Služby laserového rezania kovov vysvetlené: od cenovej ponuky po hotový diel
Pochopenie technológie laserového rezania pre výrobu kovov
Nikdy ste sa zamysleli, ako výrobcovia vytvárajú tie nemožne presné kovové súčiastky s komplikovanými vzormi a ostrými hranami? Odpoveď sa nachádza v jednej z najvýznamnejších technológií moderného spracovania materiálov: rezaní kovu laserom. Tento proces premenil spôsob, akým priemysel pristupuje k práci s kovmi, a nahradil pomalšie mechanické metódy rýchlosťou, presnosťou a vynikajúcou všestrannosťou.
Laserové rezanie je termický proces, ktorý využíva vysoce zameraný lúč svetla na roztavenie, spaľovanie alebo odparovanie kovu pozdĺž počítačom naprogramovanej dráhy, čím vznikajú presné rezy s minimálnymi stratenými materiálmi.
Čo je teda laserové rezanie presne a prečo sa stalo preferovaným riešením pre všetko – od autodiely až po architektonické kovové konštrukcie? Poďme si rozobrať základy, aby ste presne porozumeli tomu, čo sa deje, keď pošlete svoje návrhy do profesionálnej služby laserového rezania kovov .
Ako zamerané svetlo transformuje surové kovy
Predstavte si sústredenie slnečného svetla cez lupy, ale tento princíp zosilnený o niekoľko rádov. V podstate takto funguje rezanie laserom. Proces začína vo vnútri zariadenia nazývaného rezonátor, kde určité prostredie generuje intenzívne zameraný lúč koherentného svetla.
Tu sa to stáva fascinujúcim. Keď fotóny interagujú s elektrónmi v laserovom prostredí, spustia reťazovú reakciu nazývanú stimulovaná emisia. Každý excitovaný elektrón uvoľní identický fotón, čím vzniká kaskáda dokonale synchronizovaných svetelných vĺn. Tieto fotóny sa odrazujú medzi zrkadlami, až kým nedosiahnu dostatočnú intenzitu na to, aby prešli cez polopriehľadný povrch ako silný, zameraný lúč.
Keď lúč opustí rezonátor, prechádza sériou zrkadiel alebo optických káblov, než prejde cez fokusovaciu šošovku. Táto šošovka sústredí všetku energiu do extrémne malého priemeru, niekedy až na zlomok milimetra. Výsledkom je lokalizovaný bod extrémneho tepla, ktorý dosahuje teploty postačujúce na roztavenie alebo odparovanie takmer akéhokoľvek kovu.
Veda stojaca za presnou výrobou kovových dielov
Možno sa pýtate, ako dosahuje laserové rezenie kovov taký úžasný stupeň presnosti. Tajomstvo spočíva v počítačom riadenom procese. Predtým, ako začne rezaní, sa váš dizajnový súbor prevedie do G-kódu, čo je v podstate sada strojovo čitateľných inštrukcií, ktoré presne určujú, kam sa má laserová hlava pohybovať.
Keď sa zameraný lúč dotkne povrchu kovu, v závislosti od materiálu a použitej techniky sa deje jedna z troch vecí:
- Tavenie: Prúd inertného plynu pod vysokým tlakom, ako je dusík, odvádza roztavený materiál od rezu a zároveň chráni okraj pred oxidáciou
- Plamenné rezanie: Kyslík podporuje proces vytváraním exotermickej reakcie, ktorá zrýchľuje rýchlosť rezania
- Vyparovacie rezanie: Pri tenkých alebo citlivých materiáloch laser odstraňuje materiál priamo bez pomoci plynu
Táto presnosť je dôvodom, prečo sa služby laserového rezania kovov stali priemyselným štandardom pre presnosť a opakovateľnosť. CNC ovládanie umožňuje rýchle úpravy, automatizované rezné dráhy a schopnosť konzistentne vyrábať identické diely, či už potrebujete jeden prototyp alebo tisíce výrobných kusov.
V tomto sprievodcovi zistíte, ako sa jednotlivé laserové technológie porovnávajú, ktoré kovy sú najvhodnejšie pre rôzne aplikácie a ako optimalizovať svoje návrhy pre hospodárne výsledky. Či už vyhľadávate diely pre výrobný projekt alebo skúmate možnosti pre individuálnu kovovú výrobu, pochopenie týchto základov vám pomôže robiť informované rozhodnutia a efektívne komunikovať so službami poskytovateľmi.
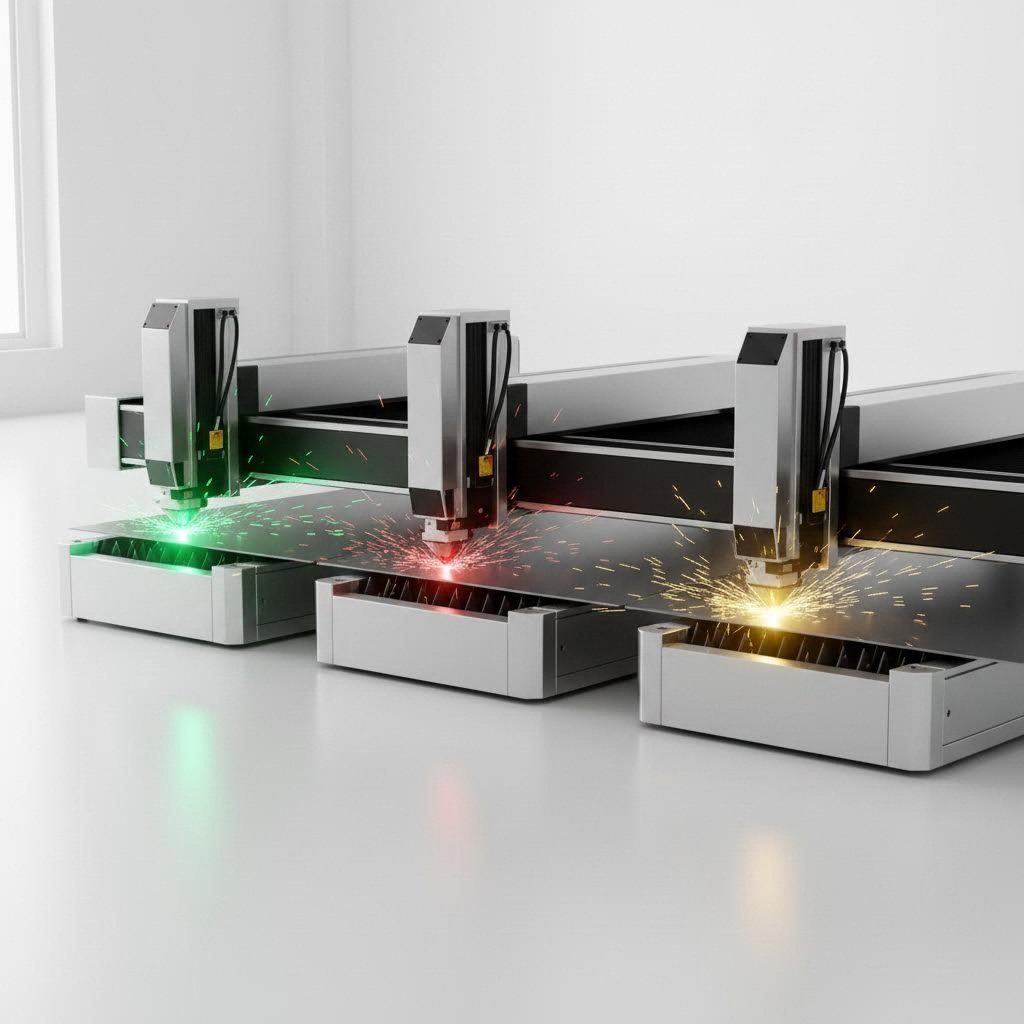

Vysvetlenie technológií CO2 vs vlákno vs Nd:YAG laser
Teraz, keď rozumiete základnej fyzike laserového rezania, tu je otázka, ktorá naozaj záleží: ktorý typ laseru by mal vykonať váš projekt? Nie všetky lasery sú rovnaké a výber nesprávnej technológie môže znamenať pomalšie výrobné časy, vyššie náklady alebo neuspokojivú kvalitu rezaných okrajov. Poďme objasniť tri hlavné možnosti laserových rezacích strojov, s ktorými sa stretnete pri zisťovaní služieb spracovania kovov.
Vláknové lasery vs. CO2 pre aplikácie na kovy
Keď hodnotíte laserový rezačný stroj pre kovy, najčastejšie sa stretnete s dvoma dominantnými technológiami: CO2 a vláknové lasery. Každá z nich vyniká v rôznych situáciách a porozumenie ich silným stránkam vám pomôže priradiť technológiu ku konkrétnym požiadavkám na materiál.
CO2 Lasery vytvárajú infračervené svetlo vlnovej dĺžky 10,6 mikrometrov pomocou zmesi plynov obsahujúcej oxid uhličitý. Tieto stroje sú pracovnou silou priemyslu od sedemdesiatych rokov 20. storočia a naďalej sú obľúbené vďaka svojej všestrannosti. Stroj na rezanie kovov pomocou CO2 lasera dokáže mimoriadne dobre spracovať hrubšie materiály, najmä nehrdzavejúcu oceľ a jemnú oceľ väčších hrúbok. Podľa výskumu spoločnosti Laser Expertise Ltd moderné systémy CO2 pracujúce pri výkone 4-5 kW dokážu rezať jemnú oceľ hrúbky až 25 mm a nehrdzavejúcu oceľ hrúbky až 20 mm.
Čo robí technológiu CO2 výnimočnou? Jej dlhšia vlnová dĺžka efektívne interaguje s organickými materiálmi, čo tieto stroje robí ideálnymi pre prevádzky, ktoré spracúvajú aj plasty, drevo alebo textil. Rovnaká vlastnosť však spôsobuje problémy pri práci s vysoko reflexnými kovmi, ako je meď alebo hliník, keď sa lúč môže odrážať späť a poškodiť optické komponenty.
Fiber Lasery predstavujú novšiu generáciu technológie laserových strojov na rezanie kovov. S prevádzkovou vlnovou dĺžkou 1,06 mikrometra dodávajú vláknové systémy vynikajúci výkon pri tenkých a stredne hrubých kovoch. Tieto stroje premenia elektrickú energiu na laserové svetlo s mimoriadnou účinnosťou, zvyčajne 30–50 %, oproti približne 10–15 % u CO2 systémov.
Keď pracujete so strojom na laserové rezanie plechov a spracovávate materiály pod 6 mm, vláknová technológia často ponúka výrazne vyššie rýchlosti rezu. Kratšia vlnová dĺžka tiež znamená, že vláknové lasery spoľahlivejšie spracovávajú odrazné kovy ako hliník, mosadz a meď. Mnoho služieb laserového rezania hlási 2 až 3-krát rýchlejšie spracovanie tenkého nehrdzavejúceho ocele v porovnaní s ekvivalentnými CO2 systémami.
