Тајне услуге за ласерско сечење метала: од пројектне фајл до испоручених делова
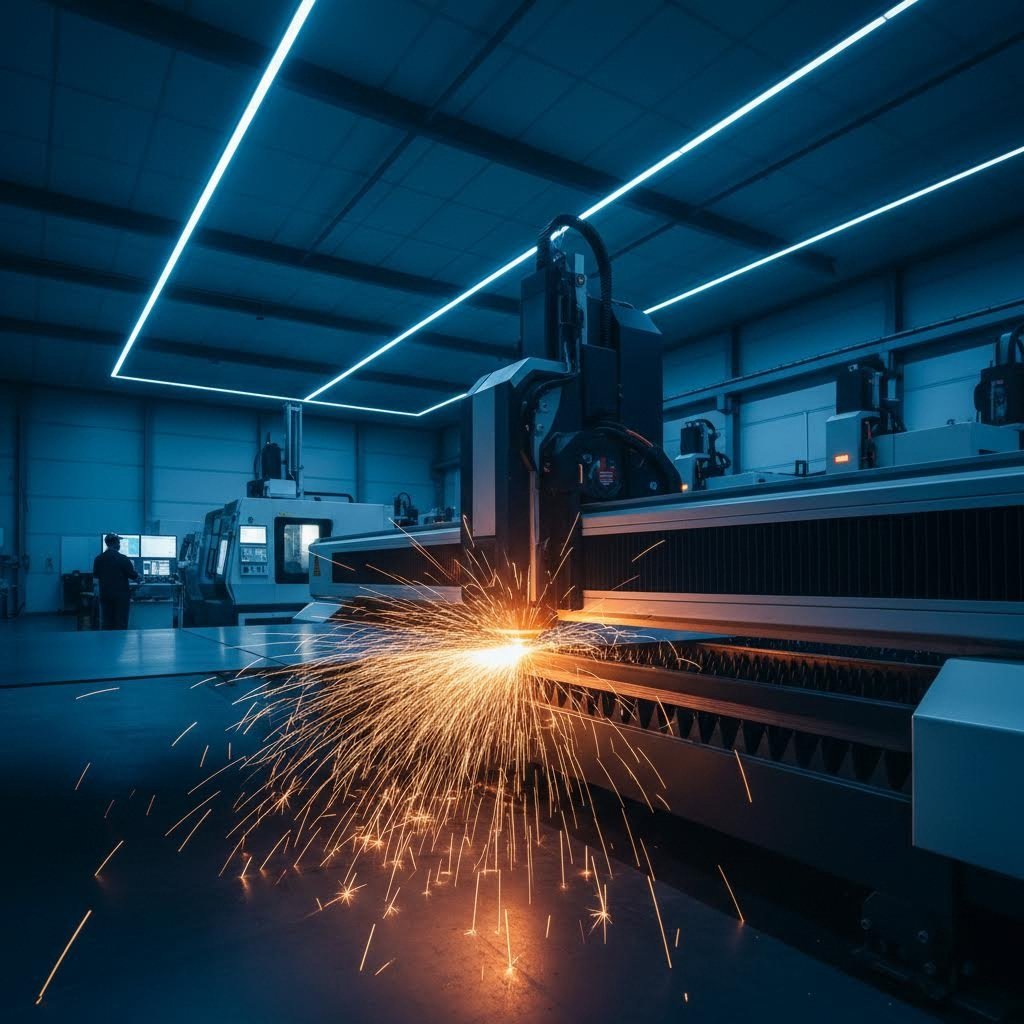

Шта ласерско резање метала заправо ради вашем материјалу
Да ли сте се икада питали како зрак светлости може да прореже чврсту челик као путер? У услузи за ласерско сечење метала, високо концентрисана светлост се користи за топиње, испаривање или спаљивање метала по путовима које контролише компјутер. Замислите да фокусирате сунчеву светлост кроз лупу, али да је појачате милионе пута и водите је са прецизном прецизношћу. То се у суштини дешава када ласер који сече метал почне да ради на вашем сировину.
Процес почиње када се ласерски зрак, често мањи од 0,32 мм у пречнику, фокусира на металну површину. То ствара температуре довољно интензивне да материјал или топли или потпуно испарава. Према Википедијска документација о ласерском сечењу , фокусирана гређа може постићи ширине резања мањих од 0,10 мм, омогућавајући невероватно прецизне резе које традиционални алати за резање метала једноставно не могу да уједначе.
Како ласерски зраци претварају сирови метал у прецизне делове
Када ласерски зрак удари метал, нешто се чудно дешава. Концентрисана енергија загрева површину до своје тачке запаљења, стварајући оно што инжењери називају "краљом". Ова кључара брзо се продубљава док материјал вре, а притисак паре одводи топљен метал од зоне за резање. Гасови под високим притиском помажу у овом процесу, чистећи остатке и остављајући чисте, прецизне ивице.
Шта чини ласерско сечење метала тако ефикасним? Зона која је погођена топлотом остаје невероватно мала. За разлику од плазме или традиционалних метода сечења, ова прецизност значи минимално искривљање и искривљење вашег делова. Видећете да делови долазе спремни за монтажу или завршну обработу са мало или без потребе за секундарном обрадом.
Савремени ласерски системи за резање метала раде са тачношћу позиционирања од око 10 микрометра и понављаемошћу од 5 микрометра. Овај ниво прецизности чини ласерско резање метала идеалним за примене које се крећу од сложених електронских компоненти до тешких аутомобилских делова.
Наука која се налази иза технологије топлотне резања
Не раде сви ласери на исти начин. Разумевање три главне методе ласерског сечења помаже вам да ефикасно комуницирате са својим пружаоцем услуга:
- Ласери од влакана: Ови системи са чврстим станом генеришу греде кроз посебно дизајниране стаклене влакне. Са таласним дужинама од 1.064 микрометра, они производе фокусне тачке до 100 пута мање од CO2 ласера. Према Тротек Ласер , влакноласни ласери су без одржавања са животом од више од 25.000 сати, што их чини избором за операције резања метала велике количине.
- Ласери са CO2: Гасни системи који користе мешавине угљен-диоксида који се електрично стимулишу. Раде на таласним дужинама од 10,6 микрометра, и одликују се неметалним материјалима, али могу сећи метале, укључујући титан, нерђајући челик и алуминијум, када су опремљени довољном снагом.
- "Снажници" за "улачење" у "светлу" Ласери чврстог стања користе кристали допирани неодијемом. Они имају исту таласну дужину као и ласери од влакна, али захтевају више одржавања, а диоде за пумпу треба заменити сваких 8.000 до 15.000 сати.
Данас водеће услуге за ласерско сечење метала све више се ослањају на технологију оптног влакна. Систем који ради на 6кВт и више сада се приближава капацитети за резање плазмених машина док одржавају врхунску прецизност. Овај напредак значи да се дебљи материјали могу обрадити са одличним квалитетом ивице, што је било немогуће са ранијим системом од 1.500 вата.
Шта је крајње? Када предате дизајн професионалној служби, сложена физика и инжењерство раде заједно да преобразе вашу дигиталну фајлу у прецизне металне делове са толеранцијама често у оквиру 0,025 мм.
Материјали које можете обрадити помоћу услуга за ласерско сечење
Звучи сложено када неко каже да може ласерски резати метал преко десетина различитих легова? Реалност је да се не понашају сви метали исто под тим концентрисаним зраком светлости. Неки ефикасно апсорбују енергију и режу као у сну. Други се боре, одражавајући зрак и одводићи топлоту од зоне пресека. Разумевање ових специфичних понашања материјала помаже вам да изаберете прави метал за ваш пројекат и ефикасно комуницирате са својим пружаоцем услуга.
