Ordering Custom Forged Crankshafts: From First Quote To Final Delivery

Understanding Custom Forged Crankshafts and When You Need One
Ever wondered what separates a championship-winning engine from one that fails under pressure? Often, the answer lies in a single critical component: the crankshaft. When you're building a high-performance engine, restoring a vintage powerplant, or developing specialized industrial machinery, off-the-shelf parts simply won't cut it. That's where ordering custom forged crankshafts becomes essential.
So, what is a crankshaft exactly? In simple terms, it's the backbone of your engine that converts the linear motion of pistons into rotational power that drives your wheels or machinery. A custom forged crankshaft takes this fundamental component and engineers it specifically for your unique application, whether that means altered stroke lengths, specialized journal sizes, or materials designed to handle extreme stress.
This guide walks you through the complete ordering lifecycle, from initial research and specification gathering to final delivery. You'll learn how to evaluate manufacturers, understand pricing factors, and ensure quality standards are met every step of the way.
What Makes a Crankshaft Truly Custom
Standard crankshafts are designed to fit a broad range of applications, which means they're built for average conditions rather than your specific needs. A truly custom crankshaft, however, is engineered from the ground up to match your exact engine specifications, RPM range, and performance goals.
Imagine you're building a stroker engine that requires a longer stroke length than factory specifications allow. A stock component simply won't work. Custom manufacturing lets you specify precise journal locations, counterweight positioning, and material composition. This level of customization ensures optimal balance, reduced vibration, and maximum power transfer, elements that become critical when pushing engines beyond their original design parameters.
Why Forging Matters for Critical Engine Components
When comparing cast vs forged crankshaft options, the manufacturing process makes all the difference. Crankshaft casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold, a method that's cost-effective but creates a less refined grain structure. The forging process, by contrast, uses high-pressure compression to shape heated steel, aligning the metal's internal grain structure for dramatically improved mechanical properties.
Here are the key benefits that make a forged crankshaft the preferred choice for demanding applications:
- Superior Strength: The forging process aligns metal grains with the component's shape, creating tensile strengths between 140,000 to 165,000 psi when using materials like 4340 steel.
- Enhanced Fatigue Resistance: Forged components withstand high RPMs, intense vibrations, and repeated stress cycles without cracking or deforming, essential for engines producing over 750 horsepower.
- Improved Grain Structure: High-pressure forging refines the steel's internal structure, resulting in better impact resistance and load-bearing capacity.
- Greater Durability: Heat treatment processes like nitriding further harden the surface, extending the crankshaft's lifespan significantly compared to cast alternatives.
For anyone working with heavy-duty engines or high-performance builds, including those upgrading a forged crankset for racing applications, these advantages translate directly into reliability when it matters most. While cast crankshafts may serve light-duty vehicles adequately, they simply lack the structural integrity needed when conditions become demanding.

Applications That Demand Custom Forged Crankshafts
When most people think about custom crankshafts, high-octane drag racing or NASCAR engines immediately come to mind. But here's the reality: the demand for custom forged components extends far beyond the racetrack. From marine vessels navigating California's coastal waters to vintage motorcycle restorations and industrial power generators, specialized applications require crankshafts engineered for their unique operating conditions.
Understanding which category your project falls into helps you communicate effectively with manufacturers and ensures your specifications match your actual performance requirements.
Racing and Performance Applications
The performance crankshaft market remains the most visible sector, with manufacturers serving everything from professional racing teams to weekend warriors building garage projects. Whether you're developing a stroker crankshaft for increased displacement or a lightweight unit for high-RPM applications, racing demands push components to their absolute limits.
Consider the motorcycle crankshaft segment, which presents unique challenges. A harley crankshaft for a V-twin performance build requires different engineering than a dirt bike crankshaft designed for motocross abuse. The Harley Davidson crankshaft, particularly in twin cam crankshaft configurations, must handle massive low-end torque while maintaining balance at cruising speeds. Meanwhile, competition dirt bike units need to survive extreme RPMs and sudden load changes during aggressive riding.
Automotive performance applications span an equally diverse range. Pro Mod drag racers need crankshafts capable of handling 4,000+ horsepower for brief bursts, while endurance racing demands components that survive 24-hour punishment. Street performance builds typically prioritize durability and streetability over maximum power output.
Industrial and Marine Crankshaft Requirements
Here's where things get interesting: industrial and marine applications often represent the most demanding operating environments, yet they receive far less attention from specialty manufacturers. A marine crankshaft California boat builder specifies must withstand constant vibration, saltwater exposure, and extended operation under load. Unlike racing applications where engines run in short bursts, marine powerplants may operate continuously for hours at substantial power levels.
Industrial generators, compressors, and pumping equipment present similar challenges. These crankshafts must deliver reliable service for thousands of hours between maintenance intervals, often in harsh environments where failure means costly downtime.
Restoration projects add another dimension entirely. When rebuilding a vintage aircraft engine or classic truck powerplant, original specifications must be matched precisely while potentially upgrading materials for improved longevity. This requires manufacturers who understand historical designs and can replicate them using modern forging techniques.
| Application Type | Typical Stroke Range | Common Material Grades | Expected RPM Range | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drag Racing | 3.5" - 5.0" | 4340, EN30B | 7,500 - 10,000+ | Maximum strength, light weight |
| Circle Track Racing | 3.0" - 4.0" | 4340, 5140 | 6,500 - 9,000 | Durability, consistent balance |
| Motorcycle Performance | 2.5" - 4.5" | 4340, Billet Steel | 8,000 - 14,000 | Compact design, high RPM capability |
| Marine Applications | 3.5" - 6.0" | 4140, 4340 | 3,500 - 6,000 | Corrosion resistance, extended life |
| Industrial/Generator | 4.0" - 8.0"+ | 4140, 4340, Forged Carbon | 1,800 - 4,000 | Longevity, vibration dampening |
| Vintage Restoration | Varies by original spec | Period-correct or upgraded | Application specific | Dimensional accuracy, authenticity |
Once you've identified your application category and understood its typical requirements, you'll need to gather the precise technical specifications that manufacturers require. The next section covers exactly what measurements and details you must prepare before approaching any crankshaft supplier.
Technical Specifications You Must Provide When Ordering
Feeling overwhelmed by the technical details? You're not alone. Many first-time buyers hesitate to approach manufacturers because they're unsure what information they need to provide. Here's the good news: gathering your specifications becomes straightforward when you follow a systematic approach.
