Tarkkuuden avaaminen: Miten moniliukusyvävalutus toimii
TL;DR
Moniliukusyvävalutusteknologia on edistynyt valmistusmenetelmä, jossa käytetään muotteja, joissa on useita liikkuvia liukuosia – tyypillisesti neljä tai enemmän – tuottaakseen pieniä, monimutkaisia ja korkean tarkkuuden metalliosia. Kuumakamariomenetelmän kehittymisenä se erottuu kyvyssään tuottaa valmiiksi muotoiltuja komponentteja erittäin nopeasti, mikä usein tekee jälkikoneoinnista tarpeetonta. Menetelmä on erittäin kustannustehokas monimutkaisten, suurten sarjojen tuotannossa, jossa tarkkuus ja yhdenmukaisuus ovat ratkaisevia.
Mikä on moniliukusyvävalu?
Moniliukuvalumuotin valaminen edustaa merkittävää edistystä metallinmuovauksessa, ja se on erityisesti suunniteltu tuottamaan pieniä, monimutkaisia komponentteja poikkeuksellisen tarkasti. Ytimessä se on erikoistunut muoto kuumanestekammion valamisesta. Toisin kuin perinteiset menetelmät, jotka käyttävät yksinkertaista kaksiosaisia muotteja, moniliukumenetelmä käyttää kehittyneempää työkalua, jossa on neljä, ja joskus jopa kuusi yksittäistä liukua. Nämä liu'ut liikkuvat kohtisuoraan toisiinsa nähden muodostaakseen täydellisen, tiiviin muottikaviteetin.
Mekanismin nerokkuus piilee sen kyvyssä luoda monimutkaisia geometrioita useista eri suunnista. Työkalun jokainen liukupala muodostaa osan kuppia tai ydintä. Kun kone käy syklin läpi, nämä liukupalat kohtaavat ja lukkiutuvat yhteen valtavalla voimalla muodostaen tarkan negatiivisen muodon lopulliselle osalle. Sulanut metalli, yleensä sinkki- tai magnesiumseos, ruiskutetaan tämän kuppimuodon sisään korkeassa paineessa 'hanakoneen' avulla, joka on upotettu sulanutta kylpyyn – tämä on tunnusomaista kuumakammiomenetelmälle. Asiantuntijoiden mukaan Sunrise Metal , tämä menetelmä on perinteisen kuumakammiomuovauksen päivitetty versio, jota käytetään pääasiassa pienien sinkkiseososien valmistukseen.
Tämän teknologian ensisijainen tarkoitus on tuottaa netto-muotoisia tai melkein netto-muotoisia osia. Tämä tarkoittaa, että komponentti nousee muotista valmiiksi muodostuneena eikä sille tarvita juuri lainkaan lisäkoneenpurua tai viimeistelyä. Kuten alan johtaja huomautti Dynacast , tämä ominaisuus mahdollistaa sisä- ja ulkopuolisten kierreiden valmistuksen suoraan valamisjakson aikana ilman kalliita lisävaiheita. Tämä tehokkuus on keskeinen syy, miksi insinöörit ja suunnittelijat käyttävät moni-osaisia muottivalutekniikoita komponenttien valmistuksessa, joissa vaaditaan sekä monimutkaisuutta että kustannustehokkuutta laajassa mittakaavassa.
Moni-osaisen tekniikan keskeiset edut
Moni-osainen muottivalutekniikka tarjoaa selvästi erottuvia etuja perinteisiin menetelmiin verrattuna, mikä tekee siitä ylivoimaisen vaihtoehdon tietyissä sovelluksissa, erityisesti pienien ja monimutkaisten komponenttien osalta. Näihin etuihin kuuluvat tarkkuus, kustannustehokkuus, nopeus ja suunnitteluvapaus. Yksilöllinen työkalurakenne on näiden parannusten perusta, ja se mahdollistaa valmistustason, jota on vaikea saavuttaa tavallisilla kaksiosaisilla muoteilla.
