Laser Metal Cutting Service Pricing Exposed: What Shops Won't Tell You

What Is Laser Metal Cutting and Why It Dominates Modern Fabrication
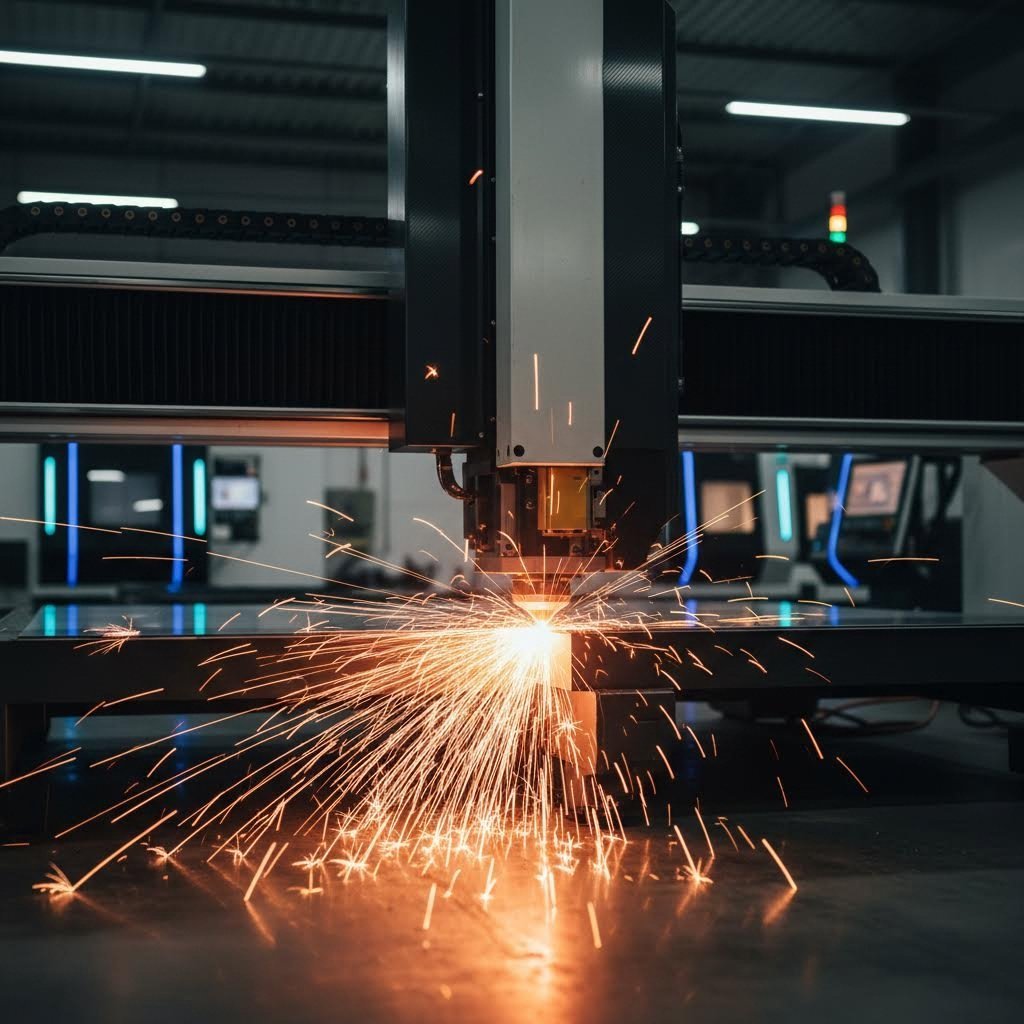
A laser metal cutting service uses concentrated beams of light to melt, burn, or vaporize metal with extraordinary precision. This high-precision thermal process focuses a coherent, modulated beam onto a point with a very small diameter, generating temperatures around 3,000°C. The result? Clean cuts through steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals without the mechanical stress that traditional cutting methods create.
When you need custom cut metal parts with tight tolerances and smooth edges, this technology delivers what mechanical cutting simply cannot match. The focused energy eliminates thermal and structural deformation, producing burr-free edges that often require no additional finishing work.
How Laser Cutting Transforms Raw Metal Into Precision Parts
Imagine directing a beam of light so powerful and focused that it instantly melts through solid steel. That's exactly what happens during metal laser cutting. The process begins when a laser source generates an intense beam, which optical components then focus onto the workpiece surface. As the beam contacts the metal, it rapidly heats a precise spot until the material melts or vaporizes completely.
Technical gases play a crucial supporting role in this transformation. Oxygen can be used to increase cutting speed on thicker iron materials through localized combustion. Nitrogen produces cleaner cuts free of oxidation—particularly important for aesthetic applications or parts requiring subsequent welding or surface treatments. Modern CNC systems manage every parameter: feed speed, laser power, gas type, and beam focus, ensuring repeatable precision across thousands of parts.
The laser cutting and fabrication process integrates seamlessly with CAD/CAM software. Your design files drive the cutting path directly, minimizing human error while optimizing cycle times. This digital-to-physical workflow represents why lazercut technology has become the backbone of modern NY metal design studios and industrial fabricators alike.
The Science Behind Focused Light Metal Fabrication
Three primary laser types power today's cutting services, each with distinct characteristics suited to different applications:
- Fiber lasers emit light at approximately 1.06 μm wavelength, which metals absorb exceptionally well. They excel at cutting reflective materials like aluminum, copper, and brass while delivering superior energy efficiency.
- CO2 lasers operate at around 10.6 μm wavelength using a gas mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium. They offer versatility across material types and remain effective for thicker metal processing.
- Nd:YAG lasers use neodymium-doped crystals to produce near-infrared light at 1.064 μm. These solid-state devices provide excellent precision for specialized applications and thin sheet processing.
Each technology serves specific manufacturing needs—a detail we'll explore thoroughly in the next section.
Modern laser metal cutting achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.003" to ±0.007", enabling precision that traditional mechanical cutting methods simply cannot replicate.
This capability explains why industries from automotive to aerospace have adopted laser cutting as their standard for precision metal fabrication. The technology combines speed, accuracy, and repeatability in ways that continue transforming how manufacturers approach custom metal components.
Fiber vs CO2 vs Nd YAG Laser Technology Explained
Choosing the right laser technology for your project isn't just a technical decision—it directly impacts your costs, turnaround time, and part quality. Most shops won't explain why they recommend one laser type over another, but understanding these differences gives you leverage when requesting quotes and evaluating cnc laser cutting services.
Each laser type operates at a different wavelength, and here's why that matters: metals absorb light energy differently depending on the wavelength hitting their surface. A wavelength that copper reflects might be exactly what aluminum absorbs efficiently. This physical property determines which laser cuts which material best—and ultimately affects your per-part pricing.
