitivity is a concern.
- Optimal methods: Fiber laser (thin to medium), plasma (thick sections), waterjet (heat-sensitive applications)
- Key consideration: Higher chromium content can affect laser cutting speed
Aluminum
Aluminum's high reflectivity once made it challenging for laser cutting, but modern fiber lasers handle it with ease. According to StarLab CNC, fiber lasers excel on aluminum sheet, while plasma cutting works well on thicker aluminum plates. Waterjet remains the premium choice when you need zero heat-affected zones—particularly important for aerospace applications where material integrity is non-negotiable.
- Optimal methods: Fiber laser (sheet gauge to 0.5"), waterjet (heat-sensitive), plasma (thicker plates)
- Key consideration: Thermal conductivity requires higher power settings for laser cutting
Carbon Steel and Mild Steel
Carbon steel is the workhorse material for metal cutting and fabrication companies. It cuts well with virtually every technology, making method selection primarily a function of thickness and required precision. Thin sheets respond beautifully to laser cutting, while heavy plate (over 1") is plasma cutting's sweet spot.
- Optimal methods: Laser (up to 1"), plasma (0.5" to 6"+), waterjet (any thickness)
- Key consideration: Plasma cutting offers the best speed-to-cost ratio on thick carbon steel
Copper and Brass
These highly reflective metals were traditionally difficult for laser systems. Today's high-powered fiber lasers have largely solved this challenge, though metal sheet cutting machine companies still exercise caution with thin copper to prevent back-reflections that can damage equipment. Waterjet cutting remains a reliable alternative that sidesteps reflectivity issues entirely.
- Optimal methods: Fiber laser (with appropriate power), waterjet (safe for all thicknesses), plasma (limited applications)
- Key consideration: Copper's thermal conductivity disperses heat rapidly, requiring adjusted parameters
Specialty Alloys (Titanium, Inconel, Tool Steels)
When you're working with exotic alloys, the stakes—and costs—escalate quickly. Sheet metal laser cutting service companies often recommend waterjet for titanium and nickel-based superalloys because the cold-cutting process preserves metallurgical properties. Wire EDM handles hardened tool steels with unmatched precision, making it indispensable for tooling applications.
- Optimal methods: Waterjet (preserves properties), wire EDM (hardened materials), fiber laser (with expertise)
- Key consideration: Many specialty alloys require post-cut testing to verify material integrity
Thickness Capabilities by Metal Type
Thickness is often the deciding factor when choosing a cutting method. Here's what you can expect from sheet metal cutting company capabilities:
Thin Gauge Materials (Under 0.125")
Laser cutting dominates this range. The concentrated beam produces minimal kerf width, tight tolerances, and pristine edge quality. Speed advantages are dramatic—a fiber laser might cut 20-gauge steel at 800+ inches per minute. Waterjet and plasma can handle thin materials but rarely make economic sense unless heat avoidance is critical.
Medium Thickness (0.125" to 0.75")
This is the competitive zone where method selection depends on priorities. Need precision and clean edges? Laser cutting delivers. Prioritizing speed and cost on conductive metals? Plasma cutting shines. Require zero heat distortion? Waterjet is your answer. According to Gauer Metal Products, the right approach depends on factors like metal type, thickness, and the precision your project demands.
Thick Plate (0.75" and Above)
As material thickness increases, plasma and waterjet take center stage. Plasma cutting processes 1" steel at over 100 inches per minute—roughly 3-4 times faster than waterjet—making it the production workhorse for structural fabrication, heavy equipment, and shipbuilding. Waterjet cutting handles even thicker materials (up to 12"+ on some systems) and remains essential when heat-affected zones are unacceptable.
Material properties dictate method selection as much as thickness. A 0.5" aluminum plate may cut beautifully with fiber laser, while the same thickness in copper might perform better on a waterjet to avoid reflectivity complications.
Understanding these material-method relationships puts you in a stronger position when discussing your project with fabrication partners. You'll know which questions to ask and can evaluate whether a shop's recommendations align with industry best practices. Next, we'll walk through the complete fabrication workflow—from your initial quote request to finished parts arriving at your dock.
