Custom Forged Lug Nuts Benefits That Keep Your Wheels From Failing
Understanding Custom Forged Lug Nuts and Why They Matter
Every time you accelerate, brake, or navigate a sharp corner, your wheels experience tremendous forces. What keeps them securely attached to your vehicle? Those small but mighty fasteners called lug nuts. While most drivers never give them a second thought, wheel hardware represents the critical connection between your vehicle and the road beneath it. When this connection fails, the consequences range from inconvenient to catastrophic.
Custom forged lug nuts represent the gold standard in wheel fastening technology. Unlike cast alternatives that are poured into molds or machined versions cut from bar stock, forged lug nuts undergo an intensive manufacturing process that fundamentally transforms the metal's internal structure. This distinction matters whether you're commuting daily, pushing real street performance limits on weekend drives, or tracking your vehicle competitively.
The Forging Difference Explained
Imagine taking a piece of metal and compressing it under extreme pressure—sometimes exceeding 2,000 tons of force. This process doesn't simply shape the material; it fundamentally reorganizes its molecular architecture. During forging, metal is heated and then compressed, forcing its grain structure to align in continuous, unbroken patterns that follow the component's contours.
Cast lug nuts, by comparison, begin as liquid metal poured into molds. While this method allows for complex shapes and lower production costs, it creates random grain structures with potential internal voids and weak points. Machined lug nuts start as solid bar stock and offer decent strength, but the cutting process actually interrupts the natural grain flow, creating potential stress points.
Think of it like wood grain. When you cut across the grain, the material weakens significantly. Forging is like working with the grain, preserving and enhancing natural strength pathways. Whether you're considering solid lug nuts for durability, titanium lug nuts for weight savings, or tuner lug nuts for aftermarket wheel compatibility, understanding this manufacturing difference helps you make informed decisions.
Why Grain Structure Matters for Wheel Hardware
According to forging experts at Queen City Forging, the aligned grain structure in forged components eliminates internal defects like porosity while creating uniform density throughout the material. This translates directly to superior fatigue resistance—crucial when your lug nuts endure thousands of stress cycles from acceleration, braking, and cornering forces.
The forging process also enables work hardening, where controlled deformation increases dislocation density within the metal's crystal structure. This makes the finished component harder and more resistant to deformation under load. For performance enthusiasts who regularly push their vehicles—or those who've upgraded components like a blow off valve for increased boost pressure—this metallurgical advantage provides measurable peace of mind.
Throughout this guide, you'll find objective, manufacturer-neutral information covering everything from material selection and compatibility requirements to proper installation techniques. Whether you're upgrading for safety, performance, or aesthetics, understanding custom forged lug nuts benefits empowers you to make the right choice for your specific application.
Strength and Durability Advantages of Forged Construction
You've heard that forged lug nuts are stronger than cast alternatives—but what does that actually mean for your wheels staying attached at highway speeds? The answer lies in metallurgical science that many competitors mention but rarely explain. When you understand why forging creates superior hardware, you'll recognize why investing in good lug nuts becomes a safety decision, not just an upgrade.
The forging process eliminates internal voids and porosity that plague cast components. According to industry research comparing forged versus cast components, forged parts typically deliver around 26% higher tensile strength and approximately 37% higher fatigue strength than their cast counterparts. These aren't marginal improvements—they represent fundamentally different performance capabilities under stress.
Why such dramatic differences? Cast metal solidifies with random grain orientation, creating microscopic weak points where cracks can initiate. Forging compresses and aligns these grains into continuous flow patterns, effectively closing internal gaps while creating uniform density throughout the component. The best lug nuts for aftermarket wheels leverage this structural advantage to handle the increased stress that performance driving demands.
Superior Fatigue Resistance Under Stress
Every time you accelerate, brake, or corner aggressively, your lug nuts experience repeated stress cycles. This cyclical loading doesn't cause immediate failure—instead, it gradually accumulates damage through a process called metal fatigue. Here's where forged construction truly shines.
Research published in Metals journal examined fatigue characteristics between forged and non-forged aluminum alloys. The findings were striking: forged specimens exhibited significantly longer fatigue life with far less scatter in test results. More importantly, the forging process elevated fatigue strength while reducing variability—meaning forged components perform consistently rather than unpredictably.
What causes this fatigue advantage? The study revealed that non-forged materials contained larger internal inclusions and defects that acted as crack initiation sites. Under repeated loading, cracks propagate from these weak points. Forged materials showed smaller maximum inclusion sizes (13 μm versus 21 μm at equivalent confidence levels), dramatically reducing failure risk during high-cycle stress conditions.
Consider what your lug nuts endure during typical driving:
- Acceleration forces that push against thread engagement
- Braking loads transferring through the wheel hub assembly
- Cornering stress creating lateral forces on wheel mounting surfaces
- Vibration exposure from road imperfections and brake bearing noise at various frequencies
- Thermal cycling from brake heat conducted through the hub
A titanium lug nut or quality chromoly option handles these repeated stresses through its aligned grain structure, while cast alternatives accumulate fatigue damage more rapidly at internal weak points.
Consistent Clamping Force Over Time
Maintaining proper wheel clamping force isn't a one-time achievement—it's an ongoing requirement throughout your lug nuts' service life. Forged construction delivers measurable advantages in clamping force retention that directly impact safety.
When you torque a lug nut to specification, you're essentially stretching it slightly to create the clamping force that holds your wheel securely. Over time, several factors work against this clamping force:
- Thermal expansion and contraction from heat cycling
- Vibration-induced settling of mating surfaces
- Stress relaxation within the fastener material
- Thread wear from repeated installation and removal
Forged lug nuts resist these degradation mechanisms more effectively because their dense, void-free structure maintains dimensional stability under thermal stress. The aligned grain structure also provides superior thread integrity, maintaining precise engagement even after numerous wheel changes.