Fiber Lasers vs CO2 Lasers for Sheet Metal Projects
Fiber lasers have revolutionized steel laser cutting over the past two decades. Operating at a 1064 nm wavelength, they deliver energy that metals absorb exceptionally well. The result? Faster cutting speeds, lower energy consumption, and reduced operating costs that shops can pass along to customers.
When you're working with thin to medium-thickness sheet metal—think laser cut sheet metal under 1 inch—fiber technology typically outperforms alternatives. These systems achieve wall plug energy efficiency of up to 50%, compared to roughly 10-20% for CO2 lasers. That efficiency translates to meaningful cost differences on high-volume orders.
Fiber lasers also excel with reflective metals that traditionally challenged older technologies. Aluminum, brass, and copper—materials that once caused cutting headaches—now process reliably with modern fiber systems. The shorter wavelength penetrates reflective surfaces that longer wavelengths simply bounce off.
CO2 lasers, operating at 10,600 nm, remain the workhorses for thicker materials and mixed-material shops. Their longer wavelength cuts through substantial steel plate thicknesses while delivering exceptionally smooth edge quality. For metal sheet laser cutting projects demanding mirror-finish edges on thick carbon steel, CO2 technology still holds advantages.
These gas-based systems also handle non-metallic materials that fiber lasers cannot touch—wood, acrylic, glass, and plastics. Shops offering diverse material capabilities often maintain both technologies to serve broader customer needs.
Matching Laser Technology to Your Material Requirements
Nd:YAG lasers occupy a specialized niche in the cnc metal cut landscape. Using neodymium-doped crystals, they produce pulsed output at 1064 nm—the same wavelength as fiber lasers but with distinct characteristics. The pulsed operation enables precise control over energy delivery, making these systems ideal for applications requiring exceptional detail or minimal heat-affected zones.
However, Nd:YAG technology comes with trade-offs. The beam quality, measured by M² value, typically ranges from 1.2 (excellent) for Nd:YAG to 1.6-1.7 for fiber lasers. Better beam quality produces smaller spot sizes and higher power density at the cutting point. For curved surface marking or ultra-fine detail work, this difference matters.
That said, fiber lasers have largely displaced Nd:YAG for general metal cutting applications. The reasons are practical: fiber systems require minimal maintenance, offer longer mean time between failures (30,000-50,000 hours versus 10,000-20,000 hours for Nd:YAG), and start cutting instantly without warm-up periods. For most laser cutz projects, these operational advantages outweigh the beam quality difference.
So how do you match technology to your specific project? Consider these factors:
- Material type: Reflective metals like copper and brass favor fiber lasers; thick carbon steel may benefit from CO2
- Thickness requirements: Thin sheets under 0.5" process fastest on fiber; ultra-thick plates may need CO2 power
- Edge quality expectations: CO2 often delivers smoother edges on thick materials; fiber excels on thin stock
- Volume and budget: Fiber's lower operating costs benefit high-volume production runs
| Specification | Fiber Laser | CO2 Laser | Nd:YAG Laser |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 1064 nm | 10,600 nm | 1064 nm |
| Best Materials | Steel, aluminum, copper, brass, titanium | Thick steel, non-metals, mixed materials | Precision metal marking, thin sheets |
| Typical Thickness Range | 0.5 mm – 25 mm (metals) | 0.5 mm – 30+ mm (varies by power) | 0.1 mm – 6 mm |
| Cutting Speed | Fastest on thin metals | Moderate; excels on thick stock | Slower; pulsed operation |
| Precision (Typical Tolerance) | ±0.003" – ±0.005" | ±0.004" – ±0.007" | ±0.003" – ±0.005" |
| Energy Efficiency | Up to 50% | 10 – 20% | ~1.3% |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low; no optics to align | High; gas tubes require replacement | Moderate; diode replacement needed |
| MTBF (Hours) | 30,000 – 50,000 | Varies by component | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, enclosures, brackets, reflective metal work | Signage, thick structural steel, mixed-material shops | Medical devices, electronics, precision components |
When requesting quotes from cnc laser cutting services, ask which technology they plan to use for your specific material and thickness. A shop recommending CO2 for thin aluminum sheet might be working with older equipment—or they might have specific quality reasons. Either way, understanding these distinctions helps you evaluate whether their recommendation serves your project or simply their equipment availability.
The materials you select ultimately determine which laser technology delivers optimal results—and material compatibility involves more considerations than wavelength alone.
Materials Compatible with Laser Metal Cutting Services
Not every metal behaves the same way under a laser beam. Some materials absorb energy efficiently and cut like butter. Others reflect that energy right back at the cutting head, creating efficiency problems and potential equipment damage. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right material for your project—and avoid costly surprises when quotes come back higher than expected.
Material properties directly influence cutting parameters, processing speed, and final part quality. Reflectivity, thermal conductivity, and oxidation behavior all play critical roles in determining how a laser cut steel sheet or custom laser cut stainless steel part will turn out.
Steel and Stainless Steel Cutting Parameters
Steel remains the most commonly processed material in any laser metal cutting service, and for good reason. Carbon steel absorbs laser energy exceptionally well, making it the easiest and most cost-effective metal to cut. The iron content readily absorbs the 1064 nm wavelength from fiber lasers, enabling fast processing speeds and clean edges.
Here's what you need to know about each steel type:
- Carbon steel: Cuts cleanly from 0.5 mm up to 25+ mm thickness. Oxygen-assisted cutting accelerates processing on thicker plates through localized combustion. Expect excellent edge quality with minimal post-processing required. This is typically your most economical option for structural components and brackets.
- Stainless steel: Requires nitrogen assist gas to prevent oxidation that would discolor cut edges. A stainless steel laser cutting service typically processes thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 20 mm, though exact capabilities vary by equipment. The chromium content creates slightly different absorption characteristics than carbon steel, often requiring parameter adjustments for optimal results.
- Galvanized steel: The zinc coating vaporizes during cutting, which can affect edge quality and create fumes requiring proper ventilation. Most shops handle galvanized material up to 6-8 mm thickness without issues, though the zinc layer may cause minor edge roughness compared to uncoated steel.
For custom laser cut stainless steel projects requiring aesthetic finishes—think architectural panels or food service equipment—specify nitrogen cutting to maintain that bright, oxide-free edge. Oxygen cutting works faster but leaves a darker edge that may require additional finishing.
Working with Reflective Metals Like Aluminum and Copper
Reflective metals present unique challenges that directly affect your project costs and timelines. Aluminum, copper, and brass have smooth surfaces and high thermal conductivity that complicate the cutting process in two critical ways.