When ordering custom forged crankshafts, manufacturers need precise measurements and material preferences before they can quote your project accurately. Missing or incorrect specifications lead to costly revisions, extended lead times, and potentially unusable components. Whether you're building an ls crankshaft stroker setup or creating a custom sbc crankshaft for a vintage restoration, the preparation process remains fundamentally the same.
Essential Measurements for Your Custom Order
Think of your specification sheet as a blueprint that guides every manufacturing decision. The more complete your initial documentation, the smoother your ordering experience becomes. Professional crankshaft request forms, like those used by industry suppliers, typically require information spanning engine details, dimensional specifications, and application requirements.
Here's a step-by-step process for gathering your specifications:
- Document Your Engine Configuration: Record the engine make, type, and code. Include the number of cylinders, expected maximum RPM, projected horsepower, and torque figures. For turbocharged or supercharged applications, note boost pressure and combustion pressure specifications.
- Measure Stroke and Journal Dimensions: Determine your original stroke length and required stroke for your build. For reference, Small Block Chevrolet crankshafts range from 3.00" stroke (265/283 engines) to 3.75" stroke (400 engines). Your sbc crankshaft identification process should confirm whether you're working with small, medium, or large journal sizes.
- Record Cylinder Spacing: This critical dimension determines journal placement along the crankshaft's length. Measure from cylinder bore centerline to centerline for accurate spacing.
- Specify Rod Journal Requirements: Document the pin diameter (rod journal diameter) and pin width your connecting rods require. These dimensions must match your rod bearings precisely.
- Determine Main Journal Specifications: Measure main journal diameter and width. Note that different engine generations within the same family often use different main bearing sizes. For example, ls1 crankshaft and ls3 crankshaft specifications share the same stroke but may have different balancing requirements.
- Calculate Counterweight Requirements: Specify the quantity of counterweights required based on your engine's balance requirements. Internal vs. external balance configurations affect counterweight sizing significantly.
- Include Reciprocating Assembly Weights: Provide the weight of pistons including pins and rings. This data allows manufacturers to optimize counterweight design for proper balance.
If you're uncertain about any measurements, work with an experienced engine builder or machine shop. They can measure existing components, reference factory specifications, or help you determine optimal dimensions for your performance goals. Many manufacturers also accept sample crankshafts for reverse engineering when documentation isn't available.
Material Selection and Heat Treatment Specifications
Beyond dimensional requirements, material selection dramatically impacts your crankshaft's performance characteristics. The most common choice for high-performance applications is 4340 chromoly steel, which manufacturers like Keomit use for their forged crankshaft set production. This material offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio and responds well to heat treatment.
When specifying materials, consider these factors:
- 4340 Steel: The industry standard for performance and racing applications. Offers superior tensile strength and fatigue resistance when properly heat-treated.
- 4140 Steel: A cost-effective alternative suitable for moderate performance builds and industrial applications where extreme loads aren't anticipated.
- EN30B: Popular in European racing applications, offering similar properties to 4340 with slightly different machining characteristics.
- Billet Crankshaft Materials: When ordering a billet crankshaft machined from solid bar stock rather than forged, expect different lead times and pricing structures. Billet manufacturing involves extensive machining from round bar stock, requiring more time and tooling wear.
Heat treatment specifications should include surface hardening requirements. Nitriding creates an extremely hard surface layer that resists wear at bearing journals, while the core maintains toughness. Specify journal hardness targets if your application demands specific wear characteristics.
For stroker builds like an ls stroker crank project, also document bore size, compression ratio, fuel type, and whether nitrous oxide will be used. These factors influence material recommendations and design decisions. Don't forget to mention oil squirter presence, as this affects journal oiling provisions.
With your specifications documented, you're ready to understand how manufacturers transform raw steel into precision components. The next section explores the forging process itself and explains why manufacturing method matters as much as material selection.
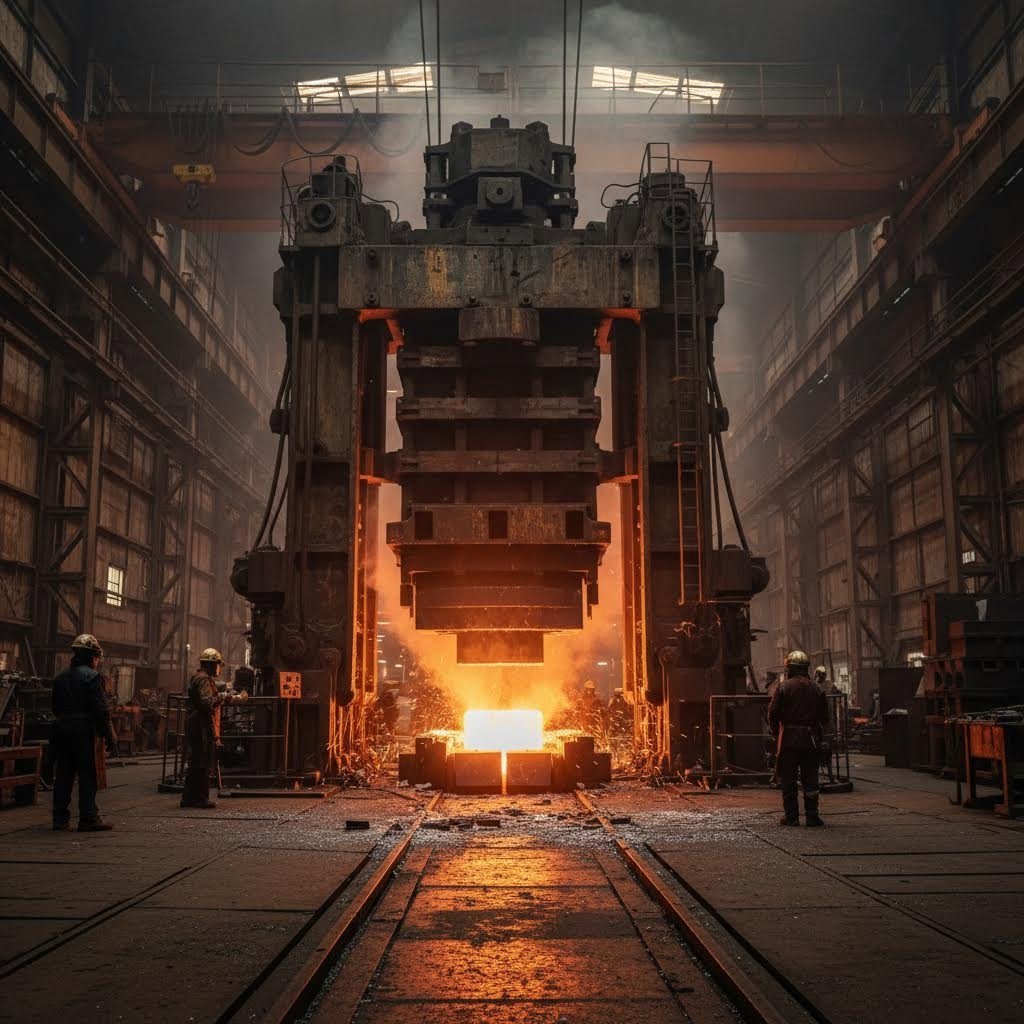

How Custom Forged Crankshafts Are Manufactured
Now that you've gathered your specifications, you might wonder what actually happens when a manufacturer receives your order. Understanding the forging of crankshaft components helps you ask smarter questions and evaluate potential suppliers more effectively. Here's where science meets craftsmanship.