The research data supports this real-world observation: forged components showed more consistent fatigue characteristics with less performance scatter. This consistency translates to predictable clamping behavior—you'll know your wheels remain properly secured rather than wondering whether your hardware is gradually losing its grip.
For daily drivers, this means fewer re-torque requirements and greater confidence during seasonal tire changes. For performance enthusiasts pushing their vehicles through aggressive driving, track days, or spirited backroad sessions, consistent clamping force prevents the gradual loosening that can precede catastrophic wheel separation.
Understanding these metallurgical foundations helps explain why quality forged hardware commands premium pricing. You're not simply paying for a brand name or aesthetic finish—you're investing in fundamental material properties that directly influence whether your wheels stay attached through thousands of miles of real-world stress. With this strength foundation established, let's examine how different materials affect these performance characteristics.
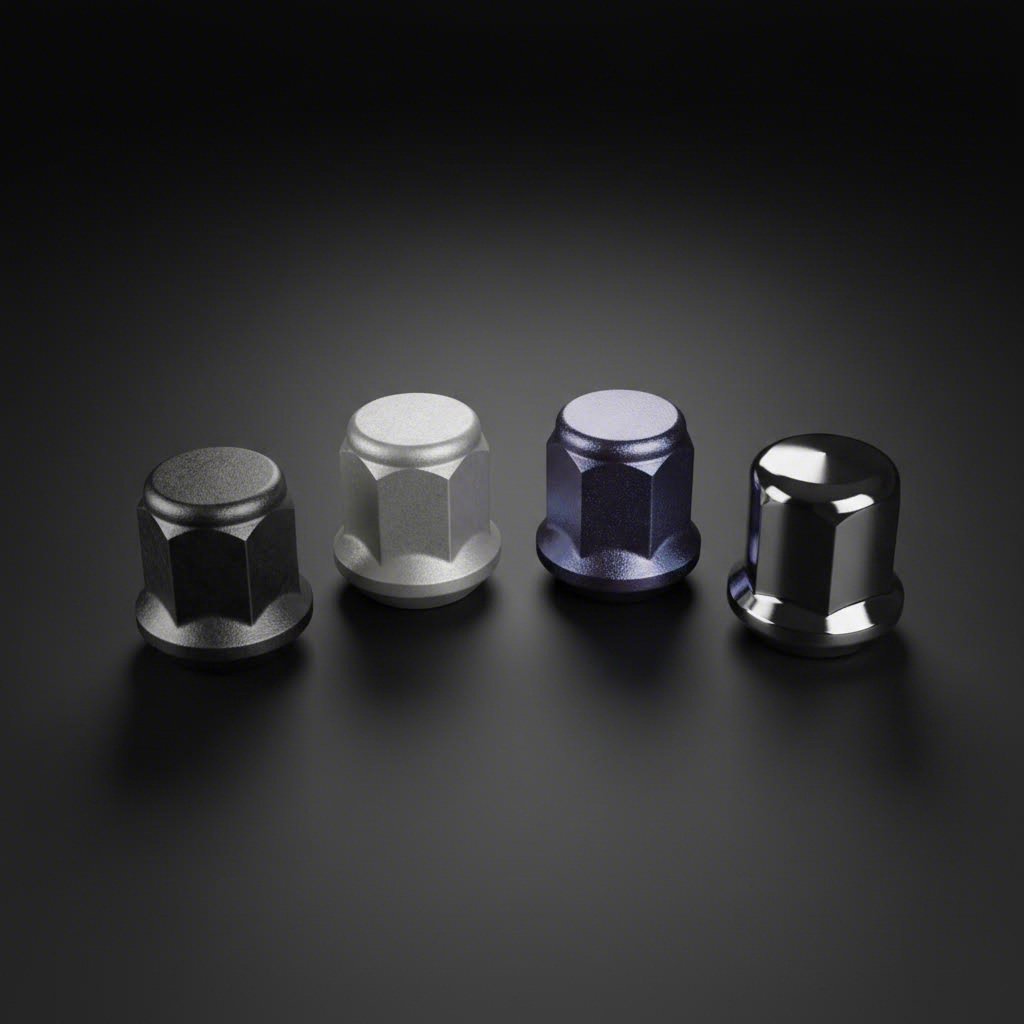

Complete Material Comparison for Forged Lug Nuts
Now that you understand why forging creates superior strength, the next question becomes: which material delivers the best performance for your specific needs? When shopping for lug nuts for aftermarket wheels, you'll encounter four primary options—each with distinct characteristics that make them ideal for different applications. Let's decode what those material specifications actually mean.
Sounds complex? It doesn't have to be. Think of material selection like choosing tires: a track-focused compound works brilliantly on dry pavement but struggles in wet conditions. Similarly, each lug nut material excels in specific scenarios while presenting trade-offs in others. Understanding these distinctions prevents expensive mistakes and ensures your wheel hardware matches your driving demands.
Material Grade Specifications Decoded
When you see designations like "4140 chromoly" or "7075-T6 aluminum," these aren't marketing terms—they're precise material specifications that define performance characteristics. Here's what these grades actually tell you:
4140 Chromoly Steel: This designation indicates a chromium-molybdenum alloy steel with specific percentages of carbon (0.40%) and alloying elements. The chromium enhances hardness and wear resistance, while molybdenum improves strength at elevated temperatures. This material delivers exceptional strength-to-weight balance for performance applications, making it a popular choice among enthusiasts who want durability without excessive mass.