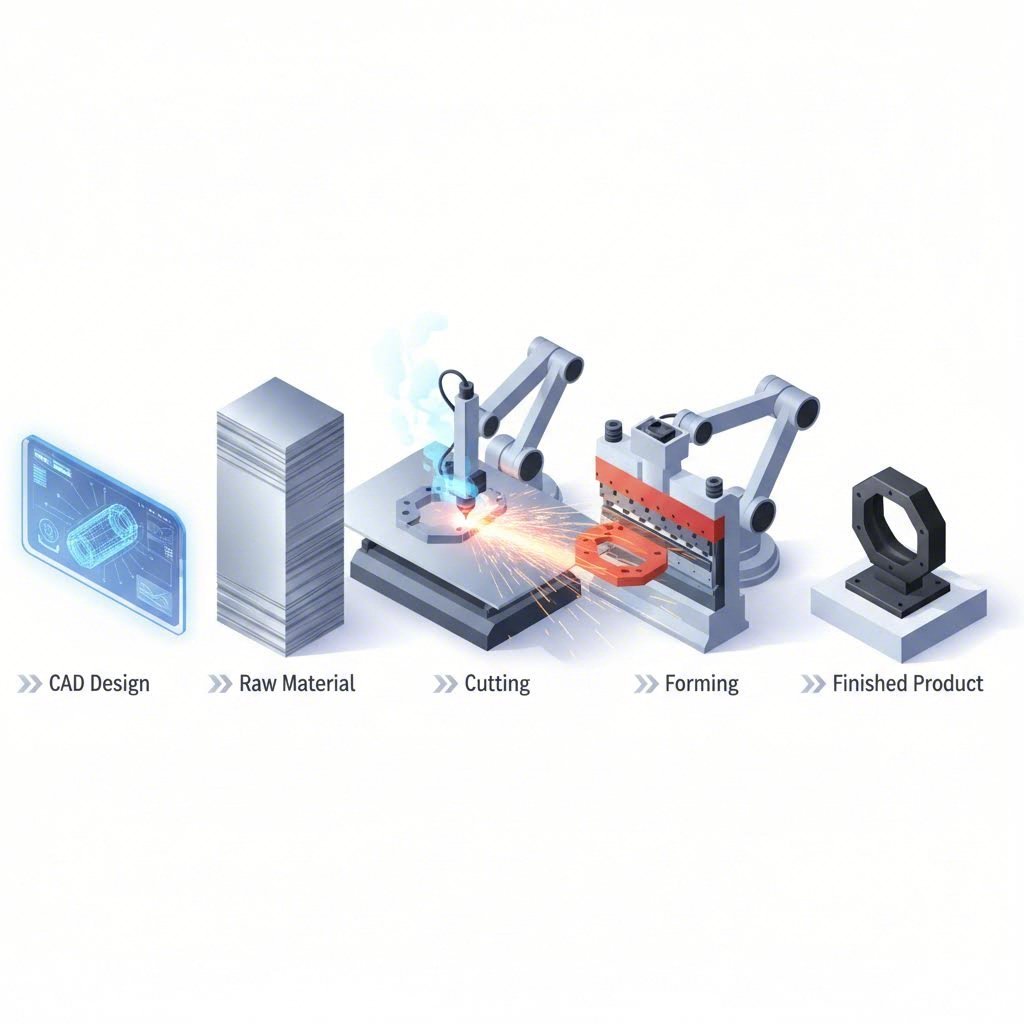
The Complete Metal Cutting Process From Start to Finish
You've selected your cutting technology and identified the right material—now what actually happens when you engage a metal cutting service company? Understanding the complete fabrication workflow removes uncertainty and helps you prepare projects that move smoothly from concept to completion.
Whether you're working with custom metal cutting companies for the first time or looking to streamline an existing relationship, knowing each stage of the process puts you in control. Let's walk through the journey your parts take from initial contact to final delivery.
From Quote Request to Finished Parts
The fabrication process follows a logical sequence, though timelines vary based on complexity, volume, and your specific requirements. According to H&S Manufacturing, sheet metal custom fabrication encompasses several distinct stages of production. Here's what to expect:
-
File Submission and Initial Contact
Your project begins when you submit design files to your chosen fabricator. Most sheet metal cutting service companies accept standard CAD formats including DXF, STEP, and IGES files. Some rapid fabrication services—like those offered by Approved Sheet Metal—provide interactive quoting systems where you upload files and receive pricing within hours. Include any special notes about tolerances, quantities, or finish requirements at this stage. -
Design Review and Engineering
During this phase, fabricators analyze your design for manufacturability. H&S Manufacturing notes that this might include creating prototypes and running feasibility studies to determine the right materials and processes. Experienced custom metal cutting company teams will flag potential issues—features that might not cut cleanly, bend radii that could cause cracking, or tolerances that require alternative approaches. This collaborative review saves time and money later. -
Quoting and Approval
You'll receive a detailed quote covering material costs, cutting operations, secondary processes, and delivery. Some laser cutting sheet metal stamping company operations offer same-day quoting for straightforward projects, while complex assemblies may require several days of engineering review. Once you approve the quote and confirm quantities, your order enters the production queue. -
Material Procurement and Preparation
Your fabricator sources the specified material—or pulls it from existing inventory. According to H&S Manufacturing, quality fabricators inspect raw materials for defects before processing. Sheet metal is cut to appropriate sizes using shears or laser equipment before the primary cutting operation begins. -
Primary Cutting Operation
This is where your parts take shape. CAD files translate into machine instructions that guide lasers, waterjets, or plasma torches along precise cutting paths. Modern equipment operates with minimal human intervention, though skilled operators monitor quality throughout. Depending on your sheet metal cutting service company's capacity and your order priority, this stage might take hours for simple jobs or days for complex production runs. -
Secondary Operations
Cutting is often just the beginning. Many parts require additional processing before they're complete—bending, welding, hardware insertion, or assembly. We'll explore these critical steps in detail below. -
Finishing and Surface Treatment
Surface treatments enhance both appearance and performance. Options range from simple deburring to powder coating, plating, or anodizing. Your fabricator applies specified finishes according to your requirements. -
Quality Inspection
Before shipping, parts undergo dimensional verification and visual inspection. Fabricators with ISO 9001 or similar certifications follow documented inspection protocols using precision measuring equipment. -
Packaging and Delivery
Parts are packaged to prevent damage during transit. Expedited services from companies like Approved Sheet Metal can deliver flat laser-cut parts as quickly as next day—order by 10:00 AM and receive parts by 10:00 AM the following day.
What Happens After Cutting
The cutting operation produces flat profiles, but most functional parts require additional processing. Understanding these secondary services helps you evaluate whether a fabricator can truly deliver finished parts—or just cut pieces that need further work elsewhere.
