High Volume Metal Stamping Automotive: Engineering & Sourcing Guide
TL;DR
High volume metal stamping automotive production is the backbone of modern vehicle manufacturing, capable of delivering millions of precision components with near-zero defects. By utilizing progressive die and high-speed stamping technologies, manufacturers can achieve production speeds exceeding 1,500 strokes per minute while maintaining tolerances as tight as +/- 0.001 inches. This process is essential for producing safety-critical parts like airbag sensors and emerging EV components such as copper busbars.
For automotive engineers and procurement managers, success relies on selecting partners certified to IATF 16949 standards who can navigate the material shift toward Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) and aluminum for lightweighting. Whether sourcing terminals, brackets, or complex lead frames, the right high-volume stamping strategy optimizes unit costs through economies of scale while ensuring strict adherence to global automotive quality mandates.
High-Volume Manufacturing Technologies
The automotive industry’s demand for millions of identical, defect-free parts requires manufacturing technologies that balance extreme speed with microscopic precision. The primary method for achieving this is Progressive Die Stamping. In this process, a continuous metal strip is fed through a press containing a series of stations. Each station performs a specific operation—cutting, bending, punching, or coining—simultaneously with every stroke of the press. As the strip moves forward, the part progressively takes shape until it is cut loose at the final station. This method is the industry standard for high-volume efficiency, allowing for the production of complex geometries without manual handling between steps.
To meet the soaring demand for electrical components in modern vehicles, High-Speed Stamping has become indispensable. Leading manufacturers leverage specialized equipment, such as Bruderer presses, which can operate at speeds up to 1,500 strokes per minute. According to Wiegel, this capability is critical for producing multi-million-piece runs of intricate parts like terminals and connectors, where cycle time directly impacts commercial viability. The ability to stamp copper alloys and exotic metals at these velocities ensures that high-volume orders for EV power systems are met on time.
Another technological leap is the adoption of Servo Press Technology. Unlike traditional mechanical presses that run on a fixed flywheel cycle, servo presses utilize high-torque motors to fully control the ram's speed and position throughout the stroke. This allows for "dwelling" at the bottom of the stroke to reduce springback in difficult materials or adjusting velocity to prevent cracking. Automation Tool & Die (ATD) highlights that servo presses, ranging from 330 to 700+ tons, are instrumental in forming complex geometries and high-strength materials that would otherwise fail in standard mechanical presses.
Key Automotive Components & EV Transition
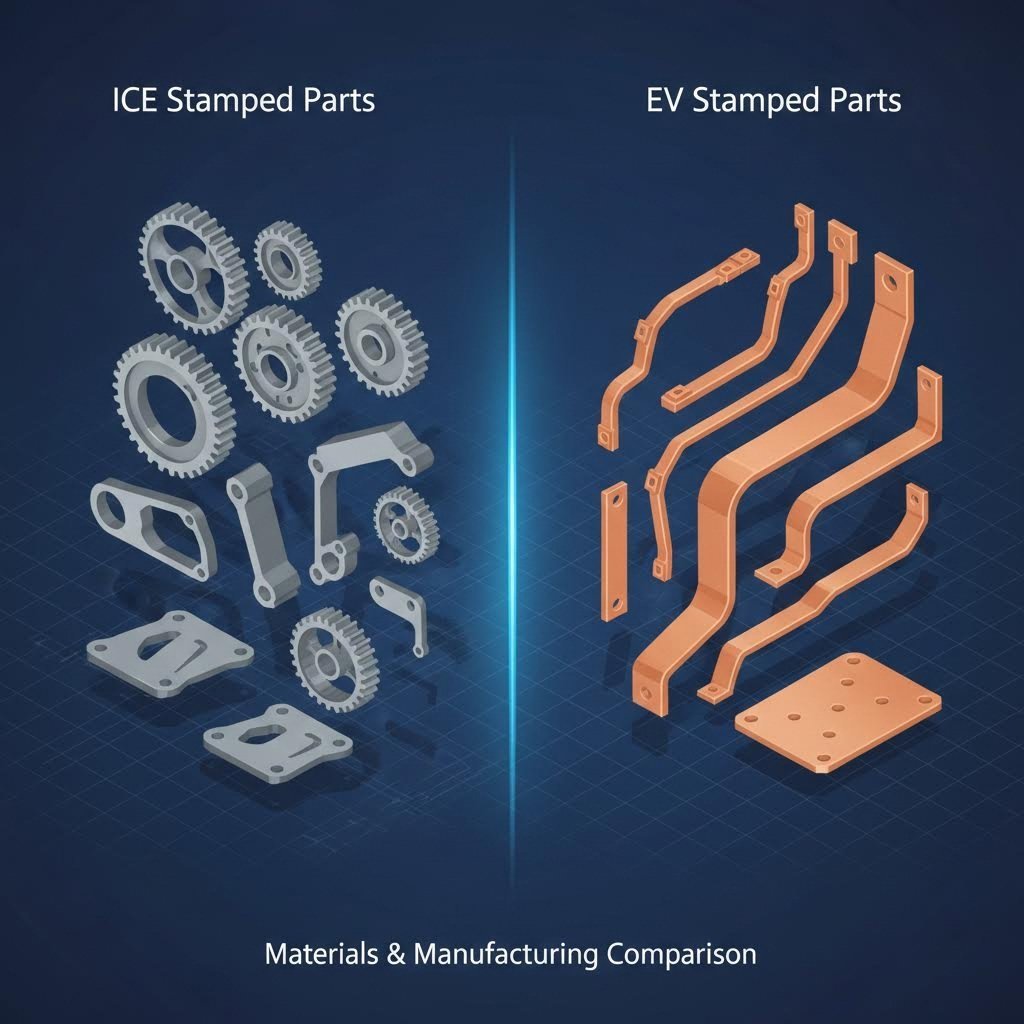
