Unlocking Strength: Forging for High-Performance Auto Parts

TL;DR
Forging is a superior manufacturing process for high-performance auto parts, creating components that are significantly stronger and more durable than those made by casting or machining. This enhanced strength comes from the forging process, which shapes metal under immense pressure, refining and aligning its internal grain structure to follow the part's contour. This results in exceptional resistance to stress, fatigue, and failure, making it essential for safety-critical applications.
Why Forging is the Superior Method for High-Performance Parts
In the demanding world of high-performance and motorsports vehicles, component failure is not an option. This is why forging for high-performance auto parts is the preferred manufacturing method over alternatives like casting or machining directly from billet stock. The fundamental advantage lies in the material's microstructure. Forging subjects metal to localized compressive forces, physically altering and refining the internal grain structure. Unlike casting, which can have porosity, or machining, which cuts through grain flows, forging forces the grain to align with the shape of the component. This continuous, unbroken grain flow results in parts with vastly superior mechanical properties.
This structural integrity translates directly to enhanced strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Forged components can withstand greater stress, impact, and cyclical loads without failing. As detailed by manufacturing experts, this makes them ideal for safety-critical applications where reliability is paramount, such as in braking and suspension systems. The process densifies the metal, eliminating internal defects and voids that can become points of failure under extreme pressure. A forged part is, therefore, not just strong, but consistently reliable throughout its service life.
The strength-to-weight ratio of forged parts is another critical benefit, particularly in the automotive industry's push for lightweighting to improve fuel efficiency and performance. For materials like aluminum, the forging process significantly improves its mechanical properties, making it more resistant to stress and strain, as highlighted in a resource from Al Forge Tech. This allows engineers to design parts that are lighter than their cast or machined equivalents without compromising on strength or durability, a crucial balance for high-performance vehicles.
Key Forging Processes for Automotive Components
The production of forged automotive parts utilizes several specialized processes, each chosen based on the component's complexity, material, and required precision. These techniques can be broadly categorized by the temperature at which they are performed—hot, warm, or cold forging—and the type of die used. Understanding these methods reveals how manufacturers achieve the precise geometries and material properties needed for peak performance.
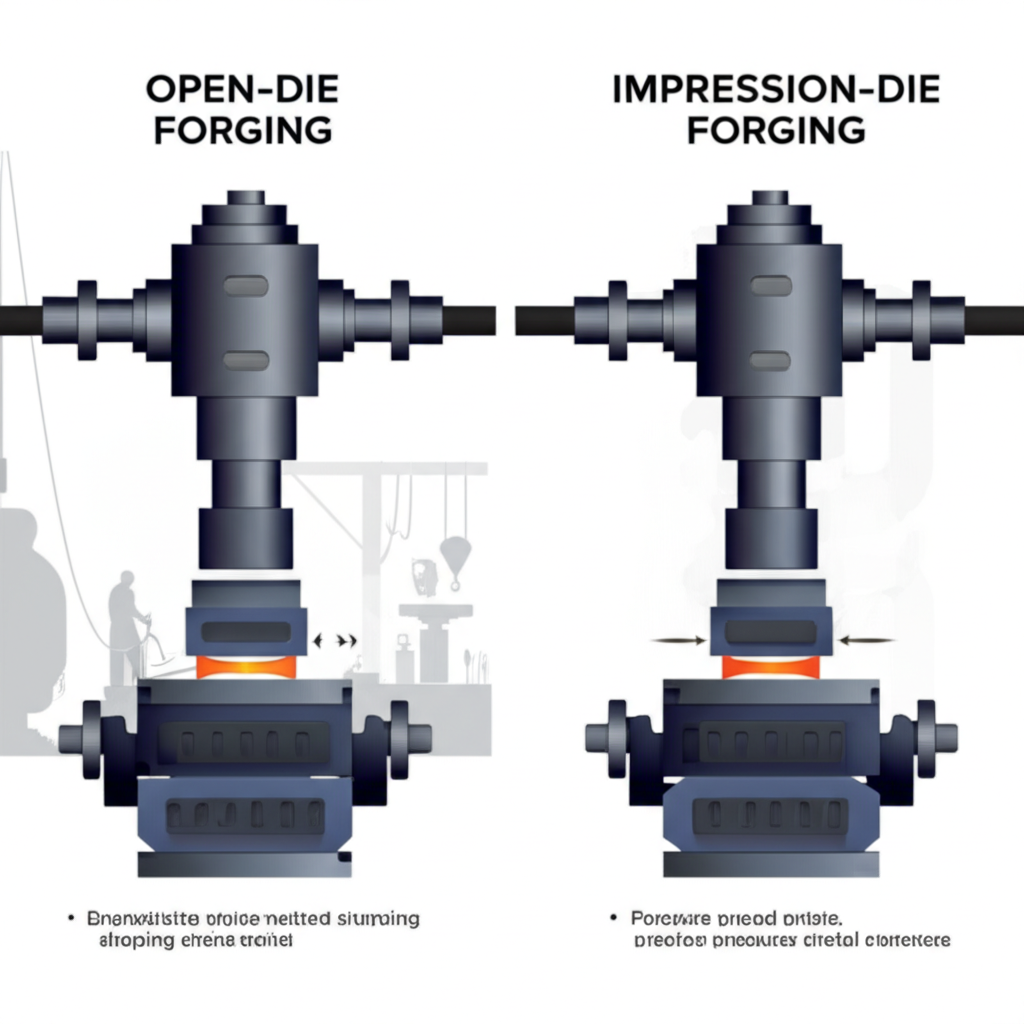
Impression Die and Open Die Forging
The most common method for automotive components is impression die forging, also known as closed die forging. In this process, a metal billet is placed between two dies that contain a precise impression of the final part. A powerful hammer or press forces the metal to flow and fill the die cavities. This technique is excellent for producing complex shapes with tight tolerances and is used for parts like connecting rods and gears. Conversely, open die forging involves shaping the metal between flat or simple dies without completely enclosing it. While less precise and often requiring secondary machining, it is versatile and suitable for larger, simpler components.