CNC Bending and Forming
Flat cut parts often need three-dimensional shape. CNC press brakes use precision tooling to create accurate bends at specified angles and locations. According to H&S Manufacturing, the forming process uses hydraulic presses and computer numerical control press brakes to achieve precise results. Common operations include V-bends, U-shaped channels, box forms, and complex multi-bend geometries. Tolerances of ±0.005 inches are achievable on properly designed parts.
Deburring and Edge Treatment
Cutting operations leave varying degrees of edge roughness depending on the method used. Laser cutting typically produces relatively clean edges, while plasma and mechanical cutting may leave more significant burrs. Deburring removes sharp edges that could cause handling injuries or interfere with assembly. Methods range from manual grinding to automated tumbling and vibratory finishing.
Welding and Joining
When your design requires multiple pieces joined together, welding creates permanent bonds. H&S Manufacturing describes how welders fuse parts together by applying heat and pressure, with the heated metal surfaces bonding and cooling to form strong joints. MIG, TIG, and spot welding each suit different applications and material combinations. Riveting provides an alternative mechanical fastening method for certain assemblies.
Surface Finishing Options
Finishing treatments protect parts and enhance aesthetics. Common options include:
- Powder coating: A dry electrostatic application process that produces durable, attractive finishes in virtually any color
- Painting: Water- or solvent-based coatings sprayed in one or more layers for corrosion protection and appearance
- Plating: Electroplating or electroless processes that apply thin metal layers to improve hardness, corrosion resistance, or conductivity
- Anodizing: An electrochemical process that creates protective oxide layers on aluminum parts
Hardware Installation and Assembly
Many fabricators offer turnkey services including PEM fastener insertion, threaded inserts, and component assembly. This consolidates your supply chain—instead of managing cutting, finishing, and assembly vendors separately, a single custom metal cutting company handles the complete package.
Working with a fabricator who offers comprehensive secondary services streamlines your supply chain and reduces the coordination burden on your team.
Understanding this complete workflow helps you set realistic timeline expectations and prepare projects that move efficiently through production. But before you submit that first quote request, you'll want to ensure your design files and specifications are properly prepared—which brings us to project preparation best practices.
Preparing Your Project for Metal Cutting Services
You've found the right cutting technology, identified your material, and understand the fabrication workflow. But here's where many projects stall: incomplete or improperly formatted design files. Custom cut sheet metal companies receive hundreds of quote requests—and the ones with complete, accurate documentation move to the front of the queue while others bounce back for clarification.
Taking time to prepare your project properly saves days (sometimes weeks) of back-and-forth communication. Whether you're working with a custom CNC metal cutting company for precision components or a high-volume fabricator for production runs, these preparation steps apply universally.
Preparing Your Design Files
Your CAD files are the blueprint that drives the entire manufacturing process. According to RapidDirect, CAD files contain necessary details about the features, dimensions, and geometry of a part—they're the structural framework for the CNC machining process.
Most custom cut sheet metal companies accept several standard file formats, though preferences vary. Here are the formats you should have ready:
- STEP (.STP): The gold standard for 3D models. STEP files offer excellent geometry preservation and work across virtually all CAD and CAM systems. If you're submitting one format, make it this one.
- DXF (.DXF): Ideal for 2D cutting operations. DXF files define flat patterns clearly and are universally accepted for laser, waterjet, and plasma cutting.
- IGES (.IGS): An older but still widely used format, particularly for surface models and legacy systems. IGES handles wireframes and 2D drawings well.
- Native CAD formats (.SLDPRT, .PRT, X_T): SolidWorks, Siemens NX, and Parasolid files retain full design history and parametric data—useful when your custom sheet metal cutting service company uses compatible software.
RapidDirect notes that STP and X_T files are known for their precise solid modeling capabilities, which is essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy during toolpath generation. When in doubt, export your design as a STEP file alongside your native format to ensure compatibility.
File Preparation Checklist
Before hitting send on that quote request, verify these critical details:
- Confirm units: Mismatched units (inches vs. millimeters) cause parts to arrive at the wrong scale. Double-check your export settings.
- Include flat patterns: For bent parts, provide the flat pattern layout in addition to the 3D model.
- Separate parts into individual files: Multi-part assemblies should be broken into discrete component files for clear pricing.
- Remove duplicate geometry: Overlapping lines confuse cutting machines and can cause double-cuts.
- Close all contours: Open paths or gaps in your geometry prevent proper cutting—ensure all shapes are fully enclosed.
Specification Details That Matter
Files alone don't tell the complete story. According to LTJ Industrial, clear documentation is critical for an accurate fabrication quote—detailed drawings, precise specifications, and complete CAD files minimize misunderstandings and unexpected costs.
When contacting custom CNC metal cutting companies, provide these specifications upfront:
- Material type and grade: Specify exactly—"304 stainless steel" rather than just "stainless." Include alloy designations, temper conditions, and any required certifications.
- Material thickness: State precise gauge or decimal thickness (e.g., "0.125 inch" or "11 gauge").
- Quantity required: Include prototype quantities, initial production runs, and estimated annual volumes if applicable.
- Tolerance requirements: According to SendCutSend, cut tolerances are typically ±0.005" for most materials—if you need tighter specs, call them out explicitly.
- Surface finish requirements: Specify if you need powder coating, anodizing, plating, or specific surface roughness values.
- Secondary operations: List bending, tapping, countersinking, hardware insertion, or assembly requirements.
- Delivery timeline: Rush orders require advance notice—include your target delivery date.
Common Mistakes That Delay Projects
Even experienced engineers make these errors. Avoid them and your project moves faster:
- Missing hole specifications: If holes need threading or countersinking, note the size and type. SendCutSend advises using threading charts to draw correct-size holes during the design process.