First, these materials bounce a significant portion of laser energy back toward the cutting head. This back-reflection reduces cutting efficiency and, without proper machine protection, can damage optical components. Modern fiber laser systems include back-reflection monitoring and automatic shutdown features specifically to handle these materials safely.
Second, reflective metals dissipate heat rapidly from the cutting zone. Copper and aluminum pull thermal energy away so quickly that achieving stable penetration becomes challenging. The solution? Pulsed cutting mode delivers energy in short, controlled bursts rather than continuous waves, allowing controlled melting without excessive reflection.
- Aluminum alloys: An aluminium laser cutting service typically handles thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 12 mm for most common alloys. The 6061 and 5052 grades cut more predictably than high-purity aluminum. Surface preparation matters significantly—remove oil, oxidation, and moisture before cutting to improve energy absorption and reduce reflection.
- Copper: One of the most challenging materials due to extreme reflectivity and thermal conductivity. Expect thickness limitations around 6 mm for most fiber laser systems. Pre-treatment with black paint or surface coatings can improve absorption, though this adds processing steps.
- Brass: Easier than pure copper due to zinc content altering surface properties. Most shops process brass up to 8 mm thickness effectively. Nitrogen assist produces the cleanest edges without discoloration.
- Titanium: Requires inert gas shielding (argon or helium) to prevent oxidation and embrittlement. Custom laser cut metal parts from titanium demand precise parameter control due to the material's reactive nature at elevated temperatures. Typical thickness range spans 0.5 mm to 6 mm depending on equipment capabilities.
When requesting quotes for reflective materials, expect higher per-part pricing than equivalent steel projects. The specialized parameters, slower cutting speeds, and additional equipment wear all factor into cost calculations.
Surface condition directly impacts cutting quality on reflective metals. Remove contaminants including oil, oxidation, film coatings, and moisture before processing—a clean surface improves laser absorption and reduces back-reflection risks.
Understanding how your chosen material interacts with laser cutting technology is only half the equation. Your design files must also meet specific requirements to ensure those materials transform into the precision parts you need.

Design File Requirements and Preparation Best Practices
Your design file can make or break a laser cutting project. Submit the wrong format, and you'll face delays while the shop requests revisions. Include features too small for the material thickness, and you'll receive parts that don't match your expectations. Yet most custom laser cutting service providers barely explain what they actually need from your files—leaving you guessing until problems emerge.
The truth? Proper file preparation directly affects your quote, turnaround time, and final part quality. Understanding these requirements before you submit saves frustration and money on every custom metal laser cutting project.
File Formats and Vector Requirements for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting machines read vector files—not photographs or pixel-based images. Why does this distinction matter so much? Vector graphics define shapes through mathematical expressions rather than individual pixels. When you zoom into a vector image, it maintains crisp, precise edges at any scale. Bitmap images, by contrast, become blurry and pixelated when enlarged.
This mathematical precision translates directly to cutting precision. The laser follows vector paths exactly as defined, producing parts that match your design specifications. Submit a bitmap file, and the shop must first convert it to vector format—a process that introduces potential errors and adds to your lead time.
Here are the file formats most custom metal cutting shops accept:
- DXF (Drawing Exchange Format): The industry standard for CAD files. Universally compatible across cutting software platforms with precise dimensional data.
- DWG (AutoCAD Drawing): Native AutoCAD format offering excellent precision. Some shops prefer DXF for broader compatibility.
- AI (Adobe Illustrator): Popular among designers and artists. Ensure all text is converted to outlines before submission.
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): Web-friendly vector format that works well for simpler designs. Verify that your software exports clean paths without unnecessary nodes.
Working with a raster image like a JPEG or PNG? Free tools like Inkscape can trace bitmap images and convert them into vector format. However, always verify dimensions after conversion—the tracing process can introduce slight scaling errors that compound into major problems on finished parts.
Avoiding Common Design Mistakes That Delay Projects
Even experienced engineers submit files with issues that delay production. Understanding these common pitfalls helps you avoid the back-and-forth revision cycles that push delivery dates further out.
Insufficient kerf allowance ranks among the most frequent problems. The kerf—the width of material removed during cutting—typically ranges from 0.1 mm to 1.0 mm depending on material type, thickness, and laser parameters. Your design must account for this material loss, or parts will come out undersized. Most cutting software can automatically offset paths to compensate, but you should understand whether your dimensions represent the final part size or the cutting path centerline.
Features smaller than material thickness create quality issues that no amount of laser power can solve. A common guideline: avoid design features smaller than the thickness of the material being cut. Attempting to cut an 8 mm hole in 10 mm thick steel, for example, typically produces poor edge quality and dimensional inaccuracy. The same principle applies to narrow slots, thin bridges, and intricate internal features.
Text handling errors catch many designers off guard. If text in your file remains editable rather than converted to outlines or shapes, the cutting software may substitute different fonts or misinterpret characters entirely. In Illustrator, this means "converting to outlines." In CAD software, you might need to "explode" or "expand" text elements. Hover over any text in your design—if it's still editable, it needs conversion before submission.
Unsupported internal cutouts create parts that literally fall apart during cutting. If your design includes internal shapes that aren't connected to the main part, those pieces will drop through the cutting bed and cannot be retained. Either submit these as separate parts or add small bridges (tabs) connecting them to the main body for removal after cutting.
Design Preparation Checklist for Custom Laser Cut Sheet Metal
Before submitting files to any custom laser cutting metal provider, work through this preparation sequence:
- Verify file format: Export your design as DXF, DWG, AI, or SVG. Avoid raster formats entirely, or trace and verify dimensions if conversion is necessary.
- Convert all text to outlines: Eliminate editable text boxes by converting to shapes or paths. This prevents font substitution issues during processing.
- Check minimum feature sizes: Ensure no internal features (holes, slots, cutouts) are smaller than your material thickness. For thin sheet metal under 3 mm, minimum hole diameters typically start around 1.5-2 mm.
- Verify spacing between cuts: Closely spaced cutting paths can cause warping, melting, or vaporization between cuts—particularly on materials with low melting points. Maintain spacing of at least 1.5x material thickness between adjacent cut lines.
- Account for kerf width: Determine whether your dimensions represent final part size or cutting path. Communicate this clearly to your service provider, or apply appropriate offsets before submission.
- Eliminate unsupported cutouts: Add bridging tabs to any internal shapes that would otherwise fall free during cutting. Plan for tab removal in post-processing.
- Optimize nesting efficiency: If submitting multiple parts, consider how they might nest together on sheet material. Efficient nesting reduces material waste and can lower your per-part cost on custom cut metal sheet projects.