Услуге за ласерску резање метала одржавати обимне инвентаре материјала који покривају све од уобичајеног угљенског челика до егзотичних специјалних легура. Сваки материјал има јединствене карактеристике које утичу на брзину сечења, квалитет ивице и укупну трошковину пројекта. Хајде да разградимо шта се дешава када се различити метали срећу са ласерским зраком.
Карактеристике резања челика и нерђајућег челика
Челик остаје радни коњ ласерских операција резања метала. Угледни челик ефикасно апсорбује ласерску енергију, што га чини једним од најлакших материјала за обраду. Видећете чисте ивице, минимално накупљање шлака и брзе брзине сечења у већини дебљина.
Када је реч о ласерском сечењу нерђајућег челика, процес захтева мало више снаге због топлотних својстава материјала. Неродно челик не проводи топлоту тако лако као алуминијум или бакар, што заправо ради у вашу корист. Топла остаје концентрисана у зони резања, омогућавајући прецизне линије резања и одличан квалитет ивице. Уобичајене категорије као што су 304 и 316 ласерски резање нерђајућих материја су рутинске операције за искусне произвођаче.
Ласерско сечење челика обично користи кисеоник као помоћни гас за угљенски челик, стварајући егзотермичну реакцију која додаје енергију сечења. За апликације за ласерски резан нерђајући челик где су окисливо слободне ивице важне, азотни гас производи светле, чисте резе спремне за заваривање или видљиве инсталације.
Радите са одражавајућим металима као што су алуминијум и барез
Ево где ствари постају занимљиве. Ласерски резан алуминијум представља изазове који многе новопристиглице изненаде. Висока рефлективност алуминијума значи да се значајан део ласерске енергије одбија од површине уместо да прође кроз материјал. Према 1Техничка анализа ЦутФаб-а , ово одражавање изазива три главна проблема: непуне резе, губитак енергије који захтева више пута пролазак и потенцијално оштећење ласерске оптике од ретро рефлектираних зрака.
Савремени ласери од влакана су у великој мери решили изазов са ласерским сечањем алуминијума. Њихова таласна дужина од 1,07-микрометра много боље се спаја са рефлектирајућим површинама него са старом CO2 технологијом. Ипак, резање алуминијума захтева више подешавања снаге и пажљиво подешавање параметара. Гас за помоћ азот спречава оксидацију и производи светле ивице које су обично потребне за апликације алуминијума.
Медь и бакар припадају ономе што произвођачи називају "црвеним металима". Ови материјали гурају ласерско сечење до својих граница. Техничка документација компаније YIHAI Laser објашњава да бакар има топлотну проводност око осам пута већу од челика. Топла буквално одлази од зоне резања, што отежава одржавање стабилног топлотног базена који је потребан за чисте резе.
Чисти бакар захтева агресивне параметре: максималну снагу, брзо време пробијања и азот под високим притиском (18-22 Бар). Чак и искусни оператори поштују бакар. Брас се понаша другачије упркос томе што изгледа слично. Његова содржина цинка (30-40%) ствара притисак паре током сечења који заправо помаже у избацивању растопљеног материјала. Међутим, овај цинк такође производи токсичне гаре које захтевају снажне системе екстракције.
| Тип материјала | Типични опсег дебљине | Квалитет сечења | Посебна разматрања |
|---|---|---|---|
| Угледни челик | 0,5 мм - 25 мм | Одлично; чисте ивице са минималним шлаком | Кисељ-асистент гас додаје енергију за резање; најјефикаснија опција |
| Нерођива челик | 0,5 мм - 20 мм | Веома добро; светле ивице са азотом | Потребно је више снаге од угљенског челика; азот спречава оксидацију |
| Алуминијум | 0,5 мм - 15 мм | Добро са правилним подешавањем | За високу рефлективност потребни су ласери од влакна; потребне су подешавања веће снаге |
| Плочице | 0,5 мм - 10 мм | Добро; може бити потребно завршну оцртају ивице | Зинк пар ствара испаре; потребна је снажна екстракција; летљиво понашање резања |
| Мед | 0,5 мм - 8 мм | Проблемно; обичан шлац | Највећа тешкоћа; екстремна топлотна проводност; захтева максималну снагу и брзу обраду |
| Специјалне легуре | Разликује се по легури | Зависно од примене | Титанијум, Инконел и алатни челика захтевају специјалне параметре |
Специјалне легуре као што су титан, инконел и алатни челик захтевају развој прилагођених параметара. Титанијум релативно добро сече уз помоћ азота, али захтева пажњу да се спречи контаминација кисеоника која утиче на својства материјала. Ови материјали обично коштају више да се обраде због споријих брзина сечења и специјализованих захтева за поставку.
Када тражите цитат, увек наведите тачну категорију материјала. Алуминијум 6061-Т6 се понаша другачије од 5052. Слично томе, 316Л нерђајући челик се разликује од 17-4 ПХ. Што је прецизнија ваша материјална спецификација, то је прецизнији ваш цитат и боље ће се завршни делови испоставити.
Објашњена способност дебљине и стандарди прецизности
Када предате дизајн у услугу за ласерско сечење метала, дебљина је важнија него што бисте могли очекивати. То утиче на све, од брзине сечења до квалитета ивица, и на крају, да ли ће ваши делови задовољити димензионе захтеве. Ипак, ове критичне информације често се сакривају иза копчића за тренутни цитат без објашњења. Поменимо то.
Разумевање могућности дебљине и прецизних толеранција помаже вам да паметније дизајнирате, постављате реалистична очекивања и ефикасно комуницирате са произвођачем. Било да радите са ласерским сечењем танког метала или гушите у дебљи простор плоча, ове спецификације директно утичу на успех вашег пројекта.
Разумевање граница дебелине за различите метале
Сваки метал има максималну дебљину коју ласер може чисто да исече. Прећи ове границе, и наићи ћете на непуну проникност, прекомерно накупљање шлака и угрожен квалитет ивице. Према Техничке спецификације Аццурл , најмоћније машине за резање ласера са влаконцем могу постићи максималну дебљину до 50 мм за одређене метале, мада практична граница за квалитетне резе обично пада испод ових максималних граница.
Ласерска снага директно одређује дебљину коју можете исећи. Машина за ласерско сечење листа метала која ради са 6кВт нуди драматично различите могућности од система од 1кВт. Ево шта можете очекивати од 6кВ ласерског резача за влакна:
- Угледни челик: До 25 мм максималне дебљине резања
- Нерођива челик: Максимална дебљина резања до 20 mm
- Алуминијум: Максимална дебљина резања до 15 mm
- Бакар: Максимална дебљина сечења до 8 mm
Зашто врста материјала ствара такву варијацију? Трпена проводност игра главну улогу. Када се ласер реже челични листови, топлота се ефикасно концентрише на зони резања. У супротном, бакар брзо одбацује топлоту, што захтева више енергије да би се одржала температура резања. Рефлекторни метали као што је алуминијум такође одбијају ласерску енергију од површине, што још више компликова обраду дебљих секција.
Према Техничка документација Сенфенг Ласера , 6кВт ласерски системи са влаконом заузимају стратешко место за производњу метала. Они обрађују материјале 50% брже од 4кВт машина на средње танке плоче док се баве дебљим металима које системи са мањом снагом једноставно не могу резати. Ова равнотежа чини их све популарнијим међу професионалним ласерским сечачима листова метала.