The transition from Internal Combustion Engines (ICE) to Electric Vehicles (EVs) has fundamentally shifted the types of stamped components required by Tier 1 and OEM buyers. While traditional ICE vehicles demand high volumes of fuel injector clips, exhaust hangers, and transmission brackets, the EV landscape prioritizes electrical conductivity and thermal management. Busbars, battery terminals, and shields are now among the highest-volume stamped parts. These components often require specialized tooling to handle copper and copper alloys without damaging their surface finish, which is critical for electrical performance.
Safety-critical components remain a constant volume driver across all vehicle types. Parts such as seatbelt housings, airbag mounts, and brake manufacturing components must withstand high impact forces and rigorous fatigue testing. Xometry notes that precision stampings are vital for these applications because they offer repeatability that casting or machining cannot match at scale. A stamped airbag bracket, for instance, must deploy exactly as designed in milliseconds; there is no margin for dimensional variance in a production run of five million units.
Lightweighting is another dominant trend influencing component design. To improve fuel efficiency in ICE vehicles and extend range in EVs, engineers are replacing heavy steel assemblies with stamped aluminum or thinner, stronger steel grades. This shift presents manufacturing challenges, as aluminum is more prone to cracking and galling during the stamping process. Experienced stampers mitigate this by using advanced lubricants and highly polished dies to ensure smooth material flow while maintaining the structural integrity required for chassis and body-in-white applications.
Material Science in Automotive Stamping
Material selection in high-volume stamping is no longer limited to mild steel. The push for safety and efficiency has popularized Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS). These materials offer exceptional tensile strength, allowing engineers to use thinner gauges to save weight without compromising safety. However, AHSS requires significantly higher tonnage presses and robust tooling materials, such as carbide, to resist the extreme wear generated during production. The "springback" effect—where the metal tries to return to its original shape after bending—is more pronounced in AHSS, requiring sophisticated die engineering to overbend the material precisely.
For the electrification of the powertrain, Copper and Brass alloys are essential due to their superior electrical conductivity. These soft metals present a different set of challenges; they are highly ductile but easily scratched or deformed. High-speed stamping of copper terminals often includes in-die monitoring systems to detect scrap or debris that could mar the delicate contact surfaces. Furthermore, many EV components require pre-plated materials (like tin or silver-plated copper) to enhance conductivity and corrosion resistance. The stamping process must be gentle enough to form the part without stripping these vital plating layers.
Aluminum stamping continues to grow for structural and cosmetic applications. While it offers excellent strength-to-weight ratios, aluminum behaves differently than steel under stress. It has lower formability limits and requires specific bend radii to avoid fracturing. Stampers must carefully control the clearance between the punch and die—typically tighter than for steel—to produce clean, burr-free edges on aluminum parts used in heat shields, brackets, and decorative trim.
