Custom Forged Wheel Hub Centric Rings: Stop That Highway Vibration Now
What Are Hub Centric Rings and Why Every Wheel Swap Needs Them
You just installed a gorgeous set of aftermarket wheels on your car. They look incredible sitting in the driveway. But then you hit the highway, and somewhere around 60 mph, an annoying vibration creeps through the steering wheel and floorboard. Sound familiar? This frustrating scenario happens more often than you might expect, and the culprit is usually a tiny gap you never knew existed.
The good news? There's an engineering solution designed specifically for this problem: hub centric rings. These precision-machined components bridge the gap between your vehicle's hub bore and your wheel's center bore, eliminating that highway vibration once and for all.
The Gap Between Your Hub and Wheel
So what are hub centric rings exactly? Think of them as precision spacers that fill the void between two critical measurements on your wheel setup. Your vehicle has a hub—the cylindrical protrusion at the end of each axle where your wheel mounts. This hub has a specific diameter called the hub bore. Meanwhile, your wheel has a center bore—the hole in the middle that slides over the hub.
When automakers design original equipment (OE) wheels, they engineer the wheel's center bore to match the vehicle's hub bore precisely. According to Les Schwab's wheel fitment guide, this hub-centric design provides a stable and secure connection, reducing the chance of imbalance that leads to steering wheel or seat vibrations.
Here's where aftermarket wheels create a challenge. Manufacturers design these wheels with oversized center bores so a single wheel model can fit multiple vehicles. While this makes business sense, it leaves you with a gap that needs filling. Without proper hub centering, your wheels rely entirely on the lug nuts to stay positioned—and that's where problems begin.
Why Wheel Centering Matters for Safety
Understanding what is hub centric versus lug centric mounting comes down to where the load transfers. With hub centric fitment, the wheel sits directly on the hub, and the vehicle's weight distributes evenly across the entire hub face. The lug nuts simply secure the wheel in place—they don't bear the centering responsibility.
Lug centric wheels, on the other hand, rely on the lug holes aligning with your vehicle's studs to center the wheel. What does hub centric mean in practical terms? It means mechanical centering rather than depending on lug tension alone. As Curva Concepts explains, hub-centric wheels eliminate the micro-movements that create vibration at highway speeds.
The physics are straightforward. When a wheel isn't perfectly centered, even by fractions of a millimeter, it creates an imbalance. At low speeds, you won't notice it. But vibration harmonics amplify with speed, and by the time you're cruising at highway velocities, that tiny imbalance becomes impossible to ignore. Worse, improperly centered wheels concentrate stress on the lug studs instead of distributing it across the hub face, leading to premature wear on critical components.
Wheel centering rings solve this by providing that precise mechanical interface between hub and wheel. When properly installed, they deliver three essential functions:
- Vibration elimination: By centering the wheel mechanically, hub centric rings remove the oscillations that travel through your steering wheel, floorpan, and chassis.
- Proper load distribution: Weight transfers evenly across the hub face rather than concentrating on lug studs, reducing stress on your wheel studs and bearings.
- Wheel protection: Consistent geometry through dynamic loads extends wheel service life and prevents the premature wear caused by improper fitment.
The bottom line? If you're running aftermarket wheels—or planning to—understanding hub centric rings isn't optional. It's the difference between a smooth, confident ride and that nagging vibration that makes every highway trip uncomfortable.
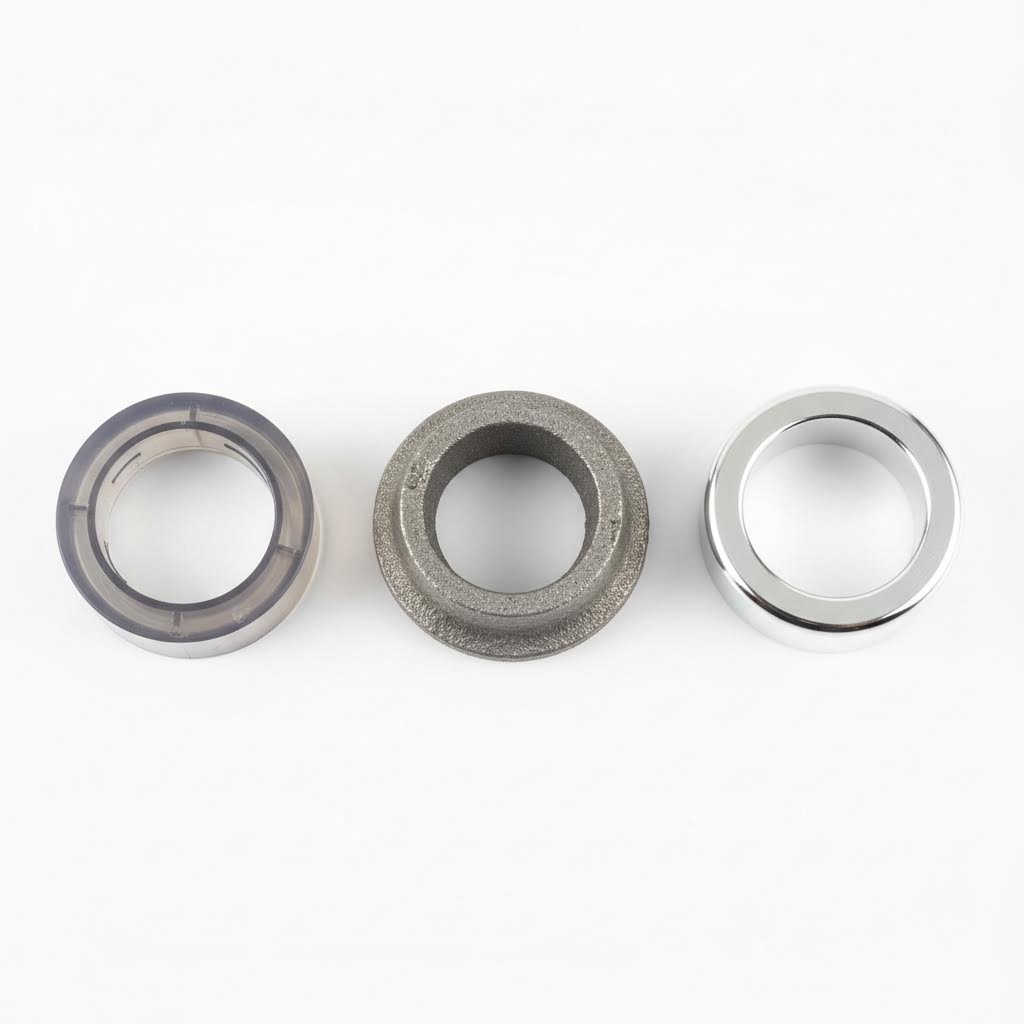

Forged vs Cast vs Plastic Hub Centric Ring Materials
Now that you understand why hub rings matter, the next question becomes: what should they be made of? Not all hubcentric rings are created equal. The material you choose directly impacts performance, longevity, and whether those rings will still function properly after thousands of heat cycles. Let's break down the three main construction methods and why the differences matter more than you might think.
