Essential Forging Tolerances for Automotive Performance
Essential Forging Tolerances for Automotive Performance

TL;DR
Forging tolerances for automotive specs are a critical set of allowable dimensional variations that dictate the precision of manufactured vehicle components. Adhering to tight tolerances is essential for ensuring parts fit correctly, perform reliably under stress, and meet the automotive industry's rigorous demands for safety and efficiency. Achieving this precision enhances component strength, minimizes material waste, and is fundamental to producing high-performance, dependable vehicles.
Defining Forging Tolerances: The Foundation of Precision Manufacturing
In manufacturing, a tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a part. Forging tolerances, specifically, define the acceptable range of deviation from the nominal dimensions specified in an engineering design. These are not arbitrary numbers; they are a crucial parameter that ensures components will fit and function correctly within a larger assembly, such as a vehicle's engine or suspension system. As noted by industry resources like Engineers Edge, these tolerances must account for factors inherent to the forging process, including die wear, material shrinkage during cooling, and potential mismatching between the top and bottom dies.
Forging tolerances are generally categorized as either “regular” or “special.” Regular tolerances, which apply when no specific standard is mentioned, are further divided into “Commercial Standard” for general practice and “Close Standard” for work requiring extra precision and cost. Special tolerances are explicitly defined on engineering drawings for critical dimensions where precision is paramount. Think of it like assembling a high-performance engine: while the overall block has a certain acceptable size (commercial tolerance), the fit of the pistons within the cylinders requires a much tighter, specific clearance (special tolerance) to ensure optimal compression and power.
Ultimately, forging tolerances represent a negotiated agreement between the designer and the forging supplier. As explained by Queen City Forging, they must be considered on a case-by-case basis because they are directly influenced by the part's design and the specific production techniques used. This foundational understanding of tolerances is the first step toward creating components that meet the demanding specifications of any high-performance industry.
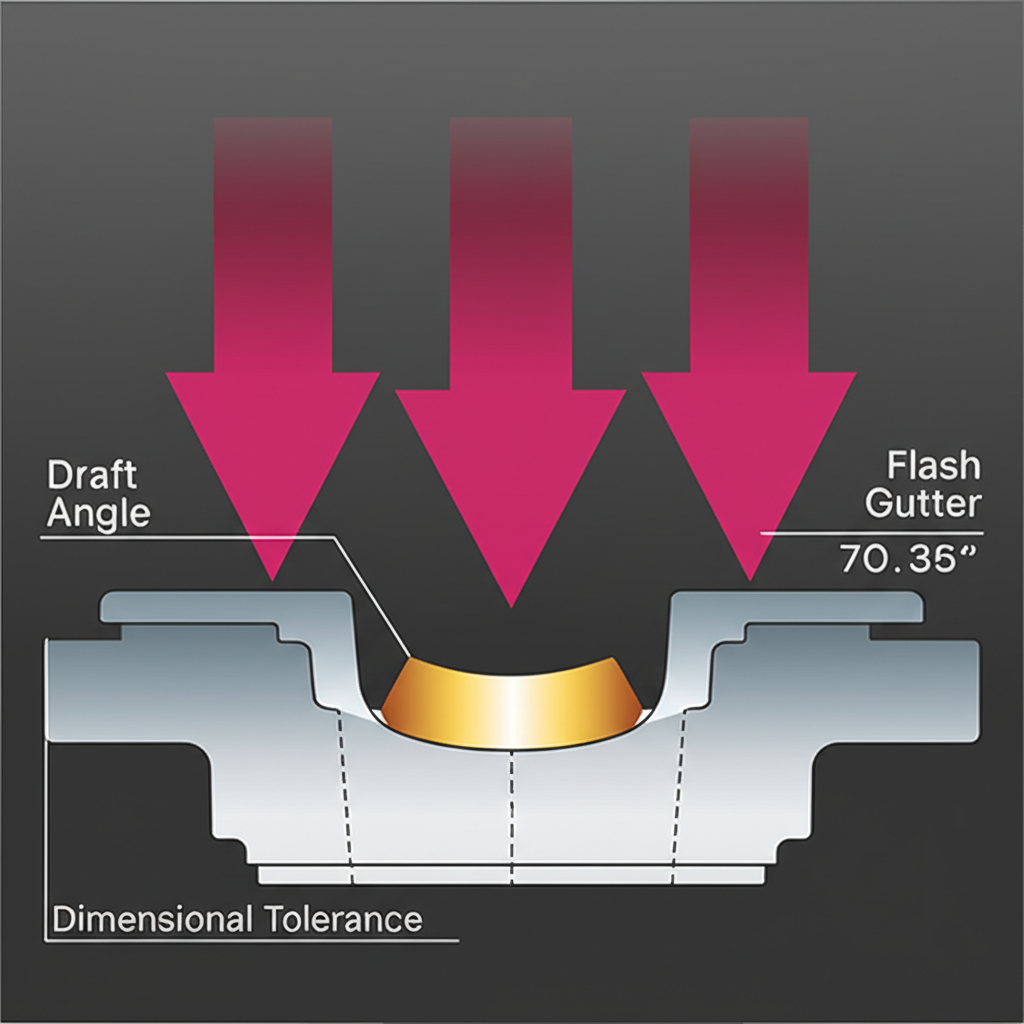
The Critical Role of Tight Tolerances in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry operates under immense pressure to deliver vehicles that are safe, reliable, fuel-efficient, and high-performing. High-precision drop forging with tight tolerances is a cornerstone manufacturing process that helps meet these demands. When automotive components are forged to exact specifications, the benefits extend across the entire vehicle, from performance to longevity. The consistent dimensional accuracy achieved through precision forging is essential for producing parts that can withstand the extreme stress, vibration, and temperature fluctuations of daily operation.
