Your Complete Automotive Welding Manual: From DIY Repairs to Advanced Industry Techniques
Why Automotive Welding Is the Foundation of Vehicle Safety and Performance
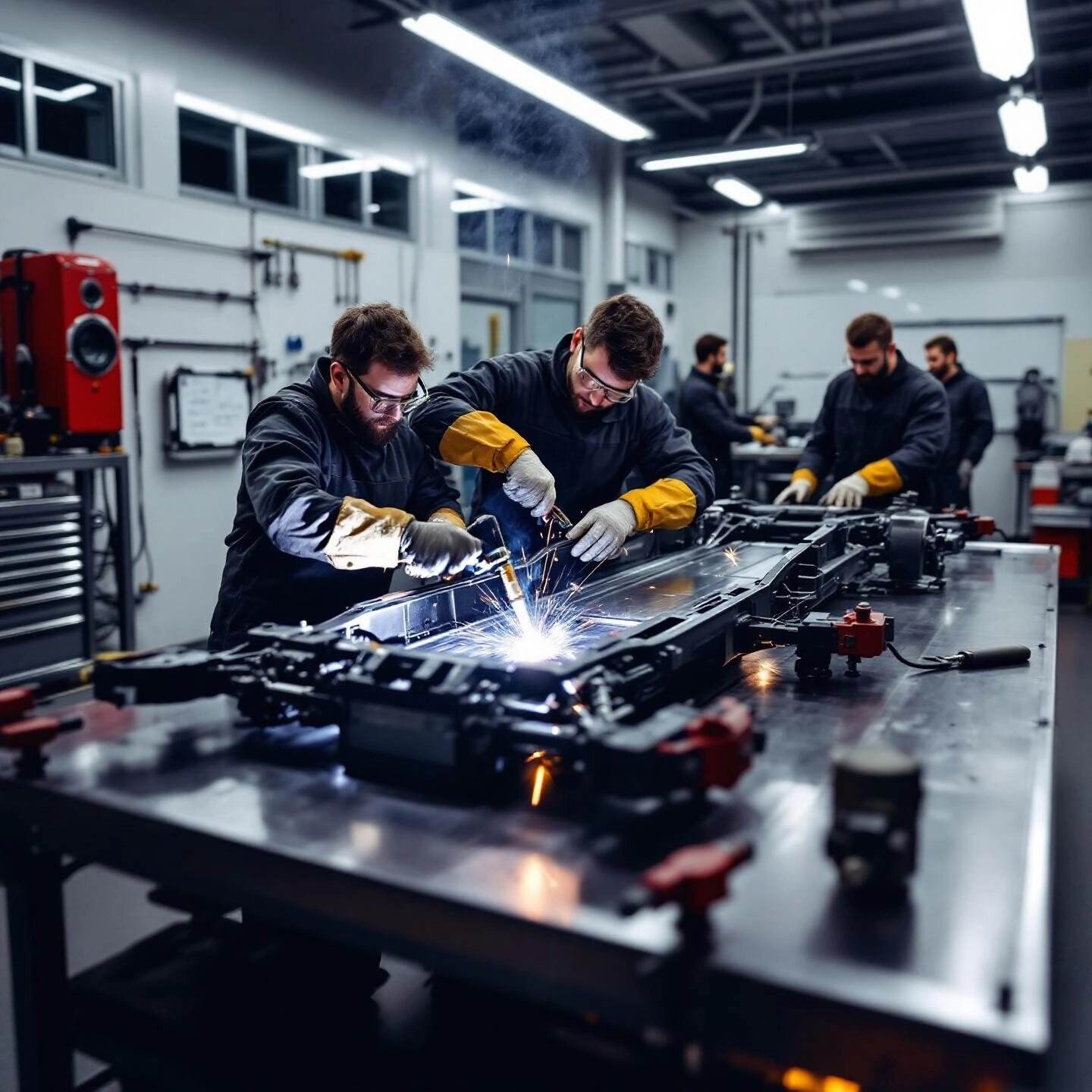
When you slide behind the wheel of your car, have you ever wondered what holds it all together? The answer is simple: welding. Automotive welding is more than just a manufacturing step—it’s the backbone of every vehicle’s safety, performance, and longevity. Whether you’re driving a classic sedan or the latest electric vehicle, expertly welded joints are what keep your car strong, reliable, and ready for the road.
The Evolution of Automotive Welding: From Handheld Torches to Intelligent Automation
Imagine the earliest days of car manufacturing. Skilled technicians spent hours manually welding steel frames, painstakingly joining each part. These early manual techniques, while effective, demanded time and expertise. As the automotive industry grew, so did the need for faster, more precise, and consistent welding methods. That’s when technology stepped in.
- Manual welding: The original method, requiring hands-on skill and attention to detail.
- Robotic and automated welding: Today, most vehicles are assembled using advanced robotic welding systems. These machines deliver unmatched speed, consistency, and accuracy, reducing human error and boosting productivity.
- Laser and intelligent welding: Recent innovations include laser welding and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring, defect detection, and adaptive quality control, especially important in complex areas like electric vehicle (EV) battery welding.
With every leap in technology, automotive welding has become more versatile and reliable. For example, modern welding methods now accommodate lightweight materials like aluminum and high-strength steel, helping manufacturers build safer, more fuel-efficient vehicles.
What You’ll Discover in This Automotive Welding Guide
Sounds complex? Don’t worry—this guide breaks it all down for you. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast tackling your first repair or a seasoned professional seeking advanced insights, you’ll find everything you need to know, including:
- Welding fundamentals: Core principles and the science behind strong, safe welds.