Yksi merkittävimmistä eduista on tuotantokustannusten dramaattinen aleneminen osan elinkaaren aikana. Tämä kustannustehokkuus johtuu useista tekijöistä. Ensinnäkin prosessi tuottaa kiillotuksia vapaat valutukset vähimmäismäärällä juoksuputkimateriaalia, mikä vähentää huomattavasti materiaalihukkaa. Toiseksi nettomuotoisten osien valmistus vähentää tai jopa poistaa tarpeen lisätoimenpiteille, kuten poraukselle, kierteitykselle tai sorvaukselle. Mukaan Techmire , tämän teknologian johtava valmistaja, tästä seuraa merkittäviä säästöjä materiaaleissa, energiassa ja työvoimassa. Ominaisuuksien, kuten kierteiden ja monimutkaisten alivalujen, suora integrointi muottiin yhdistää valmistusvaiheet ja lyhentää toimitusaikoja.
Teknologia tarjoaa myös poikkeuksellisen tarkan tarkkuuden ja osien toistettavuuden. Luja, moniheitsinen työkalusuunnittelu takaa, että jokainen osa on lähes täydellinen kopio edellisestä, säilyttäen tiukat toleranssit myös suurissa tuotantosarjoissa. Tämä yhdenmukaisuus on kriittistä komponenteille herkissä aloissa, kuten lääketarvikkeet ja kuluttajaelektroniikka. Lisäksi prosessi on erittäin nopea, noilla syklinopeuksilla, mikä tekee siitä ihanteellisen massatuotantoon. Työkalussa tapahtuva porttien poisto ja osien automaattinen erottelu juoksijoista voivat entisestään tehostaa työnkulkua.
Suunnittelijoiden ja insinöörien kannalta suurin etu on parantunut suunnitteluvapaus. Useiden eri suuntiin liikkuvien liukujen käyttömahdollisuus vapauttaa suunnittelijat yksinkertaisen avautuvan ja sulkeutuvan muotin rajoituksista. Tämä mahdollistaa erittäin monimutkaisten geometrioiden luomisen, jotka olisivat mahdottomia valmistaa yhtenä palana perinteisillä menetelmillä. Tämä ominaisuus edistää innovointia ja mahdollistaa pienempien, kevyempien ja toiminnallisempien komponenttien kehittämisen.
- Parantunut suunnitteluvapaus: Mahdollistaa monimutkaisten geometrioiden, kuten alapurojen ja poikittaishalkojen, tuotannon, joita ei voida toteuttaa kaksiosaisilla muoteilla.
- Korkea tarkkuus ja johdonmukaisuus: Luja työkaluvarustus takaa erinomaisen osien yhdenmukaisuuden ja toistettavuuden, mikä on ratkaisevan tärkeää suurten tilauserien kanssa.
- Merkitseviä kustannussäästöjä: Vähentää materiaalihukkaa ja eliminointaa useimmat jälkikäsittelytoimenpiteet, mikä johtaa alhaisempaan kokonaisosahintaan.
- Nopeus ja tehokkuus: Sisältää nopeat syklivauhdit ja automatisoidut prosessit, kuten muotissa tapahtuvan portin poiston, nopeampaa tuotantoa varten.
- Erinomainen laatu: Tuottaa välähteen vapaat valut, joilla on parantunut pintalaatu ja vähentynyt huokoisuus.

Moni-luisti vs. perinteinen painevalu: suora vertailu
Moni-luistin ja perinteisen painevalun välillä on perustavanlaatuinen ero työkalujen rakenteessa ja toiminnassa. Tämä keskeinen ero määrittää kummankin prosessin vahvuudet, heikkoudet ja tarkoitetut käyttökohteet. Vaikka molemmat ovat korkeapainepainevalutekniikoita, ne on suunniteltu ratkaisemaan erilaisia valmistushaasteita. Näiden erojen ymmärtäminen on ratkaisevan tärkeää, kun valitaan tehokkain ja kustannustehokkain menetelmä tietylle komponentille.
