A Comprehensive Overview About How Are The Cars Designed and Manufactured?
Introduction
Designing and manufacturing a vehicle is an incredibly complex and capital-intensive process. From initial market research to mass production, each step is meticulously planned to ensuring the final product meets consumer demands, safety regulations, and performance benchmarks . In this blog, we will provide an end-to-end look at how vehicles are developed, with a special emphasis on keywords like automotive manufacturing process, car design and development, and vehicle production stages.
1. Market Research Phase
Every successful Vehicle begins with a deep understanding of consumer needs. Automakers invest millions in market research to assess trends, consumer preferences, and purchasing behavior. Failing to make this research properly can lead to commercial failure, as seen in the past when certain models ignored regional preferences.
Professional agencies often conduct surveys, focus groups, and competitive analysis to guide automakers in defining the vehicle's segment, price point, and core features.
2. Concept Design Phase
The conceptualization stage involves turning ideas into preliminary designs. This process is divided into:
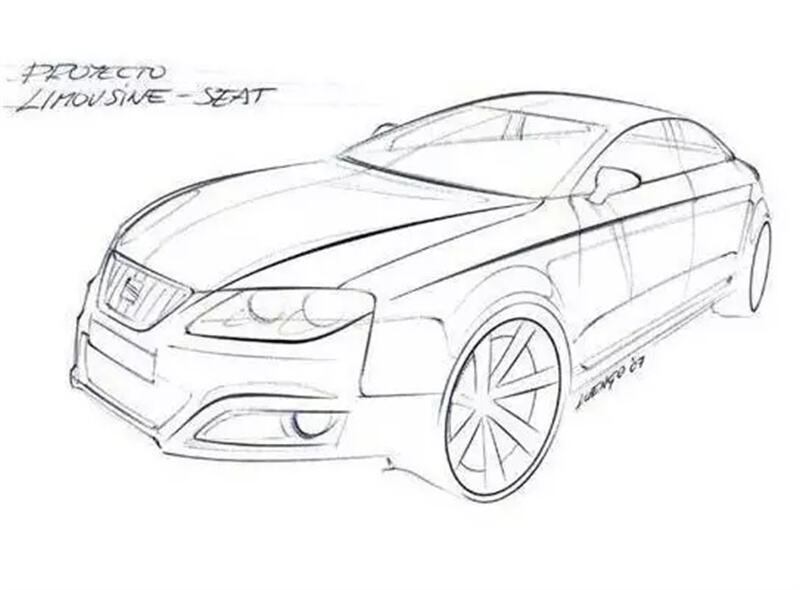

Vehicle Concept Design
A. Layout Planning
Engineers determine the basic configuration, including placement of the engine, transmission, chassis, and passenger cabin. This is usually sketched out in layout schematics.
B. Styling Design
Designers use hand-drawn sketches and digital tools to conceptualize the vehicle's exterior and interior. The focus is on aesthetics, brand identity, and ergonomics functionality .
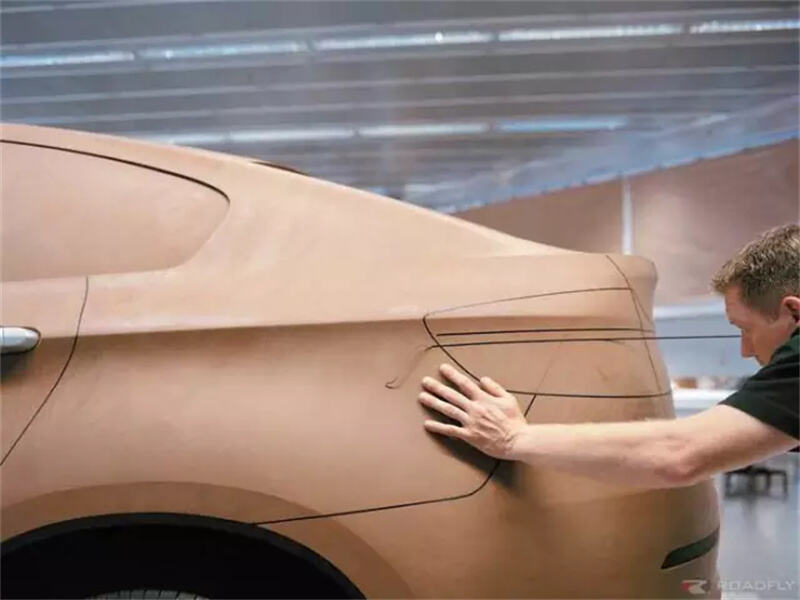
Vehicle Moulding sketches
C. Clay Modeling
Using 3D data from CAD software, a clay model is milled using a 5-axis machine. Initial 1: 5 scale models are reviewed, next, a full-size 1: 1 model for more detailed evaluation of style, proportions, and engineering feasibility.