- Features too close to edges: SendCutSend recommends keeping holes at least 1X their diameter from an edge and slots at least 1.5X their width away from edges or other cut features. Violating these guidelines weakens parts and may make them uncuttable.
- Undersized bridging: The distance between cut features should be no less than 50% of material thickness—preferably 1X to 1.5X thickness for strength.
- Omitting bend information: For formed parts, specify bend direction, bend radius, and bend sequence if critical.
- Forgetting quantity breaks: If you might order larger quantities later, ask for tiered pricing now. Setup costs spread across more units dramatically reduce per-part pricing.
Planning ahead and knowing the cut tolerances for your chosen material will speed up the design process and ensure that your parts are ready for action as soon as they come out of the box.
Investing thirty minutes in proper project preparation can save days of delays. With complete files and clear specifications in hand, you're ready to evaluate potential fabrication partners—which requires understanding what separates exceptional custom cut sheet metal companies from mediocre ones.
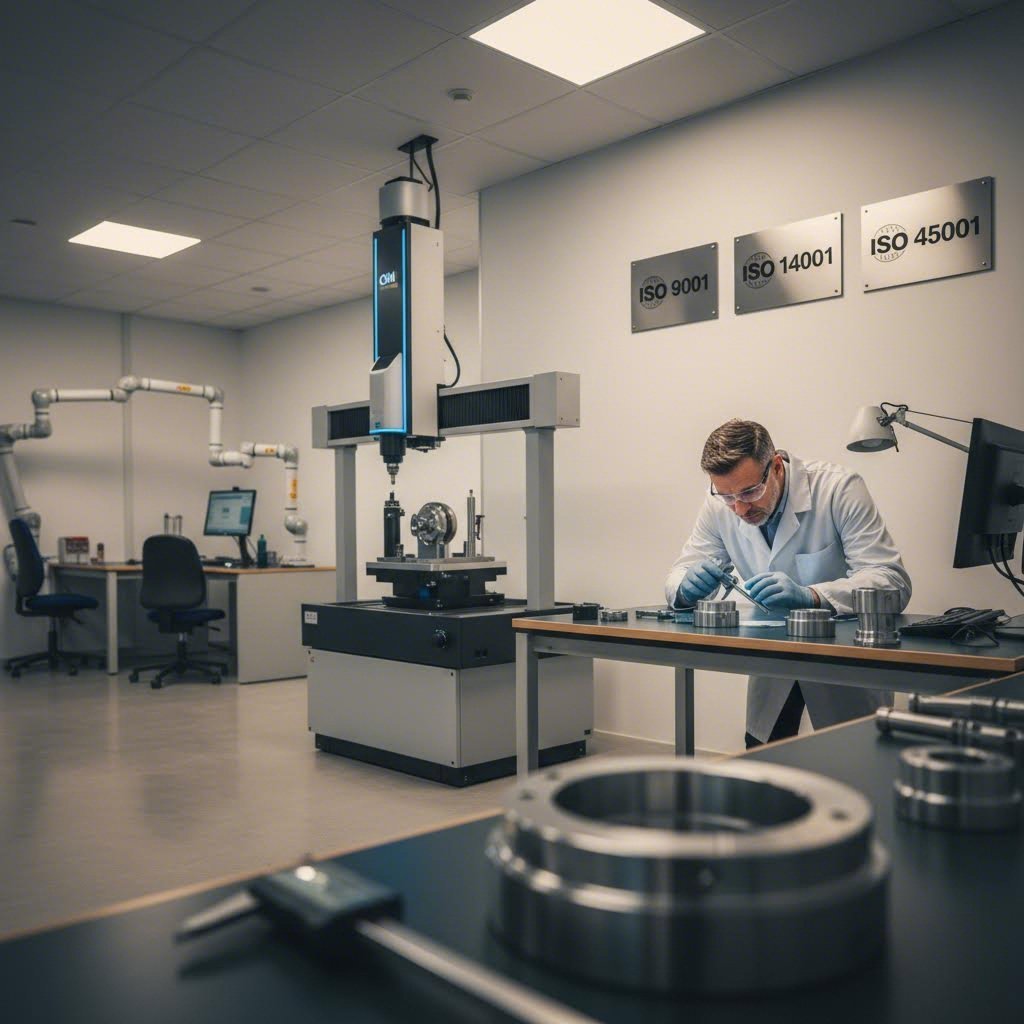

How to Choose the Right Metal Cutting Company
Your design files are ready, specifications are documented, and you understand the fabrication workflow. Now comes a decision that impacts everything from part quality to delivery reliability: which fabrication partner deserves your business? With thousands of metal cutting companies near me searches happening daily, the options can feel overwhelming.
Choosing the wrong partner leads to missed deadlines, rejected parts, and supply chain headaches. Choosing the right one? You gain a manufacturing ally who anticipates problems, suggests improvements, and delivers consistently. Let's break down the criteria that separate exceptional fabricators from the rest.
Matching Company Capabilities to Your Needs
Not every fabricator fits every project. According to MarcTech Industries, before selecting a metal fabrication company, it's crucial to understand your specific needs clearly—including product type, quantity, customization requirements, timeline, and budget constraints.
Start your evaluation with these fundamental questions:
- Does their equipment match your requirements? A metal laser cutting companies near me search might return dozens of results, but not all lasers are equal. Verify they have appropriate power levels for your material thickness and the specific cutting technology your project demands.
- Can they handle your volume? Some shops excel at prototypes and short runs while others are optimized for production quantities. Mismatched volume expectations create friction on both sides.