- Common repair types: From frame and chassis restoration to aluminum bodywork and custom modifications.
- Equipment selection: How to choose the right welder for your garage or shop.
- Safety essentials: The must-have gear and best practices to keep you protected.
- Shop selection tips: How to find and vet reputable automotive welding shops in your area.
- Advanced manufacturing: A look at laser, robotic, and AI-driven welding technologies shaping the industry’s future.
- Career paths: Opportunities in automotive welding, from repair to high-tech manufacturing.
- Chemical welders and adhesives: When to use alternatives like JB Weld, and their limitations.
By the end of this automotive welding guide, you’ll not only understand the vital role welding plays in every vehicle, but you’ll also be equipped to make smarter decisions for your next project—whether it’s a simple rust repair or a cutting-edge EV build. Ready to dive in? Let’s get started on the journey from basic repairs to the most advanced techniques in the industry.

Understanding the Core Principles of Automotive Welding
Ever wondered why some car repairs last for years while others fail after a few months? The answer often lies in the types of automotive welding used and how well the process matches the metal and the job. Choosing the right technique isn’t just about fusing metal—it’s about safety, durability, and performance. Let’s break down the most common welding methods you’ll encounter in automotive work, and why each has its place in the garage or factory.
MIG Welding: The Versatile Workhorse
- What is it? MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), uses a wire electrode fed continuously through a welding gun. An electric arc melts the wire and base metal, while an inert gas shields the weld from contamination.
- How does it work? Pull the trigger and the machine feeds wire, creating a strong arc that melts and joins the metals. The shielding gas—usually argon or a mix with carbon dioxide—keeps impurities out of the weld zone.
- Advantages: Fast, easy to learn, and suitable for a wide range of metals and thicknesses. MIG is especially popular for auto body panels, frames, and general repairs because of its speed and adaptability (Western Protective Solutions).
- Typical applications: Repairing body panels, patching frames, and custom fabrication. If you’re new to automotive welding, MIG is often the best place to start.
TIG Welding: Precision and Strength
- What is it? TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create a focused arc. A separate filler rod can be added if needed.
- How does it work? The welder holds a torch with a tungsten tip, creating a precise arc while controlling a filler rod by hand. An inert gas (often argon) shields the weld from the air.
- Advantages: Produces exceptionally clean, strong welds with minimal spatter. TIG is ideal for thin metals and non-ferrous materials like aluminum and titanium. It’s the go-to choice for high-performance and custom automotive work.
- Typical applications: Fabricating exhaust systems, repairing aluminum bodywork, and precision jobs where appearance and strength are critical. It takes more skill and time, but the results are worth it for demanding projects.
Spot Welding: The Backbone of Automotive Bodywork
- What is it? Spot welding is a form of resistance welding used to join overlapping sheets of metal by applying pressure and heat at specific points.
- How does it work? Two copper alloy electrodes clamp down on the metal sheets. When current flows, the metal heats and fuses at the contact points—forming a “spot” weld in just a fraction of a second.
- Advantages: Extremely fast, cost-effective, and perfect for high-volume production. While not as strong as TIG or MIG, spot welding is essential for assembling car bodies, doors, hoods, and trunk lids.
- Typical applications: Automotive spot welding is everywhere in vehicle manufacturing. You’ll notice neat rows of spot welds holding together sheet metal panels throughout most modern cars.
Advanced Welding Methods: Looking Ahead
Think MIG, TIG, and spot welding cover it all? Not quite. As automotive designs evolve, so do the welding technologies. Advanced methods like laser welding, friction stir welding, and hybrid processes are becoming more common, especially in electric vehicles and lightweight designs. These techniques offer even greater precision, speed, and strength—topics we’ll explore in detail later in this guide.
Understanding these core techniques is your first step to mastering automotive welding, whether you’re tackling a DIY repair or planning a high-tech manufacturing project. Next, we’ll explore how these welding processes are applied to real-world vehicle repairs, from frames to body panels and beyond.
Common Welding Repairs for Your Vehicle's Frame and Body
When your car takes a hit or starts showing its age, it’s the welds—often hidden beneath the paint—that decide whether repairs will last. Ever wondered what goes into restoring a bent frame, patching a rusty panel, or fixing a cracked chassis? Let’s break down the most common automotive welding repairs, the unique challenges of each, and why getting it right is crucial for your safety and your wallet.
Frame Repairs: The Backbone of Vehicle Safety
Imagine your car’s frame as its skeleton. If it’s damaged, everything else—steering, suspension, even how doors close—can be thrown off. Automotive frame welding is the process that restores this foundation. Here’s why it matters:
- Structural integrity: A properly welded frame disperses crash forces, helping protect passengers in a collision.
- Performance: A straight, strong frame keeps wheels aligned and handling sharp, reducing vibrations and odd noises.
- Cost savings: Welding repairs can save thousands compared to full frame replacement, letting you keep your car on the road longer.
Common signs that frame welding is needed include uneven tire wear, steering pulling to one side, clunking noises, or visible bends in the undercarriage. Skilled technicians will often cut out damaged sections and weld in new steel, using MIG or TIG processes for strength and durability. For safety-critical jobs, always insist on certified welders and high-quality parts.
Chassis Welding: Keeping Everything Connected
The chassis is more than just the frame—it’s the network of crossmembers, mounts, and supports that hold your engine, suspension, and drivetrain in place. Automotive chassis welding is essential when these parts crack, rust, or are modified for upgrades. Here’s what sets chassis repairs apart:
- Precision: Even a slight misalignment can throw off suspension geometry, affecting ride quality and safety.
- Material selection: Chassis parts may be made from high-strength steel or, increasingly, aluminum. Each requires different welding techniques and filler materials.