3. Engineering Design Phase
Once the concept is finalized, it enters into the engineering phase, where all parts and systems are designed in detail:
A. Detailed Layout Design
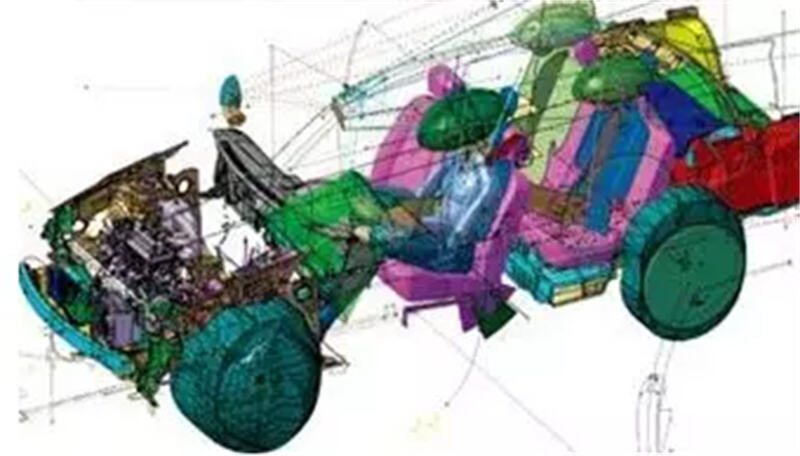
This involves specifying the dimensions, geometries, materials, and spatial arrangements of critical vehicle systems—such as the engine compartment, chassis system, and electrical system architecture—as part of the vehicle architecture definition.
Car body 3d drawing
B. Exterior Surface Data
Clay models are scanned to create 3D point cloud data, which is then processed using CAD software like CATIA or UG to generate precise digital surface models.
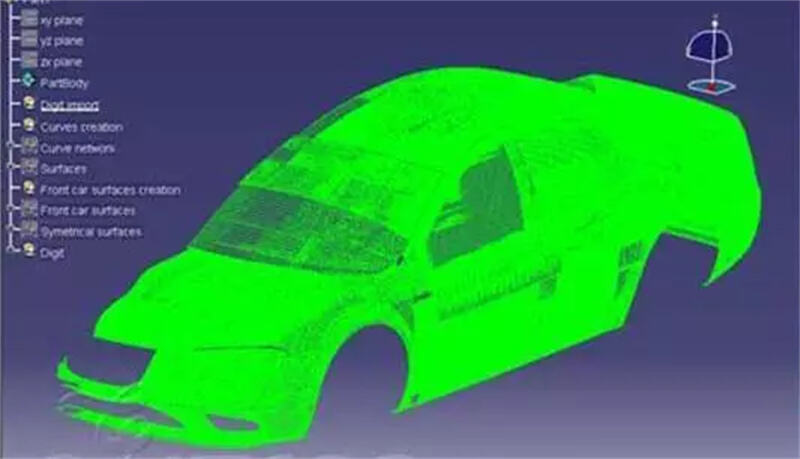

3D point cloud data
C. Powertrain Integration
Although many new models use existing engines, engineers still tailor the engine and transmission system for the new layout and performance targets.
