Which Automotive Stamping Line Is Right for You?
As an essential part of modern auto manufacturing, automotive stamping dies and automation technologies have evolved significantly. In this blog, we explore three common types of automated stamping production lines widely used in the automotive industry: progressive die stamping, transfer die stamping, and tandem stamping lines. Each has its own advantages, and understanding their differences can help automotive manufacturers select the best solution based on their specific needs.
Common Types of Automotive Stamping Production Lines
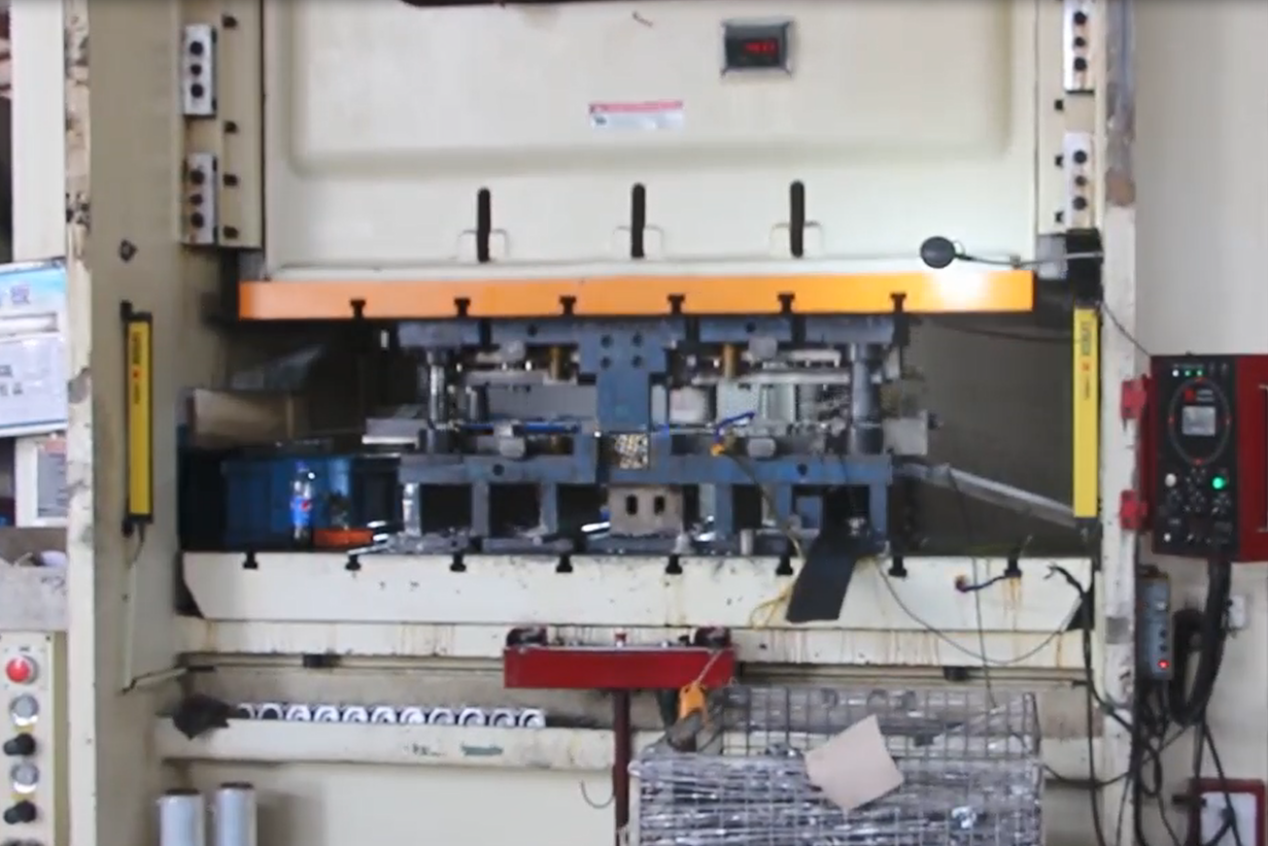
1. Progressive Die Stamping Line
Overview: The progressive die stamping line integrates coil material feeding, flattening, oiling, stamping, and unloading processes. It includes an uncoiler, leveling feeder, stamping press, progressive die, and automated unloading system. The progressive stamping die consists of multiple stations (sometimes over 20), where each performs a distinct operation like punching, trimming, flanging, shaping, and blanking. All actions are synchronized in one stroke.
Key Features:
High Production Efficiency: The line can achieve over 30 strokes per minute.
Automation Friendly: From loading to unloading, all steps are automated, minimizing labor and human error.