- Print at 100% scale: Before submitting, print your design at actual size and physically measure critical dimensions. This simple step catches scaling errors that digital review often misses.
- Remove duplicate lines: Overlapping or duplicate cut paths cause the laser to trace the same line twice, wasting time and potentially damaging edge quality.
- Specify material and thickness: Include clear documentation of your intended material type and thickness. Different materials require different parameter settings, and this information should accompany your design files.
Using standard material thicknesses is one of the easiest ways to optimize the laser-cutting process. Non-standard thicknesses often require special calibration or material sourcing, which can increase lead times and costs significantly.
Taking time to prepare files correctly upfront eliminates the revision cycles that frustrate both you and the shop. A clean, properly formatted design file moves straight to production—translating directly into faster delivery and more accurate quotes.
With your design files properly prepared, understanding what happens next—from quote request through finished parts—helps you set realistic expectations and identify quality providers.
The Complete Laser Cutting Process From File to Finished Part
Most metal laser cutting services treat their production process like a black box. You submit files, wait an unspecified amount of time, and parts eventually arrive. This opacity breeds uncertainty—and uncertainty often means you're paying more than necessary or accepting longer lead times than required.
Understanding exactly what happens between your quote request and final delivery empowers you to optimize your projects, set realistic timelines, and evaluate whether a provider actually delivers on their promises. Here's the complete workflow that quality laser cut services follow.
From Quote Request to Finished Parts
The journey from design file to finished component follows a predictable sequence—though the speed and precision of each step varies dramatically between providers. A well-organized laser cutting co can move from initial contact to shipped parts in as little as 24 hours for standard orders, while less efficient operations might take weeks for identical projects.
- Quote request submission: You upload your CAD file (DXF, DWG, STEP, or IGES) along with material specifications and quantity requirements. Advanced quoting systems immediately parse your file geometry, calculating cut path length, material requirements, and estimated processing time. According to Wuxi Lead Precision Machinery, sophisticated instant quote platforms cross-reference uploaded files against real-time machine capabilities and historical process data—evaluating factors like kerf width compensation and potential warpage risks based on part geometry.
- Design review and DFM feedback: Before cutting begins, experienced engineers review your file for manufacturability. They check tolerance specifications, identify features that might cause quality issues, and flag potential problems like insufficient spacing between cuts or unsupported internal geometries. Quality providers return actionable feedback within hours—not automated disclaimers. This design-for-manufacturing review prevents costly rework downstream.
- Material selection and sourcing: Your specified material gets pulled from inventory or ordered if specialized alloys are required. Established metal cutting services maintain deep stock of common materials—carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and specialty alloys—eliminating sourcing delays. Material certifications are verified against your requirements, particularly critical for aerospace or medical applications.
- Cutting program generation: Your design file gets nested into a cutting program that optimizes material utilization. Software arranges multiple parts efficiently across sheet stock, minimizing waste while maintaining required spacing between cuts. The program includes all laser parameters: power settings, feed speeds, gas type, and focal distance calibrated specifically for your material and thickness.
- Laser cutting operation: The programmed file drives CNC-controlled cutting heads across your material. Modern fiber laser systems with adaptive focus control and real-time monitoring deliver micron-level precision at high throughput. Automated material handling ensures consistent positioning, while integrated fume extraction maintains optical clarity throughout the cut.
- Quality inspection: Every production run undergoes dimensional verification. Critical components receive coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspection for full 3D verification of geometric features. Random samples get inspected hourly during production runs, with non-conforming parts quarantined immediately. First-article inspection reports accompany shipments for projects requiring traceability documentation.
- Finishing and secondary operations: Depending on your requirements, parts may proceed to deburring, bending, tapping, welding, or surface treatments like powder coating or anodizing. Each additional operation adds processing time but delivers ready-to-use components.
- Packaging and delivery: Finished parts get packaged for protection during transit. Standard orders from efficient metal laser cutting services typically ship within 2-4 business days of receiving cut-ready files, according to SendCutSend's published processing times.
What Happens During the Cutting Process
The actual cutting operation involves more complexity than simply tracing your design with a laser beam. Understanding these details helps you appreciate why certain design choices affect pricing and quality.
When cutting begins, the laser head positions over your material and the beam pierces through at a designated start point. For thicker materials, this pierce takes longer and generates more heat than the subsequent cutting motion. Smart nesting places pierce points in waste areas whenever possible, preventing heat marks on finished part surfaces.
As the head traverses your design path, assist gas flows coaxially with the beam. Oxygen accelerates cutting on carbon steel through localized combustion. Nitrogen produces oxide-free edges essential for stainless steel welding or visible surfaces. The choice of assist gas directly impacts edge quality, cutting speed, and final appearance.
Throughout the operation, sensors monitor for anomalies. Back-reflection detection protects optical components when cutting reflective metals. Power calibration adjusts in real-time to maintain consistent energy delivery. Statistical process control tracks dimensional accuracy across production runs, triggering recalibration before drift affects part quality.
Factors Affecting Turnaround Time
Several variables influence how quickly your parts move from quote to delivery:
- File readiness: Cut-ready files with no manufacturability issues proceed immediately. Files requiring revision cycles add days to your timeline.
- Material availability: Common materials ship from stock. Specialty alloys or non-standard thicknesses may require sourcing time.
- Order complexity: Simple flat parts process faster than designs requiring multiple secondary operations.
- Quantity: Larger production runs require more machine time, though per-part costs typically decrease with volume.
- Current shop capacity: Real-time machine loads affect scheduling. Quality providers sync ERP systems to quote lead times reflecting actual capacity—not optimistic averages.
For urgent prototypes, some providers offer 72-hour turnaround with expedited handling. Standard production runs typically complete within 5 business days for quantities up to several thousand units. Adding post-processing operations like bending, tapping, or powder coating extends these timelines proportionally.
Knowing this workflow helps you prepare files correctly, set accurate expectations with stakeholders, and identify providers who actually control their processes. The next critical factor—pricing—depends heavily on decisions you make throughout this journey.
Understanding Laser Cutting Pricing and Cost Factors
Here's what frustrates most customers about laser metal cutting service pricing: the lack of transparency. You request a quote, receive a number, and have no idea whether it's competitive or what's actually driving the cost. Some shops charge by the square inch. Others quote by the hour. A few won't even explain their methodology.
The reality? Nearly every provider uses a similar underlying formula, but they calculate inputs differently. Understanding these cost drivers puts you in control—helping you optimize designs, compare quotes intelligently, and avoid paying premium prices for standard work. Whether you're searching for where to get metal cut for a one-off prototype or sourcing a steel laser cutting service for production runs, these principles apply universally.