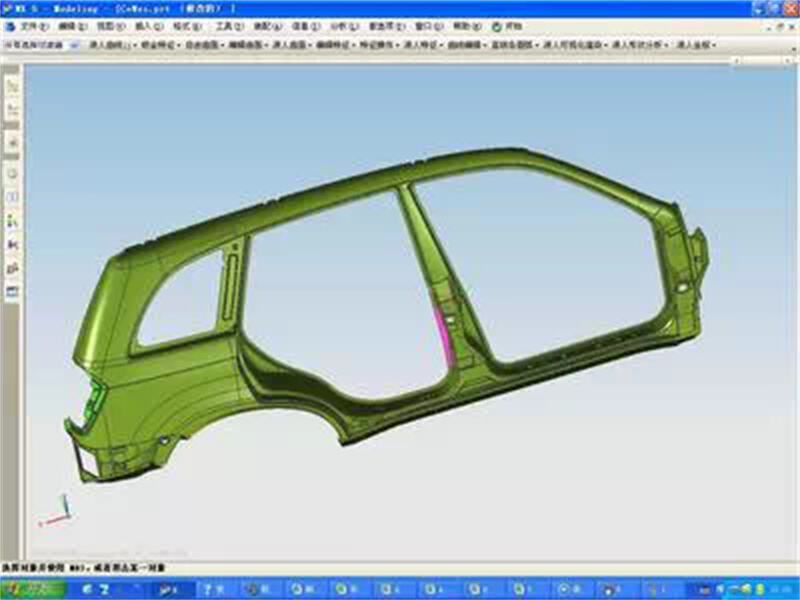
D. Body-in-White Design
The Body-in-White (BIW) is the welded sheet metal structure of the vehicle before painting. This includes structural components like the pillars, roof, and floorpan. It determines vehicle rigidity and crashworthiness.
E. Chassis Development
Engineers design and validate the chassis system, including the suspension, steering, braking, and drivetrain. These automtive components are critical for vehicle dynamics.
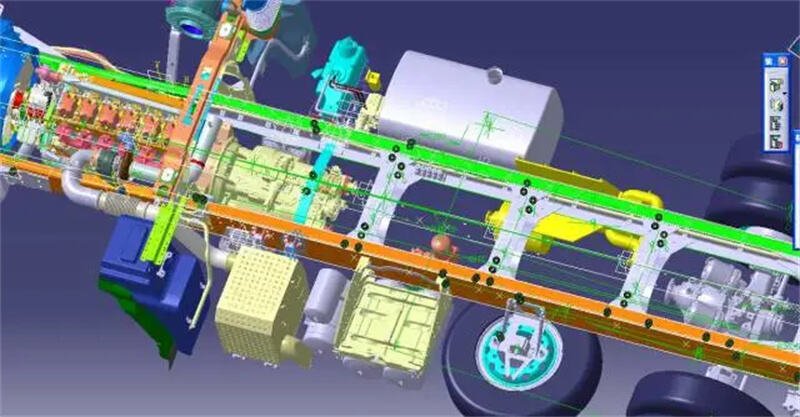
Automotive Chassis Structure
F. Interior and Exterior Trims
Most trim components (seats, dashboard, bumpers) are designed either in-house or by suppliers. Prototypes are evaluated for fit, comfort, safety, and manufacturability.