- Customization: Chassis welding is also used for performance upgrades—think roll cages or custom mounts—where strength and accuracy are non-negotiable.
For complex or high-performance projects, pre-fabricated chassis assemblies from trusted suppliers help guarantee fit and safety. Companies like Shaoyi offer precision-welded components using advanced robotic and laser welding lines, ensuring consistent quality and compliance with the strictest automotive standards. This is especially important for repairs involving critical load-bearing or crash-absorbing parts, where any weakness could have serious consequences.
Body Panel and Fender Repairs: Restoring Looks and Function
When your car gets a dent or rust spot, it’s often the body panels or fenders that need attention. Repairing these thin metal sheets presents unique challenges:
- Heat management: Car body panels are thin and prone to warping. Welders use lower power settings and techniques like skip welding to avoid creating holes or distortions.
- Surface preparation: Clean, rust-free surfaces are a must for strong, invisible welds. Technicians often use small-diameter wire electrodes for better control.
- Cosmetic finish: Good welds should be smooth and easy to blend with surrounding metal, minimizing the need for filler or sanding.
For DIYers, small patch repairs are possible, but larger or structural panel work should be left to pros with the right gear and experience.
Aluminum Frame and Panel Repairs: Special Skills Required
Modern vehicles increasingly use aluminum for frames and body panels to save weight and improve fuel efficiency. Sounds like an upgrade, right? But aluminum welding is a whole new ballgame:
- Heat sensitivity: Aluminum conducts heat rapidly and melts at lower temperatures, making it easy to warp or crack if not handled carefully.
- Corrosion risk: Improper welding can strip away protective coatings, leading to hidden rust and long-term damage.
- Specialized techniques: Professional shops use advanced TIG welding and sometimes epoxy adhesives for non-structural repairs. Precise cleaning and cooling are critical to avoid weak joints.
DIY aluminum repairs are rarely recommended. For safety and longevity, always rely on certified experts and, when possible, opt for pre-fabricated, quality-verified parts.
Why Structural Integrity—and Quality Components—Matter
Whether you’re fixing a classic car or a new EV, the quality of your welding repairs directly affects your vehicle’s safety and performance. Poor welds can lead to frame failure, misalignment, or even increased accident risk. That’s why it’s crucial to:
- Choose certified, experienced welders for frame and chassis repairs.
- Use high-quality, pre-fabricated components for complex or safety-critical assemblies.
- Insist on advanced welding techniques—like robotic or laser welding—when available, for consistent strength and reliability.
For manufacturers and serious enthusiasts, suppliers like Shaoyi provide IATF 16949-certified, precision-welded chassis and assembly parts. Their advanced robotic welding and strict quality control ensure every weld meets or exceeds industry standards, minimizing the risk of defects and maximizing your peace of mind—whether you’re restoring a daily driver or building the next track champion.
Understanding these repair types and best practices is your key to safe, long-lasting automotive welding results. Next, we’ll guide you through how to select the best welder for your own garage projects, so you can tackle repairs with confidence and the right equipment.

How to Choose the Best Automotive Welder for Your Garage Projects
Ever stood in the welding aisle, staring at rows of machines, wondering which one will actually get the job done? When you’re ready to tackle your own automotive welding repairs, having the right equipment is half the battle. But with so many choices—MIG, TIG, flux-core, spot welders—how do you pick the best automotive welder for your needs, skills, and budget? Let’s break it down so you can make a confident, informed decision.
Key Factors to Consider Before Buying a Welder
- Project Type: Are you patching body panels, fixing frames, or fabricating custom parts? Each job may require a different welding process.
- Material: Will you be welding steel, aluminum, or both? Some welders handle a wider range of metals than others.
- Skill Level: If you’re new to welding, ease of use and a forgiving learning curve are crucial. Advanced users may prioritize precision and versatility.
- Budget: Prices range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Factor in accessories, consumables, and safety gear.
- Power Requirements: Check your garage’s electrical capacity. Some welders need only a standard 120V outlet, while others require 240V.
- Portability: Will you be working in different locations, or is your welder staying put?
Comparing Welder Types: Which One Fits Your Needs?
Imagine you’re restoring a classic car or just want to fix a rusted rocker panel. The right machine makes all the difference. Here’s a side-by-side look at the most common options for automotive work:
| Welder Type | Best Use Cases | Skill Level | Material Compatibility | Power Needs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIG (Metal Inert Gas) | Body panels, frames, general repairs | Beginner to Intermediate | Steel, stainless steel, aluminum (with right setup) | 120V or 240V |
| TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) | Precision work, aluminum, thin metals, custom fabrication | Advanced | Steel, stainless, aluminum, titanium, more | 120V or 240V |
| Flux-Core (FCAW) | Outdoor repairs, thick/rusty metal, quick fixes | Beginner | Steel, some stainless | 120V |
| Spot Welder (Resistance) | Sheet metal, panel replacement, factory-style joints | Intermediate | Steel, thin metals | 120V or 240V |
MIG Welders: The Go-To for Most DIYers
If you’re hunting for the best automotive welder for general garage use, a MIG welder is often your best bet. Why? It’s user-friendly, fast, and versatile—perfect for beginners and seasoned hobbyists alike. MIG machines excel at joining thin sheet metal (like body panels) and thicker steel (such as frame sections), making them a staple in home garages and professional shops. With the right wire and shielding gas, you can even tackle aluminum repairs, though you’ll want to check the machine’s compatibility first.
