Stamping Seat Belt Buckles: Manufacturing Precision & Safety Standards Progressive die stamping line transforming steel coils into seat belt buckle components
TL;DR
Stamping seat belt buckles is a high-precision manufacturing process that transforms high-strength carbon steel into life-saving safety components using progressive die technology. This method ensures strict adherence to safety standards like FMVSS 209, delivering parts with high tensile strength and zero-defect tolerances.
For automotive engineers and procurement officers, the critical success factors include selecting the right material grades (typically carbon steel for structure and tin-phosphorus bronze for locking mechanisms) and utilizing presses with class 1-JIS precision. This guide covers the end-to-end production workflow, from material selection and 400-ton press operations to quality control and supplier sourcing.
Critical Material Selection for Safety
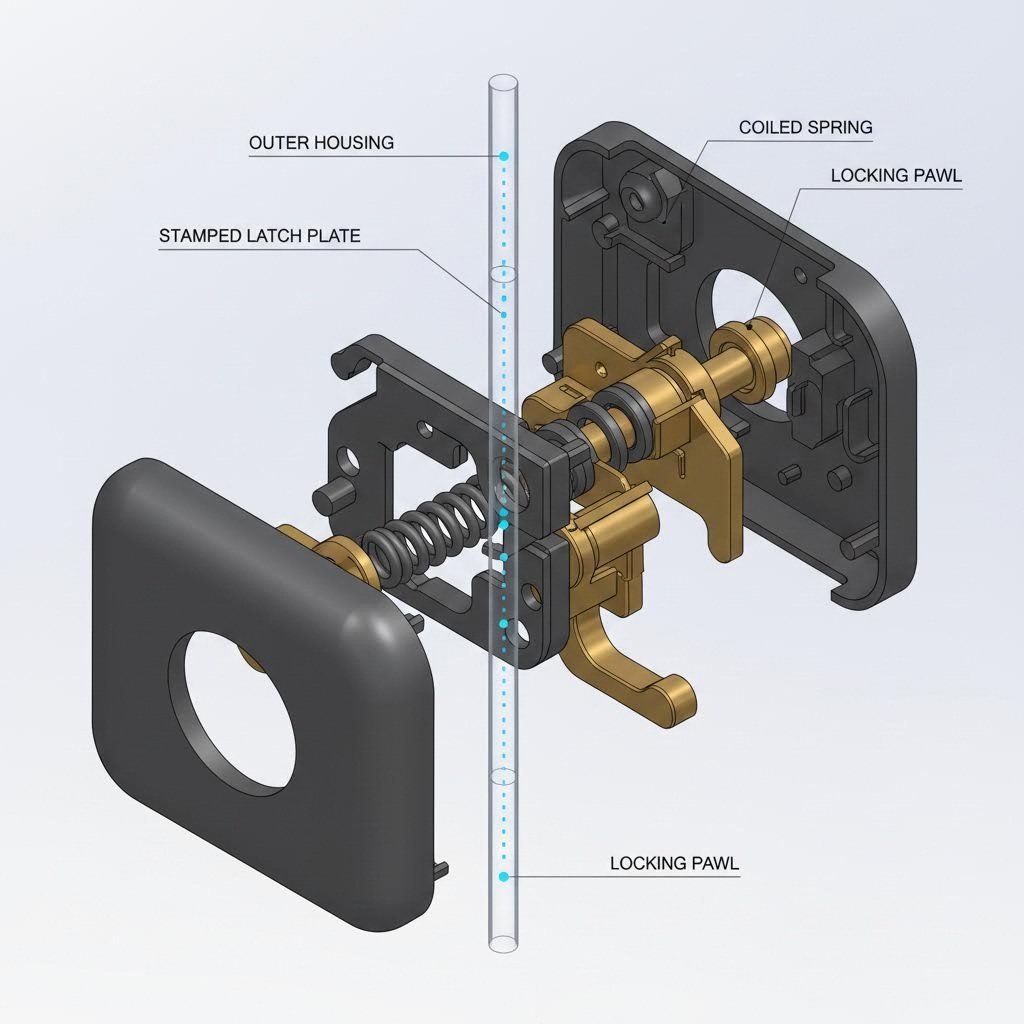
The foundation of any compliant seat belt buckle is the raw material. Unlike cosmetic automotive parts, buckle components must withstand extreme dynamic loads without deformation. The industry standard primarily relies on High-Strength Carbon Steel for the main housing and latch plates. This material is chosen for its superior yield strength and ability to maintain structural integrity under the sudden, high-impact forces of a collision (often exceeding 2,000 kgf).
For the internal locking mechanisms and springs, manufacturers often utilize Tin-Phosphorus Bronze or specialized alloy steels. These materials are selected for their excellent fatigue resistance and anti-magnetic properties, ensuring the latch remains operational after thousands of insertion cycles. In some modern designs, the internal latch plate must also be compatible with electromagnetic sensors (as seen in advanced active safety systems), requiring precise magnetic permeability specifications.
Surface treatment is equally vital. Raw stamped steel is highly susceptible to corrosion, which can seize the mechanism. To prevent this, components undergo rigorous anodizing or zinc-nickel plating. This not only meets the salt spray test requirements (typically 72 to 96 hours without red rust) but also ensures the smooth mechanical operation of the release button and latch.