7075-T6 Aluminum: The "7075" refers to an aluminum alloy containing zinc as the primary alloying element, creating one of the strongest aluminum formulations available. The "T6" indicates the tempering process—solution heat-treated and artificially aged—which maximizes strength. While impressively light, this material requires careful consideration for high-heat applications.
Grade 5 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V): This aerospace-grade titanium nut specification indicates an alloy containing 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. According to Tire Hardware's titanium comparison research, Grade 5 titanium delivers tensile strength of 950 MPa—significantly exceeding standard steel bolts at 800 MPa—while weighing 50% less. Premium options like Hyperion titanium fasteners leverage this grade for maximum performance.
Stainless Steel (304 or 316): These grades indicate chromium-nickel alloys optimized for corrosion resistance. Grade 316 adds molybdenum for enhanced protection against chlorides (road salt), making it ideal for harsh weather environments. However, stainless typically offers lower strength than chromoly for equivalent weight.
Matching Material to Your Application
Choosing the right material depends on prioritizing what matters most for your driving conditions. The following comparison breaks down key performance characteristics across all four materials:
| Material | Tensile Strength | Weight | Corrosion Resistance | Heat Tolerance | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4140 Chromoly Steel | Very High (850-1000 MPa) | Heaviest | Moderate (requires coating) | Excellent | Track days, towing, performance driving |
| 7075-T6 Aluminum | Moderate (570 MPa) | Lightest | Good (anodizing improves) | Limited | Show vehicles, lightweight builds, mild street use |
| Grade 5 Titanium | High (950 MPa) | 50% lighter than steel | Excellent (naturally resistant) | Excellent | Track use, performance enthusiasts, wet climates |
| Stainless Steel (316) | Moderate-High (580 MPa) | Similar to chromoly | Excellent | Good | Coastal areas, winter driving, daily drivers |
When you're deciding between these options, consider what actually happens during aggressive driving. Titanium wheel bolts maintain their strength even under repeated heat cycles from hard braking—situations where aluminum can soften and lose clamping force. The Tire Hardware research confirms that titanium "maintains its strength and structure, even under high heat track conditions," while steel can expand and potentially loosen.
Weight savings deserve careful context. Yes, titanium offers significant reduction over steel—roughly 50% lighter for equivalent strength components. Aluminum saves even more weight, but this comes with notable strength trade-offs that limit its suitability for aggressive driving. For dedicated track vehicles or builds focused on reducing unsprung mass, titanium represents the performance sweet spot: substantial weight reduction without compromising reliability.
However, for many daily drivers, chromoly steel remains the practical choice. It provides excellent strength at a lower price point, handles heat beautifully, and offers proven durability across millions of miles of real-world use. The weight penalty compared to titanium becomes negligible for normal street driving, where the marginal rotational mass difference won't noticeably affect acceleration or handling.
Your climate also influences material selection. If you live where road salt blankets winter highways, stainless steel or titanium's corrosion immunity becomes a genuine advantage over chromoly, which requires protective coatings to resist rust. Titanium's natural resistance to corrosion means your investment maintains its appearance and structural integrity for years, even in harsh coastal or northern environments.
With material characteristics clarified, compatibility becomes your next critical decision. The strongest titanium nut in the world won't protect your wheels if it doesn't match your vehicle's seat type and thread specifications.
Seat Types and Thread Pitch Compatibility Essentials
You've selected premium forged material with excellent strength characteristics—but none of that matters if your lug nuts don't actually fit your vehicle. Compatibility might seem straightforward, yet it's the area where most enthusiasts make costly mistakes. Using the wrong seat type or thread pitch creates dangerous conditions that no amount of material quality can overcome. Let's break down the critical specifications you need to verify before purchasing replacement lug nuts.
Here's the reality: a special lug nut designed for one application can become a liability on another. Mismatched seat types prevent proper contact with your wheel, while incorrect thread pitch causes cross-threading that weakens the connection. Understanding these fundamentals protects both your investment and your safety.
Seat Type Compatibility Guide
The "seat" refers to the surface where your lug nut contacts the wheel. This interface must match precisely—an improperly seated lug nut won't distribute clamping force correctly, potentially allowing wheel movement or concentrating stress that damages your wheel's mounting surface.
Three primary seat types dominate the automotive market:
Conical/Tapered (60-degree): The most common configuration for aftermarket wheels and many domestic vehicles. These feature an angled surface that centers the lug nut as you tighten it, creating a wedging action that enhances clamping security. When shopping for special lug nuts for aftermarket wheel upgrades, conical seats typically represent your most likely requirement.
Ball/Radius (Spherical): Predominantly found on European vehicles including BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, and Volkswagen. These feature a rounded seating surface that contacts a corresponding curved pocket in the wheel. Ball seat lug bolts require precise radius matching—using a conical nut on a ball seat wheel creates point contact instead of proper surface engagement.
Flat/Mag (Washer Style): Common on certain Japanese vehicles and specific aftermarket wheels designed for drag racing or show applications. These feature a flat seating surface with an integrated or separate washer that distributes load across a broader area. Some mag-style wheels require this configuration to prevent damage to thinner mounting flanges.
Never assume your new wheels use the same seat type as your factory wheels. Always verify seat type requirements in your wheel manufacturer's specifications before purchasing lug hardware.
Thread Pitch Identification Made Simple
Thread pitch determines whether your lug nut actually threads onto your vehicle's wheel studs. According to DrivenProducts.com, getting the wrong thread pitch causes lugs to "pinch when tightening and not fully engage"—a recipe for stripped threads and potential wheel loss.
Thread specifications combine two measurements: thread diameter and pitch. You'll see these expressed as formats like M12x1.5 (metric) or 1/2"-20 (US standard). The first number indicates thread diameter; the second specifies either the distance between threads (metric, in millimeters) or threads per inch (US standard).