Priradenie laserovej technológie k vašim požiadavkám na materiál
Nd:YAG lasery zaberajú špecializovanú nišu v oblasti rezania kovov . Tieto systémy so solidným stavom pracujú tiež na vlnovej dĺžke 1,06 mikróna, podobne ako vláknové lasery, ale namiesto optického vlákna využívajú kryštalické prostredie. Ich hlavnou výhodou je schopnosť prenášať lúč cez optické vlákna k robotickým ramenám alebo na ťažko prístupné pozície na automobilových výrobných linkách.
Podľa výskumov zdokumentovaných odborníkmi na laserové rezanie, Nd:YAG systémy vynikajú v troch konkrétnych prípadoch:
- Jemné detailné práce na tenkých materiáloch, kde sú nevyhnutné extrémne malé zamerané body
- Rezanie vysoko odrazových kovov, ako sú zliatiny striebra, v pravidelnej výrobnej prevádzke
- Aplikácie vyžadujúce flexibilný prenos lúča cez optické vlákna ku spracovávaným predmetom
Avšak Nd:YAG lasery nemôžu spracovávať väčšinu organických materiálov, pretože plasty a výrobky z dreva sú voči ich vlnovej dĺžke priehľadné. Toto obmedzenie znamená, že sa len zriedka vyskytujú vo všeobecných dielňach, ale zostávajú cennými pre špecializované výrobné bunky.
Ak chcete rýchlo zistiť, ktorá technológia laserového rezania plechov vyhovuje požiadavkám vášho projektu, tu je komplexné porovnanie:
| Faktor | CO2 laser | Vláknový laser | Nd:YAG Laser |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ideálne typy materiálov | Jemná oceľ, nehrdzavejúca oceľ, plasty, drevo, textílie | Tenké kovy, odrazivé kovy (hliník, meď, mosadz) | Odrazivé zliatiny, práca s jemnými detailmi, striebro |
| Možná hrúbka | Až do 25 mm jemnej ocele, 20 mm nehrdzavejúcej ocele | Najlepšie do 20 mm, vyniká pri tenkých kalibroch | Zvyčajne len tenké profily |
| Rýchlosť rezu (tenký kov) | Mierne | Najrýchlejšia voľba | Stredné až pomalé |
| Energetická efektívnosť | účinnosť 10-15 % pri napájaní zo siete | účinnosť zo zásuvky 30-50 % | účinnosť zo zásuvky 3-5 % |
| Požiadavky na údržbu | Vyššia (zrkadlá, dopĺňanie plynu, turbíny) | Nižšia (polovodičová, minimálna optika) | Stredná (náhrada výbojky alebo diódy) |
| Typické aplikácie | Všeobecná výroba, hrubé platne, prevádzky so zmiešanými materiálmi | Vysokozdružná výroba tenkých kovov, autodielov | Robotizované zváracie bunky, špecializované jemné rezanie |
Ktorú technológiu by ste teda mali zvoliť pri požiadavkách na cenové ponuky? Pri väčšine projektov kovovej výroby sa voľba obmedzuje na typ a hrúbku materiálu. Ak režete oceľové platne hrubšie ako 12 mm, CO2 zostáva veľmi konkurencieschopná. Pre vysokozdružnú výrobu tenkých komponentov z nehrdznúcej ocele alebo hliníka sú služby rezania vláknovým laserom zvyčajne najlepšou voľbou pokiaľ ide o kombináciu rýchlosti a kvality rezu. A ak vaša aplikácia vyžaduje mimoriadne jemné detaily alebo prácu s vysoko odrazovými špeciálnymi zliatinami, Nd:YAG môže byť hodná preplatenia.
Pochopenie týchto rozdielov vám umožní kladením lepších otázok pri vyhodnocovaní poskytovateľov služieb a zabezpečí, že vaše súčiastky budú spracované na zariadeniach optimalizovaných pre vaše konkrétne požiadavky. V ďalšej časti preskúmame, ktoré kovy sa najlepšie spracúvajú jednotlivými technológiami, a hrúbkové obmedzenia, ktoré musíte zohľadniť pri svojich návrhoch.
Sprievodca kompatibilitou kovov a hrúbkovými obmedzeniami
Už viete, ako rôzne laserové technológie fungujú, ale tu je praktická otázka, ktorá každého kupujúceho trápi: dokáže laserové rezanie spracovať konkrétny kov, ktorý váš projekt vyžaduje? Odpoveď závisí od vlastností materiálu, ktoré priamo ovplyvňujú spôsob, akým laserová energia interaguje s obrobkom. Pochopenie týchto dynamík vám pomôže už v predstihu zvoliť správny materiál a vyhnúť sa tak nákladným prekvapeniam počas výroby.
Nie všetky kovy rovnako reagujú na laserové rezanie plechov. Fyzikálne vlastnosti, ako odrazivosť, tepelná vodivosť a teplota topenia, určujú, či sa materiál oreže čisto, alebo či vyžaduje špecializované odborné znalosti. Pozrime sa, čo robí každý bežný kov jedinečným, a ako profesionálne služby dosahujú vynikajúce výsledky naprieč celým spektrom.
Rezné parametre pre oceľ a nehrdzavejúcu oceľ
Najskôr dobré správy: ak pracujete s oceľou, zvolili ste si jeden z najvhodnejších materiálov pre laserové rezanie. Laserové rezanie ocele je priamočiare, pretože uhlíková oceľ a mäkká oceľ efektívne absorbuje laserovú energiu a má primerané tepelné vlastnosti.
Laserové rezanie mäkkej ocele pri spracovaní s dusíkom ako asistenčným plynom vytvára čisté, bezoxidové okraje, alebo rýchlejšie rezy s kyslíkom. Podľa odborných smerníc pre hrúbku materiálu , tenké oceľové plechy medzi 0,5 mm a 3 mm sa ľahko režú lasermi s výkonom 1000 W až 2000 W, zatiaľ čo stredne hrubé platne od 4 mm do 12 mm vyžadujú systémy s výkonom 2000 W až 4000 W. Pre hrubé oceľové platne v rozmedzí od 13 mm do 20 mm poskytujú vysokovýkonové lasery medzi 4000 W a 6000 W potrebnú hĺbku preniknutia.
Rezanie nehrdzavejúcej ocele laserom platia podobné princípy, no treba venovať pozornosť kvalite rezaného okraja. Keďže nehrdzavejúca oceľ obsahuje chróm, ktorý sa môže pri vysokých teplotách oxidovať, mnohé aplikácie vyžadujú použitie dusíka ako asistenčného plynu, aby sa zachovala odolnosť proti korózii na rezanom okraji. Ako uvádzajú odborníci z Universal Tool, nehrdzavejúca oceľ vytvára čisté a vysokokvalitné okraje aj pri vyšších hrúbkach pomocou vláknových laserov, čo ju robí vynikajúcou voľbou pre praktické aj dekoratívne aplikácie.
Pri práci s laserovým rezaním ss (nehrdzavejúcej ocele) dbajte na tieto parametre:
- Tenká nerezová oceľ (0,5 mm až 3 mm) sa precízne reže lasermi s výkonom 1000 W až 2000 W
- Stredná hrúbka (4 mm až 8 mm) vyžaduje systémy s výkonom 2000 W až 4000 W pre hladké rezy
- Hrubá nerezová oceľ (9 mm až 20 mm) vyžaduje lasery s výkonom od 4000 W do 6000 W na správne preniknutie
- Pomocný plyn dusík zachováva prirodzenú koróznu odolnosť materiálu
Práca s odraznými kovmi ako hliník a meď
Tu sa výber materiálu stáva zložitejším. Vysoce odrazivé kovy predstavujú skutočné výzvy, ale moderná vláknová laserová technológia tieto problémy do veľkej miery vyriešila. Porozumenie tomu, prečo sa tieto materiály správajú inak, vám pomôže stanoviť realistické očakávania a efektívne komunikovať so službami poskytovateľmi.
Laserové rezanie hliníka vyžaduje starostlivé riadenie parametrov z dvoch dôvodov. Po prvé, vysoká odrazivosť hliníka spôsobuje, že späť odráža významnú časť energie laserového lúča. Po druhé, jeho vynikajúca tepelná vodivosť rýchlo odvádza teplo zo zóny rezu. Výsledok? Na dosiahnutie rovnakého rezu potrebujete viac výkonu v porovnaní s oceľou rovnakej hrúbky.
Podľa odborníci na rezanie vláknovým laserom , hliník sa výborne reže vláknovými laserovými strojmi, napriek tomu, že je náročný na starších CO2 systémoch. Pri projektoch s laserovým rezaním hliníka sa tenké plechy hrúbky medzi 0,5 mm a 3 mm dobre spracúvajú pomocou laserov s výkonom 1000 W až 2000 W. Stredné hliníkové dosky hrúbky 4 mm až 8 mm vyžadujú systémy s výkonom 2000 W až 4000 W, zatiaľ čo hrubé platne od 9 mm do 15 mm si vyžadujú výkon 4000 W alebo vyšší, aby sa prekonala odrazivosť materiálu.
Z medi a mostu tieto výzvy posúvajú ešte ďalej. Oba kovy vykazujú extrémne vysokú odrazivosť a tepelnú vodivosť, čo ich robí najnáročnejšími bežnými materiálmi pre laserové spracovanie. Vláknové lasery pracujúce na kratšej vlnovej dĺžke 1,06 mikrometra však spracúvajú mediene zliatiny oveľa spoľahlivejšie, než kedykoľvek mohli systémy CO2.
Čo sa týka medi, hrúbkové tabuľky uvádzajú, že aj pre relatívne tenké prierezy medzi 0,5 mm a 6 mm sú bežne potrebné lasery s výkonom 3000 W až 5000 W. Odborné služby kompenzujú náročné vlastnosti medi úpravou rýchlosti rezu, zvyšovaním hustoty výkonu a používaním špecializovaných konfigurácií asistenčných plynov.
