EV Battery Thermal Management: Key Solutions and Materials
TL;DR
Effective thermal management solutions for EV battery enclosures are essential to ensure operational safety, optimize performance, and extend battery lifespan. The primary strategies involve active systems like air and liquid cooling, and passive systems using phase change materials (PCMs). These are enabled by a sophisticated ecosystem of components, including thermal interface materials (TIMs), encapsulants, and dielectric coatings, all working together to dissipate heat and prevent catastrophic thermal runaway events.
The Critical Role of Thermal Management in EV Batteries
The imperative for sophisticated thermal management in electric vehicle batteries stems directly from the electrochemical nature of the commonly used lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells. These batteries offer a winning combination of high energy density and a long lifecycle, but their internal chemistry presents significant thermal challenges. The electrolyte solution that facilitates the flow of electrical charge is typically made from highly flammable organic compounds, creating an inherent fire risk if not properly managed. Maintaining the battery pack within a narrow optimal temperature range is therefore not just a matter of performance, but of fundamental safety.
The most severe risk is a phenomenon known as thermal runaway. This is a cascading event that can begin when a single cell overheats due to an internal short-circuit, overcharging, or physical damage. This initial overheating can trigger a chain reaction, causing adjacent cells to overheat and combust, leading to a fire that propagates through the entire module or pack. These fires are notoriously difficult to extinguish and represent a significant safety concern. Effective thermal management systems are the primary defense against such events, designed to dissipate heat during normal operation and isolate failing cells to prevent propagation.
Beyond preventing catastrophic failure, temperature has a profound impact on a battery's day-to-day performance and longevity. High temperatures, even those well below the point of thermal runaway, accelerate the chemical degradation of battery components, reducing power capacity and shortening its effective life. Conversely, very low temperatures can cause power and energy loss, and in extreme cold, can lead to permanent damage or failure. A well-designed thermal management system ensures the battery operates within its ideal temperature window, maximizing efficiency, charging speed, and overall lifespan.
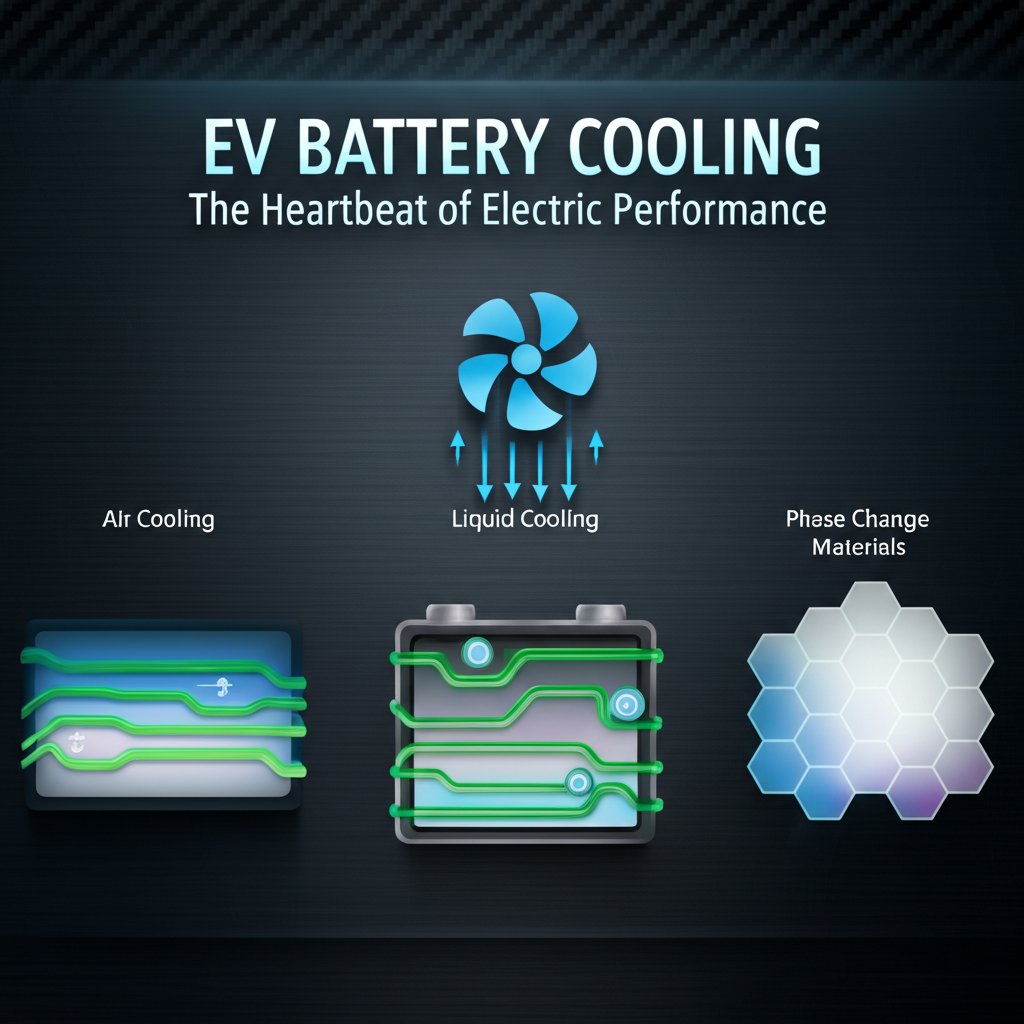
Core Thermal Management Strategies: A Comparative Analysis
Thermal management solutions for EV batteries are broadly categorized into active and passive systems. Active systems consume energy to function but offer higher performance, while passive systems rely on the principles of thermodynamics and require no external power. The choice of strategy depends on the vehicle's performance requirements, cost targets, and the power density of the battery pack.