Forged Metal vs Plastic Construction
Walk into any auto parts store, and you'll likely find plastic hub centric rings on the shelf. They're affordable, lightweight, and work fine for many daily drivers. But here's what the packaging won't tell you: plastic degrades under repeated heat cycling. Every time you brake hard or drive aggressively, your brakes generate significant heat that transfers through the hub assembly. Over time, this thermal stress causes plastic rings to warp, crack, or become brittle.
For commuter vehicles that rarely see spirited driving, plastic hub centric rings represent a budget-friendly solution. However, if you track your car, tow frequently, or simply want components that last the lifetime of your wheels, metal construction becomes essential.
Aluminum hub centric rings offer a substantial upgrade. They handle heat far better than plastic and provide the rigidity needed for precise wheel centering. But even among metal rings, manufacturing method matters enormously. Cast aluminum rings are poured into molds as molten metal, creating parts that work adequately but contain microscopic inconsistencies in their internal structure. These inconsistencies can become stress points under load.
How Forging Creates Superior Ring Strength
Forged hub rings represent the pinnacle of hub centric ring engineering. During the forging process, solid metal billets are compressed under extreme pressure while heated. According to Southwest Steel Processing, this heating and deformation process refines the internal grain structure of the metal by allowing metallurgical recrystallization to occur, resulting in a more uniform structure throughout the metal form.
Imagine the difference between a block of compressed wood fiber and a solid piece of oak. That's essentially what separates forged from cast components. The aligned grain structure in forged aluminum creates a concentric ring with superior strength-to-weight characteristics. This matters because hub rings experience constant dynamic loading—they're squeezed between your hub and wheel while supporting thousands of pounds of vehicle weight through every corner, pothole, and brake application.
The benefits extend beyond raw strength. Forged metal parts are known for their high resistance to fatigue and cracking, which becomes critical in components that must perform reliably over years of service. A concentric ring that cracks or deforms defeats its entire purpose, leaving you back where you started—with vibration and improper load distribution.
Forging also enables tighter dimensional tolerances than casting. When molten metal cools in a cast mold, slight shrinkage and surface imperfections are inevitable. Forged components, shaped while solid, can achieve precision measurements within fractions of a millimeter. For hub rings, where the difference between a perfect fit and a sloppy one might be 0.1mm, this precision matters tremendously.
| Material Type | Heat Resistance | Durability | Precision Tolerance | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic (Polycarbonate/Nylon) | Low - degrades with thermal cycling | Moderate - 2-5 year lifespan typical | ±0.2mm typical | Daily commuters, light-duty use |
| Cast Aluminum | High - handles brake heat well | Good - potential stress points from porosity | ±0.1mm typical | Street performance, occasional spirited driving |
| Forged Aluminum | Excellent - uniform heat dissipation | Superior - aligned grain resists fatigue | ±0.05mm achievable | Track use, motorsport, heavy-duty applications |
The choice ultimately depends on your application. Plastic works for budget-conscious builds on vehicles that live their lives in stop-and-go traffic. Cast aluminum suits enthusiasts who want metal durability without the premium price. But when you're pushing performance limits—whether on a racetrack or hauling heavy loads—forged aluminum hubcentric rings deliver the heat resistance, dimensional precision, and long-term reliability that demanding applications require.
Understanding materials is only half the equation, though. Even the best-engineered ring won't help if it's the wrong size. Getting accurate measurements is the next critical step in eliminating that highway vibration for good.
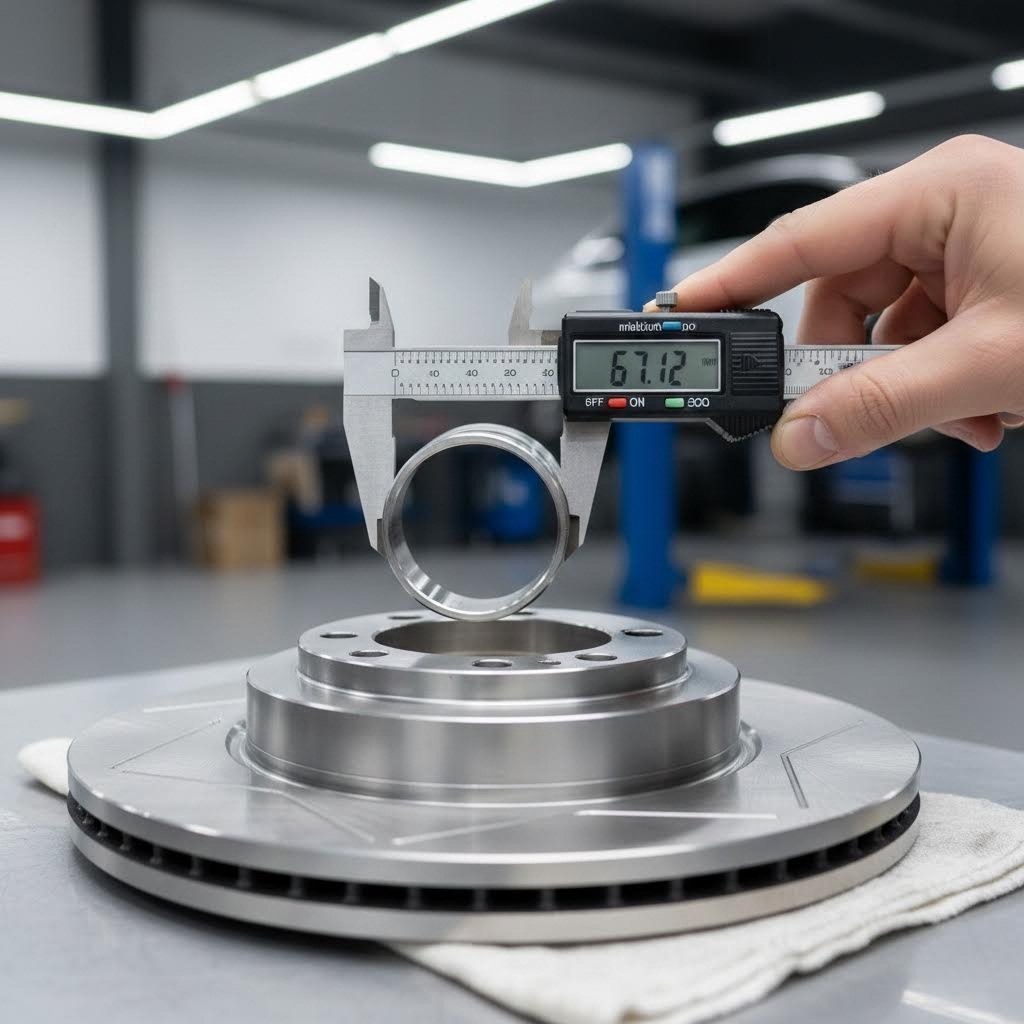

How to Measure Hub Centric Ring Sizes for Perfect Fitment
You've selected the right material for your hub centric rings. Now comes the step that separates a vibration-free ride from a frustrating one: getting your measurements exactly right. The relationship between your vehicle's hub bore and your wheel's center bore determines what size centering ring you need. Get it wrong by even a millimeter, and you're back to square one with that annoying highway shimmy.
