Ο Απαραίτητος Ρόλος της Ηλεκτρικής Διάβρωσης στην Ακριβή Κατασκευή Μητρών
TL·DR
Η Ηλεκτρική Διάβρωση Μετάλλων (EDM) διαδραματίζει αναπόσπαστο ρόλο στη σύγχρονη κατασκευή καλουπιών. Πρόκειται για μια διαδικασία υψηλής ακρίβειας που χρησιμοποιεί έλεγχο εκκενώσεων για τη διάβρωση και τη διαμόρφωση σκληρυμένων μετάλλων σε πολύπλοκες και λεπτομερείς μορφές. Αυτή η τεχνολογία είναι κρίσιμης σημασίας για τη δημιουργία ανθεκτικών, υψηλής ακρίβειας εργαλείων, φορμών έγχυσης και καλουπιών διαστάμπωσης, τα οποία συχνά είναι αδύνατο να παραχθούν με συμβατικές μεθόδους κατεργασίας.
Κατανόηση της EDM: Οι Βασικές Αρχές
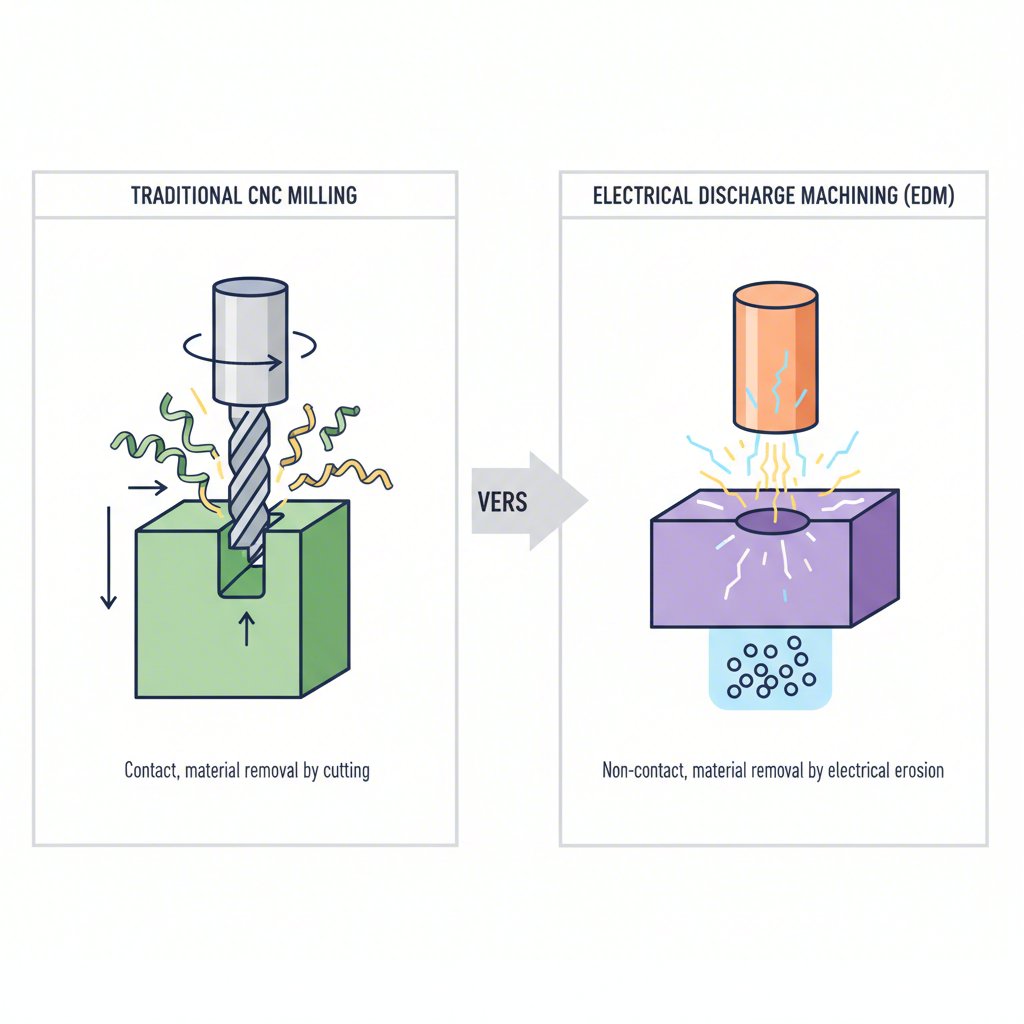
Η εκκένωση με ηλεκτρική εκκένωση, γνωστή και ως μηχανική σπινθήρα, είναι μια μη παραδοσιακή διαδικασία κατασκευής χωρίς επαφή, η οποία βασίζεται στη θερμική ενέργεια. Σε αντίθεση με τις συμβατικές μεθόδους που χρησιμοποιούν μηχανική δύναμη για την κοπή υλικού, η EDM αφαιρεί υλικό μέσω μιας σειράς γρήγορων, επαναλαμβανόμενων ηλεκτρικών εκκενώσεων—ή σπινθήρων—μεταξύ ενός ηλεκτροδίου (το εργαλείο) και του τεμαχίου εργασίας. Και τα δύο συστατικά βυθίζονται σε διηλεκτρικό υγρό, το οποίο λειτουργεί ως ηλεκτρικό μονωτή μέχρι να επιτευχθεί μια συγκεκριμένη τάση.