Шта толеранције прецизности значе за ваш пројекат
Прецизност није модна реч за маркетинг. То је мерена спецификација која одређује да ли се ваши делови правилно уклапају. Када произвођачи говоре о толеранцији, они описују дозвољено одступање од ваших одређених димензија. Према свеобухватној анализи АДХ Машин Тоол-а, висококвалификоване индустријске ласерске резаче машине могу одржавати толеранције са чврстим до ± 0,1 мм, а ласери са влаконцем постижу још чврсту прецизност од ± 0,05 мм или ± 0,025 мм у прецизним
Ево шта утиче на толеранције које можете остварити:
- Тип материјала: Метали са стабилним топлотним својствима као што је нерђајући челик производе конзистентније толеранције од топлосно проводних материјала као што су бакар или алуминијум.
- Дебљина материјала: Дебљи материјали представљају експоненцијално веће изазове. Тене листове испод 3 мм обично постижу толеранције од ± 0,1 mm, док се резиви већи од 15 mm могу проширити на ± 0, 3 mm или више због дивергенције зрака и акумулације топлоте.
- Машинска калибрација: Тачност система покрета, оптички усклађивање и редовно одржавање директно утичу на постигнуту прецизност. Линеарни мотори постижу прецизност позиционирања од ±0,001 мм, док системи са лоптом обично достижу ±0,005 мм.
- Експертиза оператера: Оптимизација параметара за специфичне комбинације дебелине материјала захтева искуство. Опитни оператери прилагођавају снагу, брзину, положај фокуса и притисак гаса како би из опреме извукли максималну прецизност.
Дебљина ствара највећи изазов толеранције. Како материјал постаје дебљи, неколико физичких феномена ради против прецизности. Гаусов профил ласерског зрака значи да је по својој природи коничан, а не савршено паралелан. У ласерском сечењу металних листова дебелим плочама, ово ствара мерељиве разлике између горње и доње ширине реза, стварајући кону. Поред тога, дубље резе чине потеже избацивање растопљеног материјала, што потенцијално утиче на квалитет ивице.
Оптичка влакна технологија од 6кВт и више решава многе од ових изазова. Виша снага омогућава брже брзине сечења, што смањује укупну топлоту у радни комад. Краће таласне дужине ефикасније се спајају са металима, стварајући уско ширину и мање зоне које су погођене топлотом. Модерни системи од 6 кВт пружају квалитет на дебљим материјалима који једноставно није био постигнут са опремом претходне генерације.
Шта то значи у пракси? За прецизна ласерска сечење материјала танке гамбе , очекују се допуне између ±0,05 мм и ±0,1 мм. Уобичајено, рад са средњом дебљином се одвија у оквиру од ± 0,1 до ± 0,2 мм. За тешке апликације плоча могу бити потребне допуне од ±0,25 mm до ±0,5 mm. Када дизајнирате ласерски резану метални листови, од самог почетка узимајте у обзир ове реалистичне могућности у својим захтевима за прилагођавање и функцију.

Припрема ваших дизајнерских датотека за успех ласерског сечења
Изаберио си свој материјал и разумеш способности дебљине. Сада долази корак који раздваја непрекидне пројекте од фрустрирајућих кашњења: припрема датотека. Према Цитирам анализу Кот Шипа. , они сваке недеље прегледају стотине датотека и стално се суочавају са истим грешкама у дизајну које се могу спречити. Добра вест? Неколико минута припреме штеди са часовима ревизије.
Било да подносите свој први пројекат за ласерску резању или свој стоти, правилна поставка датотека директно утиче на тачност цитата, брзину производње и квалитет делова. Помислите на свој дизајн као на рецепт. Чак и најбоља опрема за ласерски резач листова метала не може да произведе одличне резултате из лоше припремљених инструкција.
Формати датотека и технички захтеви за подношење
Ево нечега што многи први пут клијенти не схватају: ласерски резачи не разумеју фотографије или слике засноване на пикселима. Према Xometry-овим смерницама за дизајн, ласерско сечење захтева векторске форматске фајлове са математички прецизним ивицама. За разлику од битмапа које се састоје од пиксела, векторске слике дефинишу ивице математичким изразима који одржавају своју прецизност без обзира на скалу.
За операције ЦНЦ ласерске сечења, услуге обично прихватају ове формат:
- ДХФ (Формат за размену црта): Индустријски стандард за 2Д ласерско сечење. Компатибилан са скоро свим ЦАД програмом и ласерским резачем за металне системе.
- ДВГ (АутоЦАД Циркање): Нативан АутоЦАД формат који чува информације слоја и сложену геометрију. Добро ради за сложене дизајне.
- АИ (Адобе Илустратор): Популарна међу дизајнерима због интуитивног интерфејса. Одлично за уметнички и прилагођени ласерски рад.
- SVG (Скабилна векторска графика): Отворен стандард који ради на свим платформама. Добро за веб-основане алате за дизајн.
- СТЕП/СТП (3Д фајлови): Потребно за делове дизајниране у 3D ЦАД програмима. Према Попутства за СендЦутСенд , ово је пожељније када ваш дизајн потиче из софтвера као што је Аутодеск Фјузија.
Шта се дешава ако подносите JPEG или PNG? Ови растерски формати морају бити конвертовани у векторе пре обраде, што додаје време и често уводе нетачности. Неке услуге нуде могућности праћења, али резултати ретко одговарају специјално изграђеним векторским датотекама. Бесплатни алати као што је Инксцпе могу да прате битмап слике и конвертују их у векторски формат, иако дизајн у векторском формату од самог почетка увек даје супериорне резултате.
Маштаб је веома важан. Увек изградите своје фајлове у скали од 1:1, пожељно у инч или милиметарским јединицама. Ласерски резач листова метала буквално интерпретира ваше димензије. Ако ваш дизајн показује 50 мм, али сте намеравали 500 мм, то је тачно оно што ћете добити.
Избегавајте уобичајене грешке у дизајну које одлагају производњу
Чак и искусни дизајнери паду у ове замке. Разумевање узрока проблема у производњи помаже вам да испоручите датотеке који цитирају брзо и чисто.
Отворени или неодвојени путеви: Ово је најчешћи проблем који се дешава у служби. Када путеви не формирају затворено обличе, ласер не зна где да сече. Према техничкој документацији SendCutSend-а, претстава делова обично неће бити сива ако су отворени путеви за резање присутни. Користите функције чишћења пута и "удружавања" вашег ЦАД софтвера како бисте осигурали да се свака линија правилно повезује.
Линије су преближе једна другој: Када се линије дизајна сувише чврсто запеку или се преклапају, ласер прегори те области. Цитат Кут Схип препоручује одржавање најмање 0,010 инча (0,254 мм) растојања између критичних путева. За дебеле материјале са ниским тачкама топљења, блиско растојане резе могу изазвати локално топљење или деформацију између путева.
Карактеристике мање од дебљине материјала: Ево практичног смерника из Ксометрије: избегавајте дизајнерске карактеристике мање од дебљине вашег материјала. Резање рупе од 8 мм у челику дебљине 10 мм производи лош квалитет ивице и нетачност димензија. Иако је технички могуће, резултати ретко испуњавају очекивања.
Игнорисање Керфове компензације: Ласерски зрак уклања материјал док сече, стварајући оно што произвођачи називају "кеф". Према техничким спецификацијама Ксометрије, ширина резања обично се креће од 0,1 до 1,0 мм у зависности од материјала, ласерске снаге и брзине сечења. Ако су делови потребни прецизно монтажу, изместите пут резања тако да резање не спада изван намењених димензија. Многи софтверски пакети за ласерско сечење се баве овим аутоматски, али ако унапред наведете своје захтеве, спречите изненађења.
Текст остао као шрифти: Заборав да се текст претвори у контуре или криве често изазива проблеме. Ако произвођачу недостаје ваш специфичан фонт, он може бити потпуно другачији или потпуно нестати. Увек конвертујте текст у стазе пре извоза.
