Airbag Component Stamping: Precision Manufacturing for Safety Systems
TL;DR
Airbag component stamping is a high-precision manufacturing process designed to produce safety-critical parts like inflator housings, burst discs, and diffusers. Because these components function as high-pressure vessels during deployment, manufacturers primarily utilize deep draw stamping and progressive die techniques to ensure structural integrity and hermetic sealing. Standard materials include 1008 Cold-Rolled Steel and High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steel, selected for their balance of ductility and tensile strength.
Success in this sector requires strict adherence to IATF 16949 standards, zero-defect quality control, and advanced tooling capable of maintaining tight tolerances (often ±0.05mm) under high-volume production. The process is characterized by rigorous in-die testing, including pressure monitoring and vision inspection, to guarantee reliable performance in life-saving scenarios.
Critical Components: What Parts Are Stamped?
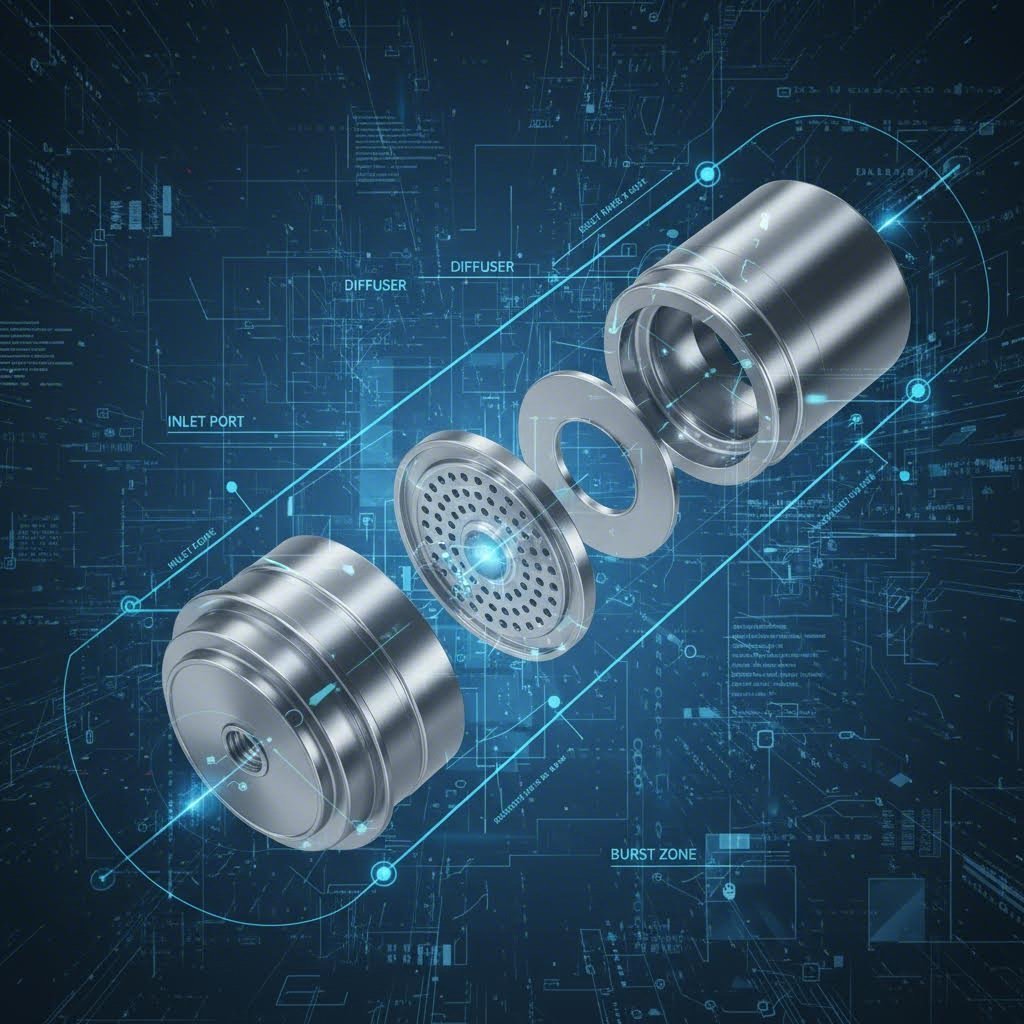
The airbag module is an assembly of highly engineered metal sub-components, each serving a distinct function in the deployment sequence. Unlike general automotive stamping, these parts must withstand explosive pressures without fragmenting.