Key Factors That Determine Laser Cutting Costs
Forget the myth that pricing depends primarily on material area. According to Fortune Laser's pricing guide, the single most important factor driving your cost is machine time—not the square footage of your sheet. A simple rectangular bracket and an intricate decorative panel made from identical material can have drastically different prices because one requires far more cutting time than the other.
The standard pricing formula breaks down like this:
Final Price = (Material Costs + Variable Costs + Fixed Costs) × (1 + Profit Margin)
Each component contributes differently depending on your specific project:
- Material type and cost: Raw material prices vary dramatically. MDF costs a fraction of stainless steel; aerospace-grade titanium costs multiples more than carbon steel. The base material cost includes not just your finished parts but also the scrap generated during cutting.
- Material thickness: This factor impacts cost exponentially, not linearly. Doubling thickness can more than double cutting time because the laser must move significantly slower to penetrate cleanly. A 6mm steel plate might take three times longer to cut than 3mm stock—not twice as long.
- Cut distance (perimeter length): Every millimeter the laser travels adds to your machine time. Complex geometries with long perimeters cost more than simple shapes, even when material area remains identical. Intricate filigree patterns can cost several times more than basic rectangular cutouts.
- Pierce count: Each time the laser initiates a new cut, it must first pierce through the material. A design with 50 small holes accumulates 50 pierce cycles—each adding time and cost. Consolidating small features or reducing hole counts directly reduces pricing.
- Tolerance requirements: Specifying tolerances tighter than functionally necessary inflates costs substantially. Holding ±0.003" requires slower, more controlled cutting speeds than ±0.010". Unless your application genuinely demands tight tolerances, accepting standard precision saves money.
- Secondary operations: Bending, tapping, deburring, powder coating, and hardware insertion each add labor and processing time. A laser-cut flat requires less handling than a formed enclosure with threaded inserts and painted finish.
- Setup fees: Most online laser cutting and steel cutting services charge setup fees covering operator time to load material, calibrate equipment, and prepare your file. These fixed costs get distributed across your order quantity—making per-part pricing decrease as volume increases.
Machine hourly rates typically range from $60 to $120 depending on laser power and capability. Metal cutting costs more than acrylic or wood because it requires more powerful equipment, consumes expensive assist gases like nitrogen or oxygen, and causes greater machine wear.
How to Optimize Your Design for Cost Efficiency
Here's what most shops won't volunteer: you control more of the final price than they do. Design decisions made before you ever request a quote determine the bulk of your manufacturing cost. Smart optimization can cut expenses by 30-50% without compromising function.
Simplify geometries wherever possible. Tight curves and sharp corners force the cutting head to decelerate and reaccelerate constantly, extending cycle time. Replacing multiple small holes with elongated slots reduces pierce count while maintaining similar functionality. Question every decorative element—does that intricate pattern actually serve your application, or does a simpler alternative achieve the same purpose?
Use the thinnest material that meets your requirements. This remains the single most effective cost reduction strategy. Before defaulting to heavy-gauge stock, verify whether thinner material satisfies structural and durability needs. The processing time difference between 2mm and 4mm steel is substantial.
Clean your design files thoroughly. Duplicate lines, hidden layers, and construction geometry all cause problems. Automated quoting systems attempt to cut everything they detect—double lines literally double the cost for that feature. Remove all non-essential elements before submission.
Consider nesting efficiency. Parts arranged efficiently on sheet stock minimize material waste. Rectangular shapes nest more efficiently than irregular profiles. If ordering multiple different parts, combining them into a single order allows the shop to nest them together, reducing your material cost per part.
Order in appropriate quantities. The per-unit cost drops dramatically as quantity increases because setup costs distribute across more parts. According to industry sources, volume discounts can reach as high as 70% for high-quantity orders. Consolidating needs into larger, less frequent orders often beats multiple small-batch purchases.
Prototype Pricing vs Production Volume Pricing
Single prototypes and low-quantity orders carry higher per-part costs—sometimes dramatically higher. This isn't shops gouging customers; it reflects the economic reality that fixed costs must be recovered regardless of quantity.
For a single prototype, setup fees, file preparation time, material handling, and quality inspection all apply to just one part. Order 100 identical parts, and those same fixed costs spread across the entire batch, dropping the per-unit expense significantly.
If you're hunting for cheap laser cutting on prototype quantities, focus on design optimization rather than shop selection. A well-optimized design from a quality steel laser cutting service often costs less than a complex design from the cheapest provider you can find.
Getting Accurate Quotes
Prepare this information before requesting quotes to receive accurate pricing quickly:
- Vector design files in DXF, DWG, or STEP format
- Material type and grade specification
- Material thickness
- Quantity required
- Tolerance requirements (if tighter than standard)
- Required finishing operations
- Delivery timeline expectations
Many online platforms now offer instant quoting—upload your file, select material parameters, and receive pricing within seconds. These automated systems calculate cut path length, pierce count, and material usage algorithmically. However, they may not flag manufacturability issues that a human review would catch.
Understanding what drives your quote empowers you to make informed trade-offs between cost, quality, and timeline. The next consideration—matching laser cutting capabilities to your specific industry application—determines whether any particular service can actually deliver what your project requires.
Industry Applications for Laser Cut Metal Components
You've seen the technology, understood the materials, and learned what drives pricing. But here's where it all comes together: the real-world applications where laser metal cutting services prove their worth. While competitors offer generic lists of industries, the details matter—because understanding exactly how this technology solves specific manufacturing challenges helps you evaluate whether it fits your project.
From chassis components that keep vehicles safe to decorative panels that transform building facades, precision laser cutting enables applications that would be impractical or impossible with traditional fabrication methods. Whether you're searching for metal laser cutting services near me or evaluating steel plate cutting services across the country, knowing these use cases helps you communicate effectively with providers and set appropriate expectations.
Automotive and Aerospace Precision Components
The automotive industry demands a rare combination: complex geometries, tight tolerances, and massive production volumes—all while keeping costs competitive. Laser cutting delivers on every front.
Why does this technology dominate automotive fabrication? According to Accurl's industry analysis, laser cutting is significantly more efficient than traditional metal fabrication processes like die cutting or plasma cutting, streamlining vehicle manufacturing where every millimeter counts. The high-power fiber laser provides precision essential for safety-critical components.
- Chassis components: Frame rails, crossmembers, and structural reinforcements require exact dimensional accuracy to maintain crash performance. Laser-cut parts meet ±0.003" tolerances consistently across production runs of thousands of units.
- Brackets and mounting hardware: Engine mounts, suspension brackets, and body panel supports demand precise hole placement for assembly line efficiency. Misaligned holes mean rejected parts and production delays.