The manufacturing method you choose fundamentally shapes your crankshaft's performance characteristics. While competitors often mention "forged" or "billet" without explanation, knowing the differences empowers you to make informed decisions that align with your project goals.
The Open-Die Forging Process Explained
Picture a solid steel bar heated to near-molten temperatures, glowing orange-red and ready for transformation. In open-die forging, this heated workpiece is placed between flat or simply shaped dies, then hammered or pressed with immense force. Unlike closed-die forging where metal fills a pre-shaped cavity, open-die forging allows the material to flow freely as it's shaped progressively into the desired form.
This process offers several distinct advantages for crankshaft production. According to Great Lakes Forge, open-die forging excels at producing components that can be customized throughout the manufacturing process. The technique accommodates one-off or short-run parts with unique shapes, making it ideal when ordering custom forged crankshafts for specialized applications.
Here's what happens during the forging sequence:
- Heating: The steel billet is heated to temperatures between 1,900°F and 2,300°F, making it malleable while maintaining structural integrity.
- Pre-Working: Initial deformation removes internal voids left from the steel's original solidification, creating a denser, more uniform material.
- Progressive Shaping: Multiple hammer or press operations gradually form the crankshaft's rough profile, including throws, journals, and counterweight locations.
- Controlled Cooling: The forged crank cools at a controlled rate to prevent internal stresses and optimize grain structure.
- Final Machining: CNC machining brings the forged blank to final dimensions with precision tolerances.
Closed-die forging, by comparison, uses matched dies that completely enclose the workpiece. While this method produces tighter tolerances directly from the forge, it requires expensive tooling that makes economic sense only for high-volume production. For custom single piece crankshaft orders or small batches, open-die forging typically offers better value and flexibility.
Forged vs Billet Crankshaft Manufacturing
The debate between forged and crankshaft billet manufacturing often generates strong opinions among engine builders. Understanding both approaches helps you choose wisely for your specific application.
A billet crank starts as a solid round bar of premium steel, typically 4340, and is entirely CNC-machined into its final shape. There's no heating or hammering involved. Every surface, journal, and counterweight is sculpted with surgical precision from the parent material. This process offers unmatched customization potential, as KingTec Racing explains, builders can specify exact stroke lengths, journal diameters, counterweight designs, and oiling passage layouts with complete flexibility.
However, here's where material science enters the conversation. When steel solidifies from molten state, it develops a grain structure. Crank casting processes produce non-uniform grains with potential voids. Machining a billet cuts through this existing grain structure, potentially exposing grain ends that become stress concentration points.
Forging produces components in which the grains are deliberately aligned in the direction of maximum strength, resulting in exceptional fatigue and impact resistance. This continuous grain flow follows the crankshaft's contours, channeling stress away from weak points rather than creating new vulnerabilities.
According to Trenton Forging, the controlled deformation during forging aligns grain structures with the component's geometry. Cracks propagate more easily parallel to grain direction, so having grains oriented perpendicular to stress points significantly improves durability. This explains why forged crankshafts dominate endurance racing and high-boost applications where fatigue resistance matters most.
So which should you choose? The decision depends on your priorities:
| Factor | Forged Crankshaft | Billet Crankshaft |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Structure | Aligned with component geometry | Uniform but non-directional |
| Fatigue Resistance | Superior under repeated stress | Excellent with proper heat treatment |
| Customization | Good within forging constraints | Unlimited design flexibility |
| Best Applications | Endurance racing, street performance, high-boost builds | Drag racing, prototype engines, extreme stroker builds |
| Typical Lead Time | Longer initial setup, faster repeat orders | Consistent machining time per unit |
For most performance applications, forged crankshafts deliver the optimal balance of strength, reliability, and value. Billet cranks shine when you need absolute dimensional freedom or are building a one-off prototype where grain flow concerns are offset by precision engineering and premium materials.
Understanding these manufacturing fundamentals positions you to evaluate suppliers effectively. But manufacturing capability means little without rigorous quality control. The next section examines the certifications, inspections, and testing protocols that separate reliable manufacturers from the rest.