- Do they offer needed secondary services? If your parts require bending, welding, finishing, or assembly, working with a single-source provider streamlines your supply chain and reduces coordination overhead.
- What's their industry experience? MarcTech emphasizes looking for providers with substantial experience in your specific industry or application. A fabricator experienced in aerospace components understands different requirements than one focused on architectural metalwork.
When searching for a metal laser cutting near me company or sheet metal cutting near me company, don't just consider distance. A fabricator 200 miles away with perfect capabilities often outperforms a local shop that's stretching beyond their expertise.
Quality Certifications That Matter
Certifications provide objective evidence that a fabricator has implemented systematic quality controls. While not every project requires certified suppliers, understanding what these credentials mean helps you evaluate leading metal cutting company services appropriately.
ISO 9001 represents the baseline quality management standard. It confirms the company has documented processes, conducts internal audits, and maintains quality records. Most professional fabricators hold this certification.
IATF 16949 builds on ISO 9001 with automotive-specific requirements. If you're sourcing components for vehicles, this certification indicates the fabricator understands advanced product quality planning (APQP), production part approval processes (PPAP), and the rigorous documentation automotive OEMs demand.
AS9100 addresses aerospace and defense requirements, adding controls for traceability, configuration management, and supplier flow-down requirements that aerospace primes mandate.
ISO 13485 applies to medical device manufacturing, covering design controls, risk management, and sterility requirements specific to healthcare applications.
According to KAL Manufacturing, reputable contract manufacturers maintain formal traceability systems, inspection documentation, and certifications (such as ISO, AS9100, or ITAR compliance) that provide the quality assurance production environments require.
Job Shops vs. Contract Manufacturers: Understanding the Difference
Your choice between a traditional job shop and a contract manufacturing partner affects pricing, responsiveness, and long-term relationship potential.
Job shops typically focus on short-run or one-off production. KAL Manufacturing explains that these shops take in work on a per-quote basis, handling a wide variety of parts with little continuity between jobs. They're built for flexibility, not repetition.
If you need a single prototype or a small quantity of custom brackets, a job shop can be cost-effective and fast. However, they may not be structured for scheduled releases, quality control tracking, or inventory programs that larger production environments require.
Contract manufacturers are designed for repeatable production and long-term relationships. They offer more robust systems for scheduling, quality assurance, material handling, and documentation. According to KAL Manufacturing, a contract manufacturer is not just a supplier—they're a production partner who works with your team to deliver to forecast demand, manage part revisions, and align delivery schedules with your operations.
Key characteristics to consider:
- Job shops: Quick-turn quoting, flexible capacity for variable work, minimal order quantities, project-based relationships
- Contract manufacturers: Scheduled production, forecasting and inventory programs, documented quality systems, supply chain integration
Selection Factor Comparison
Use this comparison to evaluate potential fabrication partners based on your project requirements:
| Selection Factor | Traditional Job Shop | Online Fabrication Service | Contract Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Certifications | ISO 9001 common; industry-specific varies | ISO 9001 typical; limited industry-specific | ISO 9001, AS9100, IATF 16949, ITAR as applicable |
| Lead Times | Variable; depends on current workload | Fast (often 1-5 days for standard cuts) | Scheduled releases; consistent delivery windows |
| Order Size Flexibility | Excellent for prototypes and small runs | Best for single parts to medium batches | Optimized for recurring production volumes |
| Service Scope | Cutting plus select secondary operations | Cutting-focused; limited secondary services | Full fabrication, finishing, assembly, kitting |
| Engineering Support | Informal; depends on relationship | Automated DFM feedback | Dedicated engineering collaboration |
| Best For | Custom one-offs, urgent prototypes | Standard cuts, rapid turnaround needs | Production programs, complex assemblies |
Geographic and Logistics Considerations
Location matters—but perhaps not in the way you'd expect. While searching for a metal cutting company near me makes sense for certain applications, geography should be weighed against capability and total cost.
When proximity matters most:
- Heavy or bulky parts where freight costs dominate
- Rapid prototype iterations requiring same-day pickups
- Projects benefiting from in-person collaboration and facility visits
- Just-in-time delivery requirements with minimal lead time buffer
When capability trumps location:
- Specialized processes only available from regional experts
- Industry-specific certifications your local options lack
- Volume production where per-part savings offset freight
- Complex secondary operations requiring integrated capabilities
The best approach often involves developing relationships with both local and regional suppliers. Local metal cutting companies near me handle urgent prototypes and short runs, while specialized partners address production volumes and complex requirements.
The difference between a job shop and contract manufacturer comes down to systems and scale. Job shops serve a transactional need. Contract manufacturers support a process.
Your fabrication partner selection directly impacts project success. Take time to evaluate capabilities, verify certifications, and understand whether a potential supplier's business model aligns with your needs. With the right partner identified, you're positioned to explore how different industries leverage these services for specialized applications.
Industry Applications for Metal Cutting Services
Ever wonder why the bracket holding your car's suspension looks different from the enclosure protecting a pacemaker? Both start as flat metal sheets processed by fabrication specialists—but the journey from raw material to finished component varies dramatically based on industry requirements. Metal cutting services for construction companies follow different rules than those supplying aerospace primes or medical device manufacturers.
Understanding how different sectors leverage these fabrication services helps you communicate requirements effectively and select partners with relevant expertise. Let's explore the specialized applications and unique demands across major industries.
