Mastering Die Design for Electric Vehicle Parts
TL;DR
Die design for electric vehicle parts is a critical manufacturing process for producing lightweight, high-strength, and complex metal components. It enables the creation of essential parts like motor housings and battery trays from materials such as aluminum, which is crucial for improving vehicle efficiency, extending range, and ensuring structural integrity. Advanced die design is the foundation of modern EV performance and safety.
The Foundational Role of Die Casting in EV Manufacturing
Die casting is a cornerstone technology for the electric vehicle industry, serving as the primary method for manufacturing components that are both lightweight and structurally robust. The relentless push for greater driving range and enhanced performance in EVs places a premium on reducing overall vehicle weight, a challenge that die casting is uniquely suited to address. By using materials like aluminum, manufacturers can produce parts that significantly lower a vehicle's curb weight, which in turn improves energy efficiency and handling dynamics.
This process involves injecting molten metal under high pressure into a sophisticated steel mold, known as a die. The ability to create complex, net-shape parts with high accuracy makes it an ideal solution for the intricate components required in EVs. Unlike other manufacturing methods, die casting allows for the integration of multiple features—such as mounting bosses, cooling channels, and reinforcing ribs—into a single, consolidated part. This consolidation reduces the need for secondary assembly operations, simplifies the supply chain, and ultimately lowers manufacturing costs while improving part reliability.
The benefits of die casting directly address major challenges in EV design, particularly packaging and thermal management. Electric vehicles are densely packed with batteries, power electronics, and motors that generate significant heat. Die-cast components, especially those made from aluminum, offer excellent thermal conductivity, allowing them to function as heat sinks that dissipate thermal energy effectively. Furthermore, the precision of the process ensures that these complex parts fit perfectly within the tight confines of an EV's chassis, optimizing space and protecting sensitive electronics.
Core Principles of Die Design for Lightweighting and Strength
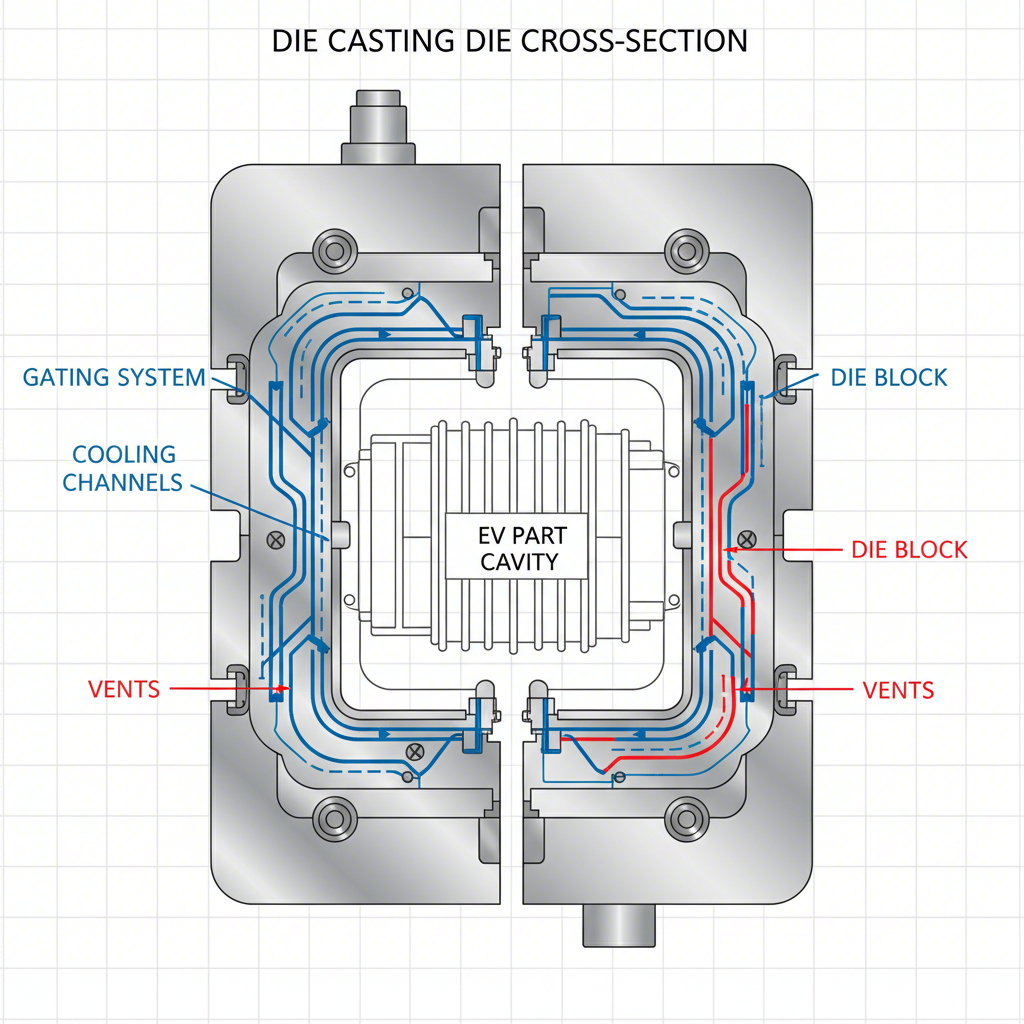
The die itself is the most critical element in the die casting process, as its design dictates the final part's quality, strength, and weight. Engineering a high-performance die for EV components is a sophisticated discipline that balances competing requirements for thin walls, structural integrity, and mass-production efficiency. A well-designed die is not merely a cavity but a complex tool engineered for precise control over the entire casting cycle.
A primary function of advanced die design is enabling thin-wall capabilities. Lightweighting is achieved by minimizing material usage without compromising strength, and modern dies can produce parts with wall sections as thin as 1–2 mm. This is made possible through optimized gating and venting systems that ensure the molten metal flows smoothly and completely fills the cavity, preventing defects like porosity. Furthermore, achieving high dimensional accuracy is paramount, especially for components like motor housings and battery enclosures. As detailed by experts at RACE MOLD, dies can be engineered to hold tolerances within ±0.05 mm, ensuring perfect alignment and fitment of internal systems.
Effective thermal management within the die is another crucial principle. The strategic placement of cooling lines controls the solidification rate of the metal, which directly impacts the material's grain structure and mechanical properties. This controlled cooling increases the density and tensile strength of the final casting. Key features of an advanced die design include:
- Strategically Positioned Gates: To control the entry and flow of molten metal into the cavity.
- Balanced Flow Distribution: Ensures uniform filling to prevent defects and weak spots.
- Optimized Cooling Lines: To manage temperature, reduce cycle times, and extend the life of the die.
- Effective Venting: Allows trapped air to escape the cavity, preventing gas porosity.
Achieving this level of precision requires deep expertise in both engineering and manufacturing. Companies specializing in this field utilize advanced CAE simulations and project management to deliver high-quality dies that meet the stringent demands of automotive OEMs. A meticulously designed die not only produces superior parts but also reduces scrap rates and minimizes the need for costly secondary machining, making it a cornerstone of efficient EV production.
Advanced Materials in EV Die Casting: A Comparative Analysis
Material selection is a critical decision in die design for electric vehicle parts, directly influencing a component's weight, strength, thermal performance, and cost. While several metals can be die-cast, the unique demands of EVs have made certain alloys the clear front-runners. The choice of material is a strategic trade-off, with engineers balancing performance characteristics against manufacturing considerations to select the optimal alloy for each specific application.
Aluminum is the dominant material in EV die casting, prized for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, superior thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Alloys like A380 and ADC12 are commonly used for large structural components such as motor housings, battery trays, and subframes. The lightweight nature of aluminum is essential for maximizing vehicle range, while its ability to dissipate heat is critical for maintaining the performance of batteries and power electronics. As noted in a Dynacast industry overview, thin-walled aluminum castings can withstand the highest operating temperatures of all die-cast alloys, making them indispensable for powertrain applications.
Zinc alloys offer a different set of advantages, particularly for smaller, more intricate components. Due to zinc's greater fluidity when molten, it can fill extremely thin and complex sections of a die, enabling the creation of parts with fine details and a superior surface finish. This often eliminates the need for secondary machining operations. A key economic benefit of using zinc is the significantly longer die life it allows—up to ten times longer than dies used for aluminum. This makes zinc a highly cost-effective choice for high-volume components like electronic enclosures, sensors, and connectors.