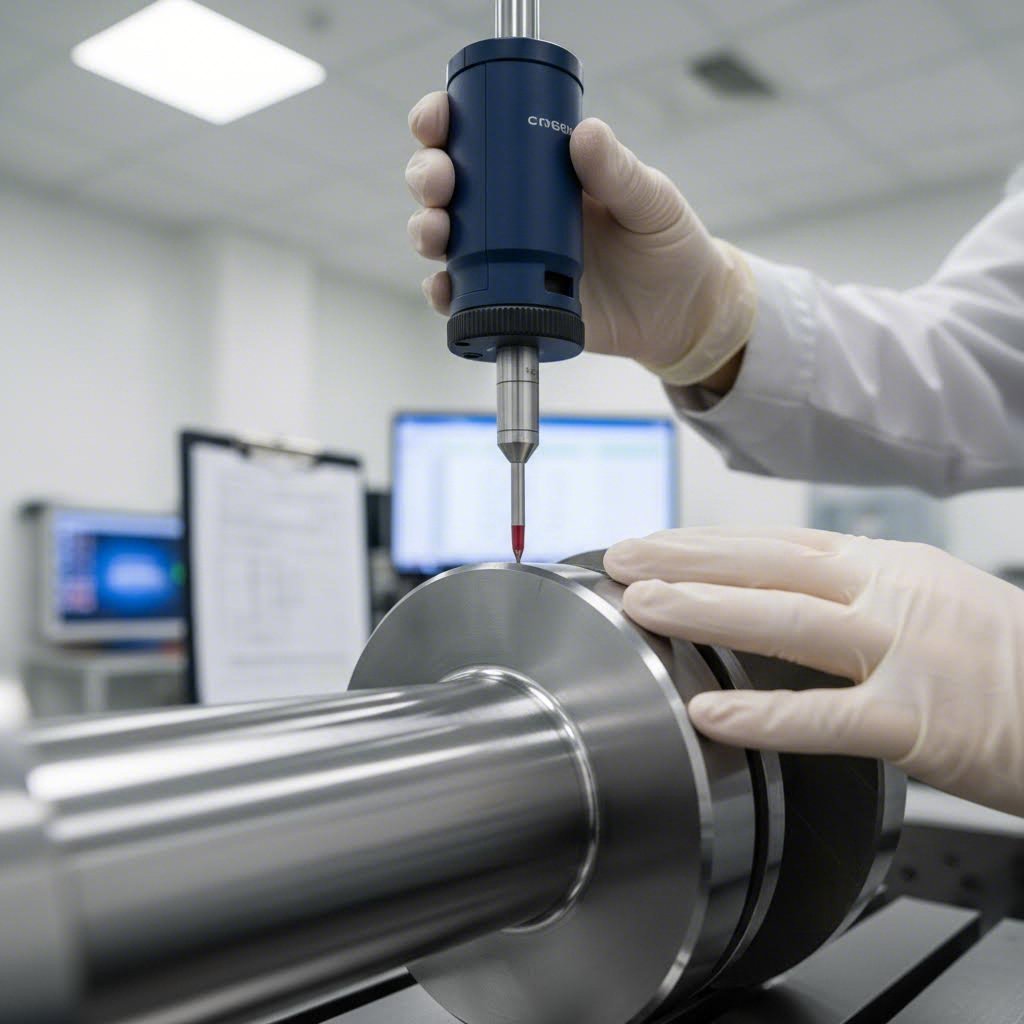

Quality Assurance and Inspection Standards to Expect
You've selected your manufacturer and submitted detailed specifications. But how do you know the finished crankshaft will actually meet those requirements? This is where quality assurance separates trusted suppliers from risky gambles. Yet surprisingly, most buyers never ask about inspection protocols until problems arise.
When ordering custom forged crankshafts, the quality control process matters as much as the forging itself. A precision crank that looks perfect can harbor invisible defects that lead to catastrophic failure under load. Understanding what certifications to look for and which testing methods to request protects your investment and ensures your engine performs reliably.
Quality Certifications That Matter
Not all certifications carry equal weight in the automotive crankshaft industry. Some represent genuine commitment to quality systems, while others amount to little more than paperwork exercises. Knowing the difference helps you evaluate potential crankshaft supply company options effectively.
The gold standard for automotive component manufacturing is IATF 16949 certification. According to DEKRA Certification, this standard was developed by the International Automotive Task Force specifically to streamline quality requirements across global automotive supply chains. IATF 16949 expands upon ISO 9001 foundations with industry-specific requirements including:
- Traceability Systems: Complete documentation tracking materials from raw steel through finished product, supporting regulatory compliance and warranty management.
- Safety-Related Process Controls: Specific protocols for components where failure creates safety risks, exactly the category crankshafts occupy.
- Customer-Specific Requirements: Flexibility to incorporate OEM and first-tier supplier quality demands without requiring multiple separate certifications.
- Continuous Improvement Frameworks: Structured approaches for identifying and eliminating defect sources over time.
For buyers, IATF 16949 certification signals that a manufacturer has invested in comprehensive quality management systems verified by independent auditors. IATF 16949 certified manufacturers like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology demonstrate this commitment through rigorous third-party audits, providing confidence that quality control extends beyond marketing claims into documented, verifiable processes.
Beyond IATF 16949, look for these additional credentials when evaluating a crankshaft shop:
- ISO 9001: The foundational quality management standard that IATF 16949 builds upon.
- SAE Compliance: Adherence to SAE J431 and J1199 specifications for automotive crankshaft dimensional and material requirements.
- API 614: Essential for crankshafts destined for petroleum, chemical, or gas industry applications.
Inspection and Testing Protocols to Request
Certifications establish framework; inspection methods deliver results. When discussing your order, ask specifically about testing protocols at each manufacturing stage. Here's what thorough quality control looks like throughout the production process:
- Incoming Material Verification: Chemical analysis and hardness testing of raw steel billets before forging begins.
- Post-Forging Inspection: Visual examination for forging defects, dimensional verification of rough forgings, and ultrasonic testing for internal voids.
- Heat Treatment Verification: Hardness testing at multiple locations to confirm proper treatment, with documentation of furnace parameters.
- Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI): Critical for detecting surface and near-surface cracks invisible to the naked eye.
- Dimensional Verification: Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspection of all critical dimensions including journal diameters, stroke length, and counterweight profiles.
- Surface Finish Measurement: Profilometer readings to verify journal surface roughness meets bearing requirements.
- Final Balance Check: Dynamic balancing verification with documented readings.
Among these methods, magnetic particle inspection deserves special attention. As industry experts explain, MPI works by magnetizing the crankshaft and applying ferrous particles to its surface. Any cracks or defects create magnetic field disturbances that cause particles to cluster visibly around the flaw. This technique detects even microscopic cracks that would otherwise go unnoticed until the crankshaft fails under stress.
The MPI process involves two primary magnetization methods:
- Direct Current (DC): Creates a constant magnetic field effective for detecting linear defects running parallel to the magnetization direction.
- Alternating Current (AC): Produces a fluctuating field more sensitive to fine surface cracks, catching smaller defects the DC method might miss.
Reputable manufacturers often combine both techniques for comprehensive coverage. Request documentation confirming MPI was performed using wet fluorescent particles under UV light, the most sensitive configuration available for eagle performance-level quality requirements.