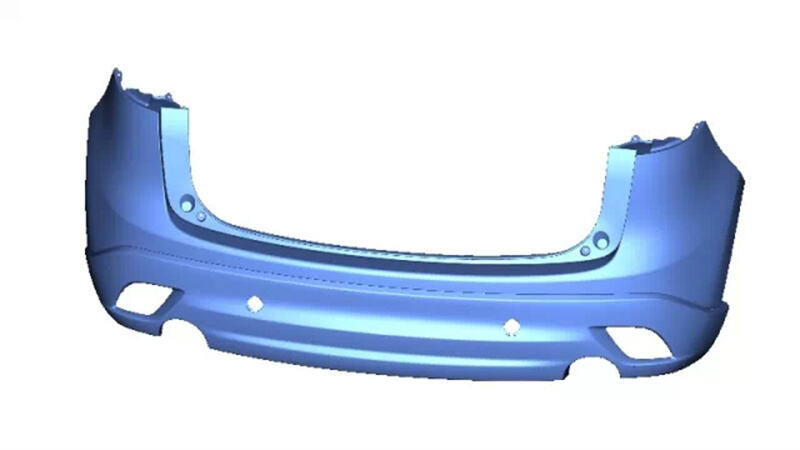
Car Bumper 3d Diagram
G. Electrical System Design
This covers the integration of lighting, infotainment, HVAC, sensors, and wiring. Electrical architecture is becoming increasingly important in modern vehicles.
4. Prototyping and Testing
After design, the vehicle enters into the prototype and testing phase, which ensures the car meets safety and performance benchmarks.
A. Wind Tunnel Testing
Aerodynamic efficiency is tested early on using clay models and refined later using full-scale prototypes.
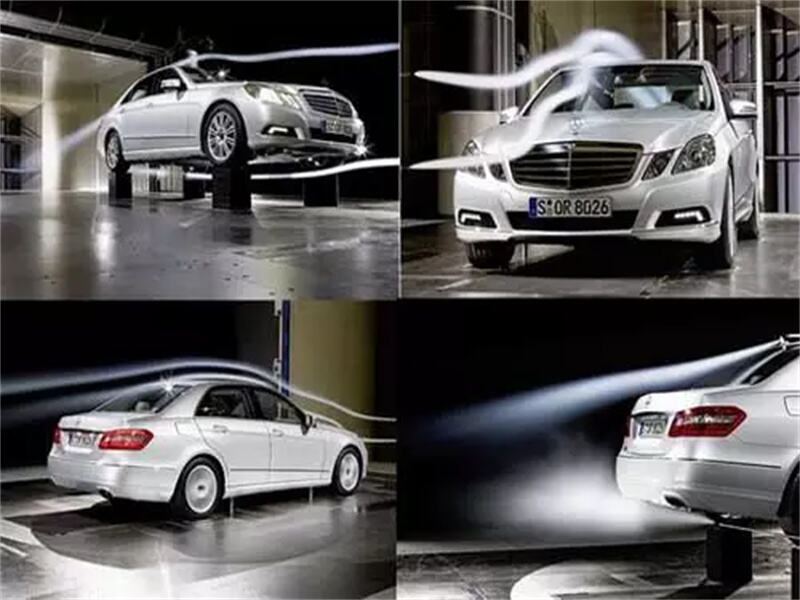

Automotive Wind Tunnel Testing
B. Proving Ground Testing
Manufacturers use test tracks to simulate different road conditions like gravel, potholes, and inclines to validate durability and ride comfort.
Proving Ground Testing
C. Real-World Road Testing
Prototypes undergo long-term road testing in various climates and terrains, from arctic cold to tropical heat, to assess reliability and adaptability.
road testing
D. Crash Testing
To meet regulatory standards, prototypes are subjected to controlled crash tests using dummies and sensors to evaluate passenger safety.