- Structural parts: A-pillars, B-pillars, and roof reinforcements use high-strength steel that traditional punching struggles to process cleanly. Laser cutting handles advanced high-strength steels without the tool wear that plagues mechanical methods.
- Exhaust system components: Heat shields, flanges, and mounting brackets require clean edges that won't create stress concentrations in high-temperature environments.
- Interior trim brackets: Dashboard supports, seat frames, and console mounting hardware need burr-free edges for worker safety during assembly.
Aerospace applications push precision requirements even further. When components fly at 35,000 feet, failure isn't an option.
The aerospace industry benefits from laser cutting's ability to produce components meeting strict tolerance levels while maintaining structural integrity—paramount in applications where weight savings directly translate to fuel efficiency and payload capacity. Steel laser cutting services supporting aerospace often hold certifications like AS9100 to demonstrate quality system compliance.
- Airframe structural elements: Ribs, spars, and skin stiffeners from aluminum and titanium alloys require precise weight control. Every gram matters when calculating fuel consumption over thousands of flight hours.
- Engine components: Turbine blade dampers, combustor liners, and exhaust components use exotic alloys that machine poorly but laser-cut cleanly.
- Avionics enclosures: Shielding housings for sensitive electronics demand EMI protection with precise dimensional control for proper sealing.
- Interior components: Seat frames, galley equipment, and overhead bin hardware balance weight reduction against durability requirements.
For hobbyists and small manufacturers, a laser cutting service for hobbyists can produce scale model components, drone parts, and custom automotive accessories using the same technology that serves major OEMs—just at smaller quantities.
Electronics and Industrial Equipment Applications
Electronics manufacturing demands precision at scales where traditional fabrication methods struggle. According to Think Robotics, sheet metal fabrication offers economical production for electronics enclosures, with laser cutting producing precise flat patterns from various materials.
- Enclosures and chassis: Server housings, control panel boxes, and equipment cabinets require precise cutouts for displays, connectors, and ventilation. Laser cutting creates these features in a single operation, eliminating multiple machining setups.
- Heat sinks and thermal management: Aluminum heat sinks with intricate fin patterns dissipate component heat efficiently. Laser cutting produces these complex geometries faster than machining while maintaining the thin wall sections that maximize surface area.
- EMI shielding: RF-tight enclosures need consistent edge quality for proper gasket seating. The clean, burr-free edges from laser cutting—Indaco Metals notes little to no post-processing required—ensure reliable shielding performance.
- Rack mounting hardware: Server rails, cable management panels, and equipment brackets require precise hole patterns matching industry-standard mounting specifications.
- PCB support structures: Card guides, standoffs, and mounting plates position circuit boards precisely within enclosures.
Industrial equipment manufacturing spans everything from factory automation to agricultural machinery. These applications typically prioritize durability and functionality over aesthetics—but still demand dimensional precision for proper assembly and operation.
- Machine guards and safety enclosures: Perforated protective panels allow visibility and airflow while preventing operator contact with moving parts. Laser cutting produces consistent hole patterns across large panel areas.
- Conveyor components: Side guides, mounting brackets, and drive housings handle continuous operation in demanding environments.
- Agricultural equipment: Harvester components, implement mounting hardware, and structural elements must withstand harsh field conditions while maintaining precise functionality.
- Material handling equipment: Forklift attachments, pallet rack components, and warehouse automation hardware require strength and dimensional accuracy.
Architectural and Decorative Metal Applications
When appearance matters as much as function, laser cutting enables designs impossible to achieve economically through other methods. This is where the technology truly showcases its creative potential.
Architectural applications have brought laser cutting beyond industrial settings into the world of design and aesthetics. The technology's ability to cut through thick steel plates and produce precise cuts makes it invaluable for combining structural strength with visual appeal—highly sought after in modern architecture.
- Decorative facade panels: Building exteriors featuring intricate geometric patterns, organic shapes, or branded imagery. These large-scale panels require consistent quality across hundreds of square feet.
- Interior partition screens: Privacy dividers, feature walls, and room separators combining functionality with artistic expression.
- Staircase components: Decorative stringers, railing panels, and baluster designs that transform utilitarian structures into design statements.
- Signage and wayfinding: Dimensional lettering, illuminated sign faces, and directional systems requiring precise character formation and consistent edge quality.
- Custom furniture elements: Table bases, chair frames, and shelving components blending industrial materials with refined design.
- Artistic installations: Sculptural elements, suspended ceiling features, and commemorative pieces pushing creative boundaries.
Urban centers have become particularly active markets for architectural laser cutting. If you're located in the Northeast, laser cutting NYC and laser cutting New York providers serve architects, designers, and fabricators requiring quick turnaround on custom metalwork. Many of these shops also offer laser engraving NYC services for adding text, logos, or surface texturing to cut components.
The signage and advertising sector particularly benefits from laser cutting's precision. Creating signs, displays, and promotional materials that are both intricate and eye-catching requires a unique combination of precision, speed, and versatility—making it ideal for impactful marketing materials that help businesses stand out in crowded markets.
Matching Applications to Service Capabilities
Not every laser cutting provider serves every industry equally well. A shop optimized for architectural panels may lack the certifications required for aerospace components. A high-volume automotive supplier might not offer the design flexibility needed for custom decorative work.
When evaluating providers for your specific application, consider these alignment factors:
- Material expertise: Does the shop regularly work with your required alloys and thicknesses?
- Tolerance capabilities: Can they hold the precision your application demands?
- Volume flexibility: Do they handle your quantity requirements efficiently—whether prototype or production?
- Secondary operations: Can they provide forming, finishing, and assembly services you need?
- Industry certifications: Do they hold quality certifications relevant to your sector?
Understanding these industry applications gives you context for evaluating potential providers. The next step—knowing exactly what criteria distinguish quality services from mediocre ones—ensures you select a partner who can actually deliver on your project requirements.

How to Evaluate and Choose a Laser Cutting Service Provider
Finding laser metal cutting services near me returns dozens of options—but how do you distinguish providers who deliver consistent quality from those who simply own cutting equipment? The difference between an adequate supplier and an exceptional partner often determines whether your project succeeds or becomes a costly lesson in vendor selection.
Most buyers focus primarily on price when evaluating custom laser cutting services. That's a mistake. The cheapest quote frequently becomes the most expensive option when parts arrive out of tolerance, materials don't match specifications, or delivery dates slip repeatedly. Understanding what separates quality providers from commodity shops empowers you to make decisions that protect your projects and your reputation.
Certifications and Quality Standards That Matter
Certifications aren't just wall decorations—they represent verified commitments to systematic quality management. When a laser cut metal service holds relevant certifications, third-party auditors have confirmed their processes meet rigorous international standards.