Beyond inspection methods, understand the documentation you should receive with your finished crankshaft. A comprehensive quality package includes:
- Material certification with heat number traceability
- Heat treatment records with hardness test results
- Dimensional inspection report with CMM data
- MPI certification confirming no rejectable indications
- Dynamic balance report
- Surface finish measurements for bearing journals
This documentation serves multiple purposes. It verifies that your crankshaft price reflects genuine quality control investment. It provides reference data if warranty issues arise. And it demonstrates compliance with industry standards if your engine build requires regulatory approval.
When evaluating the automotive crankshaft you receive, the quality of documentation often reflects the quality of the component itself. Manufacturers who invest in rigorous inspection typically produce superior products, while those cutting corners on testing rarely deliver consistent results.
With quality standards established, you're prepared to evaluate manufacturers themselves. The next section guides you through comparing domestic and international options, examining factors beyond price that determine long-term satisfaction with your supplier relationship.
How to Evaluate and Compare Crankshaft Manufacturers
So you've documented your specifications and understand what quality standards to demand. Now comes the crucial decision: which custom crankshaft manufacturer actually deserves your business? This choice extends far beyond comparing price quotes. The manufacturer you select becomes a partner in your project, and that relationship's quality often determines whether your crankshaft arrives on time, meets specifications, and performs as expected.
Whether you're considering established domestic suppliers like Eagle Specialty Products Inc or exploring international options, the evaluation process requires examining factors that competitors rarely discuss. Let's break down what actually matters when comparing your options.
Evaluating Domestic vs International Manufacturers
The domestic versus offshore decision isn't as straightforward as it might seem. Each option presents distinct advantages and challenges that vary based on your specific project requirements.
Domestic manufacturers, including well-known names like Ohio crankshaft suppliers, Molnar crankshaft producers, and Crower cranks, typically offer several inherent advantages. According to Queen City Forging, North American forgers commonly provide pre-production engineering assistance and after-sale services on a regular basis. They can offer transport and delivery services timed to meet production requirements, supporting just-in-time schedules that many racing programs depend upon.
Communication flows more easily without language barriers or time zone complications. When you call with a technical question at 2 PM, someone answers rather than an email sitting unanswered for 12 hours. Cultural familiarity with American engine platforms, whether you're ordering an eagle crankshaft upgrade or a specialty restoration piece, means less explanation required.
International manufacturers, however, offer compelling advantages that deserve serious consideration:
- Cost Efficiency: Lower labor and overhead costs often translate into significant price advantages, particularly for larger orders.
- Manufacturing Capacity: Many overseas facilities operate larger equipment capable of handling diverse project sizes.
- Material Access: Some international suppliers maintain relationships with specialty steel mills, offering material grades difficult to source domestically.
The key to successful international sourcing lies in proper vetting. Quality standards vary dramatically between offshore suppliers, and the price advantages disappear quickly if components require rework or replacement. Request IATF 16949 or equivalent certifications, demand sample components before committing to production orders, and verify communication capabilities during your initial interactions.
Proximity to major shipping ports significantly impacts delivery times for international orders. Manufacturers located near facilities like China's Ningbo Port or Rotterdam in Europe can ship products globally with reliable transit times. This geographic advantage often offsets the distance factor for buyers willing to plan ahead.
Key Questions to Ask Before Placing Your Order
Before committing to any manufacturer, whether domestic or international, thorough vetting protects your investment. These questions reveal capabilities that marketing materials often obscure:
- What is your typical lead time for custom orders? Get specific answers, not ranges. A manufacturer saying "4-6 weeks" versus "typically 5 weeks with current capacity" signals different levels of production control.
- Can you provide references from similar projects? Any established manufacturer should readily offer contacts who've completed comparable orders. Hesitation here raises red flags.
- What engineering support do you provide during the specification phase? The best suppliers catch specification errors before production begins, saving time and money.
- How do you handle specification changes after production starts? Understanding flexibility and associated costs prevents surprises.
- What inspection documentation accompanies finished components? As discussed in the previous section, comprehensive quality documentation reflects manufacturing discipline.
When evaluating suppliers like Ace Crankshaft Inc or smaller specialty shops, also inquire about their experience with your specific application. A manufacturer excelling at drag racing crankshafts may lack expertise in marine or industrial applications, despite technical capability.
| Evaluation Criteria | Domestic Manufacturers | International Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Lead Time | 4-8 weeks | 6-12 weeks (including shipping) |
| Minimum Order Quantity | Often single-unit capable | May require 3-5 unit minimums |
| Engineering Support | Direct consultation common | Varies widely by supplier |
| Certifications | IATF 16949, ISO 9001 standard | Verify independently |
| Communication | Same time zone, no language barriers | Potential delays, translation needs |
| Location Advantage | Faster domestic shipping | Cost savings, port proximity matters |
| Price Point | Premium pricing typical | Often 20-40% lower |
Requesting samples before committing to production orders remains essential, especially with unfamiliar suppliers. A sample crankshaft, even one not matching your exact specifications, reveals machining quality, surface finish standards, and documentation practices. The investment in a sample often prevents far costlier mistakes in production.
Review previous work whenever possible. Ask for photographs of similar completed projects, and if visiting the facility isn't practical, request a video tour. Modern communication tools make virtual facility assessments straightforward, and manufacturers confident in their operations welcome such scrutiny.
With your manufacturer selected and vetted, the practical questions of cost and timing take center stage. The following section addresses the pricing factors and lead time expectations that shape your project planning.
Pricing Factors and Lead Time Expectations
You've selected a manufacturer and understand quality requirements. Now the inevitable questions arise: how much is a crankshaft going to cost, and when will it arrive? These practical concerns shape project planning, yet most buyers enter negotiations without realistic expectations. Understanding the variables that drive crankshaft cost helps you budget accurately and avoid sticker shock when quotes arrive.
Here's the reality: custom forged crankshaft pricing isn't arbitrary. Every dollar reflects specific manufacturing decisions, material choices, and production complexities. When you understand what you're paying for, negotiations become more productive and expectations align with deliverables.
Factors That Influence Custom Crankshaft Pricing
When manufacturers calculate your quote, they're evaluating multiple cost drivers simultaneously. According to industry specialists, the cost of crankshaft production reflects precision engineering, advanced metallurgy, and specialized manufacturing processes designed to deliver unparalleled strength and performance.