Common thread pitches vary by manufacturer region:
- M12 x 1.5: Honda, Acura, Toyota, Lexus, Mazda, Mitsubishi, and many other Japanese and domestic vehicles
- M12 x 1.25: Infiniti, Nissan, Subaru, and select other manufacturers
- M14 x 1.5: Many modern trucks, SUVs, and European vehicles requiring larger fasteners
- M14 x 2.0: Select heavy-duty applications
- 1/2"-20: Classic American vehicles and some modern domestic applications
- 9/16"-18: Larger domestic vehicles and trucks
How do you determine your correct specifications? Start with your vehicle owner's manual, which typically lists factory lug nut specifications. Alternatively, you can measure your existing hardware using a thread pitch gauge available at any auto parts store. DrivenProducts notes that you can also take an existing lug to your local hardware store and spin it onto bolts they have available to confirm sizing.
For European vehicles, remember that many manufacturers—including Audi, BMW, and Mercedes—use wheel bolts rather than the stud-and-nut combination common on Asian and domestic vehicles. This distinction matters when shopping, as replacement lug nuts won't work on bolt-style systems.
When measuring existing lug nuts, verify both the seat type and thread specifications before ordering replacements. A precision caliper helps confirm thread diameter, while the pitch gauge verifies thread spacing. If you're upgrading to aftermarket wheels, check whether they require different seat types than your factory setup—this commonly occurs when switching from OEM to aftermarket configurations.
The consequences of incorrect sizing extend beyond simple installation frustration. Cross-threaded lug nuts damage wheel studs that require expensive replacement. Improperly seated hardware creates uneven clamping that can crack wheel mounting surfaces or allow gradual loosening. These failures can occur suddenly and without warning, making specification verification essential before your first installation. With compatibility requirements understood, let's examine when upgrading to custom forged hardware becomes genuinely necessary versus when factory equipment suffices.

When Custom Forged Lug Nuts Become Necessary
Here's a question many enthusiasts struggle with: do you actually need custom forged lug nuts, or will factory hardware serve you perfectly well? The honest answer depends entirely on how you use your vehicle. While manufacturers design OEM lug nuts to handle normal driving conditions, several scenarios push beyond "normal"—and that's where understanding the genuine benefits of forged hardware becomes valuable.
Let's cut through the marketing hype and examine when upgrading makes practical sense versus when it's simply an aesthetic choice. This decision-making guidance addresses a gap that most competitors overlook, leaving you to figure out whether that premium price tag delivers real-world value for your specific situation.
When OEM Lug Nuts Fall Short
Factory lug nuts work adequately for the conditions manufacturers anticipate: daily commuting, occasional highway driving, and typical weather exposure. However, they're designed to balance cost, adequate performance, and mass production efficiency—not to excel in demanding applications. Several scenarios reveal their limitations:
Aftermarket Wheel Installations: When you upgrade to aftermarket wheels, your factory lug nuts often won't work properly. Different seat types, varying depth requirements, and aesthetic considerations typically necessitate new hardware. If you're running lug nuts for Moto Metal wheels or other aftermarket options, purpose-matched forged hardware ensures proper engagement and appearance. Additionally, figuring out wheel offset for your new setup is just one compatibility factor—the lug nuts must also match your wheel's specifications perfectly.
Aggressive Driving Conditions: OEM hardware isn't engineered for repeated high-stress cycles from spirited driving. The fatigue resistance of standard cast or machined lug nuts may prove inadequate when you're consistently pushing performance limits, especially during hard braking that generates substantial heat transfer through the hub assembly.
Heavy Towing Applications: Towing trailers or hauling heavy loads multiplies the forces acting on your wheel hardware. The additional weight increases stress during acceleration, braking, and cornering while generating more heat from brake systems working harder. Standard lug nuts may maintain adequate clamping force under normal loads but struggle with the elevated demands of consistent towing.
Environmental Exposure: If you live in coastal areas or regions with heavy winter road salt use, factory hardware—especially uncoated steel—corrodes over time. This corrosion weakens the fasteners, makes removal difficult, and can cause seized threads that damage wheel studs. Forged titanium or stainless options resist these conditions far better.
Performance Applications Demanding Forged Hardware
When you're evaluating whether to upgrade, consider the thermal demands your driving places on wheel hardware. According to titanium bolt research, titanium alloy maintains 90% of its strength at temperatures reaching 300°C, while steel nuts top out around 250°C after special tempering treatment. Aluminum, despite its weight advantages, suffers most dramatically—losing strength as brake heat transfers through the hub during aggressive driving.
This thermal behavior matters significantly for track enthusiasts. During repeated hard braking sessions, your brake rotors can exceed 500°C, and that heat conducts through the hub into your wheel mounting hardware. Aftermarket wheel lug nuts made from titanium or quality chromoly steel handle these heat cycles without the dimensional changes or strength degradation that aluminum experiences. Understanding UTQG ratings helps you select tires appropriate for your performance goals—and the same thoughtful matching applies to selecting wheel hardware that won't become your vehicle's weak link.
The following use cases benefit most from custom forged hardware:
- Track day participants: Choose titanium or chromoly steel for repeated heat cycling and aggressive clamping requirements. The best wheel lock nuts for track use combine security features with thermal stability.
- Autocross and time attack competitors: Titanium saves unsprung weight while maintaining strength under high-stress cornering loads.
- Dedicated tow vehicles: Chromoly steel provides maximum strength for sustained heavy loads at reasonable cost.
- Off-road enthusiasts: Forged steel handles impact loads and debris exposure better than alternatives; corrosion-resistant finishes extend service life in mud and water.