TIG Welders: For Precision and Specialty Work
Planning to weld aluminum engine brackets or custom stainless exhausts? TIG welders deliver unmatched control and the cleanest, strongest welds. But there’s a catch: TIG welding takes more practice and patience to master. The equipment is also pricier. If your projects demand show-quality results or involve exotic metals, investing in a TIG welder could be worth it.
Flux-Core Welders: Portability and Power for Outdoor Jobs
Ever need to weld outside, or on dirty, rusty metal? Flux-core welders don’t require a separate shielding gas, making them ideal for outdoor and quick repairs. They’re affordable and easy to use, but tend to produce more spatter and less visually appealing welds than MIG or TIG. For heavy-duty, non-cosmetic fixes—think trailer hitches or frame patches—they’re a practical choice.
Spot Welders: Factory-Style Panel Replacement
Want to replicate OEM-style joints or replace an entire quarter panel? Spot welders are designed for joining overlapping sheets of metal, just like on the assembly line. They’re fast and strong for thin metals but limited to specific applications. Spot welders usually require access to both sides of the workpiece and are best for dedicated bodywork projects.
Tips for Making the Right Choice
- Start with a MIG welder if you’re new to automotive welding—it’s the most forgiving and versatile.
- If you plan to work on aluminum or need precise, high-strength welds, consider investing in a TIG machine as you gain experience.
- For outdoor or heavy-duty repairs, a flux-core welder offers portability and power without the need for gas cylinders.
- Spot welders are best for those focused on panel replacement or restoration work.
- Always factor in the cost of accessories—helmet, gloves, wire, gas, and safety gear—when budgeting for your new welder.
Choosing the right welder is the first step toward safe, successful repairs and custom projects. Next, we’ll cover the essential safety gear and workspace setup you’ll need to protect yourself and get the most from your new equipment.
Essential Gear and Safety Supplies for DIY Welding Projects
When you picture yourself welding in the garage, do you imagine sparks flying and metal fusing together? It’s easy to focus on the excitement of the project—but what about your safety? Whether you’re patching a rusty rocker panel or building a custom frame, welding exposes you to intense heat, UV radiation, toxic fumes, and flying debris. That’s why having the right safety gear and workspace setup isn’t just a suggestion—it’s a must for every DIY welder.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Your First Line of Defense
Imagine striking an arc without protection. Even a quick tack weld can cause burns, eye injuries, or worse. Here’s a checklist of essential PPE every automotive welder should have on hand:
| Auto-darkening welding helmet | Shields your eyes, face, and neck from UV radiation and sparks. Opt for an auto-darkening model for convenience and safety. Choose the right shade based on your welding process and wire type. |
| Safety glasses with side shields | Protect your eyes from flying particles—even when wearing a helmet. Use them during grinding, cleaning, and setup work. |
| Flame-resistant headwear | Wear a welder’s cap or bandana to safeguard your scalp and hair from sparks and spatter. Long hair should be tied back and tucked inside your jacket. |
| Welding gloves | Heavy-duty gloves shield your hands from heat and sparks. Choose the right type for your process (MIG, TIG, or stick) and inspect them for wear before each use. |
| Flame-resistant clothing | Wear tightly woven, work-weight cotton or leather. Avoid synthetic fabrics—they can melt and cause severe burns. Always button up shirts and ensure sleeves and pant legs are long enough to cover exposed skin. |
| Respiratory protection | Welding fumes are hazardous. Use a half-face respirator or, for higher safety, a powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) when working for extended periods or in confined spaces. |
| Hearing protection | Welding, grinding, and cutting can damage your hearing. Use earplugs or earmuffs as needed. |
Automotive Weld Fume Extraction: Clean Air, Healthy Lungs
Ever noticed how welding fumes linger, especially in a closed garage? Those fumes aren’t just unpleasant—they’re dangerous. Proper automotive weld fume extraction is vital for your health:
- Set up a local extraction system: Use a flexible hose and a powerful fan (ideally 150mm or 6-inch, rated at 300 m³/h or more) positioned close to your welding area. This setup efficiently removes fumes before they spread (MIG Welding Forum).
- Ensure airflow: Install louvres or vents at the opposite end of your garage to allow fresh air in. Good airflow prevents stagnant, fume-filled zones.
- For small spaces: Even a bathroom extractor fan can help, but aim for higher capacity if you weld frequently or for long periods.
- Avoid welding galvanized metal unless you have professional-grade fume extraction—these fumes are especially hazardous.
Fire Safety and Workspace Organization
- Fire extinguisher: Keep a multi-purpose (ABC) extinguisher within arm’s reach. Sparks and hot slag can ignite flammable materials in seconds.
- Clear your workspace: Remove paper, cardboard, oily rags, and other combustibles from your welding area.
- Organize tools: Store cables and hoses neatly to reduce tripping hazards. Keep tools and materials within easy reach to minimize distractions.
Choosing and Handling Automotive Welding Wire
The right automotive welding wire isn’t just about weld quality—it’s about safety, too. Here’s what matters:
- Match wire to material: Use ER70S-6 for mild steel, ER70S-3 for clean finishes, or ER80S-D2 for high-strength applications.
- Check diameter: Thinner wire (like 0.023–0.030 inch) is best for body panels; thicker wire suits frames and heavy parts.
- Store wire properly: Keep spools dry and clean to prevent rust and ensure smooth feeding.
- Inspect before use: Damaged or corroded wire can cause erratic arcs and poor welds.
Routine Maintenance: Stay Safe, Stay Sharp
- Inspect PPE, cables, and hoses before every session.
- Replace worn or damaged gear promptly—don’t take risks.
- Store safety equipment in a cool, dry place away from sunlight and chemicals.