Here are the primary factors influencing your final price, ranked from most to least impactful:
- Material Selection: The steel alloy you specify dramatically affects baseline cost. Standard 4340 steel offers excellent performance at reasonable prices, while exotic alloys like EN40B or 300M used in extreme motorsport applications carry significantly higher material costs. Harder materials also require more machining time and specialized tooling, compounding the expense.
- Design Complexity: Intricate designs with tight tolerances demand more advanced machining techniques and longer production times. As Xometry's manufacturing experts note, complex toolpaths create more movements and extend machining duration. Non-standard stroke lengths, unique journal configurations, and optimized counterweight designs all add engineering and production hours.
- Order Quantity: Single-unit custom orders carry the highest per-piece cost because setup expenses aren't distributed across multiple units. Larger production volumes benefit from economies of scale, spreading fixed setup costs across more components and reducing individual unit pricing.
- Finishing Requirements: Surface treatments like nitriding, specialized journal polishing, or premium heat treatment protocols add processing steps and cost. Each finishing operation requires equipment time, skilled labor, and quality verification.
- Machining Duration: Extended machining time translates directly to higher costs through electricity consumption, tool wear, and equipment utilization. Lightweighting features like knife-edging or gun-drilled mains require substantial additional machining.
- Tooling Requirements: Special cutting tools or custom fixtures needed for your specific design add expense. Tool purchase, maintenance, and replacement costs factor into quotes, particularly for unusual configurations.
- Balancing Precision: Achieving perfect dynamic balance for high-RPM applications requires meticulous work. Removing minute material amounts from counterweights or adding heavy metal slugs is time-consuming and demands skilled technicians.
So how much does a crankshaft cost when you factor everything together? Expect custom forged crankshafts to range from several thousand dollars for straightforward designs using standard materials to well over ten thousand for complex, exotic-material components. Racing applications pushing material limits naturally command premium pricing.
When evaluating quotes, remember that the cheapest option rarely delivers the best value. A crankshaft is a critical component where failure means catastrophic engine damage. Investing in quality manufacturing pays dividends through reliability and performance longevity.
Lead Times and What to Expect
Timing often matters as much as pricing. Whether you're preparing for a racing season or meeting production schedules, understanding realistic lead times prevents planning disasters.
Several variables affect turnaround when ordering custom forged crankshafts:
- Current Production Capacity: Manufacturers with full order books naturally quote longer lead times. Peak seasons for racing preparation create backlogs at popular suppliers.
- Material Availability: Specialty steel alloys may require sourcing time before production begins. Common materials like 4340 typically remain in stock, while exotic grades might add weeks.
- Design Complexity: Simple modifications to existing designs proceed faster than completely custom configurations requiring new engineering work.
- Heat Treatment and Finishing: Processes like nitriding require specific cycle times that can't be rushed without compromising quality.
- Quality Inspection Requirements: Comprehensive testing protocols add time but ensure the component meets specifications.
As supply chain experts at Lasso Supply Chain emphasize, engaging suppliers early in the design phase significantly reduces lead times. Collaborating with manufacturers during product development allows them to reserve production capacity and provide accurate timeline estimates.
Can you order a single custom crankshaft? Absolutely. Most specialty manufacturers accommodate single-unit orders, though per-piece pricing reflects the concentrated setup costs. If your project might eventually require additional units, discussing future quantity possibilities during initial negotiations sometimes unlocks better pricing structures.
For budget planning, expect domestic custom crankshaft orders to require four to eight weeks from order confirmation to shipping. International orders typically add shipping transit time, pushing total delivery windows to six through twelve weeks depending on origin and destination. Rush orders are sometimes possible but command premium pricing due to overtime and expedited material sourcing, as manufacturing operations VP Jason McClure notes: "Short lead times drive cost due to overtime and expedites on material and finishing."
Building buffer time into your project schedule protects against unexpected delays. Material sourcing complications, equipment maintenance, or quality issues requiring rework can extend timelines beyond initial estimates. Professional engine builders typically plan critical component orders with several weeks of cushion before absolute deadlines.
With pricing and timeline expectations established, you're prepared to navigate the actual ordering process from first inquiry through delivery coordination.
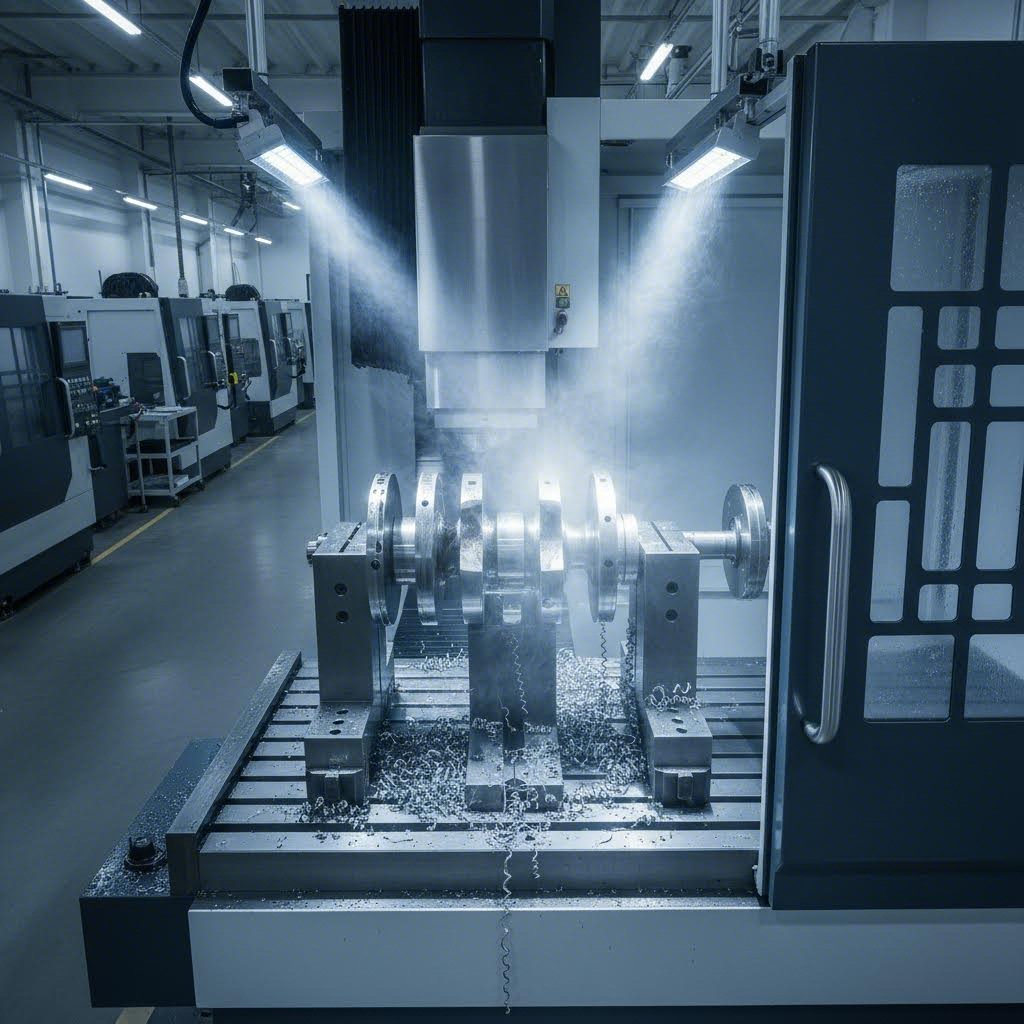
The Complete Custom Crankshaft Ordering Process
You've done your homework. Specifications are documented, manufacturers vetted, and budget expectations aligned. Now comes the moment of truth: actually placing your order and guiding it through production to delivery. This process has evolved significantly since the early days of aftermarket crankshaft development, when eagle rotating assemblies and similar performance components required extensive back-and-forth with manufacturers using paper drawings and phone calls.
