Menghadapi Tantangan Utama Industri Die Otomotif
TL;DR
Industri die otomotif sedang menghadapi badai sempurna dari berbagai tantangan kritis. Masalah utama meliputi krisis tenaga kerja yang parah, ditandai dengan penuaan populasi pekerja dan kesenjangan keterampilan yang terus berlangsung. Hal ini diperparah oleh tekanan ekonomi yang signifikan akibat fluktuasi biaya bahan baku dan rantai pasok global yang rentan. Selain itu, industri ini menghadapi kebutuhan mendesak untuk menyesuaikan teknologi dan prosesnya guna memenuhi tuntutan megatren otomotif seperti elektrifikasi kendaraan dan ringanannya (lightweighting), yang menuntut pendekatan sama sekali baru dalam desain dan manufaktur die.
Krisis Tenaga Kerja: Menghadapi 'Tsunami Perak' dan Kesenjangan Keterampilan
Salah satu tantangan paling mendesak di industri die otomotif adalah krisis struktural tenaga kerja yang mengancam kelangsungan hidup jangka panjangnya. Masalah ini bersifat ganda: gelombang pekerja terampil dan berpengalaman di bidang perkakas dan die mulai memasuki usia pensiun, sementara industri kesulitan menarik serta melatih tenaga kerja baru untuk menggantikan mereka. Pergeseran demografis ini, yang sering disebut sebagai "Silver Tsunami", menciptakan kesenjangan pengetahuan yang besar, karena puluhan tahun keahlian praktis meninggalkan lantai produksi tanpa rencana suksesi yang jelas. Masalah ini diperparah oleh penurunan historis dalam program pelatihan kejuruan dan persepsi bahwa manufaktur merupakan jalur karier yang ketinggalan zaman, sehingga sulit membangun alur bakat yang kuat.
Keterampilan yang dibutuhkan di bengkel perkakas dan cetakan modern juga berkembang secara pesat. Perkembangan menuju Industry 4.0, otomasi, dan material canggih berarti teknisi saat ini membutuhkan kombinasi keterampilan yang menggabungkan keahlian tradisional dengan kemampuan dalam perangkat lunak, robotika, dan analisis data. Hanya mencari kandidat saja tidak cukup; mereka harus memiliki kombinasi yang tepat antara kecakapan mekanis dan literasi digital. Kesenjangan keterampilan ini memberikan tekanan besar terhadap tim yang ada, membatasi kapasitas inovasi sebuah bengkel, dan pada akhirnya dapat menghambat pertumbuhan serta profitabilitas.
Mengatasi krisis tenaga kerja ini memerlukan strategi multi-aspek. Perusahaan harus berinvestasi pada program magang modern, seperti model Federation for Advanced Manufacturing Education (FAME), yang menawarkan jalur karier belajar sambil bekerja tanpa utang. Selain itu, seluruh industri harus bekerja untuk membentuk ulang citranya, menampilkan lingkungan manufaktur modern, bersih, dan berteknologi tinggi guna menarik generasi baru. Inisiatif utama meliputi:
- Kemitraan Pendidikan: Berkolaborasi dengan perguruan tinggi komunitas dan sekolah teknis untuk mengembangkan kurikulum yang relevan sesuai kebutuhan industri saat ini.
- Pelatihan Internal: Membuat program pelatihan internal dan peningkatan keterampilan yang kuat untuk membantu tenaga kerja yang ada beradaptasi dengan teknologi baru seperti perangkat lunak simulasi canggih dan robotika.
- Otomatisasi sebagai Penguat: Berinvestasi dalam otomatisasi dan robot kolaboratif (cobot) tidak hanya untuk menggantikan tenaga kerja, tetapi juga untuk menangani tugas-tugas berulang, sehingga memungkinkan teknisi terampil fokus pada pemecahan masalah dan pengendalian kualitas yang bernilai lebih tinggi.