By following this checklist and making safety a habit, you protect not just your project, but your health and future welding success. Ready to put your gear and workspace to use? Next, we’ll show you how to find reputable automotive welding shops when a DIY fix isn’t enough.
How to Find and Vet the Best Automotive Welding Shops Near You
Ever stared at a rust spot or frame crack and thought, “Should I tackle this myself, or trust a pro?” For many repairs—especially those involving safety or structural integrity—partnering with a skilled welding shop is the smartest move. But with so many choices out there, how do you separate top-tier professionals from the rest? Let’s walk through a practical approach to finding and vetting automotive welding shops near me that deliver safe, reliable results.
Start with Local Search: "Automotive Welding Near Me"
When your vehicle needs expert attention, location matters. Typing automotive welding near me into your favorite search engine is a great first step—it brings up shops that are close, convenient, and familiar with your area’s regulations. But don’t stop at the first listing. Consider shops that:
- Have a physical address and active phone number.
- Display recent reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, or Facebook.
- Showcase before-and-after photos or testimonials on their website or social media.
- Are listed on reputable industry directories or local business associations.
Key Questions to Ask Your Welding Shop
Imagine you’ve found a few promising candidates. Before handing over your keys, ask these essential questions to ensure you’re choosing a true professional:
| Are your welders certified? | Look for certifications from recognized organizations (such as AWS or local trade schools) to ensure proper training and up-to-date skills. |
| Do you have experience with my vehicle type? | Automotive welding covers everything from vintage classics to modern imports. Ask for specific experience with your make, model, or repair type. |
| Can I see examples of previous work? | Quality shops are proud to showcase finished projects—photos, case studies, or customer references. |
| What warranties or guarantees do you offer? | Reputable welders back their work with clear, written warranties on both labor and materials. |
| How do you prevent future corrosion? | Ask about post-weld treatments like primer, paint, or sealants to protect against rust—especially important for body and frame repairs. |
| Do you use OEM or high-quality replacement parts? | For structural repairs, using quality components is crucial for safety and longevity. |
| Are you insured and licensed? | Shops should carry liability insurance and have proper business licenses for peace of mind. |
Evaluating Professionalism and Communication
Ever had a shop ignore your calls or dodge your questions? That’s a red flag. Professional welders value clear, open communication. You’ll notice the difference when a shop:
- Provides detailed written estimates, outlining repair steps and costs.
- Explains repair options and timelines in plain language.
- Offers follow-up support, maintenance tips, or periodic inspections if needed.
When DIY Isn’t Enough: Why Professional Welding Matters
Some projects—like patching a small hole—may be within reach for experienced DIYers. But for anything involving structural repairs, frame straightening, or critical safety components, the expertise of a certified shop is essential. Professionals have access to advanced equipment, high-quality materials, and specialized techniques that most home garages simply can’t match. They also understand the importance of preserving your vehicle’s value and ensuring repairs meet safety standards.
Ready to take the next step? With a vetted shop on your side, you can focus on enjoying your vehicle—knowing it’s built to last. Next, we’ll dive into the cutting-edge world of laser and robotic welding, and see how these technologies are setting new standards for quality and performance in automotive manufacturing.
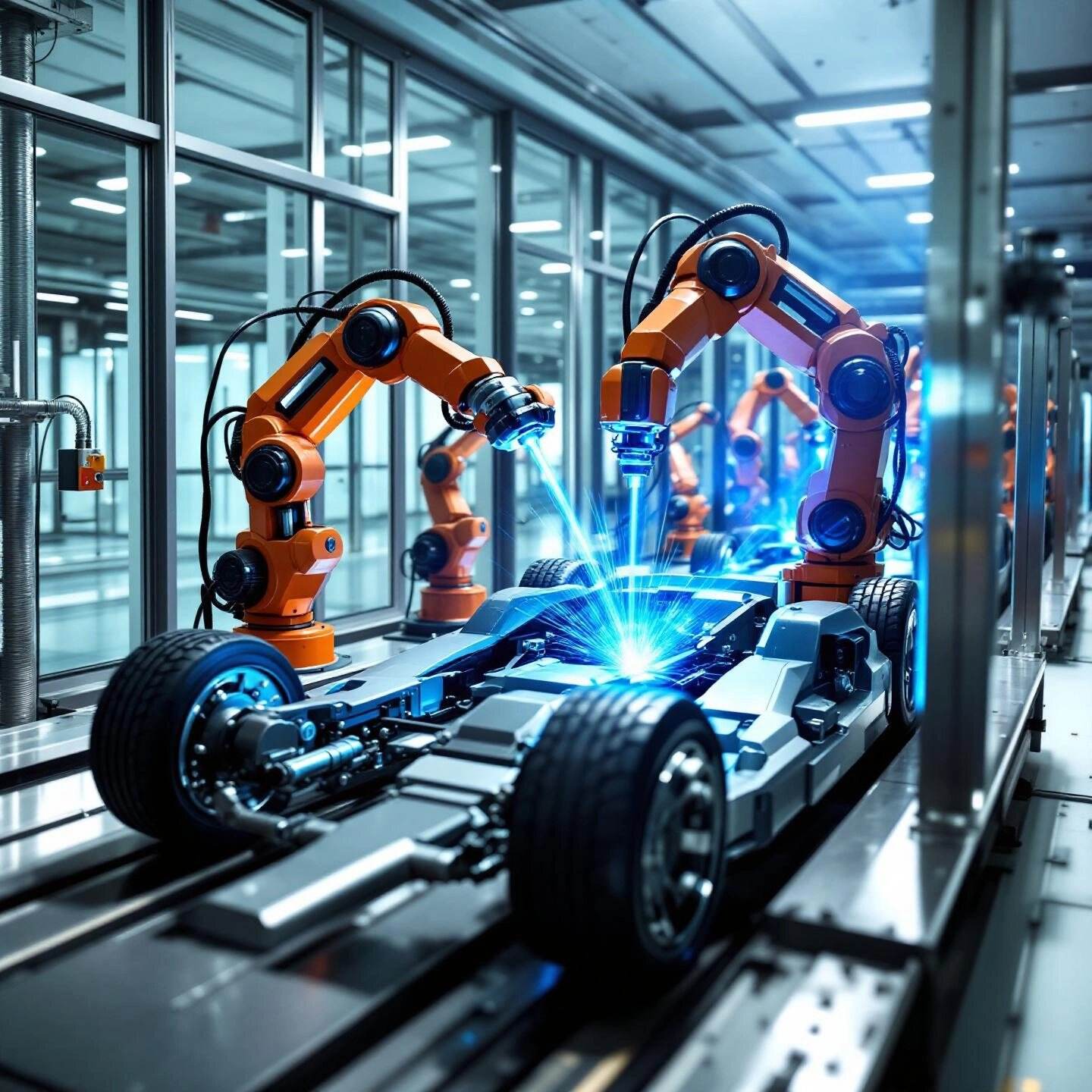
An Overview of Laser and Robotic Welding in the Auto Industry
Ever wondered how today’s vehicles stay so strong, lightweight, and reliable—while rolling off the assembly line faster than ever? The secret lies in two advanced technologies: automotive laser welding and automotive welding robots. These innovations have transformed automotive manufacturing, setting new benchmarks for precision, speed, and quality. Let’s break down how these processes work, why they matter, and what they mean for the future of automotive welding.