Automotive Manufacturing Applications
The automotive sector represents one of the largest markets for precision metal cutting. From structural chassis components to decorative trim pieces, vehicles contain hundreds of fabricated metal parts—each with specific performance requirements.
According to Pans Technology, precision machining has become a game-changer in the automotive world, enabling manufacturers to create lightweight parts that improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. With the industry's shift toward electric vehicles, lightweight components have become even more critical—McKinsey research indicates that reducing vehicle weight by just 10% can boost EV range by approximately 15%.
Typical automotive applications include:
- Chassis and structural components: Frame rails, cross members, and reinforcement brackets requiring high strength-to-weight ratios
- Suspension brackets and mounts: Precision-cut parts that must withstand repeated stress cycles without fatigue failure
- Body panels and structural supports: Components where dimensional accuracy affects fit, finish, and crash performance
- Interior components: Seat frames, dashboard supports, and trim pieces requiring aesthetic finishes alongside functional performance
- Transmission and powertrain parts: Precision-machined components demanding tight tolerances for proper operation
Automotive suppliers typically require IATF 16949 certification, demonstrating compliance with automotive-specific quality management standards. Metal die cutting companies and laser cutting specialists serving this sector must maintain rigorous production part approval processes (PPAP) and advanced product quality planning (APQP) documentation.
Aerospace and Defense Requirements
When lives depend on component reliability at 35,000 feet, tolerance for error disappears. Aerospace applications demand the tightest precision and most stringent material certifications across any manufacturing sector.
Pans Technology reports that the global market for aerospace lightweight materials is projected to reach approximately $20.7 billion by 2024—a clear indicator of how aggressively this industry pursues advanced manufacturing techniques. Precision machining creates lightweight but exceptionally strong structures that meet strict safety standards without compromising performance.
Aerospace metal cutting applications include:
- Structural airframe components: Ribs, spars, and skin panels from aluminum alloys and titanium
- Engine components: Heat-resistant nickel superalloys requiring specialized cutting techniques
- Landing gear parts: High-strength steel components with extreme fatigue resistance requirements
- Avionics enclosures: Precision housings with electromagnetic shielding properties
- Satellite and spacecraft components: Exotic materials with zero tolerance for contamination
AS9100 certification is essentially mandatory for aerospace suppliers. Material traceability from mill certification through finished part is non-negotiable—every component must trace back to its origin for safety investigation purposes.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical applications combine precision requirements with biocompatibility concerns and regulatory oversight that rivals aerospace in complexity. Die cutting metals companies and precision fabricators serving healthcare must understand both manufacturing and regulatory landscapes.
Common medical device applications include:
- Surgical instruments: Precision-cut stainless steel and titanium tools requiring burr-free edges and sterilization compatibility
- Implant components: Biocompatible materials with surface finish requirements measured in microinches
- Diagnostic equipment enclosures: Housings for imaging systems, patient monitors, and laboratory instruments
- Prosthetic components: Custom-fit titanium and specialty alloy parts often produced in single-unit quantities
- Dental devices: Small-scale precision components from corrosion-resistant alloys
ISO 13485 certification demonstrates compliance with medical device quality management requirements. Many applications require cleanroom manufacturing environments and validated cleaning processes before parts ever reach assembly.
Construction and Architectural Fabrication
Metal cutting services for construction companies operate at the opposite end of the precision spectrum from medical devices—but that doesn't mean quality standards disappear. Structural components must meet building codes, while architectural elements balance aesthetics with durability.
Construction sector applications include:
- Structural steel components: Beams, plates, and connection hardware for commercial and industrial buildings
- Architectural panels: Decorative facades, sunscreens, and building envelope elements
- HVAC components: Ductwork, brackets, and equipment supports
- Handrails and barriers: Safety-critical components meeting accessibility and building code requirements
- Custom metalwork: Signage, artistic installations, and branded elements
Laser cut metal art companies and laser cut metal design companies often serve the architectural segment, producing decorative panels, screens, and sculptural elements where visual impact matters as much as structural integrity.
Consumer Products and Electronics
From smartphone enclosures to kitchen appliances, consumer products demand cost-effective fabrication with consistent cosmetic quality. Metal cut out companies serving this sector balance precision with production volume requirements.
Typical consumer product applications include:
- Electronics enclosures: EMI-shielded housings for computers, servers, and telecommunications equipment
- Appliance components: Panels, brackets, and structural elements for household products
- Sporting goods: Bicycle frames, fitness equipment, and outdoor gear
- Furniture components: Metal frames, hardware, and decorative elements
- Retail fixtures: Display stands, shelving systems, and point-of-sale equipment
Industry-Specific Precision Requirements
Tolerance requirements vary dramatically by sector. According to Xometry, tolerances define the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension, ensuring that features are produced within acceptable limits for their intended application.
Standard ISO 2768 tolerances work perfectly for many construction and consumer applications. However, aerospace and medical components often require ISO 286 grade specifications—with tolerance limits measured in micrometers rather than thousandths of an inch.
| Industry Sector | Typical Tolerance Requirements | Common Certifications | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | ±0.005" to ±0.010" standard; tighter for critical fits | IATF 16949, ISO 9001 | PPAP documentation, material traceability |
| Aerospace | ±0.001" to ±0.005" common; sub-micron for critical components | AS9100, NADCAP | Full material traceability, special process certifications |
| Medical Devices | ±0.0005" to ±0.005" typical | ISO 13485, FDA registration | Biocompatibility, cleanroom requirements, validation |
| Construction | ±0.030" to ±0.125" common | ISO 9001, AWS certifications | Code compliance, galvanizing, weather resistance |
| Consumer Electronics | ±0.005" to ±0.015" typical | ISO 9001 | Cosmetic finish standards, EMI shielding |
Material certification requirements also vary by industry. Construction applications might accept standard mill test reports, while aerospace components require full chemical analysis and mechanical property verification for each material lot. Medical implants demand biocompatibility testing that can add months to material qualification timelines.