For general manufacturing applications, ISO 9001 certification indicates the provider maintains documented quality management systems covering everything from incoming material inspection to final part verification. This baseline certification demonstrates process discipline but doesn't address industry-specific requirements.
Automotive applications demand IATF 16949 certification. According to the International Automotive Task Force, this certification signifies that a company has developed a "process-oriented quality management system that provides for continual improvement, defect prevention and reduction of variation and waste." Major automakers including BMW, Ford, and Stellantis require suppliers throughout their supply chains to maintain this designation.
Why does this matter if you're sourcing chassis brackets or structural components? IATF 16949-certified providers have proven their ability to consistently manufacture quality parts meeting automotive industry's demanding specifications. The certification process evaluates everything from supplier management to statistical process control—ensuring systematic quality rather than luck-based outcomes.
For stainless steel laser cutting services supporting food processing or pharmaceutical applications, look for providers familiar with FDA and sanitary design requirements. Aerospace components require AS9100 certification demonstrating compliance with aviation industry quality standards.
When evaluating a metal cutting service near me, ask directly about certifications and request copies. Legitimate providers display credentials prominently and provide documentation readily. Hesitation or vague responses suggest certifications may be claimed but not current.
Equipment Capabilities and Technology
The machines a shop operates directly determine what they can—and cannot—produce effectively. As noted in Emery Laser's selection guide, advanced laser cutting machines such as fiber lasers offer superior precision, speed, and efficiency while handling complex designs with minimal material waste.
When evaluating sheet metal laser cutting services, investigate these equipment factors:
- Laser type and power: Fiber lasers excel at thin to medium materials; high-power systems handle thicker stock. Ensure their equipment matches your material requirements.
- Bed size: Maximum sheet dimensions the equipment accommodates. Larger beds handle bigger parts and enable more efficient nesting for production runs.
- Automation level: Automated material handling systems reduce labor costs and improve consistency. Ask whether they use automated loading/unloading for production quantities.
- Software capabilities: Modern CAD/CAM software like SolidWorks integration and advanced nesting optimization reduce waste and improve accuracy. Quality providers invest in current software—not outdated systems.
- Maintenance practices: Well-maintained equipment produces consistent results. Ask about calibration schedules and preventive maintenance programs.
A cnc laser cutting service running older equipment may struggle with reflective materials, tight tolerances, or thick stock that modern fiber systems handle routinely. Don't assume all providers offer equivalent capabilities.
Quality Control Processes and Tolerance Guarantees
Equipment alone doesn't ensure quality—systematic inspection and verification processes do. Understanding how a potential provider validates their work reveals whether they catch problems before parts ship or after you've discovered them.
Quality stainless steel laser cutting services implement inspection at multiple stages:
- Incoming material verification: Confirming material type, thickness, and certification matches specifications before cutting begins.
- First-article inspection: Thoroughly measuring initial parts against drawings before production continues.
- In-process sampling: Periodic dimensional checks during production runs to catch drift before it affects large quantities.
- Final inspection: Verifying completed parts meet all specifications before packaging and shipping.
- Documentation: Providing inspection reports, material certifications, and traceability records as required.
Ask potential providers about their inspection equipment. Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) provide full 3D verification of complex geometries. Optical comparators check profile accuracy. Simple calipers suffice for basic dimensions but can't verify complex features reliably.
Tolerance guarantees matter. A provider claiming ±0.003" capability should back that claim with documented evidence—not just marketing assertions. Request tolerance studies or capability data demonstrating they actually achieve claimed specifications consistently.
Turnaround Reliability and Capacity
Promised lead times mean nothing if delivery dates slip repeatedly. According to industry guidance, delays can lead to costly downtime and missed deadlines—making turnaround reliability a critical evaluation factor.
When assessing delivery performance, ask these questions:
- What's your current lead time for standard orders? Compare quoted timelines across multiple providers for reality checks.
- How do you handle expedited requests? Flexibility for urgent projects indicates capacity headroom and process agility.
- What's your on-time delivery rate? Quality providers track this metric and share it confidently. Hesitation suggests problems.
- How do you communicate delays? Proactive notification of schedule changes demonstrates professionalism; discovering delays only when parts don't arrive indicates systemic issues.
Rapid prototyping capabilities distinguish providers supporting product development. A shop offering 5-day rapid prototyping turnaround enables faster design iteration than one requiring three weeks for initial samples. For automotive metal fabrication needs, providers like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology combine IATF 16949-certified quality with 5-day rapid prototyping and 12-hour quote turnaround—demonstrating how leading manufacturers balance speed with quality system compliance.
DFM Support and Communication Responsiveness
Design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback transforms adequate suppliers into valuable partners. Providers who proactively identify design issues, suggest cost-saving modifications, and explain manufacturing constraints add value beyond simply cutting metal.
Comprehensive DFM support includes:
- Manufacturability review: Identifying features that may cause quality issues before cutting begins.
- Cost optimization suggestions: Recommending design modifications that reduce processing time without compromising function.
- Material recommendations: Advising on optimal material selections balancing performance, cost, and availability.
- Tolerance guidance: Explaining what precision is achievable for specific materials and geometries.
- Secondary operation coordination: Managing forming, finishing, and assembly requirements efficiently.
Communication responsiveness reveals organizational culture. A provider answering technical questions promptly demonstrates customer focus. One taking days to respond to simple inquiries likely struggles with complex issues. During initial interactions, note response times and answer quality—these patterns persist throughout your relationship.
Questions to Ask Before Choosing a Provider
Armed with evaluation criteria, here are specific questions that distinguish quality custom laser cutting services from commodity suppliers:
- What certifications do you hold, and can you provide current documentation? Look for ISO 9001 minimum; IATF 16949 for automotive applications.
- What laser technology do you use for my specific material and thickness? Verify their equipment matches your requirements.
- What tolerances can you guarantee, and how do you verify them? Request capability documentation, not just marketing claims.
- What's your typical lead time, and what's your on-time delivery rate? Quantified metrics beat vague assurances.
- Do you provide DFM feedback on submitted designs? Proactive manufacturability review indicates partnership mentality.
- What inspection processes do you use, and what documentation accompanies shipments? Understanding their quality verification reveals process maturity.
- Can you provide references from customers in my industry? Relevant experience reduces learning curves and risks.
- How do you handle non-conforming parts? Clear policies for addressing quality issues protect your interests.
- What secondary operations do you offer in-house? Consolidated sourcing simplifies your supply chain.
- How quickly do you typically return quotes? Quote turnaround indicates overall responsiveness. Leading providers offer 12-hour quote turnaround for standard requests.