Laser Welding: Precision and Power for Modern Vehicles
Imagine joining metal parts with a beam of light so focused it can fuse steel or aluminum in milliseconds. That’s the essence of automotive laser welding. Unlike traditional methods, laser welding uses high-powered beams—most commonly CO2 or Nd:YAG lasers—to produce deep, narrow welds with minimal heat distortion. This means parts can be joined with pinpoint accuracy, even in tight or complex spaces.
- Speed: Laser welding operates at high speeds, often several meters per minute, making it ideal for mass production of car bodies, frames, and tailored blanks.
- Precision: The focused beam allows for narrow, consistent welds, essential for thin metals and intricate assemblies.
- Strength: Welded joints achieve high strength with minimal added weight, supporting the industry’s push for lighter, safer vehicles.
- Reduced Heat Distortion: Less heat means less warping or damage to sensitive components, preserving the integrity and appearance of the finished part.
Laser welding is now widely used for engine parts, gear components, tailored blanks, and even aluminum assemblies. The technology’s ability to join different materials and thicknesses, while maintaining tight tolerances, has made it a game-changer for both structural and cosmetic automotive parts. For example, manufacturers like BMW and Audi have incorporated meters of laser welds into their vehicle bodies, boosting both torsional stiffness and crash safety.
Robotic Welding: Consistency and Efficiency at Scale
Now, imagine a factory floor where robots—guided by advanced software—move with perfect timing, delivering flawless welds thousands of times a day. Automotive welding robots have revolutionized assembly lines, taking on the most repetitive, precise, and hazardous tasks. Their impact is felt across every major carmaker, from Toyota to BMW:
- Unmatched Consistency: Robots deliver the same high-quality weld, every time—removing human error and fatigue from the equation.
- Speed and Productivity: Automated systems can handle more than 90% of all vehicle welds, dramatically increasing output and reducing production time.
- Safety: Robots operate in environments too dangerous or monotonous for people, reducing workplace injuries and exposure to fumes or heat.
- Adaptability: Modern robotic cells can switch between different parts or welding techniques, ensuring flexibility as vehicle designs evolve.
For instance, Toyota’s Burnaston plant uses over 400 robots to weld underbodies with precision measured in tenths of a millimeter, while BMW’s facilities are now up to 98% automated in their welding operations. This level of automation ensures every weld meets strict OEM standards for strength, appearance, and reliability (AZoRobotics).
How Laser and Robotic Welding Set OEM Quality Standards
So, what does this mean for car buyers and industry professionals? Simply put, these technologies ensure that every vehicle rolling off the line is built to the highest standards. Laser and robotic welding deliver:
- Repeatable Quality: Each weld is digitally monitored, inspected, and recorded—minimizing defects and maximizing safety.
- Design Freedom: Engineers can create lighter, more complex structures, knowing that advanced welding will hold everything together.
- Cost Efficiency: Although initial investments are high, the long-term savings in labor, rework, and material waste are substantial—especially at production volumes above 200 units.
Real-World Example: Shaoyi’s Advanced Welding Solutions
Looking for components that meet these demanding standards? Suppliers like Shaoyi leverage both robotic and laser welding in their state-of-the-art production lines. This means every chassis or assembly part is crafted with the same precision and consistency as those used by leading global automakers. Their IATF 16949 certification, digital quality controls, and rapid prototyping ensure that whether you’re building a prototype or a full production run, you get defect-free, high-strength welds—every time.
As the industry moves toward electric and autonomous vehicles, expect even greater reliance on these advanced welding methods. Smarter robots, hybrid laser systems, and closed-loop quality checks are making automotive welding safer, faster, and more reliable than ever before. Next up, we’ll explore how these high-tech advances are opening up new career opportunities in automotive welding—and what skills you’ll need to get started.
Exploring Career Opportunities in Automotive Welding
Ever wondered where a passion for working with metal and vehicles could take you? The world of automotive welding offers a wide range of career opportunities—whether you dream of restoring classic cars, fabricating custom parts, or joining the high-tech side of manufacturing. Let’s break down the most common automotive welding jobs and the skills and certifications you’ll need to succeed.