Perinteinen painevalu käyttää kaksiosaisia työkaluja, jotka koostuvat kiinteästä puoliskosta ja poistopuoliskosta. Tämä yksinkertainen ja robusti rakenne soveltuu hyvin suurempien osien valmistukseen, joiden geometrinen monimutkaisuus on vähäisempää. Sen sijaan moni-luistipainevalu käyttää työkalua, jossa on vähintään neljä toisiinsa nähden kohtisuorassa olevaa liukua, jotka yhdessä muodostavat muotin. Kuten yksityiskohtaisesti esitetään vertailussa, jonka Dynacast , tämä monisuuntainen lähestymistapa sopii luonteeltaan paremmin pienempiin osiin (tyypillisesti alle 400 g), joissa on monimutkaisia piirteitä. Useampien liukujen käyttö vähentää vaihteluita ja parantaa tarkkuutta näissä monimutkaisissa suunnittelussa.
Tämä työkalurakenteen ero vaikuttaa merkittävästi jälkikäsittelyyn. Perinteinen painevalu tuottaa usein osia, joissa on kihlaus (ylimääräistä materiaalia jakopinnassa), ja vaatii lisätoimenpiteitä esimerkiksi kierre- tai poikkireikien lisäämiseksi. Moniliuku-painevalutekniikkaa sen sijaan on suunniteltu tuottamaan valmiiksi muotoon olevia, kihlaamattomia osia, jotka ovat valmiita suoraan muotista. Tämä jälkikäsittelyvaiheiden eliminoiminen säästää aikaa ja kustannuksia ja parantaa osien yhdenmukaisuutta.
Selkeyttääksemme kuvaa alla oleva taulukko tiivistää keskeiset erot:
| Ominaisuus | Moniliuku-painevalu | Perinteinen painevalu |
|---|---|---|
| Työkalurakenne | Neljä tai useampi kohtisuoraan liikkuva liuku | Kaksiosainen työkalu (kiinteä ja ulostyöntöpuoli) |
| Ideaalinen osan koko | Pieni, tyypillisesti alle 400 g | Suuremmat osat, vähemmän sopivat pienoisosille |
| Geometrinen monimutkaisuus | Erinomainen erittäin monimutkaisille osille, joissa on useita ominaisuuksia | Paras yksinkertaisemmille geometrioille |