Precision and Drop Forging
High-precision drop forging is a refinement of closed die forging that offers even tighter tolerances and near-net-shape results, minimizing the need for finish machining. As explained in an article by Sinoway Industry, this meticulous control over the process is critical for parts where dimensional accuracy is non-negotiable, such as transmission and steering components. For companies seeking custom solutions, specialized providers offer advanced services. For robust and reliable automotive components, check out the custom forging services from Shaoyi Metal Technology. They specialize in high-quality, IATF16949 certified hot forging, demonstrating the industry's capability to deliver components from small-batch prototypes to mass production with exceptional precision.
Cold and Roll Forging
Cold forging is performed at or near room temperature. This process increases the metal's strength through strain hardening but is generally limited to simpler shapes and more ductile metals. It offers an excellent surface finish and high dimensional accuracy. Roll forging is a different technique where heated bars are passed between grooved rollers that progressively shape the metal. According to a knowledge base article from Zetwerk, this method is efficient for producing long, slender parts like axles and driveshafts, as it creates a favorable grain structure while reducing material waste.
Essential Materials in Automotive Forging
The choice of material is as crucial as the forging process itself in determining the final properties of a high-performance auto part. The selection depends on the specific application's requirements for strength, weight, heat resistance, and cost. The most common materials used in automotive forging are advanced steel alloys, aluminum alloys, and titanium.
Steel Alloys: Carbon and alloy steels are the workhorses of the automotive forging industry due to their exceptional strength, toughness, and availability. They are used for a vast range of components that endure high stress, such as crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, and axles. Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering are often applied after forging to further enhance the mechanical properties of steel parts, tailoring them for specific durability and performance requirements as detailed by thermal processing specialists at Paulo.
Aluminum Alloys: Aluminum is prized for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it a key material in the push for vehicle lightweighting. Forged aluminum components, such as suspension arms, wheels, and brake calipers, reduce a vehicle's unsprung mass, which improves handling, acceleration, and fuel efficiency. While not as strong as steel, its lower density provides a significant performance advantage in many applications without sacrificing durability.
Titanium Alloys: For the most extreme applications where both immense strength and low weight are critical, titanium is the material of choice. It offers a strength comparable to many steels at about half the weight, along with excellent corrosion resistance and performance at high temperatures. Due to its higher cost, forged titanium is typically reserved for elite performance vehicles and motorsport applications, used in components like connecting rods, valves, and exhaust systems.
Critical Applications: Where Forged Parts Deliver Peak Performance
The superior properties of forged components make them indispensable in areas of a vehicle where failure could be catastrophic. These parts are concentrated in the engine, drivetrain, and chassis, forming the backbone of a high-performance automobile's safety and reliability.
- Engine and Drivetrain Components: The internal combustion engine is a high-stress environment with immense heat and pressure. Key components like the crankshaft, camshafts, connecting rods, and pistons are almost exclusively forged in high-performance applications. These parts must transfer immense force reliably for millions of cycles. Likewise, drivetrain components such as transmission gears, driveshafts, and universal joints are forged to handle the torque and shock loads of aggressive driving.
- Suspension and Steering Systems: Forged parts are critical for vehicle dynamics and safety. Control arms, steering knuckles, and wheel hubs must withstand constant forces from the road while maintaining precise alignment. The strength and fatigue resistance of forged aluminum and steel ensure these components perform reliably, providing responsive handling and preventing structural failure under cornering and braking loads.
- Braking Systems: There is no greater safety-critical system than the brakes. Forged brake calipers are common in high-performance vehicles because they offer superior stiffness and heat dissipation compared to cast alternatives. This rigidity prevents the caliper from flexing under hard braking pressure, providing a consistent and firm pedal feel and ensuring maximum braking force is applied.

The Unmatched Integrity of Forged Components
Ultimately, the adoption of forging for high-performance auto parts is a testament to its unparalleled ability to produce components with superior strength, durability, and reliability. By physically refining the metal's grain structure, the forging process builds in a level of structural integrity that other manufacturing methods cannot replicate. This makes it the non-negotiable choice for critical applications where performance and safety are the highest priorities.
From the heart of the engine to the suspension that connects the vehicle to the road, forged parts provide the confidence and resilience needed to push the boundaries of automotive performance. As technology advances, precision forging techniques will continue to evolve, enabling the creation of even lighter, stronger, and more complex components for the next generation of high-performance vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 4 types of forging processes?
The four primary types of forging processes are impression die forging (also called closed die forging), open die forging, cold forging, and seamless rolled ring forging. Each method offers different advantages regarding part complexity, dimensional accuracy, and production volume, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
2. What metals cannot be forged?
Metals with limited ductility are difficult or impossible to forge. This includes materials like cast iron and certain high-carbon steels, which are too brittle and would crack under the compressive forces of forging. Similarly, some very high-strength alloys may be too resistant to plastic deformation to be shaped effectively by the process.
3. Is forging stronger than welding?
Yes, in many cases, a forged component is stronger than a welded one. Forging creates a continuous, aligned grain structure throughout the part, enhancing its overall strength and fatigue resistance. Welding, on the other hand, involves melting and fusing metal, which can introduce potential weak points, heat-affected zones, and internal stresses at the joint that may not be as strong as the base material.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