Compact Footprint: A single press acts as a complete production unit.
Safety: Enclosed systems reduce risks during high-speed operations.
Drawback: Lower material utilization due to strip layout requirements and waste during part progression.
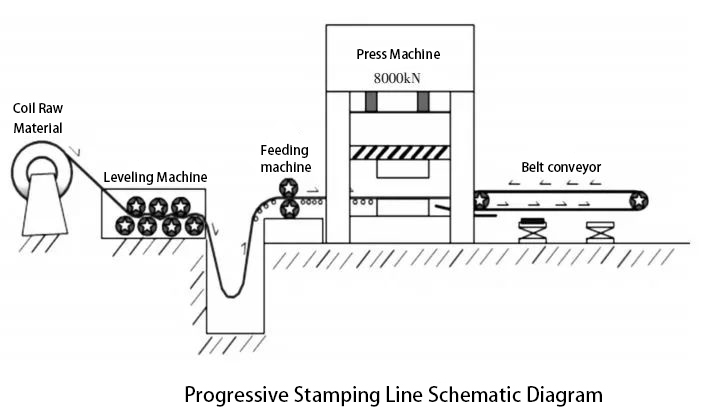
Progressive Stamping Line Schematic Diagram
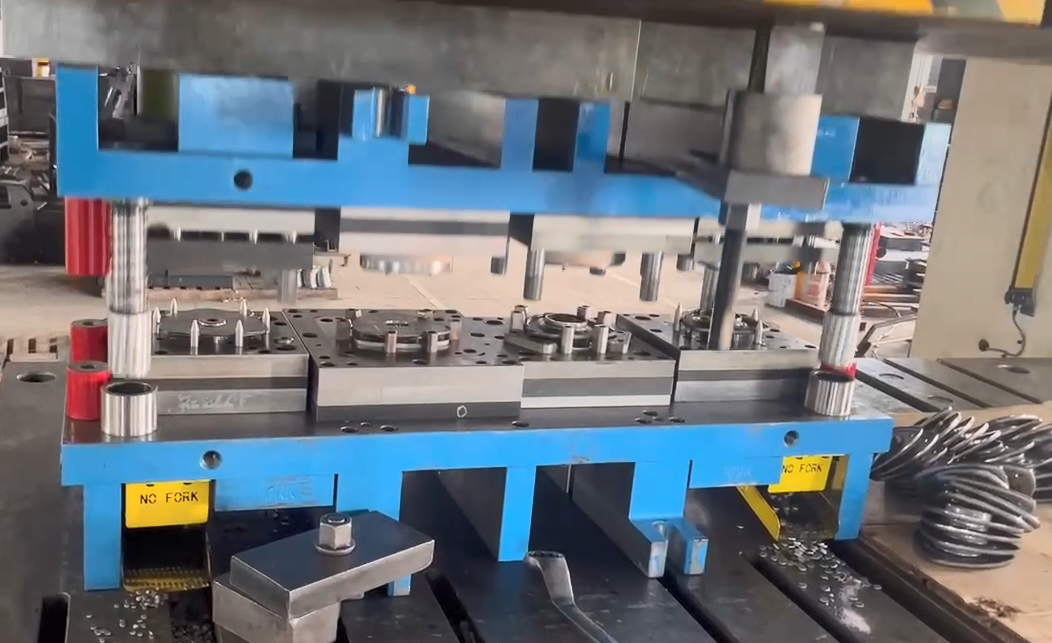

2. Transfer Die Stamping Line
Overview: A high-tonnage press is equipped with 4 to 5 individual dies, with robotic arms or feeders transferring parts between stations. It accommodates both coil and blank sheet materials.
Key Features:
Flexible Material Input: Supports both coil and sheet formats.
Mid-Level Productivity: Higher than tandem lines but typically slower than progressive systems.
Intelligent Sensors: Includes sensors for double-sheet detection, misfeed prevention, and safety monitoring.
Tooling Precision: Requires precise die height and alignment for consistent transfer.