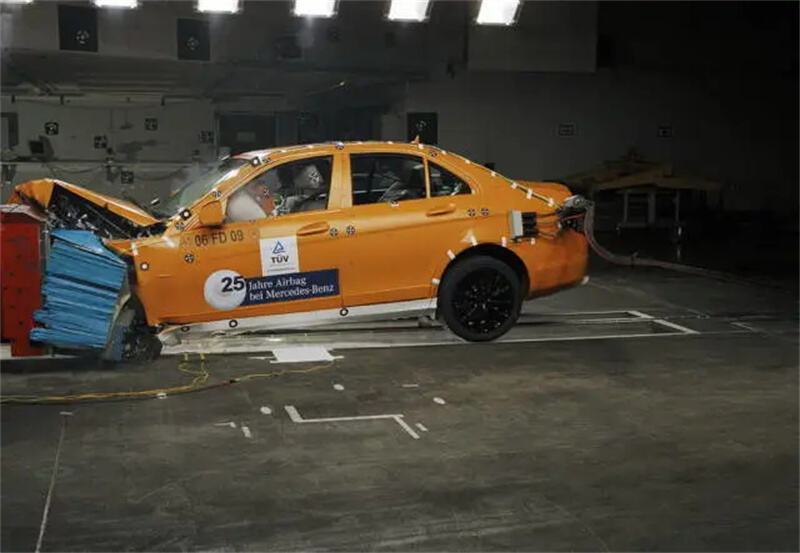

Crash Testing
5. Mass Production Phase
Once the prototype is validated, the car enters the mass production stage, which includes:
A. Stamping
Large steel or aluminum sheets are cut and stamped into body panels using precision molds. The quality of stamping dies directly affects the surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
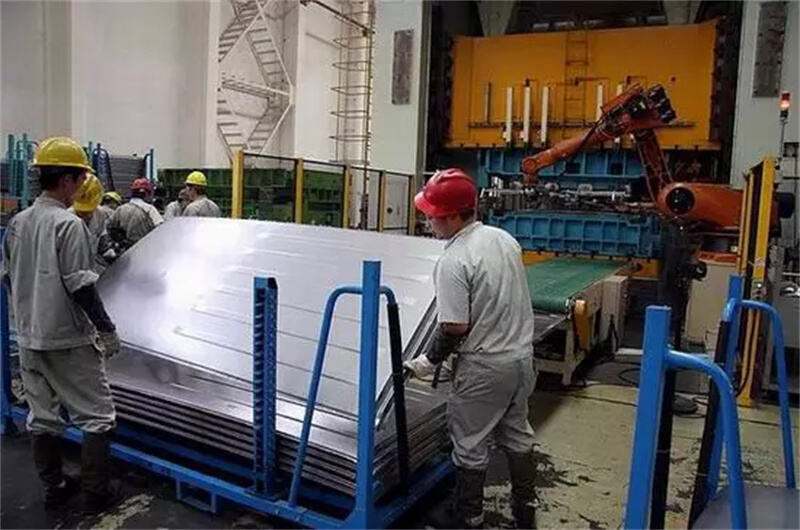

Automotive body stamping
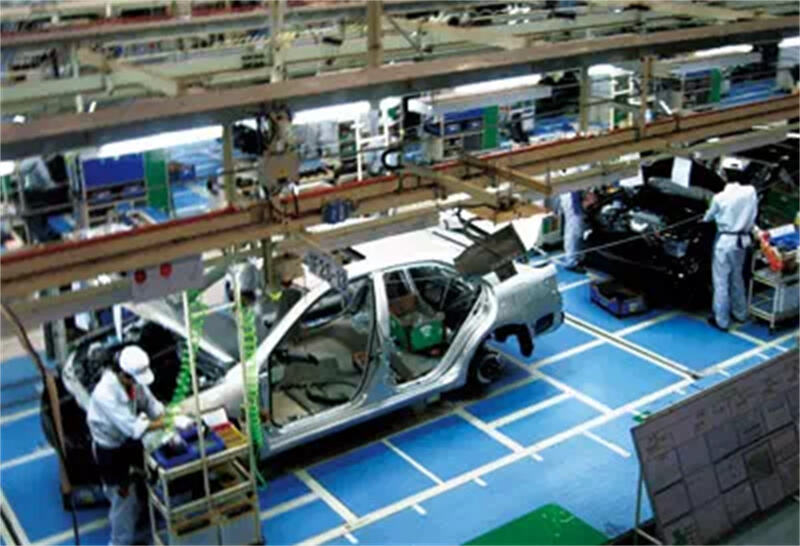
B. Welding
The BIW is assembled using robotic or manual welding. Laser welding and spot welding are common methods used to ensure structural integrity.