Understanding these industry-specific requirements helps you evaluate whether a potential fabrication partner truly has relevant experience—or is stretching beyond their expertise. A shop that excels at architectural metalwork may struggle with aerospace documentation requirements, while a precision medical device fabricator might not be cost-competitive for high-volume consumer products.
With industry applications and requirements clarified, the next critical consideration involves understanding exactly what precision and quality standards you should expect from professional fabrication partners.
Quality Standards and Precision Expectations
You've selected your fabrication partner and submitted your design files—but how do you know the finished parts will actually meet your requirements? Understanding precision tolerances and quality assurance processes separates successful projects from frustrating rework cycles. Professional metal laser cutting company operations stake their reputation on delivering parts that match specifications consistently.
Let's demystify what precision really means in metal fabrication and how to communicate your quality expectations effectively.
Understanding Precision and Tolerances
Tolerance defines how much a dimension can vary from its nominal value while still being acceptable. According to Xometry, tolerances define the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension, ensuring that features are produced within acceptable limits for their intended application.
Different cutting technologies deliver different precision levels. Knowing what to expect prevents unrealistic demands—and helps you specify tighter tolerances only where they truly matter.
Fiber lasers achieve tolerances ranging from ±0.001 to ±0.003 inches, making them the preferred choice for demanding metal fabrication projects where accuracy is paramount.
Here's what you can realistically expect from each cutting method:
- Fiber Laser: According to A-Laser, fiber lasers consistently deliver tight tolerances ranging from ±0.001" to ±0.003"—the gold standard for precision sheet metal work.
- CO2 Laser: Typically achieves ±0.002" to ±0.005" tolerances, respectable for most applications though slightly less precise than fiber systems.
- UV Laser: Reaches astonishingly tight tolerances as low as ±0.0001" for micro-machining applications requiring sub-micron precision.
- Waterjet: Generally delivers ±0.003" to ±0.010" depending on material thickness and cutting speed.
- Plasma: Produces wider tolerances around ±0.020"—acceptable for structural applications but unsuitable for precision fits.
When working with a custom laser cut metal company, understand that tighter tolerances increase cost. Specifying ±0.001" when ±0.010" would function perfectly wastes money and may extend lead times. Apply precision requirements strategically to critical features only.
Quality Assurance in Metal Cutting
Precision equipment means nothing without systematic quality controls. According to Fox Valley Metal-Tech, a loftier goal than simple quality control is providing quality assurance—a higher level of proactive rather than reactive product management that occurs throughout the production process.
Professional metal laser cutting service company operations implement multiple inspection touchpoints:
Material Verification
Quality starts before cutting begins. Reputable fabricators compare incoming materials against purchase orders, verify Certificates of Conformance (CoC), and inspect for damage or contamination. Materials may be held in quarantine areas until certification documents arrive and specifications are confirmed.
Equipment Calibration
Accurate parts require calibrated equipment. Fox Valley Metal-Tech explains that any measuring equipment used to verify product dimensions must be calibrated at specified frequencies per ISO 9001:2015 certification. This includes daily verification of calipers and micrometers against fixed reference standards, weekly third-party calibration inspections, and annual comprehensive calibration of CNC equipment.
In-Process Inspection
Dimensional verification happens throughout production—not just at the end. Common tolerances for precision weldments and machined parts range between .005" – .030", verified using calipers, micrometers, height gauges, and Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs).
Non-Destructive Testing
When specifications demand it, a sheet metal laser cutting company may perform or arrange specialized testing including visual weld inspection, pressure or leak testing, dye penetrant inspection for surface cracks, magnetic particle testing for ferromagnetic materials, and ultrasonic testing for internal defects.
Communicating Your Requirements Effectively
Clear communication prevents quality disputes. Here's how to specify your requirements:
- Reference recognized standards: Call out ISO 2768 for general tolerances or ISO 286 for critical fits rather than inventing proprietary specifications.
- Indicate critical dimensions: Mark features requiring tighter-than-standard tolerances explicitly on your drawings.
- Specify inspection requirements: If you need first article inspection reports (FAIR), CMM data, or dimensional reports, state this upfront.
- Define surface finish: Specify acceptable edge quality, burr limits, and surface roughness values where appearance matters.
Selecting the appropriate tolerance is a critical decision in the design and manufacturing process, since it affects the functionality, fit, cost, and manufacturability of the part.
Understanding these quality standards positions you to evaluate fabrication partners effectively and set realistic expectations for your projects. With quality requirements defined, you're ready to take the final step—partnering with the right fabricator to bring your designs to life.
Partnering With Metal Cutting Companies for Your Next Project
You've journeyed through cutting technologies, material considerations, fabrication workflows, and quality standards. Now it's time to synthesize everything into a practical framework you can apply immediately. Finding the right company that cuts metal isn't about luck—it's about systematic evaluation based on your specific requirements.
Whether you're sourcing a single prototype or establishing a long-term production partnership, the decision framework remains consistent. Let's consolidate your learning into actionable steps that move your project forward.
Your Metal Cutting Partner Checklist
Before contacting any fabricator, work through this comprehensive evaluation checklist. According to TMCO, selecting the right manufacturing partner goes beyond comparing quotes—it's about finding a team you can trust to bring your vision to life with accuracy, efficiency, and consistency.