Today's ordering process benefits from digital communication, CAD file sharing, and streamlined approval workflows. Yet the fundamental stages remain consistent whether you're ordering from a local crankshaft shop or an international supplier. Understanding each phase helps you maintain control throughout production and ensures your finished component matches expectations.
From Initial Inquiry to Design Approval
The journey from first contact to production authorization follows a predictable sequence. According to Western of Texas Forge & Flange, the typical ordering process for custom forged products involves several interconnected stages that build upon each other.
Here's the complete ordering timeline presented in sequential steps:
- Initial Inquiry and Consultation: Your first conversation with the manufacturer's engineering or sales team establishes project scope. Come prepared with your specification documentation, application details, and timeline requirements. Expect questions about quantity, delivery expectations, and whether you need prototyping before full production. Quality manufacturers may suggest adjustments or recommend optimal solutions based on their experience with similar projects.
- Formal Specification Submission: Submit detailed engineering drawings, CAD models, or sketches with complete dimensional information. Include material specifications, relevant industry standards (ASME, ASTM, SAE), and operating condition requirements like expected RPM range, horsepower levels, and boost pressure if applicable. The more complete your submission, the faster this phase progresses.
- Engineering Evaluation: The manufacturer's engineering team reviews your specifications for feasibility. They assess whether the design suits their production processes, verify material availability, and identify any potential issues. This evaluation typically takes three to seven business days for standard requests, longer for complex configurations.
- Quotation Development: Once evaluated, you receive a detailed quote covering material costs, tooling requirements, production expenses, heat treatment and finishing, estimated lead time, delivery terms, and payment conditions. Review this carefully, comparing against your budget expectations and timeline requirements.
- Design Review and Refinement: Before finalizing, most manufacturers conduct a formal design review. This collaborative session catches potential issues before production begins. Expect discussions about tolerance stackups, balancing approaches, and any specification clarifications needed. If necessary, a prototype may be created for approval.
- Purchase Order and Contract Agreement: Confirm your order by issuing a formal purchase order incorporating any negotiated terms. For larger projects, sign a contract agreement outlining responsibilities, milestone payments, timeline commitments, and warranty provisions.
- Material Procurement: With approval secured, the manufacturer sources and verifies raw materials against your specifications. Steel certification and heat number documentation begins at this stage, establishing the traceability chain that follows your crankshaft through completion.
- Tooling and Die Preparation: If your design requires custom forging dies or specialized machining fixtures, fabrication begins. This step adds lead time but ensures production proceeds efficiently once tooling is complete.
Communication best practices during these phases make a significant difference in outcome quality. Respond promptly to manufacturer questions, as delays on your end cascade through the production schedule. Document all specification discussions in writing, even if they occur during phone calls. Request written confirmation of any changes to the original quote or timeline.
For buyers seeking accelerated timelines, some manufacturers offer rapid prototyping services. For example, Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology provides prototyping in as little as 10 days, allowing you to evaluate form and fit before committing to full production. Their location near Ningbo Port further enables fast global shipping once production completes, an advantage worth considering when international sourcing makes sense for your project.
Production Monitoring and Delivery Coordination
Once production begins, your role shifts from specification to oversight. Staying engaged throughout manufacturing helps catch issues early and ensures the finished component meets your requirements.
The manufacturing sequence typically proceeds as follows:
- Forging Operations: The raw steel billet transforms into a rough crankshaft blank through open-die or closed-die forging. Request confirmation when this phase completes, including any initial dimensional checks performed on the forging.
- Rough Machining: CNC equipment brings the forging closer to final dimensions while maintaining material for finishing operations. This stage establishes journal locations, counterweight profiles, and overall geometry.
- Heat Treatment: Depending on your specifications, the crankshaft undergoes hardening, tempering, and surface treatment processes like nitriding. Request heat treatment documentation confirming cycle parameters and hardness test results.
- Finish Machining: Final dimensional accuracy comes from precision machining operations. Journal diameters, surface finishes, and all critical tolerances reach specification during this phase.
- Balancing: Dynamic balancing ensures the crankshaft runs smoothly at operating speeds. Request the balance report showing measured imbalance and correction details.
- Inspection and Testing: Comprehensive quality verification includes dimensional inspection, magnetic particle testing, and surface finish measurement. All documentation should be compiled for delivery with the finished component.
- Packaging and Shipping: The crankshaft receives protective packaging preventing transit damage. Labeling includes part numbers, material grades, and order reference information.
Modern manufacturing workflow software, as industry workflow experts describe, enables automated tracking and approval routing throughout production. Quality manufacturers provide regular status updates without requiring constant follow-up calls. If your supplier doesn't proactively communicate progress, establish check-in schedules at key milestones.
Shipping considerations deserve attention before production completes. For domestic orders, standard freight typically suffices, though high-value crankshafts warrant shipping insurance and signature confirmation. International shipments require additional planning:
- Customs Documentation: Ensure proper tariff classifications and country-of-origin documentation accompany the shipment.