Ваша пре-подаци контролна листа
Пре него што учините свој фајл на било коју услугу за ласерску резање, прођите кроз овај процес верификације:
- Потврдите формат датотеке: Уверите се да сте поднели само.dxf,.dwg,.ai,.eps или.step/.stp датотеке. Избегавајте мрежене датотеке и формат слике.
- Проверите скалу: Уверите се да је ваш дизајн изграђен у скали 1:1 у инч или милиметарским јединицама.
- Затворите све путеве: Проверите да ли сваки пут сечења формира затворен облик без отворених контура.
- Уклонити гужве геометрије: Избришите све одвојене тачке, дуплиране линије, празне објекте и преклапане путеве.
- Преобраћање текста: Преобразите сав текст у огледале или путеве пре извоза.
- Проверите минималне величине карактеристика: Потврдити да рупе и резци испуњавају минималне захтеве (обично најмање 50% дебљине материјала за делове резане ласером).
- Проверка размака између линија: Уверите да је између резаних путева најмање 0,01" растојања како би се спречило прегоревање.
- Уједините облике: Комбинирајте, спајајте или уједините све објекте који треба да сече као појединачни ентитети.
- Консолидирани слојеви: Поставите све геометрије за резање на исти слој.
- Прегледајте уграђене делове: Ако подносите више делова у једној датотеци, уверите се да не деле резане путеве или се преклапају.
За уграђене датотеке које садрже више делова, SendCutSend наглашава да делови никада не би требало да деле резне путеве, имају преклапају геометрију или укључују делове унутар делова. Сваки комад треба да има свој комплетан периметар. Постављање трака за уграђене делове захтева планирање; трака држи делове на месту током сечења, али их се мора уклонити након тога. Поставите их у некритичне области где мало чишћење неће утицати на функцију.
Узимајући петнаест минута да проверите ове елементе пре подношења обично штедите дане ревизије. Ваш тим за преглед дизајна ће ценити да добије чисте фајлове, а ви ћете добити цитате брже са мање питања.
Целокупно путовање од дизајна до испоруке делова
Припремили сте своје дизајнерске фајлове и одабрани материјали. Шта сада? Многи ласерски сервиси се крију иза дугме за тренутни цитат без објашњења шта се дешава након што кликнете на "пошаљи". Разумевање целог циклуса живота пројекта помаже ти да поставиш реалистична рока, предвиђаш питања и избегаваш скупа изненађења. Да спустимо завесу за процес цитирања и испоруке.
Било да тражите услугу ласерског сечења у близини мене или радите са специјализованим произвођачем широм земље, основни радни тек остаје конзистентан. Према документима SendCutSend-а, модерне услуге могу испоручити прототипе за само 2-4 радна дана, а неке нуде могућности брзе производње прототипа за сложене пројекте од 5 дана. Разумевање сваког корака помаже ти да се ефикасно носиш кроз процес.
Од тражења за цитат до завршених делова
Сваки успешан пројекат за ласерско сечење метала следи предвидиву траку. Неки кораци се одвијају аутоматски, док други захтевају ваш допринос. Ево типичног путовања које ваш пројекат води:
- Подавање датотека и почетна цитата: Ви преузимате своје векторске датотеке преко онлине платформе услуге. Автоматизовани системи анализирају геометрију, израчунавају путеве резања и генеришу прелиминарне цене. Водећи провајдери као што су они који нуде услугу ласерског сеча у близини мене опције често врате цитате у року од 12 сати или мање.
- Преглед пројекта и анализа ДФМ-а: Инжењери прегледају ваш фајл на питање производње. Они проверавају минималне величине елемената, одговарајуће толеранције и потенцијалне производне изазове. Овај критичан корак открива проблеме пре него што се почне резање.
- Избор материјала и потврда: Укажете тачну категорију материјала, дебљину и захтеве за завршетак. Произвођач потврђује доступност материјала и прилагођава цене ако је потребно. Неке услуге за ласерско сечење цеви одржавају обимне инвентарије, док друге изводе специјалне материјале по пројекту.
- Одобравање цитата и постављање налога: Када одобрите коначни цитат, ваша нарачка улази у производњу. Плаћање обично покреће распоређивање, иако неке услуге нуде нето услове за успостављене рачуне.
- Планирање производње и резање: Ваш посао се додељује одговарајућој опреми на основу врсте материјала, дебљине и сложености. Према документацији за процес Ксометрије, машина за ласерско сечење следи програмиране инструкције, са гасом који помаже у продушивању паре и капљица док ствара уско резање дуж путање сечења.
- Инспекција квалитета: Завршени делови подвргну се димензионалној верификацији и визуелној инспекцији. Критичне карактеристике се мере према спецификацијама. Делови који не испуњавају стандарде се прережу пре испоруке.
- Опаковање и испорука: Делови добијају одговарајућу заштиту на основу материјала и захтева за завршетак. Многе услуге нуде детаљно праћење наруџбине тако да тачно знате када можете очекивати испоруку.
Цео процес може се одвијати изузетно брзо. За једноставне делове у материјалима који се налазе у залихи, неке услуге за ласерско сечење у близини моје куће испоручују завршене делове у року од недељу дана од подношења првобитне податке.
Шта се дешава током прегледа дизајна
Дизајн за прегледу производње одваја професионалне услуге за ласерско сечење од основних радних радња. Током анализа ДФМ-а, инжењери процењују да ли се ваш дизајн може произвести као што је поднесен, или да ли би модификације побољшале квалитет, смањиле трошкове или спречиле неуспех.
Шта критичари траже? Прво, они проверавају да ли се све геометрије исправно преведу из формата датотека. Према техничким смерницама Ксометрије, ласерска машина за сечење ће тачно следити програмиране инструкције. Ако ваша датотека садржи проблеме, машина ће оне проблеме исећи у скупи материјал.
Инжењери ДФМ такође процењују практичне разлоге које аутоматски системи цитирања пропуштају:
- Зоне акумулације топлоте: У одређеним обрасцима, резнице које су у блиском растојању могу изазвати локално прегревање и искривавање.
- Стабилност делова током сечења: Велики делови са многим унутрашњим резацима могу се померити док материјал пада, што утиче на коначне резаке.
- Употреба у производњи Неке карактеристике могу захтевати прилагођавање параметара или пост-процесинг како би задовољиле ваше спецификације.
- Ефикасност гнездања: Инжењери могу да предложе да се делови на листу поново распореде како би се смањио отпад материјала и смањили трошкови.
Добра ДФМ подршка претвара трансакциону услугу у производње партнерство. Када инжењери примете потенцијални проблем и предлаже алтернативне методе пре него што почнете да сече, штеде вам време, новац и фрустрацију.
Колико ће ово трајати? Брза цитирања постали су индустријски стандард, а неки пружаоци одговарају у року од 12 сати. Према преглед SendCutSend процеса, стандардни наруџбине брод у 2-4 радна дана, што значи да можете ићи од пројекта до испоручених делова за мање од недељу дана за једноставне пројекте.
За оне који истражују опције за ласерско сечење у близини мене, разумевање овог радног тока помаже вам да ефикасно процените пружаоце. Питајте о њиховом процесу ДФМ-а, типичним временом обраћања и процедурама инспекције квалитета. Одговори ће открити да ли радите са правим прецизним произвођачем или са основном услугом сечења.

Када ласерско сечење побеђује алтернативне методе сечења
Ево питања која се поставља чак и искусним произвођачима: да ли треба да користите ласерско сечење или би плазма или водени струјач боље служили вашем пројекту? Искрен одговор је да ниједна ласерска технологија за резање метала не побеђује у сваком сценарију. Свака метода је одлична у одређеним ситуацијама, а слаба у другим. Разумевање ових компромиса помаже вам да одаберете прави приступ пре него што тражите цитате од услуга за резање метала.