Automotive body welding
C. Painting
The vehicle undergoes a multi-layer paint process that includes cleaning, priming, painting, and baking. This enhances corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
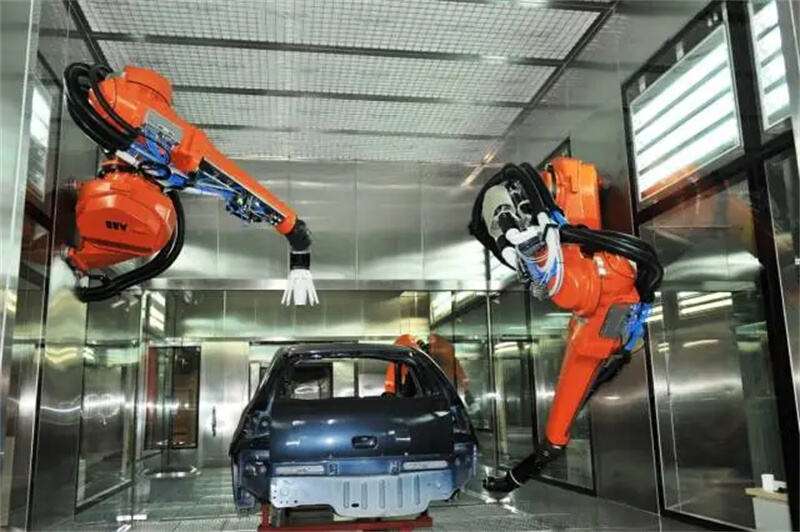

Automotive Painting Process
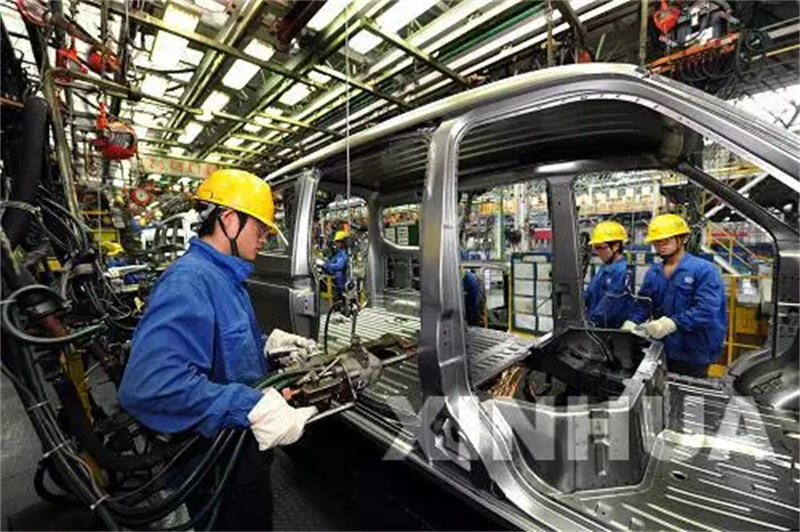
D. Final Assembly
In the final assembly line, workers and robots install engines, transmissions, electrical systems, seats, and trim components. The vehicle then goes through final inspections like wheel alignment and electrical diagnostics.

Automotive assembly
Conclusion
From idea to finished product, car manufacturing is a fusion of art, science, and engineering. Every phase – from market research to assembly – plays a critical role in creating safe, reliable, and innovative vehicles.
Understanding the automotive manufacturing process not only helps industry professionals and enthusiasts but also builds trust with customers who value transparency and technical excellence.
Stay tuned to our blog for more insights into vehicle design, engineering, and production technologies.
 Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier —
Small batches, high standards. Our rapid prototyping service makes validation faster and easier — 