Here's the good news: measuring hub centric rings sizes doesn't require specialized equipment or professional training. With a basic caliper and some attention to detail, you can nail these dimensions at home. Let's walk through exactly how to measure hub centric rings so you order the perfect fit the first time.
Measuring Your Vehicle Hub Bore Accurately
Your vehicle's hub bore is the cylindrical surface where your wheel mounts—that raised center portion of your brake rotor or hub assembly. This measurement becomes the inner diameter of your centering ring, so precision matters here.
Before you grab any measuring tools, preparation is critical. Debris, rust, and brake dust accumulate on hub surfaces and can throw off your readings by tenths of a millimeter. That might not sound like much, but it's enough to create a loose fit that defeats the purpose of using a center ring in the first place.
- Clean the hub surface thoroughly. Use a wire brush or Scotch-Brite pad to remove any rust, corrosion, or built-up brake dust from the outer cylindrical surface of the hub. Wipe it down with a clean rag afterward.
- Zero your caliper. Before measuring, close your caliper completely and verify it reads exactly 0.00mm. If using a digital caliper, ensure the battery is fresh for accurate readings.
- Position the caliper correctly. Use the outside jaws of your caliper (the larger jaws designed for external measurements). Place them around the outer diameter of the hub's cylindrical surface—not the mounting face, but the raised portion the wheel slides over.
- Take multiple readings. Rotate the caliper 90 degrees and measure again. Hubs can wear slightly oval over time, so averaging two perpendicular measurements gives you the most accurate hub bore size.
- Record the measurement in millimeters. Hub bore dimensions are universally expressed in millimeters. Common sizes vary significantly by manufacturer—for example, many BMW models use 72.6mm, while Hondas often measure 64.1mm, and Ford trucks can run 87.1mm or larger.
One critical pitfall to avoid: don't confuse the wheel hub bore with your bolt pattern measurement. Your bolt pattern (like 5x114.3) describes the diameter of the circle formed by your lug studs. The hub bore is a completely separate dimension—the physical diameter of the hub itself. These two measurements serve different purposes and aren't interchangeable.
Finding Your Wheel Center Bore Dimension
The wheel center bore is the hole on the backside of your wheel that slides over the vehicle's hub. According to Next Level Motoring's measurement guide, this dimension is usually measured in millimeters and is sometimes referred to as spigot size in certain countries. This becomes the outer diameter of your hub ring—the part that contacts your wheel.
The easiest way to find this measurement? Check your wheel manufacturer's specifications first. Most reputable wheel vendors list center bore prominently in their product descriptions, and some even print it directly on the wheel box. However, if you're working with secondhand wheels or can't locate the specs, measuring is straightforward.
- Set the wheel face-down on a protected surface. Place a towel or cardboard beneath the wheel face to prevent scratching the lip or finish.
- Locate the center bore hole. You're looking at the back of the wheel now—the large hole in the center where the hub passes through. As noted by Apex Wheels, be sure to measure the true centerbore depth, not just the chamfered portion that extends for the first 3-5mm into the hole.
- Use the inside measuring jaws of your caliper. Most calipers have smaller probes on top designed specifically for internal diameter measurements. Spread these probes outward across the center of the hole.
- Measure at the widest point. Ensure the caliper probes contact opposite sides of the bore at its true diameter. Avoid the beveled entry edge—measure where the bore reaches its full, consistent diameter.
- Record this measurement. This becomes the outer diameter (OD) of the hub ring you need. Common aftermarket wheel center bores include 73.1mm (a near-universal standard), 67.1mm, and 72.6mm, though many specialty sizes exist.
Now you have both critical dimensions. The relationship is simple: your centering ring's outer diameter must match your wheel's center bore, and its inner diameter must match your vehicle's hub bore. For example, if your vehicle has a 64.1mm hub and your wheels have a 73.1mm center bore, you need rings sized 73.1mm OD x 64.1mm ID.
When ordering hub rings, remember: the inside diameter of your wheel's center bore becomes the outside diameter of your hub ring measurement.
Double-check both measurements before ordering. A ring that's too large won't seat properly, and one that's too small won't slide onto the hub. With accurate dimensions in hand, you're ready to determine whether your specific wheel setup actually requires hub centric rings—and that's exactly what we'll cover next.