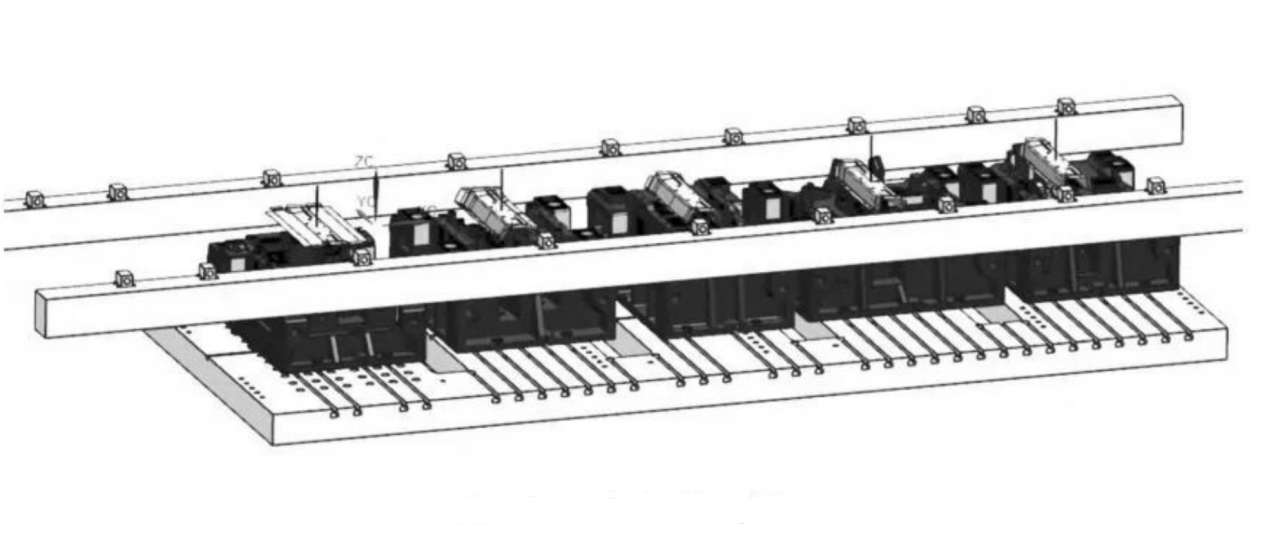
Multi-station Stamping Automation Line
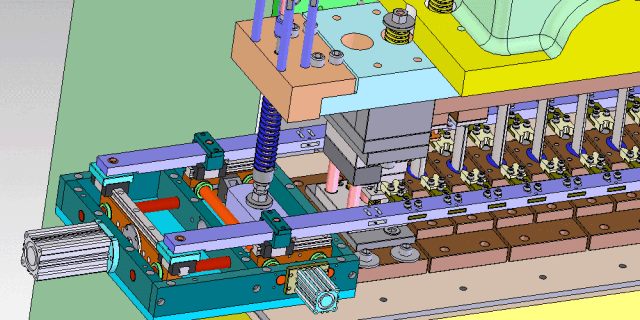
3. Tandem Stamping Line
Overview: Tandem lines consist of multiple presses arranged in series. Each press hosts one die representing a single operation. Robots or arms handle part transfer and unloading.
Key Features:
Versatile Application: Suitable for large and complex body panels.
High Flexibility: Accommodates a wide range of part shapes, sizes, and thicknesses.
Ease of Maintenance: Individual die stations allow independent adjustments and repairs.
Large Footprint: Multiple presses require more floor space.
Lower Output: Slower than progressive or transfer lines.
How to Choose the Right Stamping Line?
Choosing the right automotive stamping production line depends on the following factors:
Material Type & Properties: The material's formability, thickness, and hardness affect the press tonnage and feeding system selection.
Part Complexity: More intricate geometries may require transfer or tandem stamping for better forming results.
Monthly Production Volume: Higher volumes justify the investment in high-speed progressive stamping lines. Medium or low volumes may benefit from transfer or tandem systems.
Product Dimensions: Larger or asymmetrical parts may not be suitable for progressive dies.
Flexibility vs Efficiency:
For high-output needs: Progressive stamping is ideal.
For flexibility and customization: Tandem lines offer better adaptability.
Practical Application in the Automotive Industry
Progressive Stamping Lines: Ideal for high-volume, small to medium-sized automotive parts, such as brackets, clips, and reinforcements.
Transfer Lines: Suitable for medium-sized parts with moderate forming complexity like cross members or structural rails.
Tandem Lines: Best for large outer panels (doors, roofs, hoods) requiring complex forming and higher cosmetic standards.
Common Terms in Global Automotive Stamping
Progressive Die: PRG
Transfer Die: TRF
Tandem Line: TDM
These abbreviations are widely used internationally and represent industry-standard automation classifications.
Summary
Understanding the distinctions between progressive dies, transfer stamping, and tandem stamping lines helps auto parts manufacturers optimize cost, space, and productivity. As automotive lightweighting and efficiency become critical, the right choice of stamping automation technology ensures product consistency, factory safety, and competitive edge.
Contact us to learn how our stamping line solutions can match your automotive manufacturing needs.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