Ο βασικός μηχανισμός ξεκινά όταν εφαρμόζεται υψηλή τάση, προκαλώντας τη διάσπαση του διηλεκτρικού υγρού και το σχηματισμό πλασματικού καναλιού ανάμεσα στον ηλεκτρόδιο και το τεμάχιο. Αυτό δημιουργεί έναν έντονο σπινθήρα με θερμοκρασίες που φτάνουν από 14.500 έως 21.500 °F, γεγονός που τήξει και εξατμίζει αμέσως ένα μικροσκοπικό ποσό του υλικού του τεμαχίου. Μόλις τελειώσει ο κύκλος εκκένωσης, το διηλεκτρικό υγρό απομακρύνει τα εξατμισμένα σωματίδια (υλικά αποβλήτων) από τη ζώνη κατεργασίας. Αυτός ο κύκλος επαναλαμβάνεται χιλιάδες φορές το δευτερόλεπτο, προκαλώντας σταδιακά τη διάβρωση του τεμαχίου ώστε να αντιστοιχεί στο σχήμα του ηλεκτροδίου ή να ακολουθεί ένα προγραμματισμένο μονοπάτι.
Αυτή η διαδικασία διαφέρει ουσιωδώς από την παραδοσιακή CNC φραιζάρισμα ή τόρνευση. Επειδή δεν υπάρχει φυσική επαφή μεταξύ του εργαλείου και του τεμαχίου, η ηλεκτροδιάβρωση μπορεί να κατεργαστεί εξαιρετικά σκληρά και ανθεκτικά υλικά, όπως σκληρυμένο εργαλειοχάλυβα, τιτάνιο και καρβίδιο βολφραμίου, με εξαιρετική ακρίβεια και χωρίς να προκαλέσει μηχανικές τάσεις. Αυτή η δυνατότητα καθιστά την τεχνολογία απαραίτητη για εφαρμογές που απαιτούν λεπτομερείς περιγραφές και στενά όρια ανοχής, τα οποία δεν μπορούν να επιτευχθούν με άλλες μεθόδους.
Ο Κρίσιμος Ρόλος της Ηλεκτροδιάβρωσης στην Κατασκευή Υψηλής Ακρίβειας Καλουπιών και Μήτρων
Στον κόσμο της κατασκευής εργαλείων και μήτρων, η ακρίβεια δεν είναι απλώς ένας στόχος· είναι μια θεμελιώδης απαίτηση. Η τεχνολογία EDM αποτελεί τον λίθο γωνιά της ακρίβειας, επιτρέποντας τη δημιουργία μήτρων και εργαλείων με ένα βαθμό πολυπλοκότητας και ακρίβειας που κάποτε φαινόταν αδιανόητος. Ο κύριος ρόλος της είναι να παράγει περίπλοκα χαρακτηριστικά, όπως οξείες εσωτερικές γωνίες, βαθιές και στενές πλευρές και πολύπλοκες κοιλότητες, τα οποία συχνά είναι αδύνατο να δημιουργηθούν με συμβατικά κοπτικά εργαλεία λόγω περιορισμών στη γεωμετρία και την πρόσβαση του εργαλείου.