- Outreach dan Advokasi: Berpartisipasi dalam acara-acara seperti Hari Manufaktur untuk berinteraksi dengan siswa, orang tua, dan pendidik guna menghilangkan persepsi usang mengenai industri ini.
Tekanan Ekonomi: Biaya Material, Rantai Pasok, dan Geopolitik
Di luar lantai produksi, industri die otomotif menghadapi tantangan ekonomi yang kuat. Biaya bahan baku yang tinggi dan sering berfluktuasi, terutama logam penting seperti aluminium, magnesium, dan baja perkakas berkualitas tinggi, secara langsung memengaruhi profitabilitas. Permintaan pasar global, harga energi, dan peristiwa geopolitik dapat menyebabkan fluktuasi harga yang tajam, sehingga sulit bagi pembuat die untuk memberikan penawaran jangka panjang yang stabil dan mengelola anggaran proyek secara efektif. Tekanan harga ini merupakan pertarungan yang terus-menerus, memaksa perusahaan untuk menyerap biaya atau berisiko kehilangan penawaran di pasar yang sangat kompetitif.
Pandemi COVID-19 mengungkap kerentanan rantai pasok global, suatu kerapuhan yang terus memengaruhi industri. Gangguan dapat menunda pengiriman bahan dan komponen penting, menyebabkan penghentian produksi serta keterlambatan tenggat waktu bagi klien otomotif. Tantangan ini diperparah oleh kebijakan perdagangan internasional, tarif, dan ketegangan geopolitik, yang dapat menimbulkan ketidakpastian serta menambah biaya. Sebagai respons, banyak perusahaan di Amerika Utara sedang mengevaluasi kembali strategi pengadaan mereka, yang mendorong tren reshoring atau nearshoring untuk menciptakan jaringan pasok yang lebih tangguh dan responsif.
Menghadapi tekanan ekonomi ini membutuhkan ketangkasan strategis. Banyak produsen kini mengadopsi model rantai pasok hibrida untuk menyeimbangkan biaya dan risiko. Pendekatan ini melibatkan pertahanan sebagian pengadaan global demi efisiensi biaya, sekaligus pengembangan pemasok regional dan lokal untuk komponen-komponen kritis guna memastikan stabilitas dan memperpendek waktu tunggu. Di bawah ini adalah perbandingan dari pendekatan strategis tersebut:
| Strategi | Kelebihan | Kekurangan |