- Show vehicles and aesthetic builds: Forged aluminum or titanium in custom finishes provides the appearance upgrade without compromising structural integrity.
- Daily drivers in harsh climates: Forged stainless steel or titanium resists corrosion from road salt while maintaining reliable performance.
For typical daily drivers covering moderate mileage without aggressive driving habits, factory hardware often remains perfectly adequate. The custom forged lug nuts benefits become most compelling when your usage exceeds normal parameters—whether through performance driving, heavy loads, environmental exposure, or aftermarket wheel installations requiring different specifications.
Understanding when upgrades deliver genuine value versus marginal improvement helps you allocate your modification budget effectively. With your use case clarified, proper installation becomes the next critical factor in realizing the full potential of quality wheel hardware.
Proper Installation and Torque Specifications
You've invested in quality forged lug nuts and verified compatibility—now the installation process determines whether you'll actually realize those custom forged lug nuts benefits. Surprisingly, this is where many enthusiasts undermine their own upgrades. Improper installation can transform premium hardware into a safety liability, regardless of material quality or manufacturing precision.
According to Brake & Front End magazine, "Many people think we must tighten lug nuts until they can't turn anymore. Nothing could be further from the truth. We measure torque, but the goal is to achieve proper clamping force." This distinction matters enormously—overtightening damages threads and can actually reduce clamping effectiveness, while undertightening creates obvious loosening risks.
Torque Specifications by Application
Why don't all lug nuts use the same torque specification? Several factors influence the correct value for your specific setup:
Thread Size: Larger diameter threads (M14 versus M12) require higher torque values because they engage more material and create greater clamping force per rotation. A spark plug socket size comparison illustrates this principle—smaller fasteners require less torque to achieve proper stretch.
Material Properties: Different materials respond differently to applied torque. Aluminum lug nuts typically require lower torque specifications than steel equivalents because aluminum's lower modulus of elasticity means it stretches more readily. Overtorquing aluminum can cause permanent deformation or thread stripping.
Vehicle Application: Manufacturers specify torque values based on wheel weight, expected loads, and hub design. A compact sedan might specify 80 ft-lbs (approximately 108 Newton-meters) while a heavy-duty truck requires 140 ft-lbs or more. Always verify your specific vehicle's requirements.
The following general guidelines apply when manufacturer specifications aren't available, according to OnAllCylinders:
| Thread Size | Torque Range (ft-lbs) | Torque Range (Nm) |
|---|---|---|
| M12 x 1.25 | 70-80 | 95-108 |
| M12 x 1.5 | 70-80 | 95-108 |
| M14 x 1.5 | 85-100 | 115-135 |
| 1/2"-20 | 75-85 | 102-115 |
| 9/16"-18 | 135-145 | 183-197 |
Always prioritize manufacturer specifications over general guidelines. Your vehicle owner's manual or wheel manufacturer documentation provides the definitive torque requirements for your application.
Installation Best Practices for Longevity
Proper installation involves more than hitting the right torque number. The Tire Industry Association developed the R.I.S.T. procedure—Remove debris, Inspect surfaces, Snug the lugs, Torque to spec—specifically to address the complete installation process that prevents failures.
Follow this step-by-step procedure for optimal results:
- Inspect wheel studs carefully. Clean rusty or dirty threads with a wire brush or thread chaser. If studs appear stretched, damaged, or previously overtorqued, replace them before proceeding. Family Handyman notes that hammering out broken studs can damage wheel bearings—use proper removal tools instead.
- Clean all mating surfaces. Remove visible rust, grease, and corrosion from both the hub face and wheel mounting surface. Debris between these surfaces compresses over time, reducing clamping force and causing vibration.
- Verify seat type compatibility. Confirm your lug nuts match the wheel's seat requirements—conical, ball, or flat. Mismatched seats create dangerous point contact instead of proper surface engagement.
- Apply anti-seize sparingly. A thin coat around the hub center prevents seized wheels during future removal. However, never apply anti-seize to lug nut threads unless specifically recommended—it can alter the torque-to-clamping-force relationship.
- Hand-thread all lug nuts first. This confirms proper thread engagement and prevents cross-threading. If a lug nut doesn't spin freely by hand, stop and investigate before applying any tools.
- Snug in a star pattern. Tighten all lugs to approximately half the final torque value using a star or crisscross sequence. This centers the wheel on the hub as intended.
- Final torque with a calibrated wrench. Complete the tightening to manufacturer specification using the same star pattern. Use a quality torque wrench—not an impact gun—for this critical step.
- Verify wheel rotation. Carefully confirm the wheel rotates freely without contacting brake or suspension components before lowering the vehicle.
Why avoid impact guns for final tightening? Pneumatic impacts deliver torque in rapid bursts that can exceed your target specification before you react. Air pressure variations, worn sockets, and trigger sensitivity all create inconsistency. OnAllCylinders explicitly states: "Do not use an impact gun to tighten lug nuts!" Using torque sticks rated at 60% of final value helps during initial snugging, but always complete with a calibrated clicker or digital torque wrench.
Re-torquing Requirements: After initial installation, lug nuts should be re-torqued after the first 50 to 100 miles. This accounts for initial settling of mating surfaces, bedding-in of new components, and any minor thread engagement that occurs during initial driving. This step is especially critical with new wheels, new studs, or the best lug nut locks that may seat differently than standard hardware.
Warning Signs and Failure Modes
Even quality forged lug nuts eventually require replacement. Recognizing warning signs prevents failures before they become dangerous—much like noticing white smoke coming from exhaust signals potential engine problems, certain indicators demand attention for your wheel hardware:
- Thread stripping: If lug nuts spin freely without tightening, threads are damaged. Replace both the affected lug nut and wheel stud immediately.