Tu je komplexný referenčný sprievodca, ktorý ukazuje, čo očakávať pri bežných kovoch:
| Typ kovu | Maximálny rozsah hrúbky | Odporúčaný typ laseru | Osobitné úvahy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mäkká oceľ | Až do 25 mm | CO2 alebo vláknový | Najjednoduchšie na rezanie; pomocný kyslík zvyšuje rýchlosť; dusík vytvára okraje bez oxidácie |
| Nehrdzavejúcu oceľ | Až 20 mm | CO2 alebo vláknový | Použite dusík ako asistenčný plyn na zachovanie odolnosti voči korózii; dosiahnuteľná vynikajúca kvalita okrajov |
| Hliník | Až do 15 mm | Vláknový (výrazne uprednostňovaný) | Vysoká odrazivosť a tepelná vodivosť vyžadujú vyšší výkon; odporúča sa asistenčný dusík |
| Meď | Až do 6 mm | Iba vláknové | Extrémne odrazivý; vyžaduje vysoký výkon (3000 W a viac); nevyhnutné sú nižšie rýchlosti rezu |
| Mosadz | Až do 8 mm | Vláknový (výrazne uprednostňovaný) | Podobné výzvy ako meď; vláknovej vlnove dĺžke lepšie zvláda odrazivosť ako CO2 |
| Titán | Až do 10 mm | CO2 alebo vláknový | Najvyšší pomer pevnosti k hmotnosti; vyžaduje inertnú atmosféru na zabránenie oxidácii; prémiové cenové označenie |
Titán si zasluhuje osobitnú zmienku, pretože kombinuje vynikajúcu kompatibilitu s laserom s náročnými procesnými požiadavkami. Tento kov sa ľahšie reže laserom ako strihá alebo obrába mechanicky, čo robí laserové spracovanie obzvlášť atraktívnym pre letecký a lekársky priemysel. Titan však pri vyšších teplotách agresívne reaguje s kyslíkom, preto je nevyhnutné použiť argón alebo dusíkové krytie, aby sa zabránilo krehnutiu rezaných okrajov.
Čo by ste mali odniesť z týchto úvah o materiáloch? Po prvé, oceľ a nehrdzavejúca oceľ zostávajú najvhodnejšími voľbami pre projekty laserového rezania. Po druhé, hliník a meď sú absolútne vhodné s modernou vláknovou laserovou technológiou, ale očakávajte upravené ceny, ktoré odrážajú vyššiu spotrebu energie a pomalšie rýchlosti spracovania. Nakoniec si vždy pred finálnym potvrdením návrhu preverte špecifiká materiálu so svojím poskytovateľom služieb, keďže obmedzenia hrúbky môžu závisieť od konkrétneho vybavenia, ktoré používa.
Teraz, keď viete, ktoré materiály sú najvhodnejšie pre laserovú technológiu, možno sa pýtate, ako sa laserové rezanie vyrovnáva alternatívnym metódam. Kedy si namiesto toho zvoliť vodný lúč, plazmové alebo CNC obrábanie? V nasledujúcej časti nájdete úprimné porovnanie, ktoré vám pomôže vybrať optimálny postup pre vašu aplikáciu.
Laserový rez vs. Vodný lúč, plazma a CNC alternatívy
Tu je jedna uprimná pravda, ktorú obvykle predajne orientovaný obsah zriedkavo uznanie: laserové rezanie nie je vždy najlepšou voľbou. Prekvapené? Hoci laserová technológia vyniká v mnohých aplikáciách, pochopenie, kedy alternatívne služby na rezanie kovov dosahujú lepší výkon ako lasery, vám môže ušetriť významné množstvo času, peňazí a frustrácie. Porovnajme objektívne vaše možnosti, aby ste mohli priradiť správnu technológiu konkrétnym požiadavkám vášho projektu.
Každá rezacía metóda prináša na stôl výrazné výhody. Kľúčom je pochopiť, kde sa technológie laseru a CNC dopĺňajú, a kde alternatívy ako vodný lúč alebo plazma poskytujú lepšie výsledky. Uvažujte takto: cnc laserový rezač kovov môže byť ideálny pre váš komplikovaný návrh upevnenia, ale tá istá technológia by mohla byť zlou voľbou pre váš hrubší projekt z konštrukčnej ocele.
Kedy vodný lúč prevyšuje laserové rezanie
Vodný lúč používa vodu pod vysokým tlakom zmiešanú s abrazívnymi časticami na rezanie takmer akýmkoľvek materiálom. Podľa priemyselného testovania od Wurth Machinery sa očakáva, že trh s vodným lúčom dosiahne do roku 2034 viac ako 2,39 miliardy USD, pričom tento rast je spôsobený hlavne aplikáciami, v ktorých je nevyhnutné rezanie bez tepla.
Kedy si máte vybrať vodný lúč namiesto lasera? Zvážte tieto scenáre:
- Teplom citlivé materiály: Vodný lúč nevytvára žiadnu tepelne ovplyvnenú zónu, čo znamená žiadne skreslenie, tvrdenie ani zmeny v kovovej štruktúre vašej obrobenej súčasti
- Extrémne hrubé materiály: Vodný lúč dokáže spracovať materiály hrubé až do 12 palcov, kde laser nie je účinný
- Rezanie rôznorodých materiálov: Jeden systém na vodný rez dokáže rezať kameň, sklo, kompozity a kovy bez nutnosti výmeny zariadenia
- Odrážajúce špeciálne zliatiny: Mosadz, titán a Inconel sa spoľahlivo režú bez problémov s odrazivosťou, ktoré znepokojujú laserové systémy
- Potravinársky priemysel: Žiadne tepelné kontaminácie robí vodný lúč ideálnym pre potravinársku výrobnú techniku
Aké sú nevýhody? Rezanie vodným lúčom je výrazne pomalšie ako laserové spracovanie, najmä pri tenkých materiáloch. Prevádzkové náklady sú tiež vyššie kvôli spotrebe abrazíva a údržba si vyžaduje viac pozornosti kvôli zmesi vody a granátového piesku vznikajúcej počas rezania. Investícia do zariadenia je tiež významná – kvalitné systémy vodného rezu začínajú okolo 100 000 USD oproti 60 000 USD u menších jednotiek.
Plazmové vs. laserové rezanie pri hrubom ocelovom materiále
Ak hľadáte plazmové rezanie v blízkosti mňa pre výrobu z hrubých ocelí, kladiete si správnu otázku. Plazmové rezanie dominuje pri práci s vodivými kovmi hrubšími ako pol palca, pričom náklady zostávajú udržateľné.
Podľa porovnávacích testov je rezy plazmou oceľovej platne hrúbky 1 palec približne 3 až 4-krát rýchlejšie ako vodný lúč, pri prevádzkových nákladoch približne polovičných na lineárny stopu. Ešte presvedčivejší je rozdiel v investičných nákladoch: kompletný plazmový systém stojí okolo 90 000 USD oproti približne 195 000 USD za podobne veľké vodno-lúčové zariadenie.
Zvoľte plazmové rezanie, ak sa vaše projekty týkajú:
- Výroba konštrukčných oceľových prvkov: Nosníkov, platní a súčiastok z hrubej ocele, ktoré je potrebné rýchlo a ekonomicky rezať
- Výroba ťažkých zariadení: Súčiastok stavebných a poľnohospodárskych strojov
- Lodenícke aplikácie: Spracovanie veľkorozmerných hrubých platní, kde je rýchlosť dôležitejšia ako jemný detail
- Práca s hrubým kovom s ohľadom na rozpočet: Keď povolené tolerancie umožňujú širšie limity plazmového rezu
Plazmové rezanie však má jasné obmedzenia. Presnosť okrajov je oveľa menej presná ako pri laserovom rezaní , čo robí plazmové rezanie nevhodným pre komplikované návrhy alebo diely s prísnymi toleranciami. Zamestnanci tiež vyžadujú dodatočné bezpečnostné opatrenia kvôli elektromagnetickému žiareniu vznikajúcemu počas rezania. Ak váš návrh vyžaduje čisté okraje, malé otvory alebo komplexné geometrie, CNC laserové rezanie zostáva lepšou voľbou.
Pre úplný prehľad o tom, ako sa technológia laserového CNC porovnáva so všetkými hlavnými alternatívami, tu je komplexný prehľad:
| Faktor | Laserového rezania | Vodný lúč | Plazma | Frezovanie CNC | EDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presnosť tolerancie | ±0,1 mm až ±0,25 mm | ±0,1 mm až ±0,5 mm | ±0,5 mm až ±1,5 mm | ±0,05 mm až ±0,25 mm | ±0,005 mm až ±0,025 mm |
| Kvalita hrany | Vynikajúce, minimálne potreba dodatočného dokončenia | Dobré, možný mierne šikmý rez | Hrubejšie, často vyžaduje sekundárne dokončenie | Dobré, závisí od nástroja | Dosiahnuteľný zrkadlový povrch |
| Teplom ovplyvnená zóna | Malá, ale prítomná | Žiadny | VEĽKÉ | Žiadny (mechanický) | Veľmi malé |
| Rozsah hrúbky materiálu | 0,5 mm až 25 mm (oceľ) | Až 300 mm+ | 3 mm do 150 mm+ | Obmedzené hĺbkou rezačky | Až do 300 mm |
| Rýchlosť rezania | Veľmi rýchle pri tenkých materiáloch | Pomalý až stredne silný | Rýchle pri hrubých kovoch | Mierne | Veľmi pomalé |
| Relatívna cena | Mierne až vysoké | Vysoké prevádzkové náklady | Nízke náklady na vybavenie a prevádzku | Mierne | Ťahové |
| Najvhodnejšie typy materiálov | Tenké až stredne hrubé kovy, niektoré nekovové materiály | Akýkoľvek materiál vrátane kameňa a skla | Len vodivé kovy | Mäkšie kovy, plasty, drevo | Iba vodivé materiály |
Frezovanie CNC ponúka výhody, keď pracujete s mäkkšími kovmi ako hliník alebo potrebujete vytvoriť 3D kontúry namiesto jednoduchých 2D profilov. Mechanické rezanie nevytvára tepelne ovplyvnenú zónu, podobne ako vodný lúč, a náklady na vybavenie môžu byť nižšie pri základných operáciách. Podľa porovnania spoločnosti Xometry sa mechanické rezanie udržuje konkurencieschopné z hľadiska nákladov a flexibility v aplikáciách, kde nie je vyžadovaná extrémna presnosť.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) zaberá špecializované pozície pri ultra-precíznych pracovných úkonoch. Keď sú povinné tolerancie tesnejšie ako ±0,025 mm, alebo keď potrebujete rezať kalené nástrojové ocele, ktoré by zničili mechanické rezačky, EDM sa stáva jedinou životaschopnou možnosťou. Kompromisom je výrazne pomalšia rýchlosť spracovania.
Kedy by ste malí rezanie laserom konkrétne vyhnúť?
- Hrubé dosky nad 25 mm: Plazmový alebo vodno-abrazívny proces rýchlejší a hospodárnejší
- Aplikácie citlivé na teplo: Lekárske implantáty alebo materiály, ktoré nepretrpia žiadny tepelný vstup, vyžadujú vodno-abrazívny rez
- Nevodivé materiály: Kameň, sklo a mnohé kompozity sa lepšie režú vodno-abrazívnym spôsobom
- Ultra-precízne požiadavky: Ak sú povinné tolerancie pod ±0,1 mm, môže byť potrebné EDM
- Hrubý oceľ s obmedzeným rozpočtom: Plazma ponúka prijateľnú kvalitu za výrazne nižšiu cenu
Mnoho úspešných dielní na výrobu prevádzkuje viacero technológií práve preto, lebo žiadna jediná metóda nie je optimálna pre každú aplikáciu. Plazma a laser sa často dobre dopĺňajú, pokrývajúc prácu s tenkými presnými dielcami až po ťažkú štrukturálnu výrobu. Pridaním vodno-abrazívnej kapacity sa rozširuje všestrannosť takmer na akýkoľvek materiál bez obáv z tepla.