Μία από τις σημαντικότερες εφαρμογές της EDM είναι η παραγωγή μήτρων για την έγχυση πλαστικού και μητρών για τη χύτευση και τη διαμόρφωση μετάλλων. Για παράδειγμα, στον αυτοκινητιστικό τομέα, η παραγωγή εξαρτημάτων υψηλής ποιότητας εξαρτάται από τέλεια κατασκευασμένα εργαλεία. Κορυφαίοι πάροχοι προσαρμοσμένων μητρών διαμόρφωσης αυτοκινήτων και κατασκευής μεταλλικών εξαρτημάτων , όπως η Shaoyi (Ningbo) Metal Technology Co., Ltd., χρησιμοποιούν προηγμένες διαδικασίες για να παράγουν την ακρίβεια που απαιτείται από τους OEM και τους προμηθευτές Tier 1. Η EDM είναι κρίσιμη σε αυτό το πλαίσιο για τη δημιουργία ανθεκτικών, πολύπλοκων διαμορφωτικών μήτρων που δίνουν σχήμα σε ελάσματα για αυτοκινητοβιομηχανικά εξαρτήματα με αψεγάδιαστη συνέπεια.
Επιπλέον, η EDM είναι ιδιαίτερα κατάλληλη για την κατεργασία υλικών που έχουν ήδη ενανθρακωθεί. Οι παραδοσιακές διαδικασίες συχνά απαιτούν την κατεργασία ενός μαλακότερου υλικού πρώτα, το οποίο στη συνέχεια υφίσταται θερμική επεξεργασία, ένα βήμα που μπορεί να προκαλέσει στρέβλωση και διαστατικές ανακρίβειες. Οι μηχανές EDM εργάζονται με προ-ενανθρακωμένες κραματώδεις χάλυβες, εξαλείφοντας έτσι τον κίνδυνο παραμόρφωσης και διασφαλίζοντας ότι η τελική μήτρα ή το καλούπι τηρεί τις αυστηρότερες ανοχές. Αυτό μεταφράζεται απευθείας σε υψηλότερη ποιότητα τελικών προϊόντων, είτε πρόκειται για καταναλωτικά πλαστικά αγαθά, ιατρικές εμφυτεύσεις ή εξαρτήματα αεροδιαστημικής, και εξασφαλίζει μεγαλύτερη διάρκεια ζωής για τα ίδια τα εργαλεία.
Βασικές Τεχνικές EDM για την Κατασκευή Μητρών: Wire EDM έναντι Die-Sinking EDM
Οι κατασκευαστές καλουπιών βασίζονται κυρίως σε δύο διακριτούς τύπους ηλεκτρικής διάβρωσης, οι οποίοι είναι κατάλληλοι για διαφορετικές εφαρμογές: Die-Sinking EDM και Wire EDM. Η κατανόηση των διαφορών μεταξύ τους είναι καθοριστικής σημασίας για να εκτιμηθεί η ευελιξία της τεχνολογίας σε ένα περιβάλλον παραγωγής.
Die-Sinking EDM , επίσης γνωστή ως ram EDM ή cavity EDM, χρησιμοποιεί έναν ηλεκτρόδιο που κατασκευάζεται εξ αρχής, συνήθως από γραφίτη ή χαλκό, ο οποίος έχει το σχήμα του αρνητικού του επιθυμητού στοιχείου. Ο ηλεκτρόδιος χαμηλώνεται σταδιακά ή «βυθίζεται» στο τεμάχιο, και οι ηλεκτρικές σπινθήρες διαβρώνουν το υλικό προκειμένου να δημιουργηθεί μία κοιλότητα που αντικατοπτρίζει το σχήμα του ηλεκτροδίου. Αυτή η μέθοδος είναι ιδανική για τη δημιουργία περίπλοκων τρισδιάστατων κοιλοτήτων, τυφλών οπών και λεπτομερών εντυπώσεων που απαιτούνται για καλούπια και καλούπια διαμόρφωσης.
Σύρμα EDM , ή WEDM, λειτουργεί περισσότερο σαν μια εξελιγμένη τεχνολογικά πριονοταιριστική. Χρησιμοποιεί ένα πολύ λεπτό, συνεχώς τροφοδοτούμενο μεταλλικό σύρμα (συνήθως από ψευδάργυρο) ως ηλεκτρόδιο. Το σύρμα καθοδηγείται κατά μήκος μιας ακριβούς διαδρομής προγραμματισμένης με CNC για να κόψει ολόκληρο το πάχος ενός τεμαχίου, δημιουργώντας περίπλοκα 2D προφίλ και σχήματα. Είναι εξαιρετικά αποτελεσματικό για την παραγωγή μήτρων, εργαλείων και καλουπιών από παχιές πλάκες σκληρυμένου χάλυβα, καθώς και για τη δημιουργία εξαρτημάτων με πολύπλοκα περιγράμματα και εξαρτήματα που ταιριάζουν ακριβώς.