- Seat damage: Visible deformation, galling, or wear on the seating surface indicates compromised contact. Damaged seats create inconsistent clamping.
- Corrosion indicators: Surface rust is cosmetic, but pitting that extends into thread valleys weakens the fastener. Heavily corroded hardware becomes difficult to remove and may fail under load.
- Difficult removal: Lug nuts that require excessive force to remove may have stretched threads, seized from galvanic corrosion, or suffered heat damage.
- Visible cracks: Any cracking—even hairline fractures—means immediate replacement. Forged hardware resists cracking better than alternatives, but fatigue eventually affects all materials.
When replacing hardware, consider upgrading all lug nuts on the affected wheel rather than mixing old and new components. According to automotive experts at Family Handyman, if one stud has sheared off or multiple studs show damage, "the others are likely damaged too, and will soon fail." The same principle applies to lug nuts subjected to identical stress conditions.
Proper installation transforms your investment in quality forged hardware into reliable, long-term performance. With your lug nuts correctly installed and torqued, ongoing maintenance determines how long that performance lasts.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Your custom forged lug nuts are properly installed and torqued—but the job isn't finished. Like any precision automotive component, wheel hardware requires ongoing attention to deliver the longevity that justifies its premium price. The good news? Forged components demand far less maintenance than inferior alternatives while lasting significantly longer when properly cared for.
Think about it this way: you wouldn't ignore curb rash on expensive wheels, and the same attentiveness applies to the hardware securing them. Environmental factors constantly work against your lug nuts—road salt, humidity, brake dust, and track chemicals all affect different materials in different ways. Understanding these interactions helps you protect your investment effectively.
Maintenance Routines by Material Type
Each lug nut material responds differently to cleaning agents, environmental exposure, and maintenance procedures. What works perfectly for chromoly steel may damage aluminum finishes, while titanium's natural resistance simplifies care routines considerably.
Chromoly Steel (4140): These workhorses require the most proactive maintenance due to their susceptibility to corrosion. According to Grassroots Motorsports, keeping steel hardware clean prevents galling—the microscopic welding of thread surfaces that causes difficult removal and eventual damage. Every couple of wheel removals, blast threads with brake cleaner and use a wire brush to remove any buildup. Inspect protective coatings for chips or wear that expose bare metal.
Titanium (Grade 5): The easiest material to maintain thanks to natural corrosion resistance. Standard cleaning with mild soap and water removes brake dust and road grime without risking surface damage. Avoid harsh acidic wheel cleaners that can discolor the finish. Titanium's durability means you'll spend more time enjoying your wheels than worrying about hardware maintenance.
7075-T6 Aluminum: Anodized finishes protect aluminum lug nuts but require gentle care. Use pH-neutral cleaners only—acidic or alkaline products can damage anodizing and accelerate corrosion of the underlying aluminum. Inspect anodized surfaces regularly for scratches or wear that compromise protection. Products from brands like Gorilla wheel nuts often feature quality anodizing, but even premium coatings require appropriate care.
Stainless Steel (316): While naturally corrosion-resistant, stainless can develop surface staining from brake dust and road contaminants. Regular cleaning maintains appearance and allows easy inspection of thread condition. Unlike chromoly, stainless rarely requires protective coatings, simplifying long-term care.
The Anti-Seize Debate
Few topics generate more disagreement among enthusiasts than anti-seize compound on lug nut threads. Here's the nuanced reality that Grassroots Motorsports addresses directly: anti-seize is fundamentally a lubricant, and lubricants change torque-to-clamping-force relationships significantly—potentially by 30-40%.
For track cars experiencing high-stress conditions, dry and clean threads provide consistent, predictable clamping force when torqued to specification. Standard torque values assume dry threads; adding lubrication means those specifications no longer produce the intended clamping force. You'd either under-clamp at standard torque values or risk overstressing hardware by increasing torque to compensate.
However, for vehicles that sit outside in harsh weather and see infrequent wheel removal, anti-seize prevents seized threads that make future service difficult or impossible. The key distinction: prioritize dry threads for performance applications demanding precise clamping, while considering anti-seize for vehicles where corrosion-induced seizure presents a greater practical concern than exact clamp load.
Apply anti-seize to hub centering surfaces to prevent seized wheels—but keep it off thread surfaces for performance applications where precise torque-to-clamp relationships matter.
Environmental Impact on Different Materials
Where you drive and store your vehicle dramatically affects hardware longevity. According to WheelsHome's research on wheel nut longevity, environmental factors create specific challenges for each material:
- Road salt exposure: Chloride ions aggressively attack steel and aluminum. Stainless steel (304 grade) resists this damage, while 316 stainless with added molybdenum performs even better. Titanium remains virtually immune to salt-induced corrosion.
- Humidity and moisture: Store vehicles in controlled environments when possible—humidity below 60% prevents accelerated corrosion on steel components. Gorilla lug products and similar quality hardware often feature enhanced coatings, but environmental control extends service life for any material.
- Thermal cycling: Temperature swings from 25°C to -5°C cause repeated expansion and contraction that can loosen threads over time. This affects all materials but presents particular concerns for aluminum, which has a higher thermal expansion coefficient than steel or titanium.
- Track chemicals: Brake fluid, tire prep compounds, and cleaning chemicals used at track events can damage certain finishes. Rinse hardware thoroughly after track sessions to remove potentially corrosive residues.
Protecting Your Investment Long-Term
Expected service life varies dramatically by material and conditions. Quality forged chromoly steel typically delivers 5-10 years of reliable service with proper maintenance in moderate climates—significantly longer in dry environments. Titanium can last the lifetime of the vehicle with minimal care. Aluminum requires more frequent inspection and typically shows wear sooner under aggressive use.