Pochopenie týchto kompromisov vám umožní požadovať cenové ponuky od správnych poskytovateľov služieb a zabezpečí, že vaše súčiastky budú spracované pomocou optimálnej technológie. Po výbere spôsobu rezu nasleduje ďalší krok – optimalizácia vášho návrhu, aby sa minimalizovali náklady a maximalizovala kvalita bez ohľadu na zvolený proces.
Smernice pre optimalizáciu návrhu pre laserom rezané súčiastky
Vybrali ste si správnu technológiu rezu a overili ste kompatibilitu materiálu. Teraz prichádza krok, ktorý rozdeľuje hladký priebeh výroby od nákladných oneskorení: správne pripraviť vaše návrhové súbory. Správny návrh zohľadňujúci výrobnosť nezabráni len problémom, ale aktívne zníži vaše náklady na jednotlivé súčiastky a zároveň zlepší kvalitu. A či už vytvárate súčiastky rezané laserom pre prototyp alebo pripravujete tisíce výrobkov do sériovej výroby, tieto smernice vám pomôžu urobiť to správne hneď na prvý pokus.
Predstavujte si svoj návrhový súbor ako sadu inštrukcií pre presný systém laserového rezania kovov. Čím jasnejšie a optimalizovanejšie tieto inštrukcie budú, tým rýchlejšie a presnejšie stroj dokáže ich vykonať. Podľa odborníkov na DFM spoločnosti Jiga vedenie zásad vhodných pre výrobu už v počiatočnom štádiu návrhu vedie k presným rezom s minimálnymi odpadmi, skrátenému času rezania a zlepšenému celkovému výrobnému výkonu.
Minimálne veľkosti prvkov a špecifikácie otvorov
Tu je otázka, ktorá chytí mnohých prvotných kupujúcich nepripravených: ako malé môžu byť prvky vlastne? Odpoveď závisí od hrúbky materiálu a ak sa toto nepreberie správne, môže to znamenať neúplné rezy, nadmerné hromadenie tepla alebo diely, ktoré nebudú plniť svoju funkciu podľa zámeru.
Minimálny priemer otvoru je priamo závislé od hrúbky materiálu. Ako všeobecné pravidlo pre presné laserové rezanie platí, že priemer otvorov by mal byť aspoň rovný hrúbke materiálu. Napríklad oceľový plech hrubý 2 mm by nemal mať otvory menšie ako 2 mm v priemere. Použitie menších otvorov je technicky možné, ale vyžaduje pomalšie rezné rýchlosti a môže spôsobiť tepelné deformácie okolo obvodu otvoru.
Pri návrhu otvorov a vnútorných prvkov dodržiavajte tieto smernice:
- Vzdialenosť otvoru od okraja: Zachovajte vzdialenosť najmenej 1,5-násobku hrúbky materiálu medzi akýmkoľvek otvorom a okrajom súčiastky, aby ste predišli skresleniu a zabezpečili štrukturálnu pevnosť
- Vzdialenosť medzi otvormi: Udržujte minimálnu vzdialenosť jednej hrúbky materiálu medzi susediacimi otvormi, aby ste sa vyhli hromadeniu tepla, ktoré môže deformovať tenké mostíky medzi prvkami
- Šírka slotu: Drážky by mali mať šírku najmenej 1,5-násobok šírky rezu, aby sa zabezpečilo úplné odstránenie materiálu počas rezania
- Ostré vnútorné rohy: Skutočné vnútorné rohy s uhlom 90 stupňov nie sú možné, pretože laserový lúč má konečný priemer; navrhujte malé polomery (zvyčajne minimálne 0,5 mm) vo vnútorných rohoch
Podľa Presné rezné špecifikácie spoločnosti Datum Alloys , profesionálne služby môžu dosiahnuť tolerancie ±0,05 mm u lineárnych rozmerov a ±0,15 mm pozíciu tolerancie u prvkov. Tieto priemyselné štandardy vám pomáhajú pochopiť, čo je realisticky dosiahnuteľné pri určovaní práce pre vaše laserovo rezané CNC stroje.
Kompenzácia šírky rezu je ďalším dôležitým aspektom, ktorý mnohí návrhári prehliadajú. Rez (kerf) je šírka materiálu odstráneného samotným laserovým lúčom, typicky sa pohybuje medzi 0,1 mm a 0,3 mm v závislosti od druhu a hrúbky materiálu. Keď záležia presné konečné rozmery, váš návrh musí brať do úvahy túto stratu materiálu. Väčšina profesionálnych služieb automaticky aplikuje kompenzáciu rezu, no porozumenie tomuto pojmu vám pomôže jasne komunikovať požiadavky na rozmery.
Optimalizácia vášho návrhu pre nákladovo efektívne rezanie
Chcete znížiť svoju cenovú ponuku o 20 % alebo viac? Chytrá optimalizácia dizajnu často prináša práve takéto úspory. Zásady sú jednoduché, ak raz pochopíte, čo ovplyvňuje náklady na laserové rezanie: čas stroja, spotreba materiálu a požiadavky na dodatočné spracovanie.
Optimizácia usporiadania maximalizuje počet dielov, ktoré sa zmestia na každý list materiálu. Podľa odvetvových smerníc DFM prispieva efektívne rozmiestnenie a spoločné rezy priamo k úsporám nákladov tým, že minimalizujú odpad materiálu a skracujú celkový čas rezania. Pri návrhu vlastných plechových dielov vyrezávaných laserom zvážte tieto prístupy šetrné voči rozmiesťovaniu:
- Spoločné rezy: Navrhujte susediace diely tak, aby tam, kde je to možné, zdieľali hrany, čím sa zníži celková dĺžka rezania
- Západky tvaru: Vytvorte komplementárne geometrie, ktoré sa efektívne usadia vedľa seba bez plytvania priestorom
- Štandardné veľkosti plechov: Navrhnite rozmery dielov tak, aby sa rovnomerne delili do bežných veľkostí plechov, čím sa minimalizuje odpadový materiál
- Flexibilita orientácie: Vyhýbajte sa prvkom, ktoré obmedzujú možnosť otáčania dielov počas rozmiestňovania
Umiestnenie zámkov pre stabilitu dielu zabraňuje posunutiu malých alebo ľahkých komponentov počas rezu. Tieto malé mostíky udržiavajú diely na mieste v rámci kostry plechu, až kým nedôjde k dokončeniu rezania. Laserový rezací stroj pre plech automaticky vo väčšine prípadov spravuje zámky, no porozumenie tomuto pojmu pomáha predvídať, kde sa na hotových dieloch môžu objaviť stopy po zámkoch.
Pri príprave súborov na laserové rezanie oceľového plechu alebo iných materiálov tieto zjednodušenia návrhu znížia náklady bez toho, aby bola ohrozená funkčnosť:
- Zjednodušte geometriu: Používajte hladké, spojité čiary namiesto komplexných kriviek alebo nadmerných podrobností, ktoré predlžujú čas rezania
- Odstráňte nepotrebné prvky: Každá diera, drážka a obrys pridáva strojový čas; odstráňte dekoratívne prvky, ktoré neslúžia žiadnym funkčným účelom
- Štandardizujte hrúbky: Podľa materiálového sprievodcu spoločnosti Komacut je použitie štandardných hrúbok materiálu jedným z najjednoduchších spôsobov optimalizácie nákladov, keďže laserové rezačky sú kalibrované na štandardné veľkosti
- Zvážte montáž: Začleňte konštrukciu s výstupkami a drážkami, ktorá umožňuje samosúosovanie pri montáži a zníži tak potrebu prípravkov
Príprava formátu súboru priamo ovplyvňuje rýchlosť získania cenovej ponuky a presnosť výroby. Odborné služby bežne akceptujú CAD formáty súborov DWG a DXF. Podľa prípravných pokynov spoločnosti Datum Alloys by vaše súbory mali spĺňať tieto špecifikácie:
| Požiadavka | Špecifikácia | Prečo je to dôležité |
|---|---|---|
| Formát súboru | DWG alebo DXF (iba 2D) | Strojovo čitateľné formáty, ktoré sa priamo prekladajú na rezné dráhy |
| Váha | 1:1 (skutočná veľkosť) | Nesúlad v mierkach má za následok vyrezávanie dielov príliš malých alebo veľkých |
| Súvislosť čiar | Kompletné, nepretržité dráhy | Prelomené alebo čiarkované čiary nemôžu byť interpretované rezacím softvérom |
| Nepodstatné prvky | Odstráňte rámy s názvami, kóty a poznámky | Vo výkresu by mal byť zobrazený iba rezový obrys |
| Počet komponentov na súbor | Jedna súčiastka na súbor (preferované) | Zjednodušuje kalkuláciu ceny a zníži chyby pri spracovaní |
Čo s tými vstupnými úsekmi, ktoré môžu byť spomenuté v špecifikáciách? Podľa smerníc spoločnosti Datum je vstupný úsek krátka vstupná dráha, ktorú laser používa na začatie hladkého rezu, pričom na okraji zostane malá stopy. Väčšina profesionálnych služieb ich pridáva automaticky, pokiaľ neurčíte, že konkrétny okraj musí zostať nepoškvrnený.
Správna optimalizácia návrhu vytvára pozitívny cyklus. Lepšie rozmiestnenie znamená menej odpadu materiálu. Jednoduchší tvar znamená rýchlejší rez. Primerané rozmery prvkov znamenajú menej problémov s kvalitou. Spoločne tieto faktory znížia vaše náklady a zároveň poskytnú vysoce kvalitné laserom rezané súčiastky. Keď máte optimalizované návrhové súbory, ďalšou dôležitou oblasťou poznania je pochopenie faktorov ovplyvňujúcich kvalitu hotových súčiastok.

Kvalitatívne faktory a odstraňovanie bežných problémov pri rezaní
Vaše návrhové súbory sú optimalizované a materiál je vybraný. Teraz tu je otázka, ktorá rozhoduje o tom, či vaše laserom rezané kovové diely skutočne splnia požadované požiadavky: čo rozdeľuje kvalitný rez od podpriemerného výsledku? Porozumenie faktorom ovplyvňujúcim kvalitu hotových dielov vám pomôže jasne špecifikovať požiadavky, efektívne vyhodnocovať vzorky a riešiť problémy, než sa stanú drahými chybami.