|---|---|---|
| Offshoring | Biaya tenaga kerja dan produksi yang lebih rendah; akses ke kapasitas manufaktur berskala besar. | Waktu tunggu yang lama; biaya pengiriman tinggi; rentan terhadap risiko geopolitik dan tarif; potensi masalah kekayaan intelektual (IP). |
| Reshoring/Pemenuhan Lokal | Waktu tunggu singkat; kolaborasi dan kontrol kualitas yang lebih baik; ketahanan rantai pasok yang lebih tinggi; perlindungan IP. | Biaya tenaga kerja dan operasional yang lebih tinggi; ketersediaan tenaga ahli yang lebih terbatas di beberapa bidang khusus. |

Beradaptasi dengan Megatren Otomotif: Elektrifikasi dan Peringanan
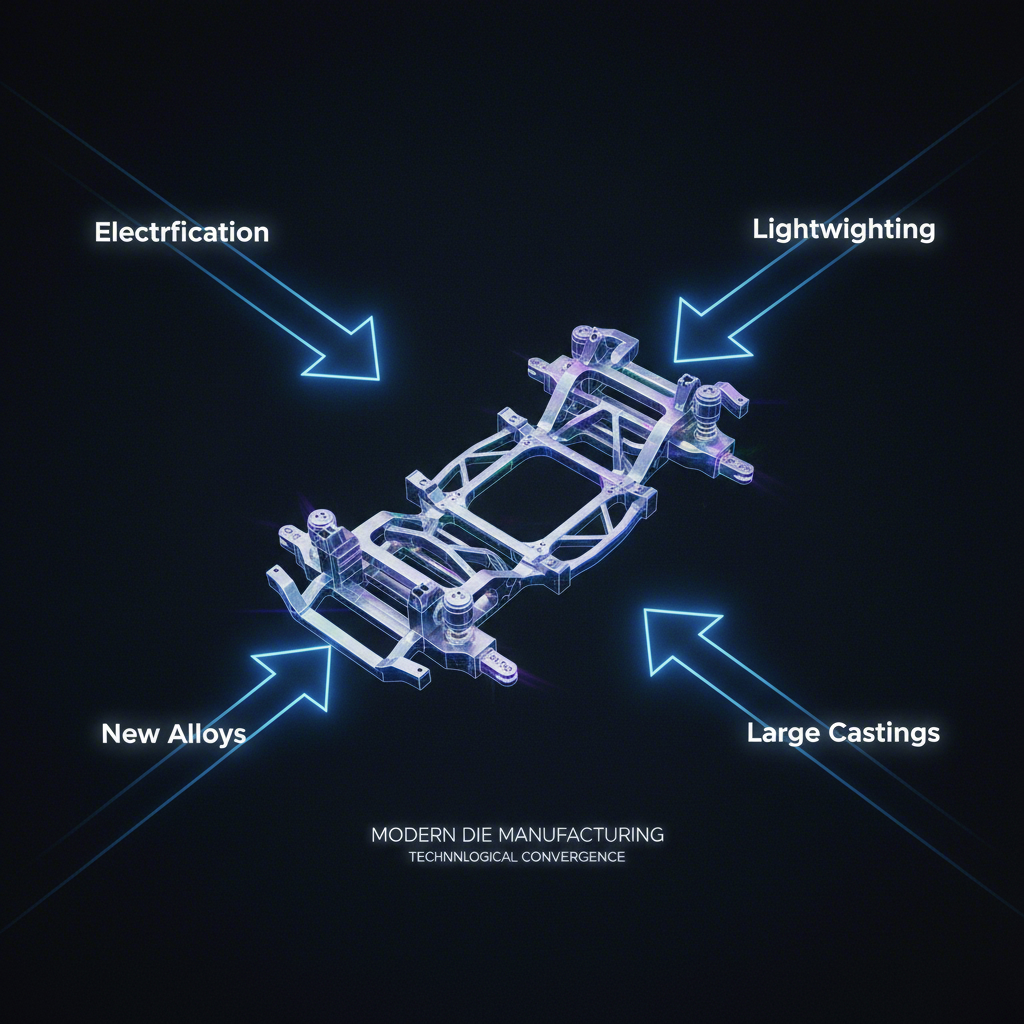
Kekuatan transformatif paling signifikan yang membentuk industri die otomotif adalah pergeseran cepat menuju kendaraan listrik (EV) dan upaya tanpa henti untuk mereduksi bobot. Ini bukan sekadar tren, melainkan perubahan mendasar dalam arsitektur kendaraan yang menuntut solusi perkakas baru. Kendaraan listrik membutuhkan komponen die-cast yang besar, kompleks, dan sangat terintegrasi, seperti enclosure baterai satu bagian dan "giga-casting" untuk struktur sasis. Produksi komponen-komponen ini memerlukan mesin cor yang lebih besar dan lebih kuat, serta cetakan dengan ukuran dan kompleksitas yang belum pernah ada sebelumnya, sehingga mendorong batas-batas manufaktur tradisional.
Secara bersamaan, dorongan untuk mengimbangi berat baterai yang besar dan meningkatkan efisiensi keseluruhan telah memperkuat fokus pada ringanisasi di seluruh kendaraan. Hal ini menuntut pembuat cetakan untuk menguasai penggunaan paduan aluminium dan magnesium canggih, yang memiliki sifat termal dan aliran yang berbeda dibandingkan material tradisional. Merancang cetakan untuk komponen struktural berdinding tipis dan berkekuatan tinggi—seperti menara kejut dan pilar bodi—memerlukan perangkat lunak simulasi canggih guna memprediksi aliran logam, mencegah cacat, serta memastikan integritas komponen. Perusahaan yang mampu menyediakan solusi canggih ini sedang menempatkan diri sebagai mitra penting dalam masa depan desain otomotif.