Према Компаративна анализа Вурт Машинери , многе успешне фабрикантске радње на крају укључују више технологија јер свака одговара различитим захтевима пројекта. Хајде да испитамо где свака метода сјаје и где се бори.
Ласерско сечење против метода водених струја и плазме
Размислите о овим три технологије као специјализованих алата, а не као директних конкурента. Ласерска машина за резање метала пружа хируршку прецизност на танким до средњим материјалима. Плазмено сечење доминира дебелим проводним металима по нижим трошковима. Водно млазње може да се носи са било којим предметом без топлотних ефеката.
Сила ласерског сечења: Када је прецизност најважнија, ласерски резач метала обично побеђује. Према Техничка документација Универзал Тоул & Инжењеринг , ласери са влаконским ласерима постижу толеранције од ± 0.001 "или боље због прецизне контроле зрака и минималне ширине резе. Фокусирана гређа ствара изузетно чисте ивице са минималном потребној пост-процесурацији. За танке листове који захтевају сложене детаље, мале рупе или сложене геометрије, ласерско сечење даје резултате који алтернативне методе једноставно не могу да се подударају.
Ограничења ласерског сечења: Свака технологија има ограничења. Ласерско сечење најбоље функционише до одређених граница дебелине, изнад којих се брзина и квалитет значајно смањују. За тешке плоче који прелазе 25 мм, плазма или водени струја често се испоставију економичнијим. Осим тога, док ласери од влакна много боље управљају одражавајућим металима него старији системи СО2, материјали као што је чист бакар и даље представљају изазове.
Предности резања плазмом: Ако радите са дебљим проводничким металима и приоритетуте брзину изнад прецизности, плазма заслужује озбиљну разматрање. Тестирање Вуртх Машинери је показало да плазмен резач 1 инчевог челика ради 3-4 пута брже од водених струја, са оперативним трошковима отприлике пола мање по стопу. За конструктивне производње челика, производњу тешке опреме и коралоградњу, плазма нуди неупоредиву вредност. Комплетни плазмен систем кошта око 90.000 долара у поређењу са око 195.000 долара за опрему за водопровод сличне величине.
Предности воденог млаза: Када се треба избећи топлотне штете или када сечете неметале, водени струјац је самосталан. Процес хладног сечења не производи зону која је погођена топлотом, што значи да нема деформације, тврдоће и не мења својства материјала у близини ивице сечења. Водецхет управља материјалима које ни ласери ни плазма не могу додирнути: каменом, стаклом, композитима од угљенских влакана и слојеним материјалима. Рат водених млазница наставља да расте брзо, а предвиђа се да ће до 2034. године достићи преко 2,39 милијарди долара.
Успоредити захтеве за ваш пројекат са правом технологијом
Избор праве методе резања метала на основу прилагођености се свезује на шест кључних фактора. Прођите кроз сваку од њих пре него што се посветите на технологију:
- Тип материјала: Ласер се одликује са челиком, нерђајућим и алуминијем. Плазма ради само на електрично проводничким металима. Водно струје сече скоро све, укључујући камен, композите и стакло.
- Употреба за дебљину: За танке до средње листове испод 15 мм, ласер обично нуди најбољу комбинацију брзине и прецизности. Дебљи проводни метали воле плазму. Водени струјац може да се носи са било којом дебљином, али ради спорије.
- Потребе прецизности: Тешке толеранције испод ± 0,005 "показати ка ласерском сечењу. Плазма производи грубе ивице које захтевају секундарно завршну обработу. Водно струје постиже добру прецизност, али оставља мале уходе / излазе.
- Квалитет ивице: Ласер производи редове спремне за употребу на одговарајућим материјалима. Плазма скоро увек захтева пост-процесурање. Водно струје ствара чисте ивице, али са мало већим радијусом на унутрашњим угловима.
- Продукција: Радовање високим количинама танких листова доприноси брзини и аутоматизацији ласера. Мање обимне дебљине плоча могу да допринесу нижим трошковима плазме.
- Буџетски ограничења: Ласер има веће капиталне трошкове, али ниже захтеве за завршну обработу по деловима. Водно млажење троши скупе абразиве. Плазма кошта мање по резу, али додаје радни рад за завршну обработу.
| Метода | Најбоље за | Дијазон дебљине | Квалитет ивице | Фактори трошкова |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ласер од влакана | Тонки до средњи листови; сложени дизајн; захтеви за високу прецизност | 0,5 мм - 25 мм (зависи од материјала) | Одлично; често спреман за монтажу | Виша цена опреме; најнижи трошкови завршног деловања; висок проток |
| Плазма | Дебљи проводни метали; конструктивни челик; трошкови осетљиви пројекти | 3 мм - 75 мм + | Грубије; обично захтева завршну обработу | Најнижа цена опреме; умерени потрошни материјали; додаје радни рад за завршну обработу |
| Воден струјач | Теплоосетљиви материјали; неметали; избегавање промена материјалних својстава | 0,5 мм - 200 мм+ | Добро; нема топлоте погођене зоне | Умерени трошкови опреме; високи потрошни материјали (абразив, зношење пумпе) |
| ЦНЦ рутинг | Мекији материјали; пластике; дрво; пена; радови великог формата | Зависни од материјала | Добро за одговарајуће материјале | Ниже трошкове за неметалне апликације |
Када би посебно требало да избегавате ласерско сечење? Према анализи Универзал Тоулса, веома дебеле плоче које су изнад капацитета вашег ласера ће сећи споро са пониженом квалитетом. Материјали који захтевају зону нулту топлоте, као што су одређене ваздухопловне компоненте са строгим металургијским захтевима, могу захтевати обраду воденим млазом. И ако тражите плазмено резање близу мене јер вам је потребно брзо и економично резање дебеле челичне плоче, тај инстинкт је вероватно исправан.
Шта је крајње? Успореди технологију са вашим специфичним захтевима уместо да се заузму за било који метод. За многе пројекте, ласерско сечење пружа оптималну комбинацију прецизности, брзине и трошкова. Али искрена проценка понекад указује на алтернативне методе. Разумевање када свака метода одликује чини вас информисанијим купцем и доводи до бољих резултата пројекта.
Индустрије и примене које се ослањају на ласерске резане делове
Сада када знате како да изаберете праву технологију резања, хајде да истражимо где услуге за резање метала ласером заправо чине разлику. Усвршеност ласерске производње далеко је изван онога што већина људи замишља. Од аутомобила којим возите до паметног телефона у џепу, ласерски резани делови се налазе у скоро сваком производном производу са којим се свакодневно суочавате.
Шта чини да је ова технологија толико широко усвојена? Према свеобухватној индустријској анализи Аццурл-а, ласерско сечење је преобразило различите индустрије својом прецизношћу и свестраношћу. Различите сектори имају веома различите захтеве за толеранције, сертификације и спецификације материјала. Разумевање ових варијација вам помаже да ефикасно комуницирате са својим специфичним потребама када радите са произвођачима ласерског резања метала.
Производња аутомобилских и индустријских компоненти
У аутомобилској индустрији, ласерско сечење представља кључни алат за израду сложених компоненти и прилагођавања. Размислите шта је заправо унутар вашег возила: задржине шасије, компоненте суспензије, делови издувног система, панели куза и безброј структурних елемената. Свака од њих захтева прецизну прецизност димензија и доследан квалитет на хиљадама производних јединица.
Према документацији за сертификацију компаније Xometry, аутомобилске апликације често захтевају сертификацију IATF 16949 за осигурање квалитета. Овај оквир, изграђен на стандардима ИСО 9001, осигурава доследност, безбедност и квалитет широм аутомобилских производа. Када купујете ласерске делове за аутомобилске апликације, рад са сертификованим добављачима није опционалан. То је захтев који ОЕМ-ови и добављачи првог нивоа захтевају током целог ланца снабдевања.
Уобичајене апликације у аутомобилу укључују:
- Компоненте шасије и оквира: Структурни задржионици, монтажни плочи и појачане плоче који захтевају чврсте толеранције и конзистентна својства материјала
- Делови система суспензије: Улазнице за руку, пружни стазаци и опрема за монтажу која захтева прецизно уградњу
- Коросеријски и опремни елементи: Компоненте унутрашњег обликовања, декоративни панели и спољни акценти
- Компоненте електричног система: Батеријски поднос, држећи за жице и сензорски монтажи
- Компоненте моторног отвора: Загревни штит, монтажни задници и подршке за прилоге
Ласерски резач машина метални систем значајно надмашава традиционалне резање или плазмен процес за аутомобилски рад. Високојакосни ласер од влакана пружа прецизност која је од суштинског значаја када се рачуна сваки милиметар.
Аерокосмичке и електронске апликације
Аерокосмичка индустрија захтева нешто што већина других сектора не захтева: нултан компромис у прецизности. Када компоненте лете на 35.000 стопа и носе путнике, толерантне спецификације постају неодговарајуће. Ласерска производња испуњава ове строге захтеве производњом компоненти које одржавају строгу прецизност димензија уз очување интегритета материјала.
Према техничкој документацији Accurl-а, ваздухопловство има користи од способности ласерског сечења да се носи са лаким, високо чврстим материјалима док се испуњавају строги нивои толеранције. Било да се ради о обради титанијских легура, алуминијумских ваздухопловних квалитета или специјализованих нерђајућих челика, процес одржава структурни интегритет који захтевају ваздухопловне апликације.
У производњи електронике, миниатюризација је све. Уређаји постају све мањи док се функционалност шири. Услуге ласерског резања метала омогућавају ову еволуцију производњом прецизних компоненти за:
- ЕМИ штитила: Заштитни хоуси који блокирају електромагнетне интерференције
- Теплодисачи и топлотна управљања: Прецизно исечене перде и канали за распршивање топлоте
- Конектори за коннекције: Миниатурни корпуси са захтевним димензионалним захтевима
- ПКБ монтажна опрема: Стадоф, заграде и конструкције за подршку
- Обуви за потрошачке уређаје: Обуке за паметне телефоне, корпусе за лаптопе и компоненте за носиве уређаје
Електронска индустрија се у великој мери ослања на прецизне способности резања, где део милиметра чини значајну разлику. Савремени ласери од влакана постижу чврсте толеранције које су потребне за ове апликације.
Архитектонске и прилагођене апликације дизајна
Прошетајте кроз било коју савремену зграду и свуда ћете срести металне елементе. Према Архитектонска документација Стелт Индустрије , прилагођена метална фабрикација омогућава архитектима и дизајнерима да надмаше конвенционалне изборе, пружајући потпуну власт над димензијама, облицима, обрадом површине и избором материјала.
Архитектонске апликације показују креативни потенцијал ласерског сечења:
- Фасаде и системи обложења: Декоративни спољни панели, перфорирани екрани и инсталације од челика против ветра
- Унутрашњи декоративни елементи: Степене, дељење просторија и геометријски зидни плочи
- Направљени знакови: Димензионална слова, брендирани логотипи и системи за проналажење пута
- Облике пејзажа: Плантери, решевице и скулптуре на отвореном
- Компоненте намештаја: Столови, кресељи и украсни материјал
Технологија која може да сече дебљи челични плочи и истовремено производи прецизне, сложене обрасце чини га непроцењивим у модерној архитектури. Било да се стварају фасаде од Кортен челика са природном рђавом патином или четкане ограде од нерђајућег челика са детаљним геометријским обрасцима, ласерско сечење претвара концепте дизајна у стварност.
За пројекте за производњу на маштапи, услуге за резање метала ласером нуде нешто што традиционалне методе не могу: могућност економског производње једнократних дизајна или ограничених серија без скупе алате. Ова флексибилност чини ласерско сечење омиљеном методом за прототипе, архитектонске узорке и инсталације на меху у којима је сваки комад јединствен.
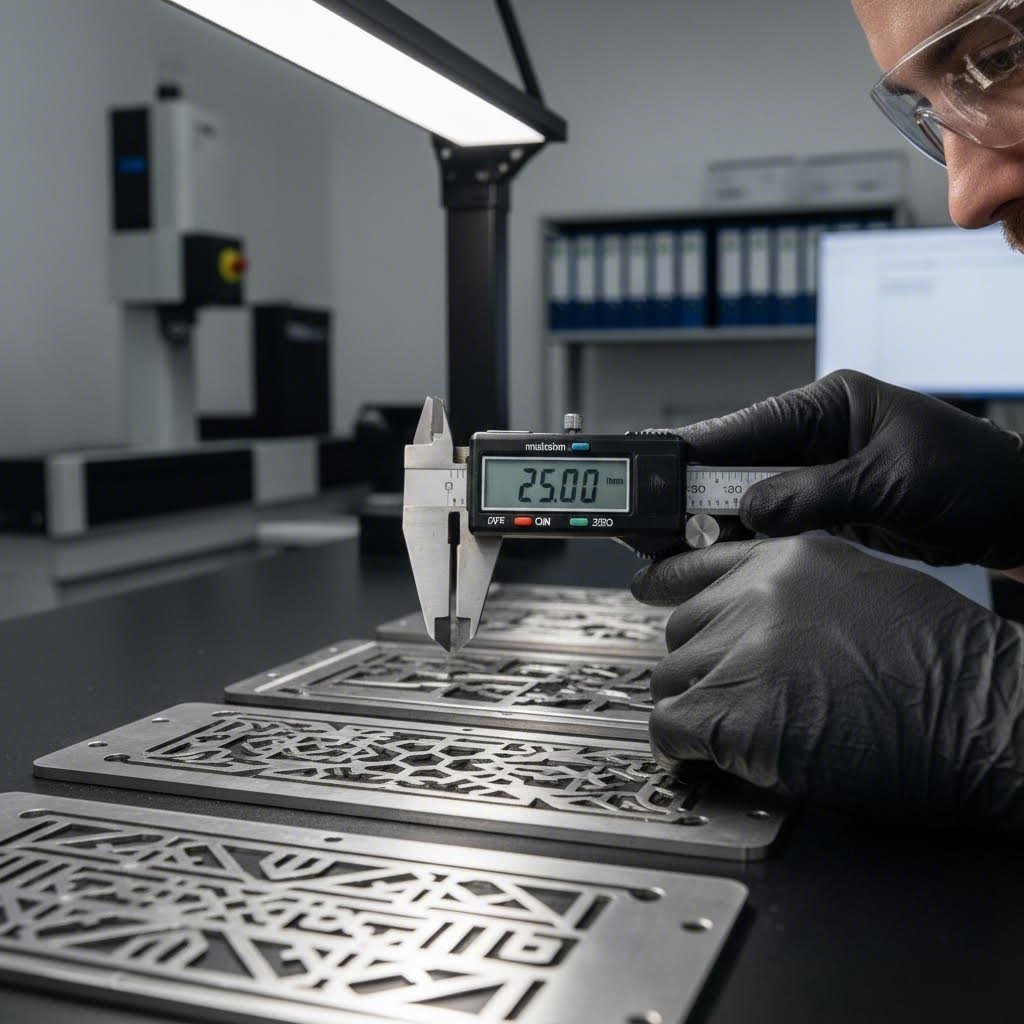

Како проценити и изабрати правог пружаоца услуга
Истражили сте материјале, разумели прецизне могућности и сазнали о животни циклус пројекта. Сада долази одлука која одређује да ли ће ваш пројекат бити успешан или не: избор правог пружаоца услуга за ласерско сечење метала. Са десетинама произвођача који се такмиче за ваш посао, како одвојите искрено способне партнере од оних који једноставно говоре добру игру?