The Progressive Die Stamping Process
High-volume production of seat belt buckles is almost exclusively performed using progressive die stamping. This process allows for the rapid, continuous production of complex geometries from a single coil of metal. The workflow typically utilizes high-tonnage presses, often ranging from 400 to 600 tons, capable of exerting the massive force needed to cut and form thick gauge steel with micron-level precision.
- Feeding: A servo feeder unspools the steel coil into the press with precise timing, ensuring minimal material waste.
- Punching & Bending: The die performs multiple operations simultaneously at different stations. As the strip moves forward, the press punches holes for the latch mechanism and bends the steel into the U-shape housing required for the buckle assembly.
- Forming & Coining: Critical features, such as the latch engagement ramp, are coined (compressed) to harden the surface and ensure smooth tongue insertion.
Modern stamping lines often integrate Class 1-JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) precision, ensuring that every stroke maintains tolerances as tight as ±0.02mm. This level of accuracy is non-negotiable; a deviation of even a fraction of a millimeter could cause the buckle to jam or false-latch, leading to catastrophic failure during an accident.
Quality Control & Defect Prevention
In the manufacturing of safety-critical components, "zero defects" is a requirement, not a goal. The most persistent challenge in stamping seat belt buckles is the management of burrs—small, sharp metal ridges left behind by the cutting process. If a burr dislodges inside the mechanism, it can jam the release button or prevent the latch from fully engaging. Manufacturers employ automated deburring systems and tumble finishing to ensure all edges are smooth and rounded.
Rigorous testing protocols validate the physical properties of the stamped parts. Tensile strength testing pulls the buckled assembly to failure to ensure it meets or exceeds the minimum load requirements (typically around 5,000 lbs or 22 kN for adult belts). Additionally, cycle testing simulates years of use by inserting and releasing the tongue tens of thousands of times to verify that the latch spring and locking plate do not suffer from metal fatigue.
Advanced manufacturers also utilize insert molding where the stamped metal skeleton is placed into a plastic injection mold. This process encapsulates the metal in a durable ABS or nylon housing. Quality control here focuses on ensuring the high temperatures of the plastic injection do not anneal or weaken the stamped metal springs.
Regulatory Standards & Compliance
No seat belt component can enter the market without strict regulatory compliance. In the United States, the governing standard is FMVSS 209 (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 209), which specifies requirements for seat belt assemblies. This standard dictates the release force (typically less than 45 lbs) and the strength of the assembly under load. Manufacturers must maintain detailed documentation and traceability for every batch of steel used.
Globally, standards such as ISO 6683 (for earth-moving machinery) and ECE R16 (Europe) impose similar but distinct requirements. For example, ISO standards for heavy machinery often require different latching geometries to accommodate work gloves or debris-heavy environments. A competent stamping partner must be versed in these regional variances and capable of providing material certifications (Mill Test Reports) that trace the steel back to the foundry.
| Standard | Region | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| FMVSS 209 | USA | Release force < 45 lbs; 5,000 lbs tensile load. |
| ECE R16 | Europe | Dynamic crash testing; retraction durability. |
| ISO 6683 | Global | Specifics for earth-moving & agricultural machinery. |
Sourcing Guide: Choosing a Manufacturer
Selecting a supplier for stamped seat belt components requires due diligence beyond price comparison. Buyers must verify that the manufacturer possesses IATF 16949 certification, the global technical specification for automotive quality management systems. This certification ensures the supplier has adequate risk management and defect prevention processes in place.
Look for manufacturers with in-house tooling capabilities. A supplier that designs and maintains its own progressive dies can respond faster to design changes and troubleshoot quality issues immediately. Ask specifically about their press capacity; manufacturers limited to smaller presses (under 200 tons) may struggle with the thick-gauge steel required for heavy-duty buckles.
For automotive companies seeking a partner capable of bridging the gap from rapid prototyping to mass production, Shaoyi Metal Technology offers comprehensive stamping solutions. With press capabilities up to 600 tons and IATF 16949 certification, they specialize in delivering high-precision automotive components—from complex control arms to safety-critical seat belt parts—scaling seamlessly from initial 50-piece prototype runs to millions of units.
Conclusion
The process of stamping seat belt buckles is a discipline defined by unyielding precision and safety. From the selection of certified carbon steel to the final progressive die strokes on a 400-ton press, every step is calculated to prevent failure. For automotive OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers, the priority must always remain on sourcing from certified manufacturers who understand that a seat belt buckle is not just a stamped part—it is the primary lifeline between a passenger and survival.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between stamped and die-cast seat belt buckles?
Stamped buckles are formed from sheet metal (usually steel) using a press, resulting in a part with high tensile strength and elasticity. Die-cast buckles are made by forcing molten metal (often zinc or aluminum) into a mold. Stamped steel is generally preferred for the main load-bearing components due to its superior structural integrity under tension, while die-casting is often used for complex decorative housings or non-load-bearing internal sliders.
2. How are stamped seat belt parts tested for corrosion resistance?
Stamped parts undergo salt spray testing (ASTM B117) to evaluate the durability of their plating or coating. The parts are exposed to a saline mist for a set period (e.g., 96 hours) and inspected for the formation of red rust. This ensures the locking mechanism will not seize up due to rust, even in humid or coastal environments.
3. Can progressive die stamping handle the complex shape of a buckle?
Yes, progressive die stamping is ideal for complex shapes. The die contains multiple stations where the metal strip is sequentially punched, bent, coined, and formed. By the final station, the flat strip has been transformed into a complex, three-dimensional component ready for assembly or insert molding.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