Use this maintenance checklist to maximize hardware longevity:
- Inspect threads and seating surfaces during every wheel removal
- Clean threads with brake cleaner and wire brush (steel) or mild soap (titanium/aluminum) every 2-3 wheel changes
- Check torque specifications quarterly for daily drivers, before each event for track vehicles
- Examine protective coatings for chips, scratches, or wear that expose base material
- Replace any hardware showing visible corrosion pitting, thread damage, or seat deformation
- Store spare lug nuts in controlled humidity environments with desiccant packs if necessary
- Rotate inspection with seasonal tire changes to build consistent maintenance habits
The cost-per-mile value proposition becomes clear when you consider that quality forged hardware outlasts multiple sets of cheaper alternatives. A single set of forged chromoly or titanium lug nuts lasting 100,000+ miles costs less than replacing budget cast alternatives every 20,000-30,000 miles—while providing superior safety throughout their extended service life.
With maintenance requirements understood, the final consideration becomes sourcing quality hardware from suppliers whose manufacturing standards match your performance expectations.
Sourcing Quality Forged Lug Nuts from Trusted Suppliers
You understand the benefits, know which material suits your application, and have installation procedures dialed in—now comes the practical question: where do you actually buy quality forged lug nuts? The market ranges from budget options at auto parts chains to premium specialty suppliers, and distinguishing genuine quality from marketing claims requires knowing what to look for behind the product listings.
When browsing options like napa lug nuts at your local store, rough country lug nuts for off-road builds, or mishimoto locking lug nuts for added security, how do you verify that "forged" actually means precision-manufactured rather than just a label? The answer lies in understanding supplier certifications, manufacturing standards, and quality control processes that separate premium hardware from dressed-up commodity parts.
Evaluating Supplier Quality Standards
Not all lug nut suppliers are created equal—and the differences matter far more than price tags suggest. According to industry certification research, reputable forged component manufacturers demonstrate their commitment through specific, verifiable credentials rather than vague quality claims.
When evaluating potential lug nut suppliers, examine these critical factors:
Manufacturing Process Transparency: Quality suppliers openly discuss their forging methods—hot forging versus cold forging, die specifications, and heat treatment processes. Vague descriptions like "precision engineered" without specifics often indicate resellers rather than actual manufacturers. According to precision forging specialists, combining hot forging with CNC machining guarantees accurate profiles and smooth finishes that comply with international standards.
Material Certification: Legitimate suppliers provide material certifications specifying exact alloy grades—4140 chromoly, 7075-T6 aluminum, Grade 5 titanium. Ask for mill certificates or material test reports. If a supplier can't document what their products are actually made from, that's a significant red flag.
Quality Control Documentation: Look for suppliers who can explain their inspection processes. Do they perform dimensional checks on finished products? What are their tolerance standards? Quality manufacturers maintain statistical process control data and can demonstrate consistent output.
Traceability Systems: Premium automotive components require traceability—the ability to track any specific part back to its raw material batch, manufacturing date, and quality inspection records. This matters if you ever need to identify potentially affected parts in a quality issue.
Key quality indicators to verify when evaluating any forged lug nut supplier: documented material certifications with specific alloy grades, transparent manufacturing process descriptions, quality control inspection records, and traceability systems linking finished products to raw material sources.
Certifications That Matter for Forged Components
Industry certifications provide third-party verification that a supplier actually maintains the quality systems they claim. For automotive-grade forged components, certain certifications carry significantly more weight than others.
IATF 16949 Certification: This represents the gold standard for automotive component manufacturing. According to DEKRA's certification overview, IATF 16949 covers "common customer-specific requirements of the automotive industry, such as traceability to support current regulatory changes, safety-related parts and processes, and warranty management processes." Suppliers holding this certification undergo rigorous annual surveillance audits to maintain their status.
Companies like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology exemplify the manufacturing standards that IATF 16949 certification demands. Their precision hot forging operations produce critical automotive components including suspension arms and drive shafts—parts where failure isn't an option. The same rigorous quality control principles that govern these safety-critical components apply to wheel hardware manufacturing, ensuring consistent material properties and dimensional accuracy.
ISO 9001 Certification: While less stringent than IATF 16949, ISO 9001 confirms that a company follows documented quality management systems. According to forging industry research, "ISO 9001 ensures that all stages of production, from design to inspection, meet high standards, reducing defects and ensuring reliable products."
Material and Process-Specific Certifications: Beyond management system certifications, look for evidence that suppliers use certified materials and maintain equipment calibration. Reputable gorilla auto lug nuts and method wheels lug nuts suppliers can document their material sourcing and testing procedures.
The certification hierarchy for automotive forging suppliers typically follows this pattern:
| Certification Level | What It Demonstrates | Audit Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | Automotive-specific quality management, OEM supplier capability | Annual surveillance, full recertification every 3 years |
| ISO 9001 | General quality management system implementation | Annual surveillance audits |
| Material Certifications | Verified alloy specifications and material properties | Per batch/shipment |
| Testing Certifications | Calibrated inspection equipment, documented test procedures | Ongoing calibration schedules |
When sourcing from any supplier, request documentation rather than accepting marketing claims at face value. Legitimate manufacturers readily provide certification copies, material test reports, and quality control documentation. Suppliers who deflect these requests or provide only vague assurances likely don't maintain the standards they advertise.
For enthusiasts building track cars or modifying performance vehicles, the extra due diligence in verifying supplier credentials pays dividends in reliability. The same precision manufacturing principles that Shaoyi applies to suspension components and drive shafts—controlled forging temperatures, precise die tolerances, and comprehensive quality inspection—distinguish premium wheel hardware from commodity alternatives that simply look similar.