Inflator Housings and Canisters
The inflator housing is effectively a pressure vessel. Manufactured primarily through deep drawn stamping, these cylindrical components house the chemical propellant. The stamping process must create a seamless container that maintains uniform wall thickness to prevent rupture at the wrong point during inflation. Variations include driver-side (steering wheel) and passenger-side canisters.
Burst Discs
Burst discs are precision-calibrated pressure relief valves. As noted by IMS Buhrke-Olson, these thin metal diaphragms are stamped to score or weaken specific lines, ensuring they open instantly at a precise pressure threshold. This controlled failure mechanism allows gas to fill the airbag bag within milliseconds while preventing over-pressurization.
Diffusers and Screens
Once the gas is released, it passes through stamped diffusers and filter screens. Diffusers, often made from 1008 Cold-Rolled Steel, distribute the gas flow evenly to inflate the bag symmetrically. Filter screens, frequently stamped from 304 Stainless Steel, capture particulates and cool the expanding gas to protect the airbag fabric from thermal damage.
| Component | Primary Material | Stamping Method | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflator Housing | 1008 Cold-Rolled Steel | Deep Draw | Contain high-pressure propellant |
| Burst Disc | Stainless Steel / Alloys | Precision Coining | Calibrated pressure release |
| Diffuser (25mm/30mm) | 1008 Cold-Rolled Steel | Progressive Die | Gas flow distribution |
| Grommet / Bracket | DDQ Steel / HSLA | Progressive Die | Mounting and wire protection |
Manufacturing Processes: Deep Draw vs. Progressive Die
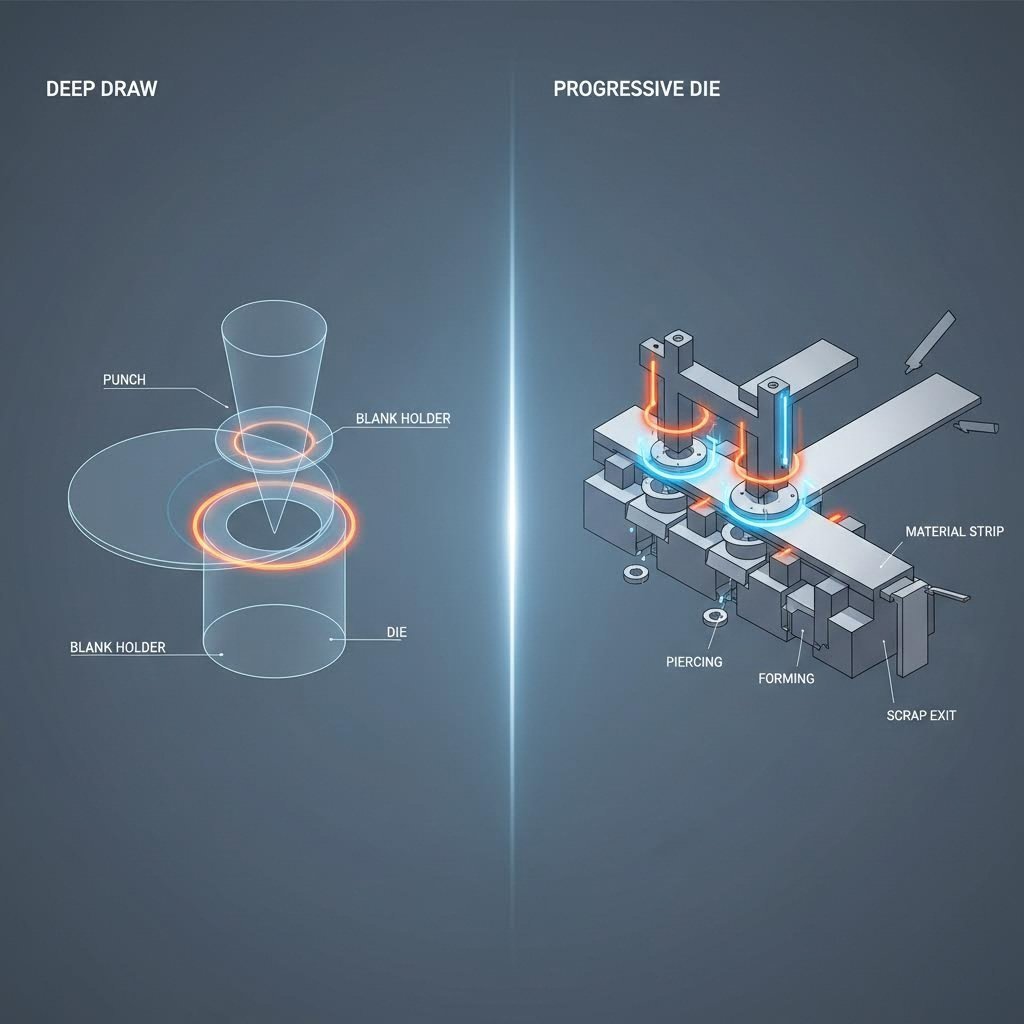
Selecting the correct manufacturing method is dictated by the component's geometry and function. For airbag systems, two dominant techniques emerge: deep drawing for containment and progressive die stamping for complex assembly features.