If you need to laser cut stainless steel near me for a critical application, these questions separate providers who can genuinely support your requirements from those who simply accept orders and hope for acceptable outcomes.
Taking time to evaluate providers thoroughly pays dividends throughout your relationship. A quality partner reduces your total cost through fewer rejections, faster iterations, and reliable delivery—savings that far exceed any premium their services might command.
With clear criteria for selecting a service provider, the final step is translating this knowledge into action for your specific project needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Metal Cutting Project
You've now seen behind the curtain of laser metal cutting services—the technology differences shops rarely explain, the pricing factors they prefer you don't understand, and the evaluation criteria that separate quality providers from equipment owners. This knowledge transforms you from a passive buyer into an informed customer who commands better pricing, faster turnaround, and superior results.
Whether you're creating custom metal cut components for a prototype, sourcing production quantities for manufacturing, or designing laser cut metal ornaments for artistic projects, the principles remain consistent. Let's distill everything into actionable guidance tailored to your specific situation.
Key Takeaways for Your Laser Cutting Project
The technology you select directly impacts cost and quality. Fiber lasers dominate thin-to-medium metal laser cut applications with superior efficiency and speed. CO2 systems excel on thicker materials and mixed-material shops. Understanding this distinction helps you evaluate whether a provider's equipment matches your requirements—or whether they're using what they have rather than what your project needs.
Material selection extends beyond basic specifications. Reflective metals like aluminum and copper require specialized parameters that affect pricing. Surface preparation matters. Thickness choices exponentially impact cutting time and cost. Choosing the thinnest material that meets your functional requirements remains the single most effective cost reduction strategy.
Design optimization belongs to you, not your supplier. File preparation, feature sizing, kerf allowance, and nesting efficiency all affect your final invoice. A well-optimized design from a quality stainless steel cutting service costs less than a complex design from the cheapest provider available.
Certifications matter—especially for critical applications. IATF 16949 certification proves automotive-grade quality systems. ISO 9001 establishes baseline process discipline. These aren't marketing claims; they represent third-party verification of systematic quality management.
The cheapest quote frequently becomes the most expensive option when parts arrive out of tolerance, materials don't match specifications, or delivery dates slip repeatedly.
Next Steps Based on Your Project Requirements
For hobbyists and makers: Start with design file preparation. Convert your concept to vector format (DXF or SVG), verify minimum feature sizes against your chosen material thickness, and remove duplicate lines. Many laser cutting service metal providers offer instant online quoting—upload your file, select materials, and compare pricing across multiple shops before committing.
For engineers and product developers: Focus on manufacturability from the start. Apply the design guidelines covered here during initial CAD work rather than discovering issues during quoting. Request DFM feedback from potential providers—their willingness to engage technically indicates partnership potential. For rapid iteration, prioritize shops offering 5-day prototyping turnaround to accelerate your development cycle.
For procurement professionals: Build your evaluation framework around the criteria outlined: certifications, equipment capabilities, quality processes, and delivery reliability. Request tolerance documentation and on-time delivery metrics—not just marketing claims. For ongoing production needs, qualify multiple sources to protect your supply chain.
For automotive applications specifically: IATF 16949 certification is non-negotiable for chassis, suspension, and structural components. If your project requires certified quality for automotive metal fabrication, Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology offers 12-hour quote turnaround combined with comprehensive DFM support and 5-day rapid prototyping—enabling you to validate designs quickly before committing to production volumes.
Whatever your application—from industrial equipment to decorative metalwork—the path forward starts with properly prepared design files, realistic material and tolerance specifications, and thorough provider evaluation. Armed with the knowledge from this guide, you're positioned to secure better outcomes than buyers who treat laser metal cutting services as commodity purchases.
Your next step? Prepare your design file according to the guidelines covered, gather your material specifications, and request quotes from providers whose capabilities align with your requirements. The difference between adequate results and exceptional outcomes often comes down to asking the right questions before you place your order.
Frequently Asked Questions About Laser Metal Cutting Services
1. How much does metal laser cutting cost?
Laser cutting steel typically costs $13-$20 per hour of machine time, but your actual price depends on multiple factors beyond hourly rates. Material type and thickness have the biggest impact—doubling thickness can more than double cutting time. Cut complexity matters significantly: intricate designs with long perimeters cost more than simple shapes. Pierce count also affects pricing, as each hole or internal cutout requires a separate pierce operation. For accurate quotes, prepare vector files (DXF or DWG format), specify your material and thickness, and include quantity requirements. Many providers offer instant online quoting for quick comparisons.
2. What is the difference between fiber laser and CO2 laser cutting?
Fiber lasers operate at 1064 nm wavelength and excel at cutting thin to medium metals—especially reflective materials like aluminum, copper, and brass. They offer up to 50% energy efficiency and require minimal maintenance. CO2 lasers use 10,600 nm wavelength and remain ideal for thicker materials and mixed-material shops. CO2 systems often deliver smoother edges on thick carbon steel and can also cut non-metals like wood and acrylic. For most sheet metal projects under 1 inch thick, fiber lasers provide faster speeds and lower operating costs.
3. What file formats are required for laser cutting services?
Laser cutting machines require vector files—not photographs or bitmap images. The most commonly accepted formats include DXF (Drawing Exchange Format), DWG (AutoCAD Drawing), AI (Adobe Illustrator), and SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics). DXF is the industry standard with universal compatibility. Before submitting, convert all text to outlines, remove duplicate lines, and verify dimensions at 100% scale. If you only have a raster image, tools like Inkscape can trace and convert it to vector format, though you should verify dimensions after conversion.
4. What materials can be laser cut?
Most laser metal cutting services process carbon steel (up to 25+ mm), stainless steel (up to 20 mm), aluminum alloys (up to 12 mm), brass (up to 8 mm), copper (up to 6 mm), and titanium (up to 6 mm). Material properties directly affect cutting parameters and costs. Steel absorbs laser energy well, making it economical to cut. Reflective metals like aluminum and copper require specialized settings and typically cost more. Surface condition matters—clean materials free of oil, oxidation, and moisture produce better results with fewer complications.
5. How do I choose the right laser cutting service provider?
Evaluate providers based on certifications, equipment capabilities, quality processes, and delivery reliability. For automotive applications, IATF 16949 certification is essential—it verifies process-oriented quality management meeting automotive industry standards. Ask about their laser technology to ensure it matches your material requirements. Request tolerance documentation rather than accepting marketing claims. Quality providers offer DFM (design for manufacturability) feedback, quick quote turnaround (12 hours or less for leading manufacturers), and transparent communication about lead times and on-time delivery rates.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