Keď skúmate komponent z laserom rezaného nehrdzavejúceho ocele alebo akýkoľvek výstup oceľového laserového rezania, päť kľúčových ukazovateľov odhaľuje skutočnú úroveň kvality: hladkosť povrchu, tvorba hrubín, konzistencia reznej medzery (kerfu), kolmosť rezu a veľkosť tepelne ovplyvnenej zóny. Podľa odborníkov na kvalitu vláknových laserov tieto faktory priamo ovplyvňujú presnosť aj funkčnosť vašich obrobkov. Pozrime sa, čo spôsobuje bežné problémy a ako ich profesionálne služby predchádzajú.
Zamedzenie krčenia a tepelného deformovania
Už ste niekedy dostali súčiastky, ktoré vyzerajú v CAD súbore dokonale, ale prišli mierne skrútené alebo vybočené? Deformácia je pravdepodobne najfrustrujúcejším problémom kvality pri laserovom rezaní kovov, pretože môže urobiť inak vynikajúce súčiastky nepoužiteľnými.
Deformácia vzniká, keď intenzívne teplo generované laserovým lúčom spôsobuje lokálne rozťahovanie a zmršťovanie kovu. Podľa inžinierskeho tímu Central Laser Services patria medzi bežné príčiny:
- Nerovnomerné rozloženie tepla: Keď rezné dráhy sústreďujú teplo do konkrétnych oblastí namiesto rovnomerného rozloženia tepelnej záťaže po celom obrobku
- Nedostatočná podpora materiálu: Súčiastky, ktoré sa počas rezania posúvajú alebo ohýbajú, vyvíjajú vnútorné napätie, keď sa nerovnomerne ochladzujú
- Nesprávne poradie rezania: Poradie, v akom sa jednotlivé prvky režú, ovplyvňuje, ako sa hromadí napätie v zostávajúcom materiáli
- Excesívna laserová energia: Viac výkonu, ako je potrebné, vytvára väčšie tepelne ovplyvnené zóny a zvyšuje tepelné napätie
Ako profesionálne služby laserového rezania plechov predchádzajú týmto problémom? Kľúčom je riadenie tepla. Kvalitní poskytovatelia kalibrujú výkon, rýchlosť a zaostrenie tak, aby vyvážili kvalitu rezu a minimálne tepelné zaťaženie. Ich montážne tímy zabezpečujú pevnú podporu materiálu počas celého procesu reznia, čím zachovávajú rozmernú presnosť a rovinnosť. Okrem toho optimalizácia umiestnenia dielov a poradia reznia minimalizuje zvyškové napätia a zároveň zvyšuje využitie plechu.
The zóna ovplyvnená teplom (HAZ) si zasluhuje osobitnú pozornosť, pretože priamo ovplyvňuje vlastnosti materiálu. Táto oblasť okolo každého rezu prechádza mikroštrukturálnymi zmenami spôsobenými tepelným zaťažením. Veľká tepelne ovplyvnená zóna môže znížiť pevnosť materiálu alebo spôsobiť krehkosť. Medzi faktory ovplyvňujúce veľkosť tepelne ovplyvnenej zóny patria úroveň laserovej energie, rýchlosť reznia, hrúbka materiálu a voľba asistenčného plynu. Vláknová laserová technológia zvyčajne vytvára menšie tepelne ovplyvnené zóny v porovnaní so staršími CO2 systémami, a to vďaka rýchlejšiemu prenosu energie a vyšším rýchlostiam reznia.
Rôzne kovy reagujú na tepelné zaťaženie odlišne. Vysoká tepelná vodivosť hliníka pomáha rýchlo rozptýliť teplo, ale vyžaduje si starostlivé riadenie parametrov, aby sa predišlo lokálnemu deformovaniu. Nerezová oceľ vydrží teplo primerane dobre, ale bez vhodného plynu na ochranu môže dôjsť ku miernej zmenšenej farby okolo rezaných okrajov. Meď predstavuje najväčšiu výzvu, pretože jej extrémna tepelná vodivosť komplikuje kontrolu hromadenia tepla.
Dosiahnutie čistých okrajov bez hrubíc
Preliezajte si prstom pozdĺž laserom rezaného okraja. Je hladký, alebo cítite drsný, vyvýšený materiál, ktorý sa zachytáva na pokožke? Tieto drsné okraje sú hrubice a patria medzi najčastejšie problémy kvality pri laserovom rezaní plechov.
Podľa odborníci na kontrolu kvality laserového rezania , hrudy vznikajú, keď je rezná rýchlosť príliš nízka alebo laserový výkon príliš vysoký, čo spôsobuje, že roztavený materiál znovu ztuhne pozdĺž rezaného okraja namiesto toho, aby bol čisto odstránený. Medzi ďalšie prispievajúce faktory patria nedostatočný tlak asistenčného plynu a nesprávne zaostrenie lúča.
Pri hodnotení hotových súčiastok od akéhokoľvek poskytovateľa laserového rezania kovov skontrolujte tieto ukazovatele kvality:
- Hladkosť povrchu: Skontrolujte reznú plochu na diagonálne pruhy; menšie stopy označujú lepšiu kvalitu rezania
- Prítomnosť hrub: Nahmatajte spodný okraj pre vystupujúci materiál, ktorý naznačuje neúplné odstránenie strusky
- Konzistencia rezu: Zmerajte šírku rezu na viacerých miestach, aby ste overili rovnomerné rezanie po celom diele
- Kolmosť: Skontrolujte, či sú rezné okraje skutočne zvislé voči povrchu materiálu, najmä u hrubších materiálov
- Zmena farby: Hľadajte zmeny farby spôsobené teplom v blízkosti okrajov, ktoré môžu poukazovať na nadmerné tepelné zaťaženie
Popáleniny a zmena farby vznikajú v dôsledku nadmerného tepla v okolí rezného priestoru. Na zabránenie týmto problémom odborné služby upravujú nastavenie výkonu lasera, vhodne zvyšujú rýchlosť rezania a používajú asistenčné plyny, ako je dusík alebo vzduch, ktoré chladia rezaciu zónu a odvádzajú nečistoty. Výber správneho typu lasera pre konkrétne materiály tiež minimalizuje riziko popálenín.
Čo rozdeľuje kvalitné laserové rezanie od nekvalitných výsledkov? Záleží to na správnej kalibrácii zariadenia, optimalizovaných rezných parametroch prispôsobených každému konkrétnemu materiálu a hrúbke a na konzistentnom monitorovaní procesu. Podľa najlepších postupov kontroly kvality zabezpečuje pravidelná kalibrácia stroja správne zarovnanie laserového lúča pre presné rezy. Obsluhy by mali sledovať a upravovať parametre na základe druhu materiálu a jeho hrúbky, aby udržali konzistenciu počas celých výrobných sérií.
Pri určovaní požiadaviek na kvalitu voči svojmu poskytovateľovi služieb buďte výslovne jasní ohľadom kritických rozmerov, požiadaviek na úpravu povrchu a akýchkoľvek hrán, ktoré musia zostať bez buriny bez sekundárnej úpravy. Porozumenie týmto faktorom kvality vám umožní efektívne vyhodnocovať vzorky a zabezpečí, že vaše hotové súčiastky budú spĺňať funkčné požiadavky. Keď sú očakávania kvality definované, ďalšou kľúčovou otázkou je porozumenie tomu, čo ovplyvňuje náklady uvidené vo vašich cenových ponukách.
Porozumenie nákladov a premenných cien pri laserovom rezaní
Navrhli ste svoje súčiasti, vybrali vhodný materiál a overili požiadavky na kvalitu. Teraz prichádza otázka, na ktorú si každý želá získať odpoveď, no málo zdrojov na ňu čestne odpovedá: koľko to vlastne bude stáť? Na rozdiel od komoditných nákupov s pevnými cenovkami, poplatky za laserové rezanie závisia od viacerých prepojených premenných, ktoré môžu vašu cenovú ponuku výrazne ovplyvniť smerom nahor alebo nadol. Porozumenie týmto faktorom pomáha realisticky plánovať rozpočet a identifikovať príležitosti na zníženie nákladov bez obeti kvality.
Tu je realita, ktorá prekvapí mnohých prvotných kupujúcich: dva zdalo by sa podobné projekty môžu mať veľmi odlišné ceny. Jednoduchý obdĺžnikový uholník môže stáť iba zlomok ceny komplikovaného dekoratívneho panelu, aj keď oba používajú rovnaký materiál. Rozdiel spočíva v čase rezania, efektivite využitia materiálu a zložitosti spracovania. Pozrime sa presne, čo ovplyvňuje vašu cenovú ponuku za laserové rezanie, aby ste mohli robiť informované rozhodnutia.
Premenné, ktoré ovplyvňujú cenové ponuky za laserové rezanie
Keď poskytovateľ služieb vypočíta cenu vášho vlastného laserového rezania, vyhodnocuje niekoľko vzájomne prepojených faktorov. Podľa odborníkov na cenové stanovenie v Komacute sú hlavnými faktormi nákladov typ materiálu, hrúbka, zložitosť konštrukcie, čas rezania, náklady na pracovnú silu a procesy dokončovania. Každý prvok prispieva k celkovým nákladom tým, že ovplyvňuje účinnosť a požiadavky na zdroje.
Typ a hrúbka materiálu tvoria základ každej citácie. Rôzne kovy majú jedinečné vlastnosti, ktoré ovplyvňujú rýchlosť rezania, spotrebu energie a opotrebovanie zariadenia. Napríklad rezanie nehrdzavejúcej ocele vo všeobecnosti vyžaduje viac energie a času ako uhlíková oceľ, čo je drahšie na jeden lineárny metr. Hustejšie materiály tento účinok zhoršujú, pretože vyžadujú väčší výkon a pomalšie rýchlosti rezania, aby dosiahli čistú penetráciu.
Podľa výskum cien od Thinklasera , výpočet nákladov materiálu nasleduje jednoduchý vzorec: Cena materiálu za jednotku plochy vynásobená využitou plochou materiálu. Tento základný náklad sa však násobí faktormi spracovania, ktoré sa výrazne líšia v závislosti od toho, čo režete.
Zložitosť dizajnu priamo ovplyvňuje čas stroja. Každý výrez vyžaduje priepichový bod, kde laser začne rez. Viac priepichových bodov a dlhších rezov zvyšuje spotrebu energie a dobu spracovania. Podľa analýzy spoločnosti Komacut komplikované dizajny s množstvom výrezov vyžadujú vyššiu presnosť, čo pridáva k nákladom práce a zariadení. Jednoduché geometrie s minimálnym počtom vnútorných prvkov sú vždy lacnejšie ako rozsiahle vzory s desiatkami dier a kriviek.