Deep Draw Stamping for Pressure Integrity
Deep drawing is essential for creating the seamless inflator housings described above. The process involves pulling a flat sheet metal blank into a die cavity to form a hollow shape where the depth exceeds the diameter. The critical engineering challenge here is managing material flow to prevent wall thinning. If the metal stretches too thin at the radius, the housing becomes a weak point that could fail catastrophically during an accident.
Progressive Die Stamping for Complex Geometries
For components like mounting brackets and grommets, progressive die stamping offers speed and geometric complexity. ESI's case study on knee airbag grommets highlights the use of a 24-station progressive tool to form parts with 0.1mm tolerances. This method feeds a metal strip through multiple stations—cutting, bending, and forming simultaneously—to produce finished parts at rates exceeding one million units per year.
Manufacturers often face the challenge of scaling these complex processes from initial validation to mass production. Companies like Shaoyi Metal Technology address this by offering comprehensive stamping solutions that bridge the gap between rapid prototyping (e.g., 50 units for testing) and high-volume manufacturing, ensuring critical components like control arms and subframes meet global OEM standards alongside airbag parts.
Advanced Servo Press Technology
Modern airbag stamping also leverages servo press technology to handle the unique stresses of the job. Conventional presses may struggle with the high shock loads generated when stamping high-strength steels. Kyntronics notes that servo-controlled actuation allows for precise force and position control, enabling in-process quality checks that detect defects immediately during the stroke, rather than at post-production inspection.
Material Science: Steel Grades and Formability
Material selection in airbag component stamping is a tradeoff between formability (for manufacturing) and high tensile strength (for safety).
- 1008 Cold-Rolled Steel: According to Metal Flow, this is the industry workhorse for inflator housings and diffusers. It offers excellent ductility, allowing for deep drawing without cracking, while providing sufficient strength for the finished vessel.
- High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel: Used for structural components like end caps and mounting brackets that must resist deformation under load. HSLA grades provide higher yield strength than mild steel but require higher tonnage presses to form.
- Deep Drawing Quality (DDQ) Steel: For parts with extreme depth-to-diameter ratios, DDQ steel is specified to minimize the risk of tearing during the forming process.
- 304 Stainless Steel: Primarily used for filter screens and internal components requiring corrosion resistance and thermal stability against the hot gas generated by the inflator.
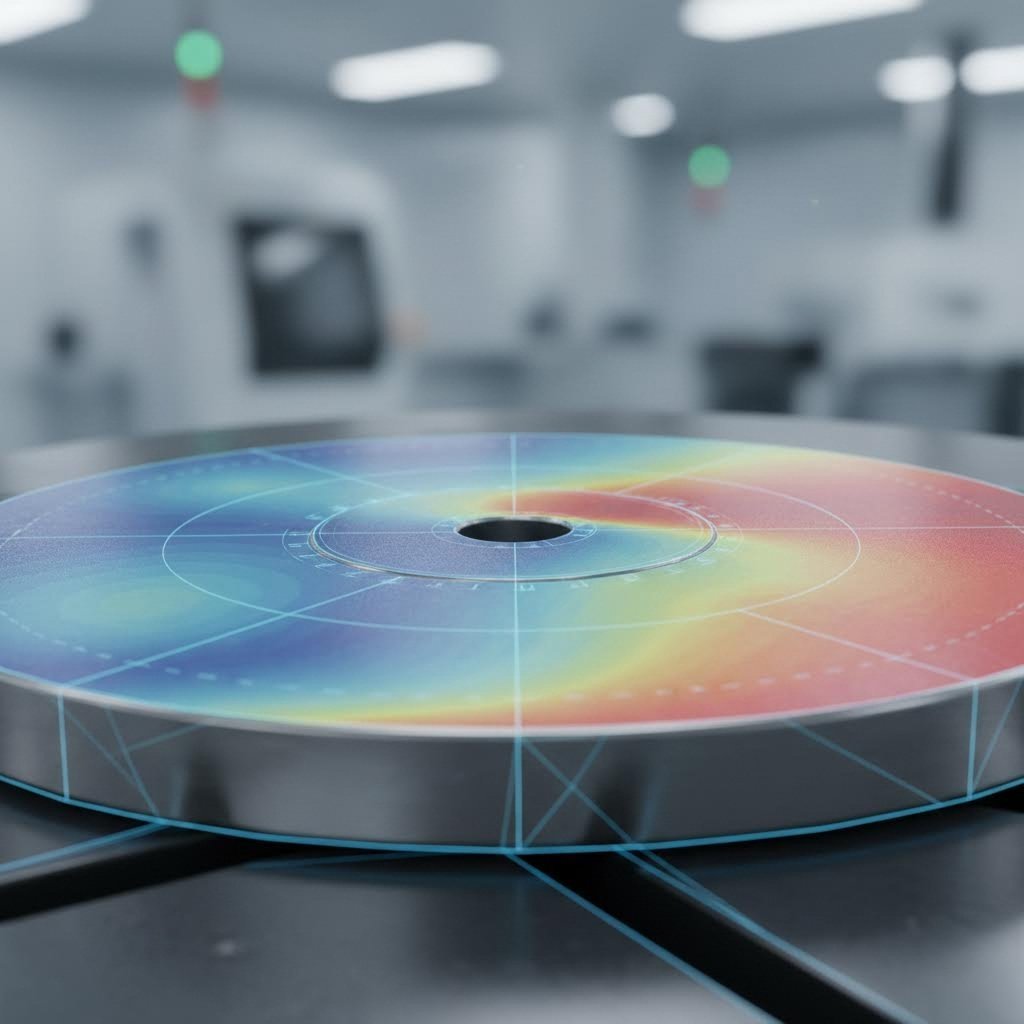
Engineering Challenges and Quality Assurance