Do You Need Hub Centric Rings for Your Wheel Setup
You've got your measurements. You understand the materials. But here's the question that really matters: do you need hub centric rings for your specific situation? The answer depends entirely on your wheel setup, and getting it wrong means either wasting money on unnecessary parts or suffering through vibrations you could have prevented.
Let's cut through the confusion with a clear decision framework. Understanding when hub centering rings are essential versus optional will save you headaches—and possibly save your lug studs from premature failure.
Aftermarket Wheels Almost Always Need Rings
Here's the reality most wheel shoppers don't realize until after installation: OEM wheels are typically hub centric by design. When automakers engineer your vehicle, they match the wheel's center bore precisely to the hub diameter. That perfect fit means factory wheels sit centered mechanically, with the hub doing the heavy lifting while lug nuts simply secure everything in place.
Aftermarket wheels tell a different story. According to ECS Tuning's wheel fitment guide, aftermarket wheels are typically designed to fit as many cars as possible unless they are custom-made for your specific application. Manufacturers intentionally machine oversized center bores so one wheel model can accommodate dozens of different vehicles. Smart business strategy—but it creates a gap problem you need to solve.
So what are hub rings doing in this scenario? They're transforming a universal-fit wheel into one that behaves like factory equipment. When you install hub centric rings for aftermarket wheels, you're essentially custom-adapting those wheels to your specific vehicle's hub diameter.
Do you need hub centric rings if you're running aftermarket wheels? In nearly every case, yes. The only exception would be wheels specifically machined for your exact vehicle—and those are rare outside of OEM replacement parts or truly custom wheel orders.
The Lug Nut Myth Debunked
Here's a myth that refuses to die: "If you torque your lug nuts properly, you don't need hub centering ring solutions." This sounds logical on the surface. After all, lug nuts are designed to secure wheels, right?
The problem is physics doesn't care about logic. When you rely solely on lug nuts to center a wheel with an oversized bore, you're asking five or six small contact points to do what an entire hub face should handle. Even with perfect torque specs, the wheel isn't mechanically centered—it's just clamped in place. As ECS Tuning explains, when the hub is smaller than the center bore on the wheel, the wheel will not be technically centered, causing vibration that feels like a wheel imbalance.
The vibration harmonics make this worse at speed. A wheel that's off-center by half a millimeter might feel fine around town. But vibration amplitude increases exponentially with rotational speed. By the time you hit 60-70 mph, that tiny imbalance becomes a steering wheel shimmy you can't ignore. Many drivers chase this problem with repeated tire balancing, never realizing the root cause is improper centering—not weight distribution.
Beyond comfort, there's a safety consideration. Lug-centric mounting concentrates stress on the studs rather than distributing load across the hub face. Over time, this accelerates wear on components that should last the life of your vehicle.
Use this framework to determine whether you need hub centric rings for your setup:
-
Hub centering rings are essential when:
- Installing any aftermarket wheels with a larger center bore than your hub diameter
- Adding wheel spacers that change the effective mounting surface
- Swapping wheels between different vehicles (cross-vehicle fitment)
- Using universal-fit wheels designed for multiple bolt patterns or hub sizes
- Experiencing unexplained vibration after ruling out tire balance issues
-
Hub centering rings may be optional when:
- Running OEM wheels designed specifically for your vehicle
- Using aftermarket wheels custom-machined to your exact hub bore
- Installing wheels with a center bore that already matches your hub within 0.1mm
When in doubt, measure. If there's any gap between your hub and wheel center bore—even a small one—a hub centering ring eliminates variables and ensures proper fitment. The cost of a quality ring set is minimal compared to chasing phantom vibrations or replacing worn lug studs down the road.
For most enthusiasts running aftermarket wheels, the question isn't really "do I need hub centric rings?" It's "which hub centric rings will give me the best long-term performance?" And that's where custom forged solutions start to outshine generic off-the-shelf options.
Why Custom Forged Hub Centric Rings Outperform Generic Options
You've done everything right. You measured your hub bore precisely. You found the center bore specs for your wheels. But when you search for hub centric rings for wheels in that exact combination? Nothing. The standard sizes available simply don't match your specific requirements.
This frustrating scenario happens more often than you'd expect—and it's exactly why custom forged hub centering rings exist. When off-the-shelf solutions fall short, precision manufacturing bridges the gap between what's available and what your vehicle actually needs.
When Standard Sizes Fall Short
Walk through any auto parts retailer, and you'll find hub rings in common sizes: 73.1mm to 64.1mm for Hondas, 73.1mm to 72.6mm for BMWs, 73.1mm to 67.1mm for Nissans. These cover the majority of mainstream applications. But what happens when your setup doesn't fit the mold?
Consider these real-world scenarios where standard wheel centric rings simply won't work:
- Rare vehicle hub bore sizes: Classic cars, European imports, and specialty vehicles often use hub diameters that aftermarket ring manufacturers don't stock. A vintage Alfa Romeo with a 58.1mm hub or a heavy-duty truck with a 106mm bore won't find solutions on standard parts shelves.
- Specialty aftermarket wheels: High-end forged wheel manufacturers sometimes use non-standard center bore dimensions. When you've invested thousands in premium rims hub centric fitment becomes critical—yet generic rings may not accommodate unusual bore specifications.
- Motorsport applications: Racing teams can't afford vibration at 150+ mph. They need centric rings for wheels machined to exact specifications, often with tolerances tighter than anything mass-produced components can deliver.
- Custom wheel spacer combinations: Adding spacers changes your effective hub diameter. The math might produce a ring dimension that simply doesn't exist as a catalog item.
According to Wheel-Size's comprehensive guide, if the ideal size proves elusive in retail outlets, specialized machinists can fabricate custom rings to meet your exact specifications. This isn't a workaround—it's often the only solution for non-standard applications.
Precision Tolerances in Custom Ring Manufacturing
Here's where custom forged rings truly separate themselves from generic alternatives: tolerances measured in fractions of a millimeter. When you're chasing down highway vibration, these microscopic differences matter enormously.
Standard mass-produced hub rings typically achieve tolerances around ±0.1mm to ±0.2mm. That sounds precise until you understand the physics. A hub centric ring that's 0.2mm undersized creates play. That play allows micro-movement under load. And micro-movement at 70 mph translates directly into the vibration you're trying to eliminate.
Custom forged manufacturing can achieve tolerances of ±0.05mm or tighter. The forging process itself contributes to this precision—compressed metal with aligned grain structure machines more predictably than cast alternatives with internal porosity. When a skilled machinist works with forged aluminum blanks, they can hold dimensions that mass-production simply can't match economically.
For motorsport applications, this precision becomes non-negotiable. A wheel that's perfectly centered at parking lot speeds might develop harmonics at triple-digit velocities. Race teams specify custom hub centering rings not because they're chasing marginal gains, but because proper centering is fundamental to vehicle dynamics at the limit.
The difference between a vibration-free ride and an annoying shimmy often comes down to tenths of a millimeter in ring fitment.
Quality manufacturing standards provide another layer of assurance. The IATF 16949 certification—the automotive industry's quality management benchmark—ensures manufacturing consistency for components destined for vehicle applications. As ABS Quality Evaluations explains, IATF 16949 emphasizes developing a process-oriented quality management system for continual improvement, defect prevention and waste reduction for organizations that manufacture components, assemblies and parts for the automotive industry.
What does this mean practically? A certified manufacturer doesn't just produce one perfect ring—they maintain systems that ensure every ring meets specification. Batch-to-batch consistency, documented quality control processes, and traceable materials become standard practice rather than happy accidents.
For enthusiasts requiring custom dimensions or high-volume applications, working with established metal technology partners delivers peace of mind that generic suppliers can't match. Companies like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology—with IATF 16949 certification and precision hot forging capabilities—offer rapid prototyping for custom ring dimensions alongside the manufacturing consistency that automotive applications demand. Their in-house engineering can translate your specific hub and wheel measurements into production-ready components, often with prototyping turnaround measured in days rather than weeks.
The investment in custom forged solutions pays dividends in applications where standard sizes fall short. You're not just buying a ring—you're buying precision-engineered vibration elimination tailored exactly to your vehicle. With the right manufacturing partner and proper specifications in hand, even the most unusual hub bore and center bore combination becomes solvable.
Of course, even the most precisely manufactured hub centric ring won't perform if it's installed incorrectly. Getting the installation process right is just as critical as selecting the right components—and that's exactly what we'll cover next.
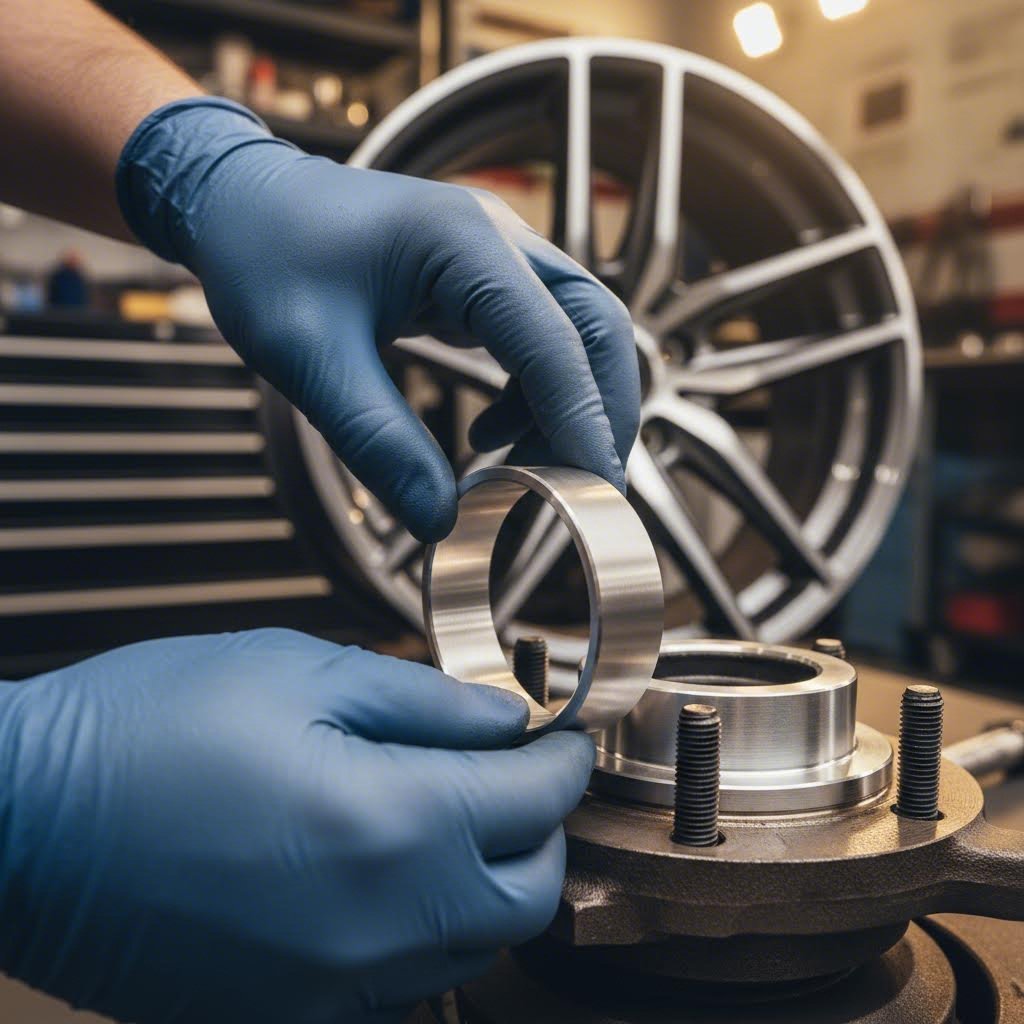

Installing Hub Centric Rings the Right Way
You've selected the perfect custom forged rings for your application. The measurements are spot-on, the material suits your driving style, and everything's ready to go. But here's where many enthusiasts stumble: installation seems simple enough that they rush through it—and end up right back where they started, chasing vibrations they thought they'd eliminated.
Proper installation of hub centric rings takes maybe ten extra minutes per wheel. Those ten minutes make the difference between a vibration-free highway cruise and another frustrating trip to the tire shop. Let's walk through exactly how to install hub centric rings so they perform as intended for years to come.