Untuk mengatasi tantangan-tantangan ini, produsen die yang berpikiran maju sedang melakukan investasi besar-besaran dalam teknologi dan proses baru. Manufaktur aditif (pencetakan 3D) digunakan untuk membuat insert cetakan kompleks dengan saluran pendingin konformal, yang secara drastis mengurangi waktu siklus dan meningkatkan kualitas produk melalui pendinginan yang lebih seragam. Simulasi CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) canggih kini menjadi hal penting untuk mengoptimalkan desain die sebelum baja dipotong, menghemat waktu dan mencegah pembongkaran ulang yang mahal. Perusahaan-perusahaan seperti Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology Co., Ltd. menggambarkan pergeseran serupa di sektor stamping, memanfaatkan simulasi canggih dan keahlian manajemen proyek untuk menyediakan die stamping otomotif dan komponen khusus bagi OEM.
Mengatasi Hambatan Produksi dan Pengendalian Kualitas
Bahkan dengan desain dan bahan yang sempurna, proses die casting itu sendiri dipenuhi tantangan teknis yang dapat memengaruhi kualitas, biaya, dan efisiensi. Hambatan produksi ini memerlukan pengawasan terus-menerus dan kendali proses untuk dapat diatasi. Para produsen harus mengelola keseimbangan yang halus antara suhu, tekanan, dan kecepatan agar dapat menghasilkan komponen yang konsisten dan bebas cacat. Beberapa masalah paling umum bersifat inheren terhadap fisika dari proses penyuntikan logam cair ke dalam cetakan baja pada kecepatan tinggi.
Di antara masalah yang paling sering terjadi adalah porositas, yang terjadi ketika gas atau udara terperangkap di dalam logam cair saat membeku, menciptakan rongga-rongga kecil yang dapat mengganggu integritas struktural komponen. Masalah lain yang sering muncul adalah "flash", di mana lapisan tipis logam berlebih keluar dari cetakan pada garis parting, sehingga memerlukan operasi pemangkasan sekunder yang menambah tenaga kerja dan limbah. Selain itu, pengelolaan keseimbangan termal sangat penting; jika cetakan terlalu dingin, dapat menyebabkan cacat seperti "cold shuts", sedangkan pendinginan yang tidak merata dapat menyebabkan distorsi bentuk dan ketidakkonsistenan penyusutan.
Pengurangan masalah-masalah ini secara efektif bergantung pada kombinasi desain cetakan yang kuat, perawatan yang teliti, serta kontrol proses yang canggih. Berikut adalah lima tantangan produksi umum beserta solusi masing-masing:
- Pembentukan Pori & Penjebakan Gas: Ini sering diatasi dengan memasukkan saluran ventilasi dan lubang peluapan yang ditempatkan secara strategis dalam desain cetakan agar udara terperangkap dapat keluar. Menggunakan pengecoran berbantu vakum, yang menghilangkan udara dari rongga sebelum injeksi, merupakan metode lain yang sangat efektif.
- Ketidakseimbangan Termal: Sistem manajemen termal canggih, termasuk saluran pemanas dan pendingin yang ditempatkan secara strategis serta penggunaan termokopel cetakan, membantu menjaga suhu cetakan yang konsisten, mencegah cacat akibat titik panas atau dingin.
- Keausan Cetakan: Tekanan dan suhu tinggi dalam pengecoran die menyebabkan keausan yang tak terhindarkan. Hal ini dikelola dengan menggunakan baja perkakas berkualitas tinggi dan tahan lama, penerapan lapisan permukaan canggih untuk mengurangi gesekan dan erosi, serta jadwal ketat pemeliharaan preventif dan inspeksi.