Where Automotive Welding Can Take You
Imagine starting your day in a busy repair shop, on a race team’s fabrication crew, or inside a state-of-the-art manufacturing plant. Each path offers unique challenges and rewards. Here are some of the top roles in the field:
- Automotive Repair Welder: Handles frame, body, and chassis repairs in workshops or dealerships. Tasks include patching rust, fixing collision damage, and restoring structural integrity in vehicles of all kinds.
- Custom Fabricator: Builds or modifies parts for hot rods, race cars, or specialty vehicles. Precision, creativity, and advanced welding skills are a must.
- Motorsport Fabricator: Works with racing teams to create lightweight, high-performance components—often under tight deadlines and with demanding specifications.
- Manufacturing/Production Welder: Joins assembly lines to weld frames, bodies, and components using robotic or manual techniques. Consistency and speed are key.
- Welding Inspector or Supervisor: Oversees quality, safety, and compliance in repair shops or factories. Requires a deep understanding of welding standards and processes.
- Robotic Welding Technician: Programs, maintains, and troubleshoots automated welding systems—an increasingly important role as factories adopt advanced robotics.
- Welding Educator or Trainer: Teaches the next generation of welders in trade schools, community colleges, or industry training centers.
Skills and Training: What Employers Look For
You might be asking, “What does it take to land one of these jobs?” Employers value a mix of technical skills, real-world experience, and a commitment to safety. Here’s what helps you stand out:
- Hands-on welding experience: Proficiency in MIG, TIG, arc, and spot welding is a must. The more processes you master, the more versatile you become.
- Blueprint reading and fabrication: Understanding technical drawings and being able to plan or fabricate custom parts is a major asset, especially in custom shops or motorsports.
- Material knowledge: Knowing how to work with steel, aluminum, and specialty alloys is increasingly important as vehicles become more advanced.
- Problem-solving and attention to detail: Whether you’re chasing down a crack in a chassis or programming a robotic arm, precision matters.
- Safety practices: Familiarity with PPE, fume extraction, and safe shop procedures is non-negotiable for every employer.
Automotive Welding Certification: Your Ticket to More Opportunities
Want to boost your credibility and unlock higher-paying roles? Earning an automotive welding certification is a proven way to show employers you have the skills they need. The American Welding Society (AWS) offers a range of credentials, including:
- Certified Welder Program (CWP): Validates hands-on skills for entry-level and experienced welders. Testing covers real-world procedures used in automotive and other industries (UTI).
- Certified Welding Inspector (CWI): For those with experience, this credential qualifies you to inspect welds for safety and compliance—a common step up for senior technicians or supervisors.
- Certified Robotic Arc Welding (CRAW): Focuses on programming and operating robotic welding systems, perfect for jobs in advanced manufacturing.
- Other specialized certifications: Options like Certified Resistance Welding Technician (CRWT) or Certified Welding Educator (CWE) cater to those pursuing niche or leadership roles.
Most programs require a mix of classroom learning, hands-on practice, and passing a performance-based test. Some roles, especially in manufacturing or inspection, may require several years of experience before you’re eligible for advanced credentials.
Career Growth: From Apprentice to Expert
Picture this: You start as an apprentice or entry-level welder, learning the ropes in a local shop or through a formal training program. With experience and additional certifications, you can move up to journeyman, master welder, or even supervisor roles. In some cities, like Philadelphia, apprenticeships often lead to full-time work—with around 90% of participants finding jobs within six months of completion (PTT.edu). The clear career ladder makes it easy to plan your next steps and aim for higher pay or more specialized work.
As the industry evolves with new materials and automation, demand for skilled welders continues to rise. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to specialize, there’s never been a better time to explore the world of automotive welding. Next, we’ll look at when chemical welders and adhesives are the right solution—and why some repairs still demand the heat and strength of a traditional weld.

When to Use Chemical Welders Like JB Weld or Plastic Welders for Car Repairs
Ever stood in the garage, tube of JB Weld in hand, wondering if it’s the answer to your car’s latest problem? Or maybe you’ve heard about plastic welding and wondered how it stacks up against traditional metal welding. Let’s break down when chemical welders and adhesives make sense—and when only a true weld will do.
Understanding the Options: Adhesives, Plastic Welding, and Traditional Welding
Imagine you’ve got a cracked plastic bumper, a stripped metal thread, or a rust hole in your frame. Each repair scenario calls for a different approach. Here’s what you need to know about the main options:
- Epoxy adhesives (like JB Weld): Two-part formulas that, when mixed, create a bond tougher than most other glues. They’re versatile and can handle a wide range of materials and conditions (J-B Weld).
- Automotive plastic welders: Specialized tools that use heat to fuse plastic components, restoring both structure and appearance—especially useful on modern vehicles packed with plastic parts.
- Professional welding: The gold standard for strength and durability, especially for load-bearing or safety-critical repairs. Involves high heat to fuse metals directly, providing unmatched joint integrity.