Preparing Your Hub Surface for Installation
Before your wheel centering ring touches anything, preparation determines success. According to Hub Centric Rings installation guide, you should clean the center bores of the rims and the wheel hubs of the car before proceeding with installation. This isn't optional maintenance—it's critical to proper fitment.
Think about what your hubs endure. Brake dust accumulates with every stop. Road salt attacks bare metal during winter months. Moisture promotes rust formation on steel hubs. All this contamination builds up on the very surface your hub ring needs to contact precisely. A ring that fits perfectly on a clean hub might not seat properly over a layer of corrosion and debris.
Here's your preparation checklist:
- Remove existing wheels safely. Use a floor jack to lift the vehicle, then support it with jack stands before removing lug nuts. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Inspect the hub surface. Look for rust scale, corrosion pitting, or accumulated brake dust on the cylindrical hub surface and the flat mounting face.
- Clean with appropriate tools. A wire brush or emery cloth works well for removing light rust and debris. For heavier corrosion, a Scotch-Brite pad or fine sandpaper removes buildup without damaging the hub surface.
- Wipe completely clean. Use a lint-free rag to remove all loose particles. Any debris left behind creates a gap that defeats the purpose of precision fitment.
- Clean the wheel center bore. Don't forget the other half of the equation. Your wheel's center bore accumulates the same contamination and needs the same attention.
One often-overlooked detail: if your aluminum hub ring will contact a steel hub (common on many vehicles), applying anti-seize compound prevents galvanic corrosion. As Monroe Aerospace explains, aluminum anti-seize offers low electrical conductivity and protection from galvanic corrosion, making it ideal for applications involving non-aluminum fasteners and components. A thin coating on the hub surface before ring installation prevents the aluminum ring from bonding to the steel hub over time—a real problem that makes future removal difficult.
Proper Torque Sequence After Ring Placement
With clean surfaces prepared, the actual installation follows a specific sequence. Rushing or skipping steps here undermines everything you've done to select the right components.
- Position the hub ring on the hub. Slide the ring onto the hub's cylindrical surface. It should fit snugly but not require force. If you're fighting to get it on, either the ring is wrong-sized or debris remains on the hub.
- Verify the ring seats flush. The hub ring must sit completely against the hub face with no gaps. A ring that's cocked or partially seated won't center your wheel properly. Push it firmly until you feel it bottom out.
- Align and mount the wheel. Lift the wheel onto the hub, guiding it so the center bore slides over the ring. The wheel should slip on smoothly—the ring is now doing its job of centering the assembly.
- Hand-thread all lug nuts first. Before reaching for your impact wrench, thread each lug nut on by hand until finger-tight. This ensures the threads engage properly and the wheel seats evenly against the hub face.
- Snug in a star pattern. Using a hand wrench, snug each lug nut following a star or cross pattern—not a circular sequence. This draws the wheel evenly against the hub without cocking it to one side.
- Final torque to specification. With the vehicle lowered and weight on the wheels, torque each lug nut to your vehicle's specification using a calibrated torque wrench. Follow the same star pattern, making two passes to ensure consistent clamping force.
Always re-torque lug nuts after 50-100 miles of driving. New installations and seasonal wheel swaps require this critical follow-up step.
What about removal? For tire rotations or seasonal wheel swaps, the process reverses simply. The hub ring typically stays attached to the wheel's center bore after removal—it friction-fits there during installation. When you reinstall, verify the ring is still properly seated in the wheel before mounting. Rings can occasionally fall out during handling, so a quick visual check prevents mounting a wheel without its centering component.
For aluminum rings that have been in service for extended periods, that anti-seize application pays dividends at removal time. Without it, aluminum can oxidize against steel, creating a bond that requires significant force to break. The compound creates a barrier that keeps the ring serviceable for easy future removal.
Installing hub centric rings properly isn't complicated, but it does require attention to detail. Clean surfaces, proper seating, and correct torque sequence ensure your precision-machined rings deliver the vibration-free performance they're designed to provide. With your wheels properly installed, there's one more configuration worth understanding: how hub rings interact with wheel spacers—a combination that requires some additional considerations.
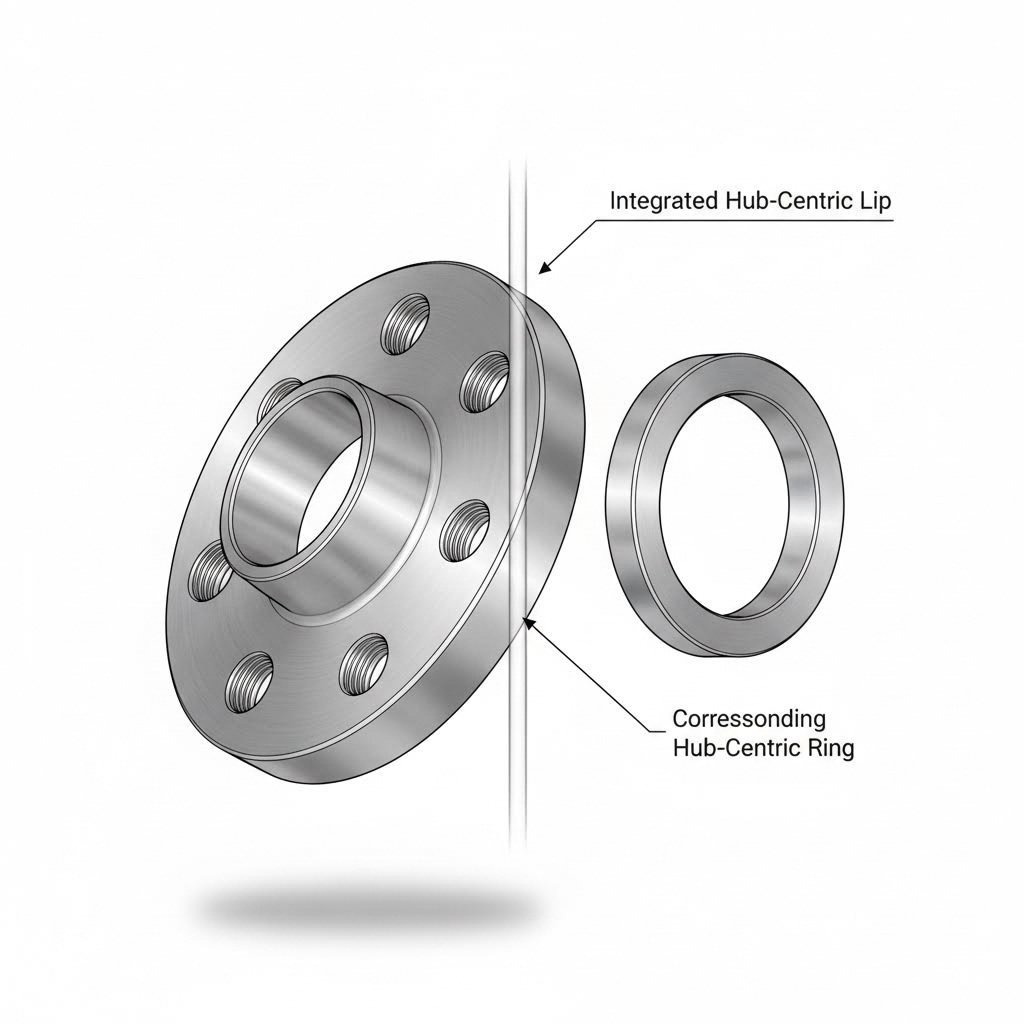
Hub Centric Rings and Wheel Spacers Working Together
You've installed your hub centric rings perfectly. Your wheels are centered, the vibration is gone, and highway driving feels smooth again. Then a new idea enters your mind: wheel spacers. Maybe you want a more aggressive stance, better brake caliper clearance, or improved handling geometry. But here's what nobody explains when selling you those spacers—they fundamentally change your hub ring requirements.