The "zero-defect" mandate in airbag manufacturing is not a buzzword; it is a literal requirement. A single failure in the field can result in fatalities and massive recalls. Consequently, the engineering focus shifts heavily toward predictive modeling and in-line validation.
Managing Springback and Work Hardening
As manufacturers move toward stronger materials to reduce weight, phenomena like springback (the metal returning to its original shape after forming) become more pronounced. Advanced simulation software (Finite Element Analysis or FEA) is mandatory to predict these behaviors and compensate for them in the tool design phase. Additionally, deep drawing causes work hardening, where the metal becomes brittle as it is formed. Process engineers must carefully control draw speeds and lubrication to maintain material ductility.
In-Die Sensing and Validation
Top-tier manufacturers integrate quality assurance directly into the stamping die. Technologies such as in-die pressure testing and vision inspection ensure that every part is verified before it leaves the press. For burst discs, consistency is paramount; the scoring depth must be controlled within microns to guarantee the disc bursts at exactly the designed pressure. Any deviation triggers an immediate machine stop, preventing defective parts from entering the supply chain.

Precision Saves Lives
Airbag component stamping represents the intersection of high-volume manufacturing and absolute engineering precision. From the deep-drawn integrity of inflator housings to the calibrated release of burst discs, every step of the process is governed by stringent safety standards. For automotive OEMs, selecting a stamping partner involves vetting not just their press capacity, but their ability to integrate advanced metallurgy, simulation, and in-line quality verification into a seamless production workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the primary types of metal stamping used for airbags?
The two primary methods are deep draw stamping and progressive die stamping. Deep draw is used for hollow, cylindrical parts like inflator housings because it creates a seamless, high-pressure vessel. Progressive die stamping is used for complex, multi-feature parts like brackets, grommets, and diffusers, allowing for high-speed production of intricate geometries.
2. What materials are most common in airbag stamping?
1008 Cold-Rolled Steel is widely used for housings and diffusers due to its excellent formability. 304 Stainless Steel is common for screens and filters requiring heat and corrosion resistance. HSLA (High-Strength Low-Alloy) steel is used for structural components that require higher tensile strength to withstand deployment forces.
3. Why are burst discs critical in airbag systems?
Burst discs act as precision pressure relief valves. They are stamped with specific score lines or thicknesses to rupture at a designated pressure. This ensures that the airbag inflates at the correct speed and force during a collision. If the stamping tolerance is off, the airbag could deploy too slowly or explode, causing injury.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —