Viktiga kallarbetsverktygsstål för högpresterande stansverktyg
TL;DR
Kallarbetsverktygsstål är specialiserade högkollegeringar utformade för stansverktyg, punschverktyg och andra verktyg som används vid temperaturer under 200°C. Dessa material väljs för sin exceptionella hårdhet, höga nötkänselighet och tillräcklig toughhet för att tåla de enorma mekaniska spänningarna vid skär- och formsättningsoperationer. Viktiga stålsorter för stansverktyg inkluderar kolfattiga, kromrika D-serien (som D2) och mångsidiga O-serien (som O1), var och en med en unik balans av egenskaper för optimal prestanda och verktygslivslängd.
Förståelse av kallarbetsverktygsstål: Grunden för stansverktyg
Kallarbetsverktygsstål utgör en avgörande kategori av specialmaterial som är utformade för att prestera utmärkt i krävande industriella tillämpningar där verktyg arbetar vid eller nära rumstemperatur. Enligt definition av branschledare som voestalpine , dessa stål är särskilt formulerade för tillverkning av verktyg där yttemperaturen i allmänhet inte överstiger 200°C (cirka 400°F). Denna egenskap skiljer dem från varmarbetsstål, som är utformade för att behålla sin hållfasthet vid höga temperaturer. För stansverktyg, som innebär formning och skärning av plåt med hög påverkan, är kallarbetande stål det ovedersägliga materialvalet.
Den främsta funktionen hos dessa stål är att tåla betydande mekanisk påkänning och slitage vid kallbearbetningsprocesser. Deras unika metallurgiska sammansättning, vanligtvis hög i kol och rik på legeringselement som krom, molybden och mangan, ger en kombination av viktiga egenskaper. Detta gör dem idealiska för tillverkning av slitstarka och exakta stansverktyg, punschverktyg och omformningsverktyg som kan klara miljontals cykler utan haveri. Förmågan att behålla ett skarpt skär och motstå deformation under tryck är avgörande för att säkerställa komponenternas kvalitet och tillverkningseffektiviteten.
Valet av kallarbetsstål för verktyg är en noggrann balans mellan flera nyckelkaraktäristika som direkt påverkar prestanda och livslängd för ett stansverktyg. Dessa grundläggande egenskaper inkluderar:
- Hög Hårdhet: Förmågan att motstå intryckningar och deformation, vilket är avgörande för att bibehålla verktygets exakta geometri.
- Utömordentlig utslitningsresistens: Förmågan att tåla slitage och erosion från kontakt med arbetsstyckmaterialet, vilket förlänger verktygets livslängd.
- Tillräcklig seghet: Motståndskraft mot avbitning, sprickbildning eller katastrofal brott under de plötsliga, höga påfrestningar som är vanliga vid stansoperationer.
- Bra dimensionsstabilitet: Förmågan att behålla sin storlek och form efter värmebehandling och under långvarig användning, vilket säkerställer konsekvent och noggrann delproduktion.
I slutändan beror effektiviteten i en stansoperation till stor del på kvaliteten på den verktygsstål som används. Ett välvalt kallarbetsstål garanterar inte bara tillförlitlig prestanda utan minimerar också driftstopp kopplat till verktygsservice och utbyte, vilket gör det till en grundsten inom modern industriell tillverkning.
Viktiga sorter av kallarbetsstål för högpresterande verktyg
Att välja rätt sort kallarbetsverktygsstål är ett avgörande beslut som direkt påverkar prestanda, livslängd och kostnadseffektivitet för stansverktyg. Olika sorter är konstruerade med specifika legeringsinnehåll för att erbjuda en unik balans av egenskaper. De vanligaste och mest effektiva sorterna faller inom distinkta kategorier, främst kolkraftiga, kromrika 'D'-serien och oljehärdande 'O'-serien, tillsammans med avancerade specialsorter.
Stål från D-serien, särskilt D2, är en världsstandard för många kallarbetstillämpningar tack vare sin extremt höga slitstyrka. Det höga krominnehållet (vanligen 12 %) bildar hårda karbider som motstår slitage, vilket gör D2 till ett utmärkt val för långa produktionsserier och för stansning av slipande material. Emellertid kan den höga hårdheten innebära en kompromiss vad gäller lägre slagseghet jämfört med andra sorter, vilket gör det mer benäget att spricka vid tillämpningar med kraftig påverkan.
O-serien, där O1 är ett framträdande exempel, erbjuder en mer balanserad egenskapsprofil. Som en oljehärdande stål ger den god härdbarhet med minimal deformation vid värmebehandling. O1 är känt för sin goda slagfasthet och tillräcklig nötfasthet, vilket gör det till ett mångsidigt och ekonomiskt val för allmänna verktyg, särskilt för korta till medellånga produktionsserier och för skärning av mjukare material. Dess toleranta natur gör det till ett pålitligt alternativ för ett brett utbud av blanknings- och formskärningsoperationer.
Under senare år har avancerade stålsorter som DC53 och DCMX fått ökad spridning tack vare sin överlägsna prestanda. DC53, som framhålls av leverantörer som International Mold Steel , är en modifiering av D2 som ger betydligt högre slagfasthet samtidigt som den bibehåller utmärkt nötfasthet. Detta gör den mindre benägen att spricka eller klibba, vilket förlänger verktygslivslängden i krävande tillämpningar. På liknande sätt har matrix-typstål som DCMX från Daido Steel är konstruerade med en mycket fin och jämn karbiddistribution, vilket förbättrar slagfasthet, bearbetbarhet och dimensionsstabilitet efter värmebehandling.
För att underlätta val använder följande tabell några av de viktigaste materialkvaliteterna som används för stansverktyg:
| Kvalitet | Primär nytta | Slitstyrka | Hållbarhet | Vanlig applikation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2 (1.2379) | Exceptionell slitstyrka för långa produktionsserier. | Mycket hög | Bra | Högvolymsskärande och formningsverktyg, gängvalsverktyg. |
| O1 (1.2510) | Bra allmänprestanda med god dimensionsstabilitet. | Bra | Mycket Bra | Allmänt skärande och punscheringsverktyg, mätinstrument, mandrar. |
| A2 (1.2363) | Balanserad slitstyrka och slagfasthet. | Hög | Hög | Verktyg för medellång produktion, som stansar, punscher och omformningsverktyg. |
| DC53 | Bättre slagfasthet än D2 med hög nötningsmotstånd. | Mycket hög | Excellent | Punscher, stansverktyg och verktyg benägna att klibba. |
| S7 | Exceptionell stötfasthet. | Medium | Exceptionell | Verktyg som kräver hög slagstyrka, till exempel mejslar och punscher. |
Avgörande egenskaper för att utvärdera optimal diesprestanda
Att välja den bästa verktygsståltypen för kallbearbetning till ett stansverktyg kräver en djup förståelse av dess grundläggande mekaniska egenskaper och hur de samverkar. Det optimala valet är sällan det material som ensamt är hårdast eller tuffast, utan det som erbjuder den bästa balansen mellan egenskaperna för den specifika tillämpningens krav. Korrekt utvärdering av dessa egenskaper är nyckeln till att maximera verktygets prestanda och livslängd.
Slitstyrka är stålets förmåga att motstå materialförlust på grund av slitage, adhesion eller erosion under stanscykeln. I högvolymproduktion eller vid arbete med slipande material som höghållfasta stål är hög slitstyrka avgörande för att bibehålla stansen skärande kanter och konturer. Stål med en hög volym hårda karbider, såsom D2, presterar utmärkt i detta avseende. Otillräcklig slitstyrka leder till snabb verktytsdovhet, dålig komponentkvalitet och ofta nödvändig stopptid för underhåll.
Hållbarhet är förmodligen en av de viktigaste egenskaperna för stansverktyg. Den representerar materialets förmåga att absorbera energi och motstå kipping eller sprickbildning under de enorma, upprepade slagkrafterna från stanspressen. Ett verktyg tillverkat av ett stål som är alltför sprött, även om det är mycket hårt, kommer att gå sönder i förtid. Därför väljs ofta sorter som S7 (känd för sin slagstyrka) eller avancerade sorter som DC53 (med förbättrad seghet) för tillämpningar som innebär tung omformning eller genomstansning.
Tryckstyrka är stålets förmåga att tåla höga tryck utan att deformeras eller kollapsa. Under en stansoperation utsätts stansens ytor för extrema tryckkrafter. Hög tryckhållfasthet säkerställer att stansens arbetsytor behåller sin exakta form, vilket är avgörande för att tillverka delar som uppfyller strama toleranser. Denna egenskap är nära kopplad till hårdhet och är avgörande för mynt- eller formslagningsoperationer som kräver fina detaljer.
Att uppnå rätt balans av dessa egenskaper är särskilt viktigt i komplexa tillämpningar som fordonsproduktion. Företag som är specialiserade inom denna sektor måste till exempel uppfylla stränga standarder för precision och hållbarhet. En sådan expert, Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology Co., Ltd. , utnyttjar djupa kunskaper i materialval för att tillverka högpresterande anpassade stansverktyg för fordonstillverkare och Tier 1-leverantörer, vilket visar hur avgörande rätt stål är för att uppnå effektivitet och kvalitet i krävande produktionsmiljöer.
För att hjälpa till att prioritera dessa egenskaper för ditt specifika användningsområde, överväg följande frågor:
- Vilket material och tjocklek har arbetsstycket som ska stansas? (Mer abrasiva eller tjockare material kräver högre slitstyrka).
- Hur stor förväntas produktionsomfattningen vara? (Större serier motiverar stål med högre slitstyrka).
- Innebär operationen höga stötkrafter, såsom kraftig blankning eller perforering? (Detta prioriterar slagstyrka).
- Är toleranserna på delen extremt strama? (Detta kräver hög tryckhållfasthet och dimensionell stabilitet).
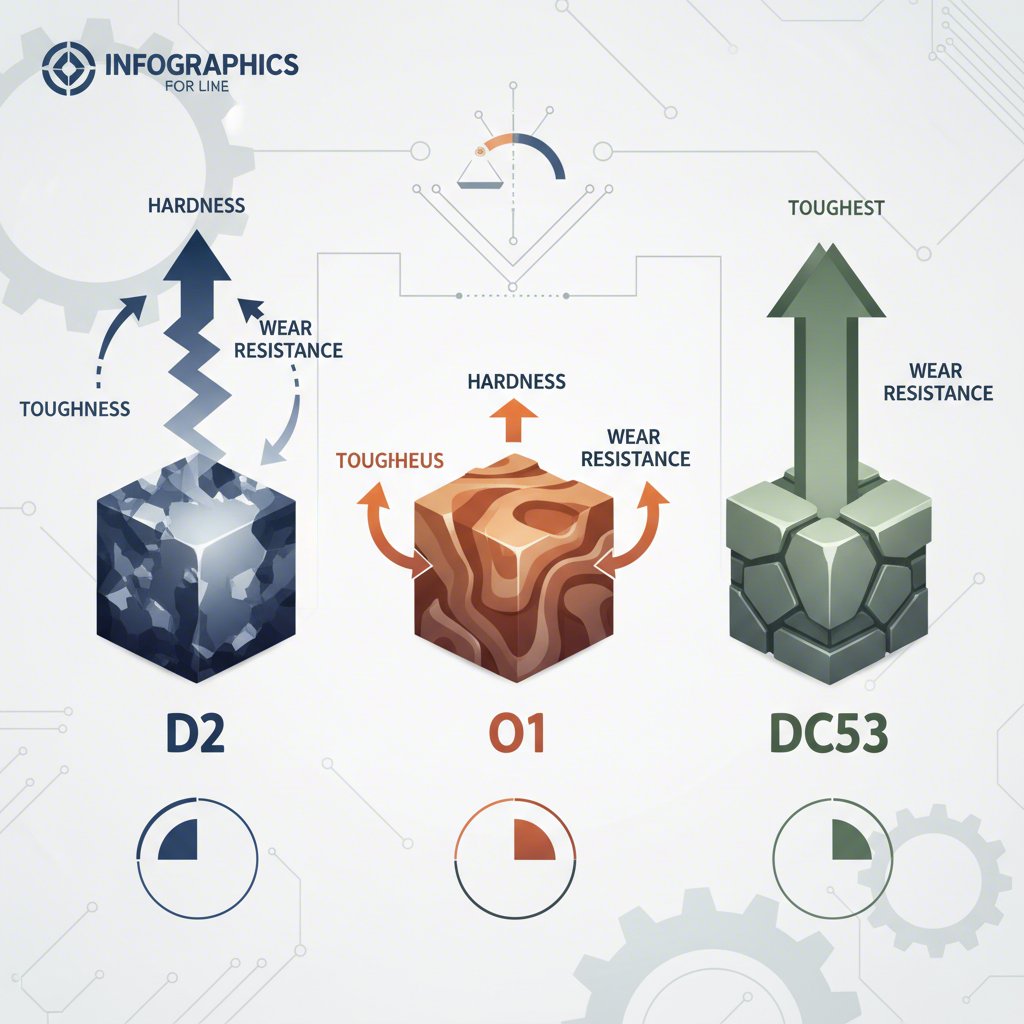
Göra det slutgiltiga stålvalet
Resan mot att välja den idealiska kallarbetsverktygsstål för stansverktyg är en teknisk process som bygger på att balansera prestandakrav med ekonomiska förhållanden. Som vi har undersökt finns det ingen enda 'bästa' ståltyp; det optimala valet är alltid beroende av sammanhanget. Beslutet hänger på en noggrann analys av den specifika stansapplikationen, från det material som formas till produktionsvolymen och delens komplexitet.
En viktig insikt är den inneboende avvägningen mellan slitagebeständighet och slagfasthet. Högpresterande slitagebeständiga stål som D2 är perfekta för långa, kontinuerliga produktionsserier med mindre krävande former, men kan riskera att spricka vid hög påverkan. Omvänt kan tåligare stål som S7 klara enorma stötar men kan slitas snabbare, vilket kräver mer frekvent underhåll. Moderna stålsorter som DC53 och andra pulvermetallurgiska stål syftar till att minska detta klyfta genom att erbjuda en överlägsen kombination av båda egenskaperna, även om de ofta har en högre initial kostnad.
Slutligen innebär en framgångsrik urvalsprocess samarbete mellan verktygsdesigners, ingenjörer och materialleverantörer. Genom att noggrant utvärdera de kritiska egenskaperna – slitstyrka, tandighet, tryckhållfasthet och dimensionsstabilitet – mot arbetsuppgiftens unika krav kan tillverkare säkerställa skapandet av slitstarka, pålitliga och mycket effektiva stansverktyg som levererar kvalitetsdelar under en lång livslängd.
Vanliga frågor
1. Vilket stål används för stansverktyg?
Stansverktyg tillverkas oftast av kallarbetsverktygsstål. Denna kategori inkluderar stålsorter som D2, känt för sin höga slitstyrka, och O1, som uppskattas för sin goda balans av egenskaper och enkla värmebehandling. För mer krävande applikationer används avancerade sorters som A2, S7 (för stötsäkerhet) och specialstål som DC53 för att förbättra tandighet och förlänga verktygslivslängden.
2. Vilket verktygsstål används för formgjutning?
Tryckgjutning använder varmarbetade verktygsstål, inte kallarbetade stål. Eftersom tryckgjutning innebär att injicera smält metall måste formarna tåla extremt höga temperaturer. De vanligaste stålsorterna för detta ändamål är H11 och H13, vilka är utformade för att behålla sin hårdhet och motstå termisk utmattnings- och erosionspåverkan vid upphöjda temperaturer.
3. Vilket stål är bäst för smidningsverktyg?
På liknande sätt som vid tryckgjutning är smidning en högtemperaturprocess som kräver varmarbetade verktygsstål. Sorter som AISI H11 och H13 används omfattande för smidningsverktyg på grund av sin utmärkta seghet, styrka vid hög temperatur samt motståndskraft mot värmeorsakad sprickbildning och slitage. Valet beror på smidningstemperaturen och komplexiteten hos den del som ska formas.
4. Vilka typer av stål skulle användas för verktyg, kallhuggjärn och fjädrar?
Dessa tillämpningar använder olika typer av stål beroende på deras krävda egenskaper. Verktyg används vanligtvis kallarbetsverktygsstål (som D2 eller O1) för blankning eller varm arbetsverktygsstål (som H13) för smidning. Kallmejslar kräver exceptionell slagbeständighet, vilket gör S-seriens verktygsstål som S7 idealiska. Fjädrar tillverkas av kolfattiga fjäderstål (som 1075 eller 1095) eller legerade fjäderstål (som 5160), som är utformade för hög brottgräns och elasticitet.
 Lilla partier, höga standarder. Vår snabba prototypservice gör validering snabbare och enklare —
Lilla partier, höga standarder. Vår snabba prototypservice gör validering snabbare och enklare —