Tu je prehľad kľúčových faktorov ovplyvňujúcich cenu vašich individuálne rezaných kovov:
- Materiálové náklady: Cena surového materiálu plus faktor odpadu na základe toho, ako efektívne sa vaše diely umiestnia na štandardné veľkosti plechov
- Prevádzkové náklady stroja: Spotreba energie lasera vynásobená prevádzkovými hodinami plus náklady na energiu za hodinu
- Náklady na prácu: Čas nastavenia plus čas prevádzky plus akýkoľvek čas následnej úpravy, vynásobený sadzbou práce
- Poplatky za zložitosť dizajnu: Ďalšie poplatky za komplikované vzory vyžadujúce špecializované programovanie alebo pomalšie rezné rýchlosti
- Náklady na nastavenie: Jednorazové poplatky za konfiguráciu stroja, obzvlášť významné pri objednávkach malých šarží
- Sekundárne operácie: Procesy ako odhrotovanie, ohýbanie, zváranie alebo povrchová úprava zvyšujú náročnosť práce a čas používania zariadení
Množstvo a veľkosť dávky výrazne ovplyvňujú cenu za kus. Pevné náklady na nastavenie sa rozpočítavajú medzi všetky súčiastky v objednávke, preto väčšie množstvá znižujú náklady na jednotku. Podľa analýzy odvetvia môže hromadné objednávanie výrazne znížiť náklady na jednotku rozdelením pevných nákladov na väčší počet kusov. Navyše väčšie objednávky často spĺňajú podmienky pre zľavy na materiál od dodávateľov, čo ďalej zníži celkové náklady.
Požiadavky na dobu dodania môže výrazne ovplyvniť ceny. Objednávky s expedícnym spracovaním zvyčajne nesú vyššie poplatky, pretože môžu vyžadovať prácu nadčas, prerušenie plánu iných úloh alebo prioritné zabezpečovanie materiálov. Štandardné dodacie lehoty takmer vždy ponúkajú lepšiu hodnotu než núdzne termíny.
Vyváženie rýchlosti a rozpočtu vo vašom projekte
Chcete znížiť svoju okamžitú cenovú ponuku na laserové rezanie bez toho, aby ste obetovali kvalitu dielov? Chytrí kupujúci používajú niekoľko overených stratégií na optimalizáciu nákladov pri splnení požiadaviek projektu.
Podľa výskumu optimalizácie dizajnu efektívne rozmiestnenie maximalizuje využitie materiálu tým, že usporiada diely tesne vedľa seba na listoch materiálu, čím minimalizuje odpad. To znižuje potrebu surových materiálov a skracuje rezný čas, čo vedie k významným úsporám. Pokročilý softvér na rozmiestňovanie pomáha optimalizovať rozloženie, zvyšuje efektivitu a znižuje odpad.
Zvážte tieto stratégie na zníženie nákladov pri príprave svojich projektov vlastného kovového rezania:
- Zjednodušte geometrie: Znížte počet výrezov a odstráňte zbytočné dekoratívne prvky, ktoré neslúžia funkčným účelom
- Používajte štandardné hrúbky materiálu: Nestandardné rozmerové triedy vyžadujú špeciálne objednávanie a často majú vyššiu cenu
- Optimalizujte pre efektívne rozmiestnenie: Navrhujte diely tak, aby sa efektívne zmestili na štandardné veľkosti plechov a minimalizovali odpad
- Konsolidujte objednávky: Zlúčte viaceré čísla dielov do jednej objednávky, aby ste spoločne využili náklady na nastavenie
- Vyberte vhodné materiály: Nezadávajte nerezovú oceľ, ak uhlíková oceľ vyhovuje funkčným požiadavkám
- Dodržiavajte štandardné dodacie lehoty: Vyhnite sa poplatkom za expedíciu tým, že budete plánovať vopred a zahrnete rezervu do harmonogramu projektu
- Dôsledne zvážte množstvá prototypov: Objednajte dostatočné množstvo prototypov na overenie návrhov, ale vyhýbajte sa nadmernému objednávaniu pred definitívnym uzatvorením návrhu
Online systémy na žiadanie cenových ponúk zmenili spôsob, akým si zákazníci objednávajú služby laserového rezania. Moderné platformy vám umožňujú nahrať návrhové súbory a do niekoľkých minút získať automatické odhady. Pre rýchle získanie presných ponúk pripravte pred začiatkom nasledujúce informácie:
- Kompletné návrhové súbory vo formáte DXF alebo DWG v mierke 1:1
- Typ materiálu a konkrétna označenie zliatiny
- Hrúbka materiálu
- Požadované množstvo
- Všetky potrebné sekundárne operácie (ohýbanie, vkladanie komponentov, úprava povrchu)
- Požiadavky na termín dodania
- Požadované certifikácie kvality pre váš odvetvie
Podľa odporúčaní odvetvia pomáha získanie ponúk od viacerých poskytovateľov porozumieť trhovým sadzbám a nájsť najlepšiu hodnotu. Pri porovnávaní celkových nákladov projektu nezabudnite započítať poplatky za nastavenie, náklady na dopravu a akékoľvek náklady na ďalšie spracovanie, ako je leštenie, farbenie alebo montáž.
Čo si realisticky môžete predstavovať? Hoci konkrétne ceny sa líšia podľa regiónu, poskytovateľa a aktuálnych nákladov na materiál, vzťah medzi množstvom a cenou za kus sleduje predvídateľné vzory. Prípravné náklady, ktoré sa pri objednávke 10 kusov zdajú významné, sa pri rozložení na 1 000 dielov stanú zanedbateľnými. Efektivita použitia materiálu sa so zvyšovaním množstva zlepšuje, pretože poskytovatelia môžu optimalizovať rozmiestnenie rezných tvarov na viacerých platniach. Práca na jeden kus sa zníži, keď operátori získajú zručnosti s konkrétnymi požiadavkami vášho zadania.
Porozumenie týmto cenovým dynamikám vám umožní viesť produktívne rozhovory s poskytovateľmi a urobiť informované kompromisy medzi nákladmi, kvalitou a časovým harmonogramom. Keď máte stanovené rozpočtové očakávania, ďalším krokom je pochopiť, ako rôzne priemyselné odvetvia aplikujú technológiu laserového rezania na svoje špecifické požiadavky a čo to znamená pre vaše projekty.

Použitie v priemysle od automobilového po architektonické kovorobné práce
Rozumiete technológii, materiálom a nákladom. Ale tu je to, čo skutočne oddeľuje úspešné projekty od tých problematických: uvedomenie si, že rôzne priemyselné odvetvia vyžadujú zásadne odlišný prístup k laserovému rezaniu kovov. Nosník pre projekt domáceho označenia má takmer nič spoločné so stavebnou súčiastkou určenou na výrobnú linku automobilov, aj keď oba vychádzajú z rovnakých oceľových plechov.
Prečo je to dôležité pre váš projekt? Pretože požiadavky špecifické pre dané odvetvie určujú všetko – od tolerančných špecifikácií až po certifikačnú dokumentáciu. Porozumenie týmto rozdielom vám pomôže efektívne komunikovať so službami a zabezpečí, že vaše súčiastky budú spĺňať normy vyžadované pre vašu aplikáciu. Podľa výskumu aplikácií v priemysle transformovala technológia laserového rezu rôzne odvetvia vďaka svojej presnosti a všestrannosti – od vytvárania detailných klenotov až po výrobu kritických komponentov v leteckom a automobilovom priemysle.
Požiadavky na presnosť v automobilovom a leteckom priemysle
V automobilovom priemysle priemyselné laserové rezanie predstavuje kľúčový nástroj na výrobu komplikovaných súčiastok a individuálnych úprav. Každý milimeter má význam, keď vyrábate diely pre podvozky, systémy zavesenia a konštrukčné zostavy. Prípustná chyba? V podstate nulová.
Podľa odborníci na výrobu vozidiel , laserové rezanie v tomto odvetví je výrazne efektívnejšie ako tradičné procesy tvárnenia kovov, ako napríklad strihanie v dies alebo plazmové rezanie. Vysokovýkonný laser, zvyčajne vláknový laserový rezač, poskytuje presnosť nevyhnutnú v automobilových aplikáciách, kde musia súčiastky dokonale zapasovať do tisícov montovaných vozidiel.
Typické projekty laserovej výroby v automobilovom priemysle zahŕňajú:
- Komponenty podvozka: Konštrukčné uchytenia, priečne nosníky a vystužovacie dosky vyžadujúce presné prispôsobenie pre zvárané zostavy
- Súčasti zavesenia: Ramená riadenia, uchytenia pružín a súčasti stabilizačného tyčenia s prísnymi požiadavkami na tolerancie
- Karosérijské panely: Zosilnenia dverí, pilierové konštrukcie a komponenty odolné voči haváriám, kde presnosť rozmerov ovplyvňuje bezpečnostný výkon
- Komponenty priestoru motora: Tepelné clony, montážne konzoly a nosníky príslušenstva, ktoré musia odolávať tepelným cyklom a vibráciám
- Interiérové komponenty: Rámy sedadiel, konzoly palubnej dosky a nosné konštrukcie skryté pod obloženiami
Čo odlišuje laserové rezanie súčiastok pre automobilový priemysel od bežnej výroby? Požiadavky na certifikáciu. Podľa odborníkov na riadenie kvality certifikácia IATF 16949 spĺňa všetky požiadavky ISO 9001 a ďalej ich rozširuje, aby zabezpečila dodržiavanie slimnej výroby, prevenciu chýb, elimináciu odchýlok a zníženie odpadu. Táto certifikácia, ktorú podporujú asociácie automobilového priemyslu, stanovuje referenčný štandard pre výber dodávateľov a budovanie spoľahlivých dodávacích reťazcov.
Pre výrobcov, ktorí pôsobia v automobilovom priemysle, prináša certifikácia IATF 16949 hmatateľné výhody vrátane konzistentnej kvality prostredníctvom monitorovaných a meraných procesov, zníženia výrobných odchýlok prostredníctvom vylepšených výrobných postupov a prevencie chýb prostredníctvom overených a osvedčených výrobných metód. Spoločnosti ako Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology osvedčujú tento prístup, ktorý zabezpečuje kvalitu certifikovanú podľa IATF 16949 pre podvozky, systémy zavesenia a konštrukčné súčasti, pričom ich kapacity sa pohybujú od rýchleho prototypovania do 5 dní až po automatizovanú sériovú výrobu.
Leteckých aplikáciách posúvajú služby precízneho laserového rezania na absolútne limity. Podľa výskumu v oblasti leteckej výroby je potreba ľahkých materiálov s vysokou pevnosťou v tomto odvetví nepochybne dôležitá. Presnosť je charakteristickou vlastnosťou leteckých komponentov a laserové rezanie s jeho vysokou presnosťou a schopnosťou spracovávať špecializované materiály je pre tieto náročné aplikácie ideálne vhodné.