| Jälkikäsittelyn tarve | Vähäinen tai ei ollenkaan; tuottaa nettomuotoisia osia | Vaati usein jälkikäsittelytoimenpiteitä (kiiltojen poisto, poraus, kierteitys) |
| Kustannustehokkuus | Erittäin kustannustehokas monimutkaisille osille suurissa määrissä | Taloudellisempi suurille, yksinkertaisille osille |
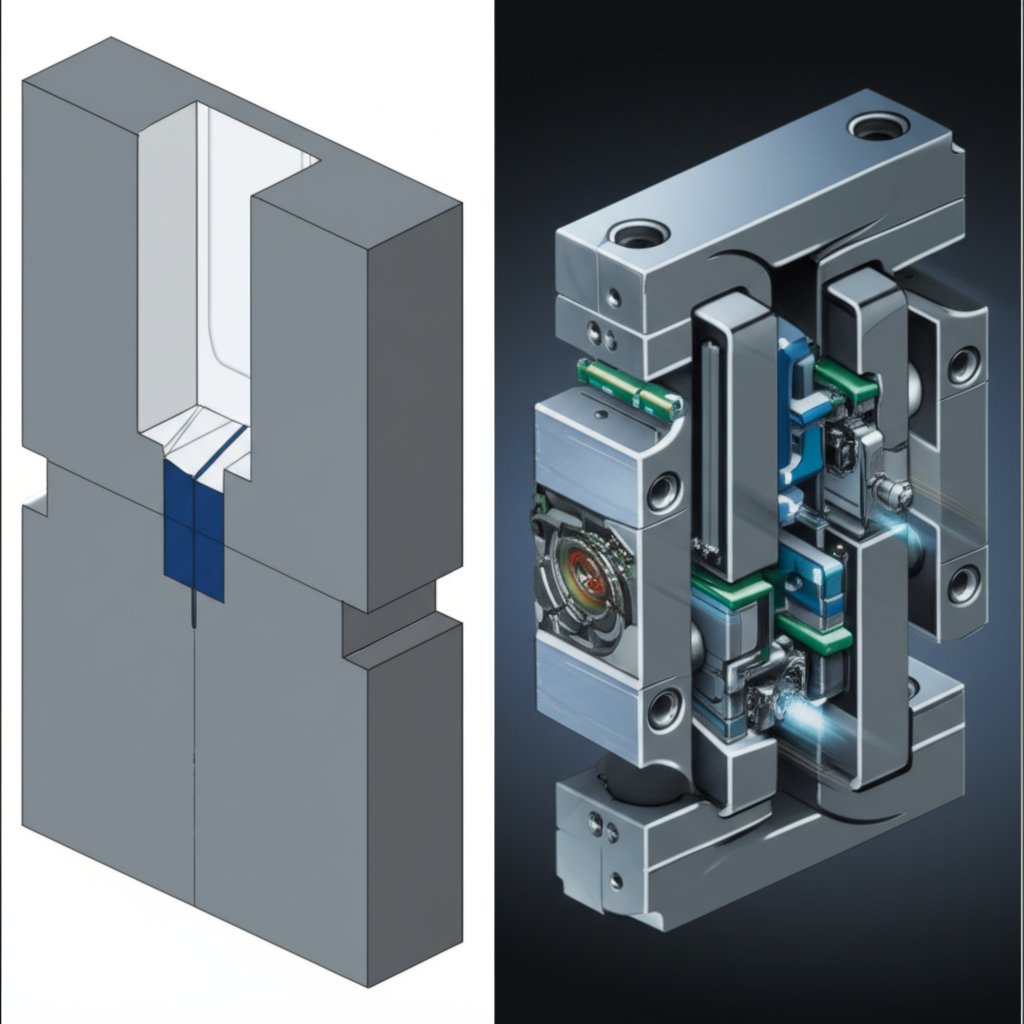
Monisuuntainen painevalukäsittely ja sen sovellukset
Monisuuntainen painevalukäsittely on erittäin tarkka ja automatisoitu prosessi, joka on suunniteltu nopeutta ja tarkkuutta varten. Koska se on kuuman kammion menetelmä, injektointimekanismi on upotettu sulan metallin kylpyyn, mikä mahdollistaa erittäin nopeat sykliajat. Prosessin voi jakaa useisiin selkeisiin vaiheisiin, jotka toistuvat saumattomasti tuottaakseen tuhansia identtisiä osia.
Toimintasykli on tehokkuuden malliesimerkki:
- Muotti sulkeutuu: Työkalun neljästä kuuteen kohtisuoraan liikkuvaa liukua liikkuu sisäänpäin ja kohtaavat tarkasti muodostaakseen tiiviin ja täydellisen muottikammiön. Ne lukitaan yhteen voimakkaalla kytkeytymismekanismilla.
- Injektiota varten: Upotetussa 'hanhinkaularossa' oleva mäntä työntää etukäteen mitatun määrän sulanutta metallia (sinkki-, magnesium- tai lyijylejeeringiä) suihkupäästä korkeassa paineessa ja nopeudessa muottikammioon.
- Jähdyttäminen: Sulanut metalli jäähtyy ja jähmettyy muutamassa sekunnissa vesisäätimellä varustetussa muotissa, ottamalla täsmälleen kammion muodon.
- Pistetään pois: Liukut vetäytyvät takaisin ja kiinteäksi jähmettynyt osa, joka on nyt valmis valuliitos, poistetaan muotista, usein ilmalla autettuna. Monissa järjestelmissä osa erotellaan automaattisesti juoksupiiristä.