Understanding how hub centric spacers interact with centering rings prevents the frustrating scenario of installing spacers only to discover your carefully selected rings no longer work. Let's break down this relationship so you can plan your setup correctly from the start.
How Spacers Change Your Ring Requirements
When you bolt a wheel spacer between your hub and wheel, you're creating a new mounting surface. This changes everything about your hub ring calculation. According to D-Motus wheel specialists, hub centric wheel spacers replicate the hub centric mounting of the vehicle's original wheels, ensuring that the additional space created between the wheel and the hub assembly doesn't compromise the integrity of the wheel connection.
Think about what physically happens. Your original hub bore—the measurement you carefully took earlier—no longer directly contacts your wheel. The spacer sits in between. Now your wheel's center bore needs to mate with the spacer's outer surface, not your vehicle's hub. This creates two potential centering points instead of one:
- Spacer to hub interface: The spacer's center hole must fit precisely over your vehicle's hub bore
- Wheel to spacer interface: Your wheel's center bore must fit precisely over the spacer's hub-centric lip
Here's where confusion enters. A hub bore adapter or center bore adapter style spacer might have a different outer diameter than your original hub. If you purchased hub rings sized for your original hub-to-wheel combination, they likely won't work with spacers in the equation. The math simply changes.
For example, imagine your vehicle has a 64.1mm hub bore and your aftermarket wheels have a 73.1mm center bore. Without spacers, you need 73.1mm to 64.1mm hub rings. But install a quality hub centric spacer with a 67.1mm outer lip, and suddenly your wheel needs to center on that 67.1mm surface—requiring completely different rings.
Hub Centric Spacers vs Separate Ring Solutions
The good news? Quality wheel spacer hub rings solutions come in two main configurations, each with distinct advantages depending on your application.
Integrated hub centric spacers feature built-in centering lips machined directly into the spacer body. As BONOSS explains, hub-centric spacers are centered on the hub bore, ensuring perfect fitment. The spacer itself handles both centering duties—it fits your vehicle's hub precisely while providing a machined lip for your wheel to center on. For most enthusiasts, this represents the cleanest solution.
However, integrated designs have limitations. The spacer's hub-centric lip typically comes in a single diameter. If that diameter doesn't match common wheel center bores, you might still need a wheel hub spacer ring to bridge the gap. This is especially common with universal-fit aftermarket wheels designed for multiple applications.
Separate ring solutions offer more flexibility but add complexity. With this approach, you use one ring between the hub and spacer (if needed), and another ring between the spacer and wheel. This stacking approach accommodates unusual combinations but requires precise measurement of multiple interfaces.
| Factor | Hub Centric Spacers (Integrated) | Spacer + Separate Ring Combination |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower if standard ring sizes work |
| Convenience | Single component handles centering | Multiple parts to track and install |
| Precision | Excellent—machined as one unit | Good—depends on ring quality |
| Flexibility | Limited to spacer's fixed lip diameter | Accommodates unusual size combinations |
| Best For | Common wheel/hub combinations | Rare sizes, custom wheel setups |
What about bolt pattern adapters? These present additional considerations. A wheel spacer hub centric ring setup becomes more complex when you're also changing bolt patterns—say, adapting 5x100 wheels to fit a 5x114.3 vehicle. In these cases, the adapter must handle both the bolt pattern conversion and hub centering simultaneously. Quality adapters include machined hub-centric features on both sides, but you'll want to verify the outer lip matches your wheel's center bore before purchasing.
When planning any spacer installation, measure the spacer's hub-centric lip diameter before ordering rings. Don't assume your existing rings will work. And for applications thicker than 15mm, D-Motus recommends bolt-on hub centric spacers that attach to your vehicle's studs while providing their own studs for wheel mounting. These bolt-on designs offer the most secure connection for aggressive stance setups.
The bottom line? Wheel spacers don't eliminate the need for proper centering—they change how you achieve it. Whether you choose integrated hub centric spacers or a combination approach with separate rings, ensuring precise fitment at every interface keeps your wheels vibration-free and your studs stress-free. With your spacer and ring combination sorted, the final step is selecting components that match your specific driving demands.
Choosing the Right Hub Centric Rings for Your Application
You've absorbed a lot of information—materials, measurements, installation techniques, spacer considerations. Now comes the moment of truth: making a purchasing decision that actually solves your vibration problem. Where can I buy hub centric rings that match my specific needs? The answer depends on understanding what separates a smart purchase from a frustrating one.