Према Водич за процену танких металних делова , пронаћи правог партнера захтева проверу свих фактора од способности и квалитета до искуства у служби за купце. Најјефтиније понуде ретко пружају најбољу вредност. Хајде да прођемо кроз критеријуме који су заиста важни када се процењују услуге за ЦНЦ ласерско сечење.
Важно питања која треба да поставите пре него што изаберете пружаоца услуга
Пре него што се обавежете да користите неког пружаоца услуга прецизног ласерског сечења, прикупите одговоре на ова основна питања. Одговори откривају много више о способностима него што би рекламни тврдње икада могли.
Коју опрему користе? Модерни метални ласерски резачи директно утичу на резултате вашег пројекта. Према AccuPath-овом водичу за избор, алати које компанија користи утичу на успех вашег пројекта. Напређене машине раде брже и режу прецизније, лако управљајући сложеним дизајнима и тежим материјалима. Питајте их конкретно о нивоима ласерске снаге, да ли користе влаконске или CO2 системе, и старост њихове опреме. Трговац који користи 6кВ фиберне ласере даје драматично различите резултате од једног који користи старије 2кВ системи.
Да ли могу да се побрину за ваше специфичне материјале? Не обрађују се све операције ласерског резача метала свим материјалима. Неки се специјализују за челик и нерђајуће, док други одликују алуминијумом или егзотичним легурама. Пре него што тражите цитат, потврдите да провајдер има искуство са вашим тачним квалитетом материјала. Према издању Thin Metal Parts, већина произвођача помаже са челиком, алуминијем и баком, али за специјалне захтеве потребно је унапред потврдити.
Колико је њихових производних капацитета? Питајте о производњи и да ли могу да се повећају од прототипа до пуне производње. Достављач савршен за вашу прву наруџбу од 50 комада може да се бори када вам је потребно 5.000 комада месечно. Разумевање њихових способности спречава болесне прелазе касније.
Колико брзо могу да преврте цитате? Брзина цитирања често указује на општу оперативну ефикасност. Када истражујете опције за ласерско сечење метала у близини, тражите пружаоце који реагују у року од 24 сата или мање. Неки водећи произвођачи, укључујући произвођаче као што су Шаои (Нингбо) Технологија метала , понуди 12-часовни цитат за обраћање. Ова реакција показује да је рад добро организован и да цени ваше време.
Да ли нуде ДФМ подршку? Дизајн за помоћ у производњи одваја услуге трансакционог сечења од стварних произвођачких партнера. Достављачи квалитета прегледају ваше фајлове, идентификују потенцијалне проблеме и предлажу побољшања пре него што почне резање. Свеобухватна подршка ДФМ-у спречава скупе грешке и често смањује трошкове по деловима кроз оптимизацију.
Сертификати и стандарди квалитета који су важни
Сертификати нису само значке на веб страници. Они представљају верификоване обавезе конзистентног квалитета, документованих процеса и континуираног побољшања. Према преглед сертификације Хартфорд Технолошиес-а, сертификације квалитета показују посвећеност купцу и њиховој професији, производећи премије компоненте док пружају додатни слој сигурности купцима.
Ево шта вам свака главна сертификација говори о пружаоцу:
- ИСО 9001: Основно сертификатирање управљања квалитетом. Потврђује да организација одржава документоване процедуре, прати мерила квалитета и спроводи континуиране процесе побољшања. Сваки озбиљан ЦНЦ ласерски резач за рад са металом треба да има ову основну сертификацију.
- ИАТФ 16949: Критично за аутомобилске апликације. Ова сертификација се гради на ИСО 9001 са додатним захтевима специфичним за производњу аутомобила, укључујући контроле дизајна производа, верификацију производних процеса и стандарде за кориснике. Приликом снабдевања услуга за резање ласерских цеви за аутомобилске компоненте, сертификација ИАТФ-а није опционална. Произвођачи као што је Шаои демонстрирају ове стандарде квалитета кроз своје операције сертификоване по ИАТФ 16949 које служе прилоге шасије, суспензије и структурних компоненти.
- АС9100: Стандард ваздухопловне индустрије који осигурава да делови испуњавају строге захтеве безбедности и квалитета. Ако ваши делови за ласерско резање лете, радите само са провајдерима сертификованим за АС9100.
- ISO 13485: Од суштинског значаја за примене медицинских уређаја, осигурање да компоненте испуњавају строге захтеве безбедности и тражимости.
- ИСО 14001: Сертификација за управљање животном средином која указује на одговорне производње.
Поред сертификација, проценити њихове процесе инспекције квалитета. Питајте их коју опрему за мерење користе, колико често калибрирају машине и који проценат делова се прегледа. Према AccuPath-овим смерницама, компаније са строгим правилима квалитета дају чисте резе и глатке ивице, смањујући додатни рад након резања.
Ваш контролни список за процену пружалаца услуга
Користите ову свеобухватну контролну листу када упоређујете потенцијалне пружаоце услуга за ласерску резање метала:
- Капацитет опреме: Тип ласера (ласина у односу на СО2), ниво снаге, максимална величина листа и старост опреме
- Опције материјала: Диапазон метала у залихама, искуство са специјалним легурама и могућности снабдевања материјалима
- Сертификације: ИСО 9001 најмање; ИАТФ 16949 за аутомобил; АС9100 за ваздухопловство; ИСО 13485 за медицинску
- Време обраћања: Брзина одговора на цитат, стандардна време за испоруку и могућности за брзе наруџбе
- Квалитет подршке ДФМ-а: Процес инжењерског прегледа, предлози за оптимизацију дизајна и комуникација током прегледа
- Реактивност комуникације: Једина контактна тачка, времена одговора на питања и проактивна ажурирање пројекта
- Инспекција квалитета: Инспекцијска опрема, распореди калибрације и стопе узорка за инспекцију
- Способности за производњу прототипа: Приступачност брзе производње прототипа, минималне количине наруџбине и подршка прелазу из прототипа у производњу
- Прозирност цена: Потпуни цитати без скривених накнада, јасно објашњење фактора трошкова и спремност да се разговара о оптимизацији
- Референције за клијенте: Примери портфолија, искуство из индустрије и сведочења из сличних апликација
Према Тин Метал Партс-у, ефикасна комуникација чини производњу непрекидном. Када тражите понуде или процене пружалаца, наведите своју контактну тачку. То упростива комуникацију и оптимизује цели производни процес. Проверите да ли су спремни да одговоре постављајући питања и посматрајући колико брзо и темељно одговарају.
За апликације у аутомобилу и прецизној производњи, тражите добављаче који показују комплетан пакет: сертификацију ИАТФ 16949, могућности брзе производње прототипа који се крећу од концепта до делова за само 5 дана и свеобухватну ДФМ подршку која оптимизује ваше дизајне пре почетка производње Ове могућности, примером су произвођачи као што су Шаои , указује на пружаоца спремног да функционише као прави партнер за производњу, а не једноставно као услуга сечења.
Запамтите, најнижи цитат често кошта више на дугу основу. Према анализи АцуПатха, нискоцена услуга могу да немају добре алате или квалификоване раднике, што изазива грешке или оштећење материјала. Ако сада трошите више, касније ћете избећи скупе грешке. Процените пружаоце холистички, уравнотежујући трошкове са капацитетом, сертификацијом и квалитетом комуникације како бисте пронашли партнера који пружа доследне резултате пројекат за пројектом.