- Susut dan Ketidakkonsistenan: Saat logam mendingin, ia menyusut. Desain cetakan yang tepat, yang dapat memperkirakan penyusutan ini dan mendorong pendinginan seragam, merupakan solusi utama. Pemilihan paduan dengan tingkat penyusutan yang dapat diprediksi dan minimal juga memainkan peran penting.
- Flash: Memastikan kedua bagian cetakan sejajar sempurna dan menerapkan tekanan penjepitan yang tepat adalah kunci untuk mencegah terbentuknya flash. Perawatan rutin cetakan untuk memperbaiki keausan pada garis parting juga sangat penting.
Membuka Jalan Maju dalam Manufaktur Cetakan Otomotif
Industri cetakan otomotif berada pada persimpangan kritis, yang ditandai oleh tantangan besar sekaligus peluang signifikan. Konvergensi krisis tenaga kerja, tekanan ekonomi yang terus-menerus, dan revolusi teknologi besar-besaran yang didorong oleh elektrifikasi dan ringanisasi memaksa terjadinya transformasi mendasar. Kelangsungan hidup dan keberhasilan tidak lagi dijamin hanya oleh keterampilan tradisional semata; kini hal tersebut bergantung pada kemampuan perusahaan untuk berinovasi, beradaptasi, serta melakukan investasi strategis dalam sumber daya manusia, teknologi, dan proses yang tangguh.
Langkah ke depan memerlukan pendekatan yang holistik. Perusahaan harus menjadi pengembang talenta yang proaktif, membangun tenaga kerja terampil masa depan melalui magang modern dan kemitraan pendidikan. Mereka juga harus menjadi strategi yang cerdas, menghadapi ketidakpastian ekonomi global dengan rantai pasok yang fleksibel dan tangguh. Yang paling penting, mereka harus menjalankan peran sebagai pemimpin teknologi, memanfaatkan otomasi, material canggih, dan perangkat digital untuk menyediakan solusi perkakas canggih yang akan mendukung generasi kendaraan berikutnya. Bengkel-bengkel yang berhasil menjelajahi lanskap kompleks ini akan muncul bukan hanya sebagai pemasok, tetapi sebagai mitra yang sangat dibutuhkan dalam masa depan mobilitas.
Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan
1. Apa itu komponen die casting di industri otomotif?
Die casting adalah proses manufaktur yang digunakan untuk memproduksi berbagai komponen logam untuk kendaraan dengan cara menyuntikkan logam cair ke dalam cetakan yang dapat digunakan kembali (die) di bawah tekanan tinggi. Komponen-komponen ini dihargai karena kekuatannya, ringan, serta kemampuannya dibentuk menjadi bentuk yang kompleks. Contoh umum dalam industri otomotif meliputi blok mesin, rumah transmisi, komponen suspensi, braket, dan bagian struktural seperti menara shock dan balok melintang.
2. Apa tren paling signifikan yang saat ini memengaruhi industri otomotif?
Tren paling signifikan dan transformatif yang saat ini memengaruhi industri otomotif adalah elektrifikasi. Perpindahan global dari mesin pembakaran internal (ICE) ke kendaraan listrik (EV) sedang mengubah segala hal, mulai dari desain kendaraan dan rantai pasok hingga proses manufaktur. Tren ini mendorong permintaan akan jenis komponen baru, seperti pelindung baterai ringan dan coran struktural terintegrasi, yang pada gilirannya menciptakan tantangan serta peluang baru bagi industri peralatan dan cetakan.
 Produksi dalam jumlah kecil, standar tinggi. Layanan prototipisasi cepat kami membuat validasi lebih cepat dan mudah —
Produksi dalam jumlah kecil, standar tinggi. Layanan prototipisasi cepat kami membuat validasi lebih cepat dan mudah —