Which Method Fits Your Repair? A Quick Comparison Table
| Repair Scenario | JB Weld (Epoxy Adhesive) | Automotive Plastic Welder | Professional Welding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cracked plastic bumper or headlight tab | Temporary fix, not recommended for high-stress areas | Best solution; restores structure and appearance | Not applicable |
| Stripped metal threads (oil pan, valve cover) | Effective for low-stress, non-structural repairs | Not applicable | Can be used for permanent fix (weld and re-tap) |
| Rust hole in body panel | Temporary patch only; not a structural repair | Not suitable | Recommended for lasting, safe repair |
| Cracked or broken frame/chassis | Not recommended—insufficient strength | Not suitable | Essential for safety and integrity |
| Bonding dissimilar materials (metal to plastic) | Possible with specialized adhesives; check compatibility | Not suitable | Limited; may require mechanical fasteners |
Pros and Cons: When Adhesives or Plastic Welding Make Sense
- Epoxy adhesives (JB Weld automotive): Great for quick fixes, filling small gaps, or bonding non-load-bearing parts. They’re waterproof, heat-resistant, and easy to apply. But they lack the sheer and tensile strength needed for structural repairs and require precise surface prep for a lasting bond.
- Automotive plastic welders: Ideal for repairing plastic bumpers, fenders, and interior panels. This method restores original strength and is more eco-friendly than replacing parts. However, it’s only suitable for thermoplastic materials and requires the right tools and technique.
- Professional welding: The only safe choice for frames, chassis, suspension mounts, and safety-critical components. It creates a permanent, load-bearing bond that adhesives simply can’t match.
Key Takeaways: Safety First
- Use JB Weld automotive and other epoxies for non-structural, low-stress repairs—think small brackets, minor leaks, or cosmetic fixes.
- Reach for an automotive plastic welder when repairing plastic bumpers, fenders, or panels. It’s the best way to restore both form and function.
- Always choose professional welding for anything involving the vehicle’s structure, suspension, or safety systems. Adhesives are not a substitute for proper welds when it comes to strength and crashworthiness.
Imagine patching a rusted frame with glue—sounds risky, right? That’s because it is. When safety, longevity, and performance are on the line, only a true weld will do. In the next section, we’ll wrap up this guide with a summary of the most important takeaways and how to approach your next repair or project with confidence.
Conclusion
When you look back at everything covered in this guide, one thing stands out: the strength, safety, and performance of any vehicle depend on the quality of its welds. Whether you’re a weekend DIYer patching a rusty panel or a professional fabricator working on the latest EV chassis, understanding automotive welding solutions is the key to success. But with so many techniques, materials, and technologies available, how do you make the best choices for your next project?
Building Confidence in Your Welding Projects
- Master the basics first. Knowing when to use MIG, TIG, spot welding, or advanced methods helps you match the right process to the job. This ensures every weld is strong, clean, and reliable (Number Analytics).
- Prioritize safety and quality. The best results come from careful preparation, proper PPE, and a focus on structural integrity. Don’t cut corners—your safety and your vehicle’s longevity depend on it.
- Leverage technology for high precision automotive welding. Advanced solutions like laser and robotic welding deliver unmatched consistency, speed, and strength—especially for complex or safety-critical assemblies.
- Know when to go pro. Some repairs, especially those involving frames or chassis, require the expertise, equipment, and quality controls of a certified shop or supplier.
- Choose components that meet industry standards. High-quality, pre-fabricated parts ensure safer, longer-lasting repairs and upgrades.
Why High-Precision Welding and Trusted Suppliers Matter
Imagine tackling a major repair with confidence, knowing every weld and component meets or exceeds OEM standards. That’s where suppliers like Shaoyi come in. Their state-of-the-art robotic welding lines, IATF 16949 certification, and rigorous quality checks provide peace of mind—whether you’re restoring a classic or building a next-generation EV. By choosing high-precision assemblies and industry-compliant parts, you minimize risk, reduce rework, and ensure every project is built to last.
Ready for Your Next Automotive Welding Challenge?
- Are you planning a DIY repair or custom build? Start by reviewing the core welding principles and safety tips from this guide.
- Need advanced solutions for complex assemblies? Explore suppliers who specialize in high-precision automotive welding.
- Looking to upskill or launch a career? Consider formal training and industry-recognized certifications to unlock more opportunities.
Remember, every successful project starts with knowledge and ends with quality. By applying the insights from this guide and partnering with trusted experts, you’ll approach your next automotive welding project—big or small—with complete confidence. For more resources, expert advice, or to connect with leading suppliers, keep exploring and never stop learning. Your journey to safer, stronger vehicles begins with the right weld—every time.
Automotive Welding: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What type of welding is most commonly used in automotive repairs?
MIG welding is the most widely used process for automotive repairs because it is versatile, efficient, and suitable for joining steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Its ease of use makes it ideal for both body panels and frame work, while advanced shops may also use TIG and spot welding for specific applications.
2. How do I choose the right welder for automotive projects at home?
Selecting the right welder depends on your project type, materials, budget, and skill level. MIG welders are typically the best starting point for DIYers due to their versatility and beginner-friendly features. For projects involving aluminum or precision work, consider a TIG welder. Always assess your power supply and workspace needs before purchasing.
3. What safety equipment is essential for automotive welding?
Essential safety gear includes an auto-darkening welding helmet, flame-resistant clothing, welding gloves, safety glasses, and respiratory protection. Proper ventilation or fume extraction is crucial to remove hazardous gases, and a fire extinguisher should always be within reach in your workspace.
4. When should I use chemical welders like JB Weld instead of traditional welding?
Chemical welders such as JB Weld are suitable for non-structural, low-stress repairs—like filling small gaps, sealing leaks, or bonding minor components. For any structural, safety-critical, or load-bearing repairs, traditional metal welding is necessary to ensure strength and durability.
5. What makes Shaoyi’s automotive welding chassis parts stand out?
Shaoyi offers IATF 16949-certified chassis parts manufactured with advanced robotic and laser welding for exceptional precision and consistency. Their comprehensive quality control, rapid prototyping, and proven track record with global automotive brands ensure reliable, defect-free assemblies that meet or exceed industry standards.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 