Узимање следећег корака ка свом пројекту ласерског сечења
Сада сте истражили комплетан пејзаж услуга ласерског резања метала, од физике како ласери претварају сировину у прецизне делове, кроз избор материјала, припрему фајлова и процену провајдера. Питање више није да ли се ласерски рез одговара вашем пројекту. То је како да се крећете напред са поверењем са првом наредбом или стотим.
За почетак не треба да будеш савршен. То захтева радњу вођену оквиром одлучивања који сте управо научили. Да издвојимо тај оквир у практичне следеће кораке који претварају знање у резултате.
Ваш акциони план за почетак
Прелазак од истраживања до резултата прати логичан редослед. Без обзира да ли истражујете онлине платформе за ласерско сечење или радите директно са специјализованим произвођачима, овај акциони план води ваше следеће потезе:
- Јасно дефинишите захтеве пројекта: Документирајте тип материјала, дебљину, количину, потребе за толеранцијом и све захтеве сертификације пре него што контактирате добављаче. Што су прецизнији ваши захтеви, то су тачнији и цитати.
- Припремите своје дизајнерске датотеке правилно: Извоз чисте векторске датотеке у DXF, DWG, или STEP формата у 1:1 маштабу. Затворите све путеве, конвертујте текст у контуре и проверите да минималне величине карактеристика испуњавају смернице дебелине материјала.
- Провајдери се процењују према критеријумима квалитета: Проверите могућности опреме, релевантне сертификације, квалитет подршке ДФМ-у и одговорност комуникације. Не дозволите да вам цена само управља одлуком.
- Захтевите цитате из више извора: Упоредите најмање три пружаоца за значајне пројекте. Погледајте изван цене по деловима да бисте проценили укупну вредност укључујући време за реализацију, осигурање квалитета и квалитет подршке.
- Почни са прототипом: Пре него што се обавежете на производњу количина, потврдите свој дизајн малом партијом. То потврђује и ваше спецификације и способности пружаоца.
Разумевање наплате за ласерско сечење унапред спречава изненађења у буџету. Према анализи цене Комакута, примарни фактори трошкова укључују врсту материјала, дебљину, сложеност дизајна, време сечења и процес завршног обраде. Оптимизовање дизајна за ефикасно гнезданје и поједностављене геометрије смањује трошкове без жртвовања функционалности.
Кључни подаци за успешне пројекте ласерског сечења
Након истраге сваког аспекта процеса ласерског сечења метала, ови увиди заслужују посебан нагласак:
Квалитет припреме датотека одређује успех пројекта више од било ког другог фактора. Петнаест минута провере затворено путање, правилно масштабирање и минималне величине карактеристика спречава дане ревизије и скупе накнаде за ремикс.
Најјефтиније ласерско резање ретко даје најбољу вредност. Провајдери се процењују целосна, балансирајући трошкове по делу са капацитетима опреме, статусом сертификације, квалитетом подршке ДФМ-а и одговорношћу комуникације.
Успореди технологију сечења са вашим специфичним захтевима, а не да се заузме само једна метода. За танке до средње листове који захтевају прецизност и чисте ивице, ласерско сечење обично даје оптималне резултате. За веома дебеле плоче или топлотно осетљиве материјале, плазма или водени струјач могу бити боље корисни.
За читаоце у аутомобилској или прецизној производњи, критеријуми за процену постају још критичнији. Сертификација IATF 16949 није опционална за рад у аутомобилском ланцу снабдевања. Моћ брзе производње прототипа која се креће од концепта до делова за само 5 дана убрзава циклусе развоја. И свеобухватна ДФМ подршка ухвати проблеме пре него што постану скупи производствени проблеми.
Произвођачи као што су Шаои (Нингбо) Технологија метала показати шта треба тражити од добављача квалитета: ИАТФ 16949 сертификовани операције, 12-часовни цитат за обраду, 5-дневна брза прототипирање, и свеобухватна ДФМ подршка за шасију, суспензију и структурне компоненте. Ове способности представљају стандард који треба да очекујете од било ког озбиљног партнера за прецизну производњу.
Ваш пројекат ласерског резача метала почиње са једним кораком: припремањем прве конструкције и тражењем прве цитат за ласерско резање. Знање које сте стекли позиционира вас да се уверите у процес, ефикасно комуницирате са добављачима и постигнете резултате који задовољавају ваше прецизне спецификације. Технологија је доказана, пружаоци су способни, и пут напред је јасан.
Често постављена питања о услугам за резање метала ласером
1. у вези са Који материјали се могу обрадити помоћу услуга за ласерско сечење метала?
Услуге за резање метала ласером обрађују широк спектар материјала укључујући угљенски челик, нерђајући челик, алуминијум, месин, бакар и специјалне легуре као што су титанијум и Инконел. Угледни челик сече најефикасније због одличне апсорпције ласерске енергије, док одражавајући метали као што су алуминијум и бакар захтевају више подешавања снаге и технологију ласерских влакана. Достављачи квалитета као што је Шаои одржавају обимне инвентаре материјала и могу саветовати о оптималном избору материјала за ваше специфичне захтеве апликације.
2. Уколико је потребно. Колико дебелог метала може да сече ласерски резач?
Способности дебелине зависе од ласерске снаге и врсте материјала. Ласер са 6кВ трака обично сече угљенски челик до 25 мм, нерђајући челик до 20 мм, алуминијум до 15 мм, а бакар до 8 мм. Систем са већим напоном који прелази 12 кВт може обрађивати још густије материјале. Међутим, квалитет и прецизност сечења опадају док се приближите максималној дебљини, тако да треба да размотрите своје захтеве за толеранцијом приликом избора дебљине материјала.
3. Уколико је потребно. Који су формати датотека потребни за услуге ласерског сечења?
Ласерска сечење захтева векторске формат фајлова укључујући ДХФ, ДВГ, АИ, СВГ, и СТЕП / СТП за 3Д дизајне. Ови формати користе математичке изразе да прецизно дефинишу ивице, за разлику од слика заснованих на пикселима као што су JPEG или PNG. Увек подносите датотеке у скали 1: 1 са затвореном стазом, конвертованим текстом и минималним величинама карактеристика одговарајућим дебелини вашег материјала како бисте осигурали тачан цитат и производњу.
4. Уколико је потребно. Колико дуго траје да се добију делови резани ласером?
Време за реализацију варира у зависности од пружаоца и сложености пројекта. Водеће услуге нуде цитате у року од 12-24 сата и испоручују стандардне наруџбе у 2-4 радна дана. Брзо прототипирање може произвести делове за само 5 дана, док сложена или велика производња могу захтевати дуже време. Поставници као што је Шаои нуде 12-часовни цитат и 5-дневно брзо прототипирање за аутомобилске апликације.
5. Појам Које сертификације треба да тражим у пружаоцу услуга за ласерско сечење метала?
Основне сертификације укључују ИСО 9001 за управљање квалитетом у основи и ИАТФ 16949 за аутомобилске апликације. Аерокосмички пројекти захтевају сертификацију AS9100, док компоненте медицинских уређаја захтевају ISO 13485. Ови сертификати потврђују документоване процедуре, праћење квалитета и континуиране процесе побољшања. За рад на ланцу снабдевања аутомобила, сертификација ИАТФ 16949 је обавезна и показује посвећеност строгим стандардима квалитета потребним за шасију, суспензију и структурне компоненте.
 Мале партије, високи стандарди. Наша услуга брзе прототипирања чини валидацију бржем и лакшим
Мале партије, високи стандарди. Наша услуга брзе прототипирања чини валидацију бржем и лакшим 