Let's synthesize everything into actionable selection criteria. Whether you're building a weekend track car or simply want smooth highway commutes, these decision factors will guide you toward hub center rings that perform exactly as intended.
Matching Ring Material to Your Driving Style
Your application dictates your material choice—not the other way around. Making the wrong call here means either overspending on components you don't need or watching inadequate rings fail when conditions get demanding.
For daily drivers that rarely see spirited driving, quality plastic aftermarket wheel hub rings represent a sensible choice. They're budget-friendly, resist corrosion in salt-heavy winter climates, and won't seize to steel hubs over time. If your vehicle lives its life in stop-and-go traffic with occasional highway cruising, plastic delivers adequate performance without unnecessary expense.
However, the calculus changes entirely for performance applications. Track days generate sustained braking heat that plastic simply cannot survive. Aggressive canyon driving, towing heavy loads, or any situation involving repeated hard braking demands metal construction. Forged aluminum hub rings for rims in these applications aren't a luxury—they're a requirement.
Consider your honest driving habits:
- Commuter/daily driver: Quality polycarbonate or nylon rings offer 2-5 years of reliable service at minimal cost
- Enthusiast street driving: Cast aluminum provides heat resistance for occasional spirited runs
- Track use/autocross: Forged aluminum handles sustained thermal cycling without degradation
- Heavy-duty/towing: Forged construction resists the constant stress of high-load applications
- Motorsport competition: Precision-forged rings with tight tolerances eliminate variables at the limit
Hub centric wheels perform their best when every component in the system matches the application's demands. Mixing budget components with performance driving creates weak links that eventually fail—usually at the worst possible moment.
Finding a Reliable Manufacturing Partner
Material selection matters, but so does where to buy hub centric rings. The manufacturer behind your components determines whether those precision tolerances actually exist or merely appear in marketing copy. Not all hub rings for aftermarket wheels deliver the dimensional accuracy they claim.
When evaluating sources, prioritize these criteria:
- Automotive quality certifications: Look for IATF 16949 certification—the automotive industry's quality management standard. According to Carbo Forge's automotive manufacturing page, IATF 16949 certified facilities utilize world-class operating efficiencies with consistency in quality, production, and on-time deliveries. This certification indicates systematic quality control rather than occasional inspection.
- Precision manufacturing capabilities: Suppliers should specify achievable tolerances. Generic claims of "precision fit" mean nothing without numbers. Quality manufacturers publish tolerance specifications—typically ±0.05mm for forged components.
- Material traceability: Reputable manufacturers document material sources and maintain batch records. This matters if you ever need to verify component specifications or address quality concerns.
- Custom dimension capabilities: If standard sizes don't match your hub bore and wheel center bore combination, you need a manufacturer capable of producing custom specifications—not a reseller limited to catalog items.
For enthusiasts requiring custom dimensions or high-volume applications, working with established metal technology partners offers advantages that generic suppliers cannot match. Companies like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology combine IATF 16949 certification with precision hot forging capabilities and in-house engineering. Their rapid prototyping—available in as little as 10 days—means custom ring dimensions don't require months of waiting. When your hub bore and wheel combination falls outside standard specifications, this manufacturing flexibility becomes invaluable.
The measurement accuracy you achieved earlier means nothing if your rings aren't manufactured to match. A supplier claiming 73.1mm to 64.1mm dimensions that actually delivers 73.0mm to 64.3mm has given you a loose, vibration-prone fit despite your careful preparation.
The cheapest hub centric rings often cost more in the long run when you factor in replacement parts, repeated tire balancing, and the time spent chasing vibrations that proper components would have prevented.
Before finalizing any purchase, verify the manufacturer's specifications match your measurements exactly. Confirm material composition—especially for metal rings where "aluminum" could mean cast or forged. And for non-standard applications, confirm custom manufacturing capabilities before assuming standard catalog sizes will work.
Your hub rings for rims represent a small investment compared to your wheels, tires, and the vehicle itself. Selecting quality components from certified manufacturers ensures that investment delivers years of vibration-free driving rather than recurring frustration. With the right hub centric rings properly installed, that highway shimmy becomes a solved problem—and you can finally enjoy those aftermarket wheels the way they were meant to perform.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hub Centric Rings
1. Are hub centric rings legal?
Yes, hub centric rings are completely legal and represent the proper method for fitting aftermarket wheels to vehicle hubs. They ensure the hub carries the vehicle's load rather than concentrating stress on lug studs. Using hub centric rings is actually the recommended approach for any aftermarket wheel installation where the wheel's center bore exceeds the vehicle's hub diameter.
2. Are custom wheels hub-centric?
Most aftermarket wheels are not hub-centric by design. Manufacturers intentionally machine oversized center bores so one wheel model can fit multiple vehicles with different hub sizes. This universal-fit approach means you'll typically need hub centric rings to bridge the gap between your wheel's center bore and your vehicle's specific hub diameter for proper centering and vibration-free performance.
3. How exact do hub centric rings need to be?
Hub centric rings require precise sizing—the ring's outer diameter must match your wheel's center bore exactly, while the inner diameter must match your vehicle's hub bore. Quality forged rings achieve tolerances of ±0.05mm, while standard rings typically offer ±0.1-0.2mm. Even 0.2mm variance can cause vibration at highway speeds, making accurate measurement critical before purchasing.
4. Do I need hub centric rings if my lug nuts are properly torqued?
Yes, properly torqued lug nuts don't eliminate the need for hub centric rings. When wheels have oversized center bores, lug nuts only clamp the wheel in place without mechanically centering it. This creates micro-movements under dynamic loads that amplify into noticeable vibration at highway speeds. Hub centric rings provide true mechanical centering that lug tension alone cannot achieve.
5. What's the difference between forged and plastic hub centric rings?
Forged aluminum rings offer superior heat resistance, tighter tolerances (±0.05mm), and exceptional durability for performance applications. Plastic rings work adequately for daily commuters but degrade under repeated heat cycling from aggressive braking. For track use, towing, or spirited driving, forged rings from IATF 16949 certified manufacturers like Shaoyi Metal Technology provide the precision and longevity demanding applications require.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 