Για να διευκρινιστεί πότε ένας κατασκευαστής καλουπιών ενδέχεται να επιλέξει το ένα αντί του άλλου, λάβετε υπόψη την ακόλουθη σύγκριση:
| Χαρακτηριστικό | Die-Sinking (Ram) EDM | Σύρμα EDM |
|---|---|---|
| Τύπος ηλεκτρόδου | Στερεό, ειδικά σχεδιασμένο ηλεκτρόδιο (γραφίτης ή χαλκός) | Λεπτό, μονόκλωνο μεταλλικό σύρμα (συνήθως από ψευδάργυρο) |
| Κύρια Εφαρμογή | Δημιουργία 3D κοιλοτήτων, καλουπιών, τυφλών οπών και πολύπλοκων εντυπώσεων | Κοπή 2D προφίλ, μήτρων, καλουπιών και περίπλοκων περιγραμμάτων μέσω ενός τεμαχίου |
| Δημιουργούμενη Γεωμετρία | Πολύπλοκα τρισδιάστατα αρνητικά σχήματα | Περίπλοκα δισδιάστατα περιγράμματα, κωνικά σχήματα και διαμήκεις κοπές |
| Αλληλεπίδραση τεμαχίου | Η ηλεκτροδή εισχωρεί στο τεμάχιο για να δημιουργήσει κοιλότητα | Ο σύρμας διαπερνά πλήρως το τεμάχιο για να κόψει ένα προφίλ |
Κύρια οφέλη και πλεονεκτήματα της χρήσης της μέθοδος EDM στη βιομηχανία καλουπιών και μήτρων
Η ευρεία υιοθέτηση της μεθόδου EDM στην κατασκευή καλουπιών και μήτρων οφείλεται σε ένα μοναδικό σύνολο πλεονεκτημάτων που αντιμετωπίζουν άμεσα τις πιο κρίσιμες προκλήσεις της βιομηχανίας. Τα οφέλη αυτά ξεπερνούν την απλή αφαίρεση υλικού, προσφέροντας ανωτέρα ποιότητα, ελευθερία σχεδίασης και αποδοτικότητα σε σύγκριση με τις παραδοσιακές μεθόδους κατεργασίας.
Τα σημαντικότερα πλεονεκτήματα περιλαμβάνουν:
- Κατεργασία εξαιρετικά σκληρών υλικών: Η μέθοδος EDM είναι αδιάφορη ως προς τη σκληρότητα του υλικού, καθώς ο μηχανισμός της είναι θερμικός και όχι μηχανικός. Μπορεί να κατεργαστεί εύκολα σκληρυμένα εργαλειοχάλυβα, καρβίδιο βολφραμίου και εξωτικές κράμες που θα φθείρονταν γρήγορα ή δεν θα ήταν δυνατό να κοπούν με συμβατικά εργαλεία.
- Δημιουργία πολύπλοκων και λεπτών γεωμετριών: Εφόσον η διαδικασία είναι χωρίς επαφή, δεν υπάρχουν δυνάμεις κοπής που θα μπορούσαν να παραμορφώσουν ευαίσθητα στοιχεία. Αυτό επιτρέπει τη δημιουργία οξειών εσωτερικών γωνιών, βαθιών και στενών εγκοπών και λεπτών τοιχωμάτων, τα οποία δεν είναι εφικτά με φρεζάρισμα.
- Ανεπανάληπτη Ακρίβεια και Λείανση Επιφάνειας: Η ηλεκτροδιάβρωση (EDM) μπορεί να επιτύχει εξαιρετικά αυστηρές ανοχές, συχνά εντός ±0,0002 ιντσών. Η διαδικασία μπορεί να ρυθμιστεί με ακρίβεια για να παράγει λεία επιφάνεια, η οποία ελαχιστοποιεί ή ακόμη και εξαλείφει την ανάγκη για χειροκίνητη λείανση, εξοικονομώντας σημαντικό χρόνο και εργασία.
- Χωρίς Μηχανική Τάση στο Τεμάχιο: Η απουσία άμεσης επαφής μεταξύ του εργαλείου και του εξαρτήματος σημαίνει ότι δεν εισάγεται μηχανική τάση. Αυτό είναι κρίσιμο για τη διατήρηση της διαστατικής σταθερότητας ευαίσθητων ή λεπτών τοιχωμάτων και για την αποφυγή στρέψης ή ρωγμών.
Τελικά, αυτά τα οφέλη συνδυάζονται για να καταστήσουν την EDM απαραίτητη τεχνολογία για κάθε σύγχρονο κατασκευαστή εργαλείων και καλουπιών. Επιτρέπει την παραγωγή εργαλείων υψηλότερης ποιότητας και μεγαλύτερης διάρκειας ζωής, τα οποία με τη σειρά τους παράγουν ανώτερα τελικά εξαρτήματα, ενισχύοντας τον κρίσιμο ρόλο της σε ανταγωνιστικές και υψηλού επιπέδου βιομηχανίες όπως η αεροδιαστημική, η ιατρική και η αυτοκινητοβιομηχανία.