With supplier evaluation criteria established, you're equipped to make informed purchasing decisions that deliver the genuine custom forged lug nuts benefits discussed throughout this guide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Vehicle
You've explored the metallurgical science behind forging, compared material options, verified compatibility requirements, and learned proper installation techniques. Now it's time to synthesize everything into actionable guidance tailored to your specific situation. Whether you're daily driving, chasing lap times, crawling trails, or building a show-stopping display vehicle, the right custom wheel bolts deliver measurable benefits when matched to your actual needs.
The custom forged lug nuts benefits we've covered aren't abstract advantages—they translate directly to wheels that stay securely mounted through whatever conditions you encounter. Let's distill the key insights into a practical decision framework.
Key Takeaways for Your Decision
Throughout this guide, four primary advantages consistently distinguish forged lug nuts from cast or machined alternatives:
- Superior strength from aligned grain structure: Forging eliminates internal voids and weak points, delivering approximately 26% higher tensile strength and 37% higher fatigue resistance than cast components.
- Consistent clamping force retention: Dense, void-free construction maintains dimensional stability through thermal cycling and vibration exposure, keeping your auto wheel nuts properly torqued over time.
- Material options matched to specific demands: From lightweight titanium for track enthusiasts to corrosion-resistant stainless for harsh climates, the right material choice addresses your particular driving environment.
- Long-term value proposition: Quality forged hardware outlasts multiple sets of cheaper alternatives, reducing cost-per-mile while providing superior safety throughout extended service life.
These advantages compound over time. A single investment in properly matched forged lug nuts eliminates the repeated replacement cycles, inconsistent performance, and potential safety concerns associated with budget alternatives.
Matching Benefits to Your Specific Needs
Your ideal lug nut configuration depends entirely on how you actually use your vehicle. Here's a quick-reference summary organized by application type:
- Daily Drivers: Forged chromoly steel offers the best balance of strength, durability, and value. Prioritize corrosion-resistant coatings if you encounter road salt or coastal conditions. Standard torque specifications and quarterly inspections maintain reliability with minimal effort.
- Track Use: Titanium or heat-treated chromoly steel handles repeated thermal cycling from aggressive braking. The weight savings from titanium—50% lighter than steel—reduces unsprung mass for measurable performance gains. Many owners of the best sports cars choose titanium specifically for this combination of strength and weight reduction.
- Off-Road Applications: Forged steel with durable protective coatings withstands impact loads, debris exposure, and the vibration inherent to trail driving. Focus on thread engagement and seat integrity during regular inspections after challenging terrain.
- Show Vehicles: Titanium or quality anodized aluminum provides the aesthetic upgrade you're seeking without compromising structural integrity. For vehicles that see limited driving, corrosion resistance matters less than appearance and verified quality.
Regardless of application, never compromise on compatibility. The strongest lug nut manufactured becomes dangerous when mismatched to your wheel's seat type or vehicle's thread pitch. Understanding the parts of a tire wheel assembly—from hub face to mounting surface to lug seat—ensures every component works together as designed.
As you move forward with your purchase decision, prioritize these factors in order: first, verify exact compatibility with your wheel and vehicle specifications; second, select material appropriate for your driving demands and environment; third, source from suppliers with documented quality certifications; and finally, consider aesthetics and budget within those constraints.
Quality forged lug nuts represent one of the most cost-effective safety upgrades available for any vehicle. They protect your wheel investment, maintain reliable performance across thousands of miles, and provide genuine peace of mind every time you drive. Armed with the knowledge from this guide, you're equipped to make an informed decision that keeps your wheels exactly where they belong—securely attached to your vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions About Custom Forged Lug Nuts
1. What are the benefits of forged lug nuts compared to cast alternatives?
Forged lug nuts deliver approximately 26% higher tensile strength and 37% higher fatigue resistance than cast alternatives. The forging process compresses metal under extreme pressure, aligning grain structure to eliminate internal voids and weak points. This translates to superior clamping force retention, better heat tolerance during aggressive braking, and extended service life—often lasting 5-10 years or more with proper maintenance.
2. How much weight do titanium lug nuts save compared to steel?
Titanium lug nuts weigh approximately 50% less than steel equivalents while maintaining comparable or superior strength. Grade 5 titanium delivers tensile strength of 950 MPa—exceeding standard steel at 800 MPa. This weight reduction decreases unsprung mass, improving acceleration response, braking performance, and overall handling feel, making titanium ideal for track enthusiasts and performance-focused builds.
3. Do forged lug nuts affect wheel security and ride quality?
Yes, forged lug nuts positively impact wheel security by maintaining consistent clamping force through thermal cycling and vibration exposure. Their dense, void-free construction resists the stress relaxation that loosens cheaper alternatives over time. This reliable connection between wheel and hub contributes to stable handling, reduced vibration, and the peace of mind that comes from knowing your wheels remain securely mounted.
4. What seat type and thread pitch do I need for my vehicle?
Seat types include conical/tapered (most aftermarket wheels), ball/radius (European vehicles like BMW and Audi), and flat/mag (specific applications). Thread pitches vary by manufacturer—M12x1.5 for Honda, Toyota, and many domestics; M12x1.25 for Nissan and Subaru; M14x1.5 for trucks and European vehicles. Always verify your vehicle's specifications in the owner's manual or measure existing hardware before purchasing.
5. How do I find quality forged lug nut suppliers with reliable manufacturing standards?
Look for suppliers with IATF 16949 certification—the automotive industry's gold standard for quality management. Reputable manufacturers like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology provide documented material certifications, transparent forging processes, and traceability systems. Request mill certificates specifying exact alloy grades and ask about quality control inspection procedures. Avoid suppliers who cannot provide this documentation.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 