Active Cooling Systems
Active systems use mechanical components to move a cooling medium and transfer heat away from the battery pack. The two primary methods are:
- Air Cooling: This is the simplest form of active management, using fans to circulate air around the battery modules and through cooling channels. It is relatively inexpensive and lightweight. However, its effectiveness is limited by the low thermal capacity of air, making it less suitable for high-performance EVs or vehicles operating in hot climates where the ambient air temperature is high.
- Liquid Cooling: This is the most common and effective method for modern EVs. A liquid coolant, typically a water-glycol mixture, is circulated through a network of tubes or cold plates that make contact with the battery modules. The liquid absorbs heat from the cells and transports it to a radiator, where it is dissipated into the environment. This method offers superior and more uniform cooling but adds complexity, weight, and cost to the system.
Passive Cooling Systems
Passive systems manage heat without powered components, making them simpler and more reliable, though often less powerful than active systems.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): These materials absorb large amounts of latent heat when they change phase, typically from solid to liquid. PCMs are integrated into the battery pack and absorb heat generated by the cells, melting in the process. This keeps the cell temperature stable. When the battery cools, the PCM solidifies, releasing the stored heat. While highly reliable, their capacity is finite, and they are best suited for managing intermittent heat loads rather than sustained high-power operation.
Strategy Comparison
| Strategy | Effectiveness | Complexity | Cost | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Cooling | Low to Moderate | Low | Low | Hybrids, early-generation or lower-cost EVs |
| Liquid Cooling | High | High | High | Most modern high-performance EVs |
| Phase Change Material (PCM) | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Peak temperature management, hybrid systems |
Essential Materials and Components in Thermal Systems
The effectiveness of any thermal management strategy relies on an ecosystem of specialized materials engineered to transfer, block, or manage heat and electricity within the battery enclosure. These materials are the unsung heroes that enable the cooling systems to function efficiently and safely.
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs): Even surfaces that appear smooth have microscopic imperfections that create air gaps. Since air is a poor conductor of heat, these gaps impede thermal transfer. TIMs are used to fill these gaps between a heat source (like a battery cell) and a cooling component (like a cold plate), ensuring efficient heat flow. These can take the form of thermally conductive adhesives, dispensable gap fillers, greases, or pads. Using dispensable fillers instead of solid pads can also help reduce vehicle weight, which is critical for maximizing range.
Encapsulants: These materials, often polyurethane foams, serve a dual purpose. First, they provide structural support, unitizing the battery assembly and protecting cells from shock and vibration. Second, and more critically, they act as a fire barrier. In the event of a single cell entering thermal runaway, a flame-retardant encapsulant can isolate the event, preventing the fire and intense heat from spreading to adjacent cells. This containment is crucial for giving vehicle occupants time to evacuate safely.
Dielectric Coatings: In a high-voltage environment like a battery pack, preventing electrical arcing is paramount. Dielectric coatings are applied to components like bus bars, cooling plates, and cell casings to provide electrical insulation. Advanced coatings are also designed to be thermally conductive, allowing them to contribute to heat dissipation while preventing short circuits. This dual functionality is essential for creating compact and energy-dense battery designs.
Insulating Materials: While some materials are designed to conduct heat away, others are designed to block it. Low-conductivity insulating materials, such as mica, ceramic papers, or aerogels, are strategically placed to shield healthy cells from the heat of a malfunctioning neighbor. This is another key strategy in preventing cell-to-cell thermal runaway propagation, forming a critical part of the battery's layered safety system.
System-Level Integration: Designing the Battery Enclosure Ecosystem
Effective thermal management is not about a single component, but about a holistic system where materials and strategies work in harmony within the battery enclosure. This integrated approach, often called a thermal management ecosystem, balances the need for thermal conductivity to cool cells during normal operation with the need for thermal insulation to protect cells during an off-normal event like thermal runaway. Every element, from the cell chemistry to the final enclosure, plays a role.
The design must consider the entire heat transfer path. Heat must move efficiently from the core of the battery cell, through a TIM, into a cold plate, and finally to a radiator. At the same time, the system must prevent that same heat from moving laterally from one cell to another in a failure scenario. This requires careful material selection and placement, creating a sophisticated thermal architecture that is both conductive and insulating where needed.
The structural design of the enclosure itself is fundamental, providing the framework for all thermal components and acting as the ultimate barrier against external environmental hazards like moisture and road salt. For automotive projects demanding such precision-engineered components, consider custom aluminum extrusions from a trusted partner. Shaoyi Metal Technology offers a comprehensive one-stop service, from rapid prototyping that accelerates your validation process to full-scale production, all managed under a strict IATF 16949 certified quality system.
Finally, a complete system-level design also incorporates venting strategies. If a cell does fail and enter thermal runaway, it releases a significant amount of hot gas. Controlled vents are designed to allow these gases to escape the pack in a managed way, preventing a dangerous pressure buildup while protecting adjacent cells from the hot ejecta. This integration of cooling, insulation, structural integrity, and venting defines a truly robust and safe EV battery enclosure.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