- Transit Insurance: International freight carries higher damage risk; insure for full replacement value plus shipping costs.
- Delivery Timing: Factor port delays and customs clearance into your project schedule. Holiday periods in either country can extend transit times significantly.
- Import Duties: Understand applicable duties and taxes before the shipment arrives to avoid customs holds.
When your crankshaft arrives, inspect it immediately against the specification sheet and quality documentation. Verify journal dimensions with precision measuring equipment, check surface finishes, and confirm documentation completeness. Report any discrepancies to the manufacturer promptly; most reputable suppliers address legitimate issues quickly when notified early.
The aftermarket crankshaft industry has matured considerably from its origins serving early hot rodders. Today, whether you're sourcing crankshafts for sale from established domestic suppliers or exploring international manufacturing partnerships, the ordering process benefits from decades of refined best practices. Following these proven steps transforms what could be a frustrating experience into a straightforward path from initial inquiry to successful delivery.
With your custom crankshaft in hand, you're nearly ready to complete your engine build. The final section consolidates everything covered into actionable takeaways and a practical checklist for your next custom ordering project.
Taking the Next Step in Your Custom Crankshaft Project
You've journeyed through the complete lifecycle of ordering custom forged crankshafts, from understanding why forging matters to navigating manufacturer relationships and production timelines. Now it's time to put that knowledge into action. Whether you're a first-time buyer feeling more confident or an experienced engine builder refining your process, the path forward becomes clearer when you have a structured approach.
Success in custom crankshaft procurement comes down to four critical factors: thorough specification preparation, careful manufacturer evaluation, demanding quality standards, and realistic timeline planning. Miss any one of these elements, and your project risks delays, cost overruns, or components that don't meet performance requirements.
Your Custom Crankshaft Ordering Checklist
Before reaching out to manufacturers, confirm you've addressed each of these essential items:
- Engine Configuration Documented: Make, model, cylinder count, expected RPM range, and horsepower targets recorded
- Dimensional Specifications Gathered: Stroke length, main journal diameter, rod journal diameter, and cylinder spacing measured or researched
- Material Requirements Determined: Steel grade selected based on application demands (4340 for most performance builds)
- Reciprocating Assembly Weights Available: Piston, pin, and ring weights documented for proper counterweight sizing
- Manufacturer Shortlist Created: Multiple suppliers identified with relevant experience and certifications verified
- Budget Range Established: Realistic cost expectations set based on complexity and material requirements
- Timeline Buffer Built: Project schedule includes cushion for unexpected delays
- Quality Documentation Requirements Listed: Material certifications, inspection reports, and balance data specified upfront
For those seeking replacement crankshafts for restoration projects, add original equipment specifications and any deviation tolerances to your documentation. Engine crankshafts for vintage applications often require matching historical dimensions while potentially upgrading materials for improved longevity.
Moving Forward With Confidence
The knowledge you've gained transforms what many consider an intimidating process into a manageable project. You understand why forged cranks outperform cast alternatives, what specifications manufacturers need, how quality control protects your investment, and what realistic pricing and timelines look like.
The most successful custom crankshaft projects balance three competing priorities: quality that ensures reliability, cost that fits your budget, and lead time that meets your schedule. Compromising too heavily on any single factor creates problems. Invest in quality where it matters most, plan timelines with realistic buffers, and remember that the cheapest option rarely delivers the best long-term value.
First-time buyers should start with a single conversation with a reputable manufacturer's engineering team. Bring your specification documentation, ask questions freely, and evaluate how responsive and helpful they are before committing. That initial interaction reveals much about the partnership you're entering.
Experienced builders can leverage this framework to refine existing processes. Perhaps you've overlooked certain quality documentation or haven't fully explored international manufacturing options. Each project offers opportunities to improve your approach.
Your custom crank shaft represents the heart of your engine build. The effort invested in proper ordering, from gathering precise specifications to verifying quality certifications, pays dividends through reliable performance and longevity. Whether you're building eagle cranks-level competition engines or restoring a classic crankshaft for motorcycle applications, the fundamentals remain consistent.
Take what you've learned here and apply it to your next project. The manufacturers exist, the processes are proven, and you now have the knowledge to navigate them successfully. Your custom forged crankshaft awaits.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ordering Custom Forged Crankshafts
1. What company makes custom crankshafts?
Several reputable manufacturers specialize in custom crankshafts, including Bryant Racing, Winberg Crankshafts, and Eagle Specialty Products in the United States. International options like Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology offer IATF 16949 certified manufacturing with rapid prototyping capabilities. When selecting a manufacturer, evaluate their certifications, engineering support, lead times, and experience with your specific application type.
2. How much horsepower can a forged crankshaft handle?
A quality 4340 forged crankshaft typically handles engines producing up to 1,500 horsepower reliably. For applications exceeding this threshold, billet crankshafts become the preferred choice due to their superior material uniformity. However, the actual capacity depends on factors including material grade, heat treatment quality, journal size, counterweight design, and whether the engine uses forced induction or nitrous oxide.
3. How much does a custom forged crankshaft cost?
Custom forged crankshaft pricing ranges from several thousand dollars for straightforward designs using standard 4340 steel to over ten thousand dollars for complex configurations with exotic materials. Key cost factors include material selection, design complexity, order quantity, finishing requirements like nitriding, and balancing precision. Single-unit orders carry higher per-piece costs since setup expenses cannot be distributed across multiple units.
4. What is the typical lead time for custom crankshaft orders?
Domestic custom crankshaft orders typically require four to eight weeks from order confirmation to shipping. International orders add shipping transit time, extending total delivery to six through twelve weeks. Factors affecting turnaround include current production capacity, material availability, design complexity, heat treatment requirements, and quality inspection protocols. Some manufacturers offer rapid prototyping in as little as 10 days for initial samples.
5. What specifications do I need to provide when ordering a custom crankshaft?
Essential specifications include engine make and configuration, stroke length, main journal diameter, rod journal diameter, cylinder spacing, counterweight requirements, and reciprocating assembly weights. You should also specify material grade preferences, heat treatment requirements, expected RPM range, horsepower targets, and whether the engine uses forced induction. Working with an experienced engine builder helps ensure accurate measurements when original documentation is unavailable.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