Συχνές Ερωτήσεις
1. Ποια είναι η αρχή λειτουργίας της EDM με βύθιση καλουπιού;
Η EDM με βύθιση καλουπιού, επίσης γνωστή ως ram EDM, λειτουργεί δημιουργώντας έναν ειδικά διαμορφωμένο ηλεκτρόδιο (συχνά κατασκευασμένο από γραφίτη ή χαλκό) που αποτελεί το αρνητικό της κοιλότητας που πρόκειται να κατεργαστεί. Αυτός ο ηλεκτρόδιος βυθίζεται σε διηλεκτρικό υγρό και πλησιάζει προς το τεμάχιο. Ηλεκτρικές εκκενώσεις (σπινθήρες) εμφανίζονται μεταξύ του ηλεκτροδίου και του τεμαχίου, προκαλώντας φθορά του υλικού ώστε να δημιουργηθεί αποτύπωμα που ταιριάζει ακριβώς στο σχήμα του ηλεκτροδίου.
2. Ποια είναι η χρήση μιας μηχανής EDM για την κατασκευή καλουπιών;
Στην κατασκευή καλουπιών, η ηλεκτροδιάβρωση χρησιμοποιείται για τη δημιουργία πολύπλοκων κοιλοτήτων και χαρακτηριστικών σε προ-σκληρυμένο εργαλειοχάλυβα, οι οποίες θα διαμορφώσουν τα τελικά πλαστικά ή μεταλλικά εξαρτήματα. Είναι απαραίτητη για την παραγωγή χαρακτηριστικών όπως βαθιές πτέρυγες, οξείες εσωτερικές γωνίες και περίπλοκα υφές, τα οποία είναι δύσκολο ή αδύνατο να επιτευχθούν με τη συμβατική φρέζα CNC. Αυτή η ακρίβεια διασφαλίζει ότι τα τελικά εξαρτήματα που παράγονται με έγχυση πληρούν ακριβώς τις προδιαγραφές.
3. Ποιος είναι ο ρόλος της ηλεκτροδιάβρωσης;
Ο κύριος ρόλος της ηλεκτροδιάβρωσης είναι η διαμόρφωση και η κατεργασία ηλεκτρικά αγώγιμων υλικών με τη χρήση θερμικής ενέργειας από ελεγχόμενους ηλεκτρικούς σπινθήρες. Εκτιμάται ιδιαίτερα για την ικανότητά της να κατεργάζεται πολύ σκληρά υλικά με υψηλή ακρίβεια, να δημιουργεί πολύπλοκες γεωμετρίες χωρίς μηχανική δύναμη και να παράγει λεπτές επιφανειακές κατεργασίες. Η βασική της λειτουργία είναι η αφαίρεση υλικού σε εφαρμογές όπου οι συμβατικές μέθοδοι αποτυγχάνουν.
4. Τι είναι η ηλεκτροδιάβρωση στην κατεργασία CNC;
Το EDM είναι ένας ειδικός τύπος κατεργασίας CNC (Computer Numerical Control). Ενώ η παραδοσιακή κατεργασία CNC περιλαμβάνει ένα κοπτικό εργαλείο που έρχεται σε φυσική επαφή και αφαιρεί υλικό, το CNC EDM χρησιμοποιεί μια υπολογιστικά ελεγχόμενη διαδρομή για να καθοδηγήσει έναν ηλεκτρόδιο. Το σύστημα CNC ελέγχει την κίνηση του ηλεκτροδίου (στο EDM σύρματος ή βυθιζόμενο EDM) για να δημιουργήσει σπινθήρες ακριβώς εκεί που πρέπει να αφαιρεθεί το υλικό, επιτρέποντας την αυτοματοποιημένη δημιουργία εξαιρετικά πολύπλοκων και ακριβών εξαρτημάτων.
 Μικρές παραγωγικές σειρές, υψηλοί πρότυποι. Η υπηρεσία γρήγορης δημιουργίας πρωτότυπων μας κάνει την επαλήθευση ταχύτερη και ευκολότερη —
Μικρές παραγωγικές σειρές, υψηλοί πρότυποι. Η υπηρεσία γρήγορης δημιουργίας πρωτότυπων μας κάνει την επαλήθευση ταχύτερη και ευκολότερη —