Technology and Capability Verification
- Confirm they operate appropriate cutting equipment (laser, waterjet, plasma) for your material and thickness requirements
- Verify secondary operation capabilities—bending, welding, finishing—if your parts require processing beyond cutting
- Assess their capacity to handle your volume requirements, from prototypes through production runs
- Evaluate engineering support availability for design optimization and DFM feedback
Quality and Certification Requirements
- Verify ISO 9001 certification as a baseline quality indicator
- Confirm industry-specific certifications (IATF 16949 for automotive, AS9100 for aerospace, ISO 13485 for medical) when applicable
- Request information about inspection equipment and quality documentation capabilities
- Ask about material traceability systems and certification documentation
Project Preparation Essentials
- Prepare design files in accepted formats (STEP, DXF, IGES) with closed contours and correct units
- Document material specifications including grade, thickness, and any required certifications
- Identify critical tolerances and call them out explicitly—don't over-specify where standard tolerances suffice
- List all secondary operations, finish requirements, and hardware insertion needs
- Establish realistic timeline expectations based on complexity and volume
Partnership Evaluation Factors
- Assess communication responsiveness during the quoting process—it predicts ongoing relationship quality
- Evaluate whether they ask clarifying questions about your application, indicating genuine engagement
- Consider geographic proximity for freight-sensitive parts or rapid iteration needs
- Review customer references and industry experience relevant to your sector
Taking the Next Step
With your checklist complete, you're ready to engage potential partners effectively. According to UPTIVE Advanced Manufacturing, the right manufacturing company will deliver accurate parts, reduce lead times, and offer tailored solutions for each stage of your product's development.
Here's your action plan for moving forward:
For Prototype and Development Projects
When speed and iteration matter most, prioritize fabricators offering rapid turnaround and engineering collaboration. Custom metal laser cutting companies with instant quoting systems can accelerate your development cycle significantly. Look for partners providing comprehensive DFM support who can identify potential manufacturing issues before cutting begins.
For Production Programs
Long-term production requires different evaluation criteria. OEM metal cutting companies and contract manufacturers offering scheduled releases, inventory programs, and consistent quality documentation become essential partners. A CNC metal cutting company with robust quality systems prevents the supply chain disruptions that derail production schedules.
Consider manufacturers like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology, which exemplifies the IATF 16949-certified quality standards discussed throughout this guide. Their combination of 5-day rapid prototyping, comprehensive DFM support, and 12-hour quote turnaround demonstrates how leading oem cnc metal cutting companies accelerate automotive supply chains for chassis, suspension, and structural components—from initial concept through automated mass production.
Building Long-Term Relationships
The best fabrication partnerships extend beyond transactional quotes. TMCO emphasizes that choosing a partner isn't just about the current project—it's about building a long-term relationship based on trust, performance, and shared goals. A reliable cnc metal cutting company becomes an extension of your engineering team, suggesting improvements and anticipating challenges before they impact your timeline.
A turnkey manufacturing partner manages your project from concept to completion—eliminating the inefficiencies of coordinating multiple vendors while maintaining complete visibility throughout production.
You now understand how different cutting technologies work, which methods suit specific materials, and what quality standards to expect from professional fabricators. You know how to prepare your projects for success and evaluate potential partners systematically. The path from quote request to finished parts is clear—your next project starts with a single outreach to a qualified fabrication partner who matches your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Metal Cutting Companies
1. How much does metal cutting cost?
Metal cutting costs vary based on material type, thickness, cutting method, and complexity. Laser cutting typically ranges from $0.50 to $2 per linear inch for sheet metal. Hourly rates generally fall between $20 and $30. Plasma cutting offers lower per-foot costs for thick materials, while waterjet cutting commands premium pricing due to slower speeds. Volume discounts significantly reduce per-part costs on production runs, and secondary operations like bending and finishing add to the total.
2. Will a hardware store cut metal for you?
Hardware stores offer limited metal cutting services, typically restricted to pipe cutting and basic shearing of thin materials. For precision sheet metal fabrication, custom shapes, or thicker materials, you need professional metal cutting companies equipped with laser, waterjet, or plasma systems. These fabricators handle CAD files, maintain tight tolerances, and offer secondary operations that hardware stores cannot provide.
3. How to get a piece of metal cut?
To get metal professionally cut, prepare your design files in DXF or STEP format, specify material type and thickness, and contact a metal cutting company for a quote. Most fabricators accept online file submissions and provide quotes within 12-24 hours. Include tolerance requirements, quantity needed, and any secondary operations like bending or finishing. For simple cuts, some online fabrication services offer instant pricing with delivery in just a few days.
4. What is the difference between laser cutting and plasma cutting?
Laser cutting uses a focused light beam achieving tolerances of ±0.005 inches, ideal for thin to medium materials requiring precision and clean edges. Plasma cutting uses superheated ionized gas, processing thick conductive metals 3-4 times faster than other methods but with wider tolerances around ±0.020 inches. Choose laser for intricate designs and precision fits; select plasma for thick structural steel where speed and cost matter more than edge quality.
5. What certifications should I look for in a metal cutting company?
ISO 9001 certification indicates baseline quality management systems. For automotive applications, IATF 16949 certification demonstrates compliance with automotive-specific requirements including PPAP documentation. Aerospace suppliers need AS9100 certification, while medical device fabricators require ISO 13485. These certifications verify that the company maintains documented processes, calibrated equipment, and systematic quality controls essential for regulated industries.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