- Kierros toistuu: Kone aloittaa välittömästi seuraavan kierroksen, mikä mahdollistaa jatkuvan, nopeakäyntisen tuotannon.
Tätä prosessia tehostavat edistyneet ohjausjärjestelmät. Nykyaikaisissa koneissa on usein prosessiparametrit ja annostuksen valvontajärjestelmät (PPCS) sekä suljettu silmukka -ohjaus, jotka mahdollistavat reaaliaikaiset säädöt varmistaakseen, että jokainen yksittäinen osa täyttää tiukat laaturiippuvuudet. Järjestelmät seuraavat muuttujia, kuten ruiskutusnopeutta, täyttöaikaa ja painetta, ja korjaavat automaattisesti poikkeamat.
Yksilöllisten ominaisuuksiensa vuoksi monitoimisen muotin valaminen käytetään laajalla skaalalla eri aloilla kriittisten komponenttien valmistuksessa. Sen kyky tuottaa pieniä, monimutkaisia ja kestäviä osia tekee siitä välttämättömän nykyaikaisessa valmistuksessa.
Yleisiä sovelluksia ovat:
- Autotalous: Pienet hammaspyörät, anturikuoret, liittimet ja sisäosat.
- Kulutuselektroniikka: Liittimet kuituoptiikkaan, matkapuhelinkomponentit ja lämmönpoistimet.
- Lääketieteelliset laitteet: Tarkkuuskomponentit kirurgisiin työkaluihin, diagnostiikkalaitteisiin ja lääkeannostelujärjestelmiin.
- Mekaaninen varuste: Monimutkaiset lukitusluvat, kiinnikkeet ja hammaspyörät erilaisiin mekaanisiin laitteisiin.
Usein kysytyt kysymykset
1. Mitkä materiaalit soveltuvat parhaiten monitoimiseen muotin valamiseen?
Moniliukuisten muottien valaminen on kuuman kammion prosessi, mikä tekee siitä ideaalin matalan sulamispisteen metallien valmistukseen ilman että ne kuluttavat koneen ruiskutuskomponentteja. Sinkkiseokset ovat yleisin materiaali erinomaisen virtauskyvyn, lujuuden ja valukelpoisuuden vuoksi. Magnesium- ja lyijyseoksia käytetään myös usein. Alumiinia voidaan käyttää moniliukuisten muottien valamisessa, vaikka se olekin yhtä yleinen kuin sinkki.
onko moniliukuisten muottien valaminen kallis prosessi?
Moniliukuisten muottien valamisen alkuperäiset työkalut voivat olla monimutkaisempia ja siten kalliimpia kuin perinteiset työkalut. Kuitenkin oikeassa sovelluksessa – pienissä, monimutkaisissa osissa, jotka tuotetaan suurissa määrissä – se on erittäin kustannustehokasta. Säästöt johtuvat jälkikäsittelytoimenpiteiden eliminoimisesta, materiaalihävikin vähentymisestä ja erittäin korkeista tuotantonopeuksista, mikä merkittävästi alentaa kappalekustannuksia tuotantokauden aikana.
minkä kokoisia osia tämän tekniikan avulla yleensä valmistetaan?
Moniliu'utteinen tekniikka on erityisesti optimoitu pienien ja miniatyyristen komponenttien valmistukseen. Vaikka yleistä standardia ei ole, osat ovat tyypillisesti alle 400 grammaa (noin 0,9 puntaa). Prosessi soveltuu erinomaisesti ohuthuomaisiin, monimutkaisiin ja tiukkatoleranssisiin osiin, joiden valmistus suuremmassa mittakaavassa tai muilla valamismenetelmillä olisi vaikeaa tai mahdotonta.
 Pienet erät, korkeat standardit. Nopea prototyypinkehityspalvelumme tekee vahvistamisen nopeammaksi ja helpommaksi —
Pienet erät, korkeat standardit. Nopea prototyypinkehityspalvelumme tekee vahvistamisen nopeammaksi ja helpommaksi —