Quality Standards & The Zero-Defect Mandate
In the automotive sector, quality certifications are not optional add-ons; they are licenses to operate. IATF 16949 is the global technical specification and quality management standard for the automotive industry. It goes far beyond general ISO 9001 requirements, mandating strict risk management, defect prevention, and supply chain consistency. A stamper without this certification cannot typically supply Tier 1 or OEM customers. This standard enforces a "zero-defect" mindset, where the goal is not just to detect bad parts but to prevent them from ever being made.
To achieve this, high-volume stampers employ the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) and Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP). PPAP validates that the manufacturing process has the potential to produce product that consistently meets all requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate. This involves rigorous measurement and documentation of the first several hundred parts, often utilizing Cpk (process capability) analysis to statistically prove stability.
On the factory floor, technology enforces these standards. JV Manufacturing explains that automated vision systems and in-die sensors are crucial for maintaining quality at high speeds. These sensors monitor press tonnage, part ejection, and dimensional accuracy in real-time. If a part deviates by even a fraction of a millimeter, or if a slug is not properly ejected, the system instantly stops the press to prevent tool damage and segregate the suspect part. This 100% inspection capability is the only way to guarantee the parts-per-million (PPM) quality levels demanded by automotive assembly lines.
Cost Drivers & Strategic Sourcing
The economics of high-volume stamping are driven by economies of scale. While the upfront investment in progressive dies (hard tooling) can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, this cost is amortized over the life of the program. For a part running 5 million units a year, a $50,000 die adds only a penny to the unit cost. Conversely, using a lower-cost "soft tool" method suitable for prototyping would result in a prohibitively high piece price and slow delivery. Procurement teams must balance these factors, often locking in long-term agreements to justify the capital expenditure on tooling.
An effective sourcing strategy also considers the supplier's ability to scale. Many automotive programs begin with a prototyping phase requiring rapid turnaround before ramping up to mass production. For programs requiring a seamless transition from initial validation to mass production, suppliers like Shaoyi Metal Technology offer integrated solutions, leveraging presses up to 600 tons and IATF 16949-certified precision to scale from 50 prototypes to millions of critical components. Verifying a supplier's full range of automotive stamping capabilities ensures they can handle both the agility needed for development and the robust capacity required for launch.
Final cost factors include material utilization and cycle time. A well-designed progressive die maximizes the number of parts per strip (material yield) and minimizes scrap. "Near-net shape" stamping reduces the need for secondary operations like machining, further cutting costs. When requesting a quote, providing complete CAD data, annual volume forecasts, and specific alloy grades allows the stamper to engineer the most cost-efficient strip layout, directly impacting the bottom-line price per part.

Engineering the Future of Mobility
As the automotive landscape shifts toward electrification and autonomous systems, the role of high-volume metal stamping becomes even more critical. The industry is moving beyond simple metal forming into a realm of complex, integrated manufacturing where precision, material science, and speed converge. Sourcing partners who combine IATF 16949 rigor with advanced servo and high-speed technologies will be the ones to successfully support the next generation of vehicle architectures. For buyers and engineers, the focus must remain on validating technical depth—ensuring that the chosen supplier has not just the capacity, but the capability to deliver zero-defect performance millions of times over.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between progressive die and transfer die stamping?
Progressive die stamping feeds a continuous strip of metal through multiple stations within a single die, making it faster and more cost-effective for smaller, high-volume parts. Transfer die stamping involves cutting the part loose from the strip early and mechanically transferring it between separate die stations. Transfer dies are typically used for larger parts (like frames or shells) that require more complex forming operations that cannot be done while attached to a strip.
2. Why is IATF 16949 certification important for metal stamping?
IATF 16949 is a specific quality management standard for the automotive sector that emphasizes defect prevention, supply chain consistency, and continuous improvement. For a metal stamping company, holding this certification demonstrates that they have the rigorous process controls, documentation (PPAP), and risk management systems necessary to prevent failures in safety-critical automotive components.
3. What materials are most common in EV stamping?
Electric Vehicle (EV) stamping heavily utilizes copper and copper alloys (such as C11000 or beryllium copper) for busbars, terminals, and connectors due to their high electrical conductivity. Aluminum is also widely used for battery enclosures, heat shields, and structural brackets to reduce overall vehicle weight and offset the heavy mass of battery packs. Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) remains common for structural crash protection components.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