Aerospace priemysel profituje z možnosti laserového rezania vyrábať súčiastky spĺňajúce prísne limity tolerancií. Tento proces zaisťuje zachovanie štrukturálnej integrity materiálov, čo je nevyhnutné v aplikáciách, kde by zlyhanie malo katastrofálny charakter. Typické projekty vo výrobe lietadiel zahŕňajú titanové konštrukčné komponenty, hliníkové povrchové panely a špeciálne zliatinové uchytenia, pri ktorých úspora hmotnosti meraná v gramoch môže viesť k výraznému zlepšeniu spotreby paliva počas celej prevádzkovej životnosti lietadla.
Architektonické a umelecké kovové aplikácie
Zmeňte svoj pohľad z funkčnej presnosti na vizuálny dopad a vstúpite do sveta architektonických a umeleckých kovových diel. Tu vlastné laserové rezanie kovov otvára kreatívne možnosti, ktoré boli pomocou tradičných výrobných metód jednoducho nemožné.
Podľa odborníkov na architektonické aplikácie mala technológia laserového rezania významný dopad na stavebný priemysel. Jej použitie pri výrobe oceľových konštrukcií a podrobných architektonických prvkov prináša do oblasti novú úroveň kreativity a presnosti. Schopnosť tejto technológie rezať hrubé oceľové platne a vytvárať presné rezy ju robí neoceniteľnou pre modernú architektúru.
Projekty architektonických laserovo rezaných kovových plechov zvyčajne zahŕňajú:
- Dekoratívne fasády: Obklady budov s komplikovanými vzormi, ktoré počas dňa vytvárajú dynamické efekty tieňov
- Prepážky na zabezpečenie súkromia: Perforované kovové panely vyvažujúce vizuálne súkromie s priepustnosťou svetla a vzduchu
- Komponenty schodiska: Ornamentálne schodnicové dosky, dekoratívne stupnice a výroby zábradlí na mieru
- Propagačné tabule a orientačné systémy: Objemové písmená, osvetlené lánové nápisy a smerové systémy
- Prvky interiérovej architektúry: Prepážky miestností, stropné prvky a komponenty nábytku na mieru
Požiadavky sa výrazne líšia od automobilovej oblasti. Hoci je stále dôležitá rozmerná presnosť, zameranie sa posúva k kvalite hrán, úprave povrchu a vizuálnej konzistencii pri veľkých dekoratívnych paneloch. Architektonické projekty často uprednostňujú estetickú dokonalosť pred mikrometrovou toleranciou vyžadovanou mechanickými zostavami.
Výroba elektroniky a skríň predstavuje ďalšiu hlavnú oblasť použitia. Podľa výskumu elektronického priemyslu zohráva laserové rezanie kľúčovú úlohu pri miniaturizácii elektronických zariadení. Priemysel vo veľkej miere závisí od presných rezacích schopností, kde zlomok milimetra môže znamenať výrazný rozdiel.
Typické projekty elektronických skríň zahŕňajú:
- Šasi servera: Rackové skrine s presnými vzormi vetilácie a upevňovacími prvkami pre komponenty
- Skriňa ovládacieho panela: Priemyselné skrine s výrezmi pre displeje, spínače a správu káblov
- Odstínenie EMI: Špecializované skrine blokujúce elektromagnetické rušenie v citlivých zariadeniach
- Puzdrá spotrebného elektronického zariadenia: Vysokokapacitné skrine pre sieťové zariadenia, napájacie zdroje a audio komponenty
Aplikácie pre prototypovanie zaslúžia si špeciálne zmienku, pretože využívajú najväčšiu silnú stránku laserového rezania: schopnosť prejsť od digitálneho návrhu k fyzickej súčiastke bez nutnosti investície do nástrojov. Podľa výskumu aplikácií výskumu a vývoja je technológia laserového rezania neoceniteľná pre vývoj prototypov a výrobu experimentálnych súčiastok. Jej presnosť a všestrannosť umožňujú vytvárať komponenty s komplikovanými dizajnami a úzkymi toleranciami, ktoré sú nevyhnutné v procese vývoja.
Pri prototypovaní hraje schopnosť laserového rezania rýchlo a presne vyrábať súčiastky kľúčovú úlohu v iteračnom procese návrhu. Inžinieri môžu otestovať priľahlosť, funkčnosť a estetiku, než sa rozhodnú pre výrobné nástroje. Služby ponúkajúce možnosti rýchleho prototypovania, ako poskytovatelia s dodacou lehotou 5 dní pre prvé kusy, umožňujú návrhovým tímom rýchlo overiť koncepty a s istotou prejsť do výroby.
Tu je zhrnutie toho, ako sa požiadavky líšia v jednotlivých hlavných odvetviach:
| Priemysel | Hlavné požiadavky | Typické tolerancie | Kľúčové certifikácie |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilový priemysel | Rozmerná presnosť, opakovateľnosť, stopovateľnosť | ±0,1 mm až ±0,25 mm | IATF 16949, ISO 9001 |
| Letectvo | Integrita materiálu, optimalizácia hmotnosti, dokumentácia | ±0,05 mm až ±0,15 mm | AS9100, Nadcap |
| Architektúra | Vizuálna kvalita, úprava hrán, konzistencia vzoru | ±0,5 mm bežné | Konkrétne pre projekt |
| Elektronika | Presné výrezy, čisté hrany, EMI aspekty | ±0,1 mm až ±0,2 mm | ISO 9001, UL zoznamy |
| Prototypovanie | Rýchlosť, flexibilita dizajnu, schopnosť iterácie | Závislé od aplikácie | Závisí od konečného použitia |
Pochopenie týchto špecifických požiadaviek jednotlivých odvetví vám umožní vybrať si poskytovateľov služieb, ktorých kapacity zodpovedajú požiadavkám vašej aplikácie. Dielňa špecializujúca sa na architektonické kovové práce môže nemusieť mať systémy riadenia kvality potrebné pre automobilovú výrobu, zatiaľ čo certifikované zariadenie pre letecký priemysel môže byť pre dekoratívne informačné panely neprimerane drahé.
S týmto pochopením toho, ako rôzne priemyselné odvetvia využívajú technológiu laserového rezania, nasleduje ďalší kľúčový krok – vyhodnotenie potenciálnych poskytovateľov služieb podľa kritérií, ktoré sú dôležité pre vašu konkrétnu aplikáciu a požiadavky.
Výber správneho poskytovateľa služieb kovového laserového rezania
Ovládete technológiu, rozumiete kompatibilite materiálov a viete, akej kvality očakávať. Teraz prichádza možno najdôležitejšie rozhodnutie vo vašom projekte: výber správneho partnera, ktorý bude skutočne vyrábať vaše súčiastky. Laserový rezač kovov je len tak dobrý, aké je tímové zázemie ho prevádzkujúce, a rozdiel medzi vynikajúcim a priemerným poskytovateľom môže rozhodnúť o úspechu projektu alebo o nákladných oneskoreniach.
Tu je to, čo mnohí nákupcovia zistia príliš neskoro: najnižšia cenová ponuka zriedkavo prináša najlepšiu hodnotu. Keď hľadáte služby laserového rezania v mojej blízkosti alebo vyhodnocujete poskytovateľov po celom štáte, cena predstavuje len jeden z faktorov vo väčšej rovnici. Podľa odborníkov na kovospracovanie z Ametals môže výber správneho partnera na odovzdanie práce v skutočnosti znížiť váš stres, skrátiť vaše náklady a zvýšiť efektivitu. Kľúč spočíva v tom, vedieť, čo hodnotiť okrem konečnej sumy v cenovej ponuke.
Certifikácie a kvalitatívne normy, ktoré treba overiť
Keď záleží na presnosti, certifikácie sú vaším prvým filtrom na rozlíšenie serióznych služieb laserového rezania kovov od dielní, ktoré jednoducho vlastnia laser. Ale čo tieto certifikácie vlastne znamenajú a ktoré z nich sú dôležité pre vašu konkrétnu aplikáciu?
Certifikát ISO 9001 stanovuje základ pre systémy riadenia kvality. Podľa odvetvových hodnotiacich smerníc, hoci certifikácie nie sú zárukou, normy ISO 9001 vám poskytujú istotu, že spolupracujete so servisom, ktorý má pevne stanovený systém riadenia kvality. Táto certifikácia označuje zdokumentované procesy, pravidelné audity a systematické prístupy k prevencii chýb, nie len ich následnému odhaľovaniu.
Certifikácia IATF 16949 pre autotechnické aplikácie ide výrazne ďalej. Táto norma zahŕňa všetky požiadavky ISO 9001 a navyše pridáva špecifické požiadavky pre automobilový priemysel týkajúce sa štíhleho výrobného procesu, prevencie chýb a stopovateľnosti v rámci dodávateľského reťazca. Ak vyrábate komponenty pre vozidlá alebo dopravné prostriedky, táto certifikácia by mala byť nepostrádateľná.
Pri hodnotení poskytovateľa služieb CNC laserového rezania sa opýtajte nasledujúcich otázok na overenie:
- Akú presnosť a aké tolerancie dokážete dosiahnuť? Vyžiadajte si konkrétne údaje namiesto vágnych uistení
- Ako často kalibrujete svoje zariadenia? Pravidelná kalibrácia zaisťuje konzistentnú presnosť v priebehu času
- Aké kontroly vykonávate u hotových výrobkov? Pochopte ich kontrolné body kvality
- Môžete poskytnúť certifikáty materiálov a stopovateľnosť? Kritické pre regulované odvetvia
- Aká je vaša miera chýb a ako riešite nezhodné diely? Ich odpoveď odhaľuje zrelosť procesu
Okrem formálnych certifikácií priamo vyhodnoťte schopnosti vybavenia. Podľa odporúčaní na hodnotenie vybavenia chcete dielňu, ktorá má moderné laserové rezačky a iné nástroje strojníckej dielne, pretože novšie systémy majú automatizované manipulovanie s materiálom, minimálny čas na nastavenie a vysokú úroveň presnosti. Konkrétne sa opýtajte, akú hrúbku ich laser dokáže rezať, aká je presnosť a s ktorými kovmi môžu pracovať.