Magnesium stands out as the lightest of all structural metals, offering the highest strength-to-weight ratio. It is an ultra-lightweight option for components where every gram counts, such as steering wheel frames and instrument panels. However, its use can be more complex due to its reactive nature. The table below summarizes the key properties of these primary materials.
| Property | Aluminum Alloys | Zinc Alloys | Magnesium Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | Low | High | Very Low |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Good (balanced performance) | Excellent (for high-volume, complex parts) | Moderate (higher material cost) |
| Common EV Applications | Motor housings, battery trays, structural parts | Electronic enclosures, connectors, small complex parts | Interior structures, ultra-lightweight components |
Critical Applications: A Component-by-Component Breakdown
Virtually every major system in an electric vehicle relies on components produced through precision die casting. The ability to manufacture strong, lightweight, and geometrically complex parts at scale makes it the ideal process for a wide range of critical applications. From the powertrain to the battery system, die-cast parts provide the structural integrity, thermal management, and protection necessary for safe and efficient vehicle operation.
Motor Housings: This is one of the most critical die-cast components in an EV. The motor housing must protect the internal rotor and stator, provide structural rigidity to maintain precise alignment under high torque, and efficiently dissipate heat. Modern designs, as highlighted by experts at EMP Tech, often feature integrated liquid cooling channels, or "water jackets," that are cast directly into the housing. This advanced technique offers far superior thermal management compared to bolted-on cooling plates, enabling motors with higher power density.
Battery Trays and Enclosures: The battery pack is the heart of an EV, and its enclosure is vital for safety and performance. Die-cast battery trays securely hold the battery modules, protect them from road impacts and vibrations, and play a crucial role in thermal management. These large, complex castings must be incredibly strong to protect the cells in a crash scenario while remaining as light as possible to avoid hurting the vehicle's range.
Power Electronics and Inverters: Components like inverters, which convert DC power from the battery to AC power for the motor, generate significant heat. Die-cast housings for these electronics are designed with integrated heat sinks—thin fins that increase the surface area to dissipate heat into the air or a cooling system. The high thermal conductivity of aluminum makes it the perfect material for ensuring these critical systems operate within their optimal temperature range.
Other important die-cast components found throughout an EV include transmission cases, structural nodes for the vehicle frame, and various electrical parts. A comprehensive list from suppliers of stamped metal parts, like Standard Die, includes parts such as busbars for conducting high-voltage electricity, EMI shields to protect sensitive electronics, and various connectors and terminals. The widespread use of die casting across these applications underscores its indispensable role in building the next generation of electric vehicles.
The Future of EV Die Design: Advanced Techniques and Sustainability
The evolution of die design for electric vehicles is rapidly advancing, driven by OEM demands for higher performance, greater component integration, and increased sustainability. The future of the industry lies in mastering sophisticated casting techniques and embracing a circular economy model. Suppliers who innovate in these areas will be pivotal in shaping the next generation of EV manufacturing.
One of the most significant advancements is the widespread adoption of Vacuum Die Casting. In this process, a vacuum removes nearly all the air from the die cavity just before the molten metal is injected. This drastically reduces gas porosity, a common defect that can create weak spots or cause leaks in fluid-carrying channels. The result is a denser, stronger part that is pressure-tight and can be heat-treated for maximum strength—a critical requirement for high-performance motor housings and structural components.
The trend toward Integrated Functionality is also accelerating. Engineers are no longer designing simple enclosures; they are creating multi-functional systems. Casting features like liquid cooling channels, mounting points for electronics, and cable routing paths directly into a part reduces assembly time, lowers weight, and improves reliability. This level of integration requires incredibly complex dies and advanced process control but delivers a far superior end product. To ensure longevity, these components also require advanced surface treatments, such as a multi-layer e-coat system, which can provide protection against corrosion for over 1,000 hours in salt spray tests.
Finally, Sustainability has become a central pillar of the industry. The core promise of EVs is a reduced environmental footprint, and that extends to their manufacturing. Aluminum is infinitely recyclable without losing its mechanical properties, making it an ideal material for a circular economy. The use of recycled, or "low-carbon," aluminum is a major trend, as it consumes approximately 95% less energy than producing aluminum from primary ore. Die casting facilities are increasingly implementing closed-loop recycling systems where all process scrap is re-melted and reused on-site, minimizing waste and further reducing the carbon footprint of EV components.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