The advantages of maintaining tight forging tolerances for automotive components are significant and directly impact the final product's quality and cost-effectiveness. As detailed in a guide by Sinoway Industry, these benefits are multi-faceted:
- Superior Strength and Durability: The forging process refines the metal's grain structure, aligning it with the component's shape. This enhances its mechanical properties, making parts highly resistant to fatigue, shock, and wear. Critical parts like crankshafts, connecting rods, and steering knuckles rely on this forged strength to prevent failure.
- Enhanced Safety and Reliability: For safety-critical systems like brakes and suspension, there is no room for error. Precise tolerances ensure that components fit and function together flawlessly, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. Studies have shown that components with precise tolerances can improve overall performance and reliability significantly.
- Weight Reduction: Modern automotive design prioritizes weight reduction to improve fuel efficiency. High-precision forging can create strong, lightweight parts, eliminating unnecessary material without compromising structural integrity. This helps manufacturers meet increasingly strict emissions and fuel economy standards.
- Cost-Effectiveness at Scale: While achieving tighter tolerances can require more advanced tooling, the drop forging process is highly efficient for high-volume production. It minimizes material waste (or flash) and often reduces the need for extensive secondary machining, leading to lower per-unit costs in mass production.
Navigating Forging Standards and Guidelines
To ensure consistency and quality across the industry, forging tolerances are often guided by established standards. Organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) provide specifications that cover materials, dimensions, and pressure ratings for forged components. For example, the ASME B16.11 standard outlines detailed requirements for forged fittings, while DIN standards like DIN 1.2714 specify material grades with high wear resistance suitable for close die forgings. Adhering to these standards ensures interoperability and a baseline of quality for parts sourced from different suppliers.
The achievable tolerance also depends heavily on the forging method. Open-die forging, where the metal is not completely confined by the dies, generally has looser tolerances. In contrast, closed-die (or impression-die) forging, where the metal is forced into a precisely machined cavity, allows for much tighter dimensional control. This precision is why closed-die forging is overwhelmingly preferred for complex automotive parts like gears and suspension components.
The following table provides a general overview of typical tolerances for different forging types, though specific values can vary based on part size, material, and complexity.
| Forging Method | Typical Tolerance Range | Common Automotive Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Closed-Die / Impression-Die Forging | ±0.5 mm to ±1.5 mm (can be tighter) | Connecting rods, gears, crankshafts, steering knuckles |
| Open-Die Forging | ±1 mm to ±3 mm (or ±0.03″ to ±0.125″) | Large shafts, rings, initial shaping of ingots |
| Precision (Net-Shape) Forging | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | High-performance gears, turbine blades |
Key Design and Material Considerations for Optimal Forging Tolerances
Achieving optimal forging tolerances is not merely a matter of specifying a number; it is the result of a holistic approach that begins in the design phase. Several key factors interact to determine the final precision of a forged component. Engineers and designers must balance these considerations to create a part that is both manufacturable and meets performance requirements. As explored in a technical brief by Frigate Manufacturing, a well-thought-out design is fundamental to success.
The following considerations are critical in influencing the achievable tolerances for any forged automotive part:
- Part Geometry and Complexity: Simpler shapes are inherently easier to forge with high precision. Complex designs with deep cavities, sharp corners, or thin walls can impede metal flow within the die, leading to dimensional variations. Generous radii and fillets are crucial for smooth material flow and preventing defects.
- Material Selection: Different materials behave differently under heat and pressure. Alloys like steel, aluminum, and titanium each have unique thermal expansion rates, flow characteristics, and cooling shrinkage. The choice of material directly impacts die design and the final tolerances that can be held. For instance, aluminum's high thermal conductivity requires different process controls than steel.
- Die Design and Draft Angles: The die itself is a master tool that dictates the part's shape. Proper die design, including the incorporation of draft angles (slight tapers on vertical surfaces), is essential for allowing the finished part to be removed without damage. Insufficient draft can cause distortion and compromise tolerances.
- Forging Temperature and Process Control: The temperature of both the workpiece and the dies must be meticulously controlled. Variations in temperature can lead to inconsistent material flow and shrinkage, directly affecting dimensional accuracy. Automated processes provide the consistency needed for high-volume automotive production.
Successfully navigating these factors often requires collaboration with a forging specialist. For companies seeking high-quality components, partnering with an experienced provider is key. For example, Shaoyi Metal Technology offers specialized IATF16949 certified hot forging services for the automotive industry, demonstrating the expertise in die manufacturing and process control needed to meet stringent automotive specifications from prototyping to mass production.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the DIN standard for forging?
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) standards cover various aspects of forging. A relevant example is DIN 1.2714, a material standard for a Cr-Ni-Mo-V alloyed steel recommended for closed-die forgings due to its high toughness, wear resistance, and hardness. This standard ensures the material itself is suitable for producing durable, high-strength components.
2. What is the ASME standard for forging?
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) provides numerous standards applicable to forging. A key one is ASME B16.11, which specifies requirements for forged steel fittings, including their ratings, dimensions, tolerances, marking, and material requirements. This standard is crucial for ensuring consistency and safety in high-pressure applications.
3. What is the tolerance of open die forging?
Open-die forging typically has wider tolerances compared to closed-die methods because the workpiece is not fully enclosed. Tolerances can range from approximately ±0.03 inches to ±0.125 inches (roughly ±0.8 mm to ±3.2 mm) before machining, depending on the size and complexity of the component. This method is better suited for larger parts or initial shaping operations where exact precision is secondary.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