Tu je komplexný rámec na vyhodnotenie potenciálnych dodávateľov:
| Kritériá hodnotenia | Čo hľadať | Červené vlajky |
|---|---|---|
| Výbava a Možnosti | Moderné vláknové a CO2 systémy, automatizované manipulovanie s materiálom, uvedené špecifikácie hrúbky a presnosti | Vágné odpovede o schopnostiach, zastaralé vybavenie, neschopnosť špecifikovať tolerancie |
| Odbornosť na materiály | Skúsenosti s vašimi konkrétnymi kovmi, pochopenie materiálovo-špecifických výziev, vhodné možnosti asistenčných plynov | Obmedzený rozsah materiálov, žiadne skúsenosti s reflexnými kovmi, ak sú potrebné |
| Kvalifikačné certifikáty | Minimálne ISO 9001, IATF 16949 pre automobilový priemysel, zdokumentované postupy kontroly kvality | Žiadne certifikácie, neochota zdieľať dokumentáciu kvality |
| Sekundárne služby | Ohýbanie, zváranie, úprava povrchu, vkladanie komponentov dostupné interné | Musí podceňovať kritické sekundárne operácie, čo predlžuje dodací termín a zvyšuje riziko chybovania pri odovzdávaní |
| Podpora DFM | Prehľad dizajnu pre výrobnosť zahrnutý, aktívne návrhy na optimalizáciu | Žiadne spätne väzby k dizajnu, prijíma súbory presne tak, ako sú odovzdané, bez kontroly |
Hodnotenie doby dodania a komunikácie
Ako rýchlo viete získať cenovú ponuku? A ako rýchlo sa dajú odoslať súčiastky? Tieto otázky majú obrovský význam, keď sú časové plány projektu tesné. Rovnako dôležité však je, ako poskytovateľ komunikuje počas celého procesu.
Podľa smerníc na hodnotenie zákazníckej obsluhy dbajte na to, ako dobre Váš potenciálny partner pre laserové rezanie komunikuje s Vami. Mal by počúvať Vaše potreby a ešte dôležitejšie, mal by klásť dobré otázky. Jasna komunikácia je kľúčová pre rýchle a presné splnenie práce.
Pri hodnotení schopností obratu hľadajte tieto služobné vlastnosti, ktoré poukazujú na reaktívnu, zákazníkom orientovanú prevádzku:
- Rýchlosť reakcie na požiadavku cenovej ponuky: Poskytovatelia najvyššej úrovne ponúkajú rýchly obrat cenovej ponuky, pričom lídri v odvetví poskytujú odhady do 12 hodín od prijatia kompletných návrhových súborov
- Rýchlosť prototypovania: Schopnosť rýchlo vyrobiť prvé kusy overuje návrhy pred záväzkom vo výrobe. Hľadajte poskytovateľov, ktorí ponúkajú možnosť rýchleho prototypovania do 5 dní
- Škálovateľnosť výroby: Overte, či dokáže dielňa zvládnuť malé sériové výroby prototypov aj väčšie výrobné množstvá bez straty kvality
- Dostupnosť podpory DFM: Komplexná spätná väzba zameraná na výrobnú vhodnosť pomáha optimalizovať vaše súčiastky ešte pred začatím rezania, čím sa zníži počet iterácií a nákladov
- Digitálne komunikačné nástroje: Podľa odvetvových odporúčaní by poskytovatelia mali umožniť jednoduché zasielanie výkresov a aktualizáciu informácií cez e-mail alebo online portály
Schopnosti prototypovania si zasluhujú osobitný dôraz. Pred tým, ako sa pustíte do výroby, múdri nákupní overia svoje návrhy pomocou fyzických vzoriek. Tento krok odhalí problémy so zapadnutím, odhalí neočakávané výrobné výzvy a potvrdí, že poskytovateľ skutočne rozumie vašim požiadavkám. Laserový rezač v blízkosti so schopnosťou rýchleho prototypovania vám umožní rýchlo iterovať a prejsť do výroby s istotou.
Zvážte poskytovateľov ako Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology ktoré kombinujú viaceré funkcie služieb, na ktoré by mali kupujúci klásť dôraz: 5-dňové rýchle prototypovanie pre rýchlu validáciu dizajnu, ponuku pripravenú do 12 hodín pre reaktívne plánovanie projektu a komplexnú podporu DFM na optimalizáciu výrobnej technologickej postupnosti ešte pred zahájením výroby.
Dôležitá je aj flexibilita. Podľa odborníkov na hodnotenie služieb flexibilita umožňuje, aby ste celú prácu zvládli u jedného dodávateľa namiesto toho, aby ste ju museli rozdeľovať na rôzne miesta. Hľadajte dodávateľa, ktorý zvládne bežné rezanie, ale zároveň dokáže spracovať špeciálne objednávky. Pri službách laserového rezania rúr alebo špecializovaných aplikáciách overte, či poskytovateľ má konkrétne skúsenosti s geometriou vašich súčiastok.
Aké otázky by ste mali položiť potenciálnym dodávateľom počas ich hodnotenia?
- Môžete mi ukázať príklady podobných projektov, ktoré ste už dokončili?
- Aký je váš bežný dodací termín pre moje množstevné požiadavky?
- Nabúdzate akcelerované možnosti, ak sa zmení môj harmonogram?
- Ako riešite zmeny v návrhu po vyhotovení cenovej ponuky?
- Čo sa stane, ak diely nespĺňajú špecifikácie?
- Môžete poskytnúť referencie od zákazníkov z môjho odvetvia?
- Aké sekundárne operácie dokážete vykonávať vo vlastných priestoroch?
Podľa odporúčaní overenia referencií si vyhradte čas na overenie zručností s predchádzajúcimi a aktuálnymi klientmi. Referencie a recenzie vám umožňujú zistiť viac o tom, aké je spolupracovať s tímom, ako aj potvrdiť ich súbor zručností. Zatiaľ čo online recenzie poskytujú východiskový bod, priame rozhovory s referenciami odhalia komplexný obraz.
Portfólio poskytovateľa odhaľuje šírku i hĺbku skúseností. Hľadajte množstvo rôznych typov projektov, ktoré preukazujú všestrannosť, ako aj viaceré príklady konkrétnych zručností relevantných pre vašu aplikáciu. Ak váš projekt vyžaduje komplikované vzory, overte si, že majú túto schopnosť, a nie len všeobecné skúsenosti s presným rezaním.
Správna služba laserového rezania v blízkosti mňa sa stáva skutočným partnerom, nie len dodávateľom. Predvída problémy ešte predtým, ako nastanú, navrhuje vylepšenia, na ktoré ste nepomysleli, a aktívne komunikuje počas celého procesu výroby. Nájsť takéhoto poskytovateľa si vyžaduje dôkladné hodnotenie na začiatku, ale investícia sa vráti pri každom projekte, ktorý im zveríte.
Často kladené otázky o službách laserového rezania kovov
1. Koľko stojí laserové rezanie kovov?
Náklady na laserové rezanie kovov závisia od niekoľkých prepojených faktorov, vrátane druhu a hrúbky materiálu, zložitosti dizajnu, množstva a rýchlosti dodania. Rezanie ocele sa zvyčajne pohybuje medzi 13–20 USD za hodinu strojového času, ale vaše celkové náklady zahŕňajú aj cenu materiálu, poplatky za nastavenie a akékoľvek sekundárne operácie, ako je ohýbanie alebo dokončovanie. Hromadné objednávky výrazne znížia náklady na jednotku tým, že rozložia fixné náklady na nastavenie na väčší počet súčiastok. Pre presné cenové ponuky pripravte kompletné návrhové súbory vo formáte DXF alebo DWG a požiadajte o cenové ponuky od viacerých poskytovateľov.
2. Ktoré kovy je možné efektívne rezať laserom?
Laserové rezanie vynikajúco zvláda bežnú oceľ, nehrdzavejúcu oceľ a uhlíkovú oceľ, čo sú najvhodnejšie materiály pre laser. Moderné vláknové lasery efektívne spracovávajú aj odrazivé kovy ako hliník (až do 15 mm), meď (až do 6 mm) a mosadz (až do 8 mm), hoci na tieto materiály sú potrebné vyššie výkony kvôli ich odrazivosti a tepelnej vodivosti. Titán sa tiež dobre reže, ale vyžaduje si chránenie netečným plynom, aby sa zabránilo oxidácii. Každý kov má špecifické obmedzenia hrúbky v závislosti od výkonu lasera, pričom bežná oceľ sa môže rezať až do 25 mm na systémoch s vysokým výkonom.
3. Aký je rozdiel medzi vláknovým laserom a CO2 laserom pri rezaní?
CO2 lasery pracujú na vlnovej dĺžke 10,6 mikrónov a vynikajú pri rezaní hrubších materiálov (až 25 mm jemnej ocele) a tiež nekovov, ako sú plasty a drevo. Fiber lasery využívajú kratšiu vlnovú dĺžku 1,06 mikrónov, čo umožňuje 2-3-násobne rýchlejší rez tenkých kovov a lepší výkon na reflexných materiáloch, ako je hliník, meď a mosadz. Fiber lasery ponúkajú tiež účinnosť 30–50 % oproti 10–15 % u CO2 systémov a vyžadujú menej údržby vďaka svojmu pevnému dizajnu.
4. Ako pripravím návrhové súbory pre služby laserového rezania?
Odovzdajte návrhové súbory vo formáte DWG alebo DXF v mierke 1:1 s úplnými, nepretržitými obrysami čiar. Odstráňte všetky nadbytočné prvky, ako sú rámiky výkresov, kóty a poznámky – mal by sa objaviť iba rezný geometrický tvar. Dodržiavajte pokyny pre návrh zohľadňujúci výrobné možnosti: zachovajte minimálny priemer otvorov rovný hrúbke materiálu, dodržiavajte vzdialenosť otvoru od okraja 1,5-násobok hrúbky materiálu a navrhujte vnútorné rohy s malými polomermi (minimálne 0,5 mm), keďže skutočné 90-stupňové vnútorné rohy nie sú možné. Zvážte efektivitu rozmiestnenia na plechy tak, že navrhnete diely, ktoré sa efektívne zmestia na štandardné veľkosti plechov.
5. Kedy si mám vybrať vodno-trieskové alebo plazmové rezanie namiesto laserového?
Vyberte vodno-trieskové rezanie pre teplotne citlivé materiály, ktoré vyžadujú nulovú tepelne ovplyvnenú zónu, extrémne hrubé materiály (až do 30 cm) alebo pri rezaní zmiešaných materiálov, ako je kameň, sklo a kompozity. Plazmové rezanie je rýchlejšie ako laserové pri hrubých vodivých kovoch s hrúbkou viac ako pol palca a ponúka 3 až 4-násobnú rýchlosť oproti vodno-trieskovému rezaniu s približne polovičnými prevádzkovými nákladmi. Laserové rezanie zostáva najlepšie pre tenké až stredne hrubé kovy, ktoré vyžadujú tesné tolerancie (±0,1 mm), komplikované tvary a čisté okraje s minimálnou dodatočnou úpravou.
 Malé dávky, vysoké štandardy. Naša služba rýchlejho prototypovania urobí overenie rýchlejšie a jednoduchšie —
Malé dávky, vysoké štandardy. Naša služba rýchlejho prototypovania urobí overenie rýchlejšie a jednoduchšie —
